Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6ymw; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.71 Å)
- Summary
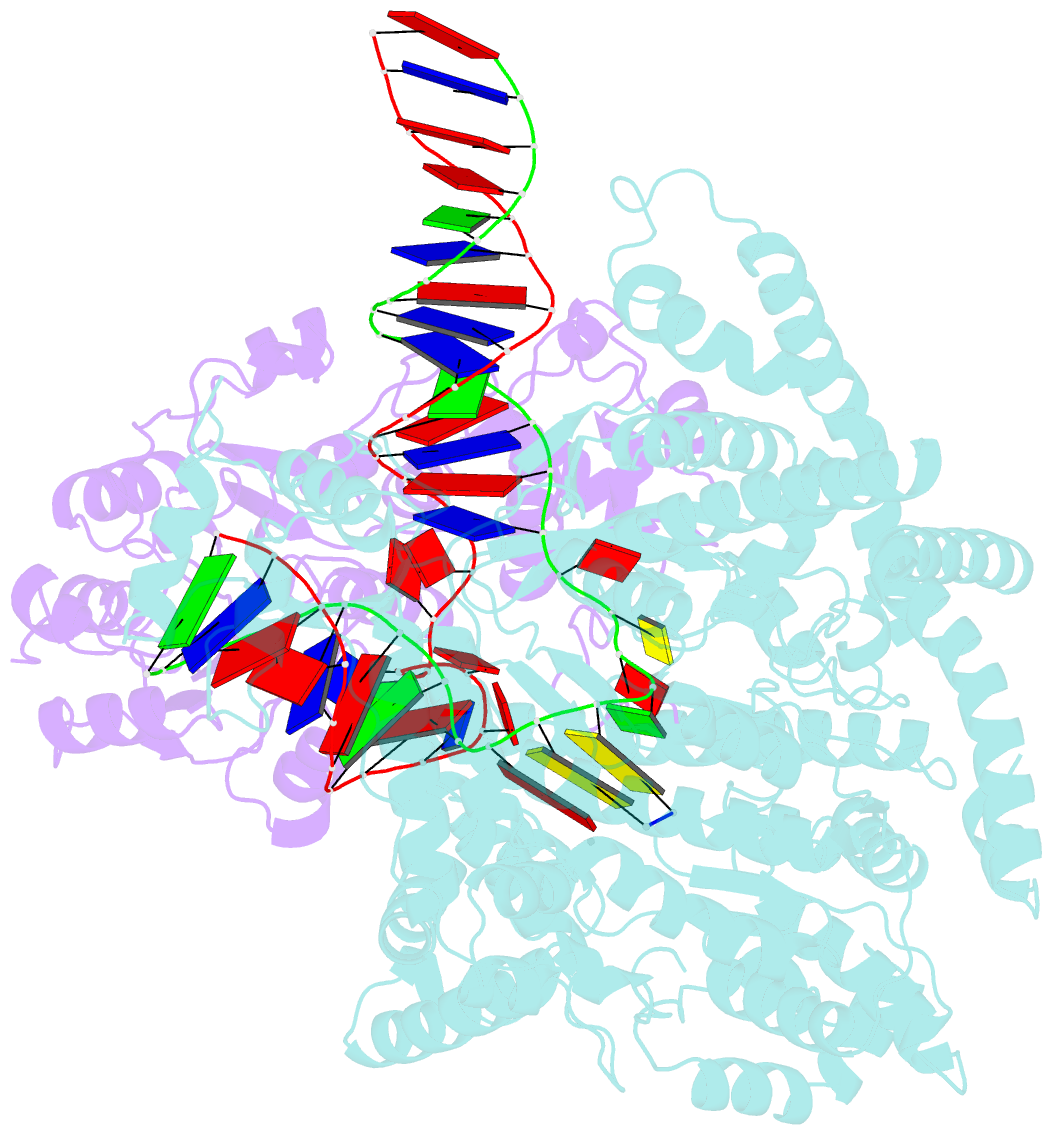
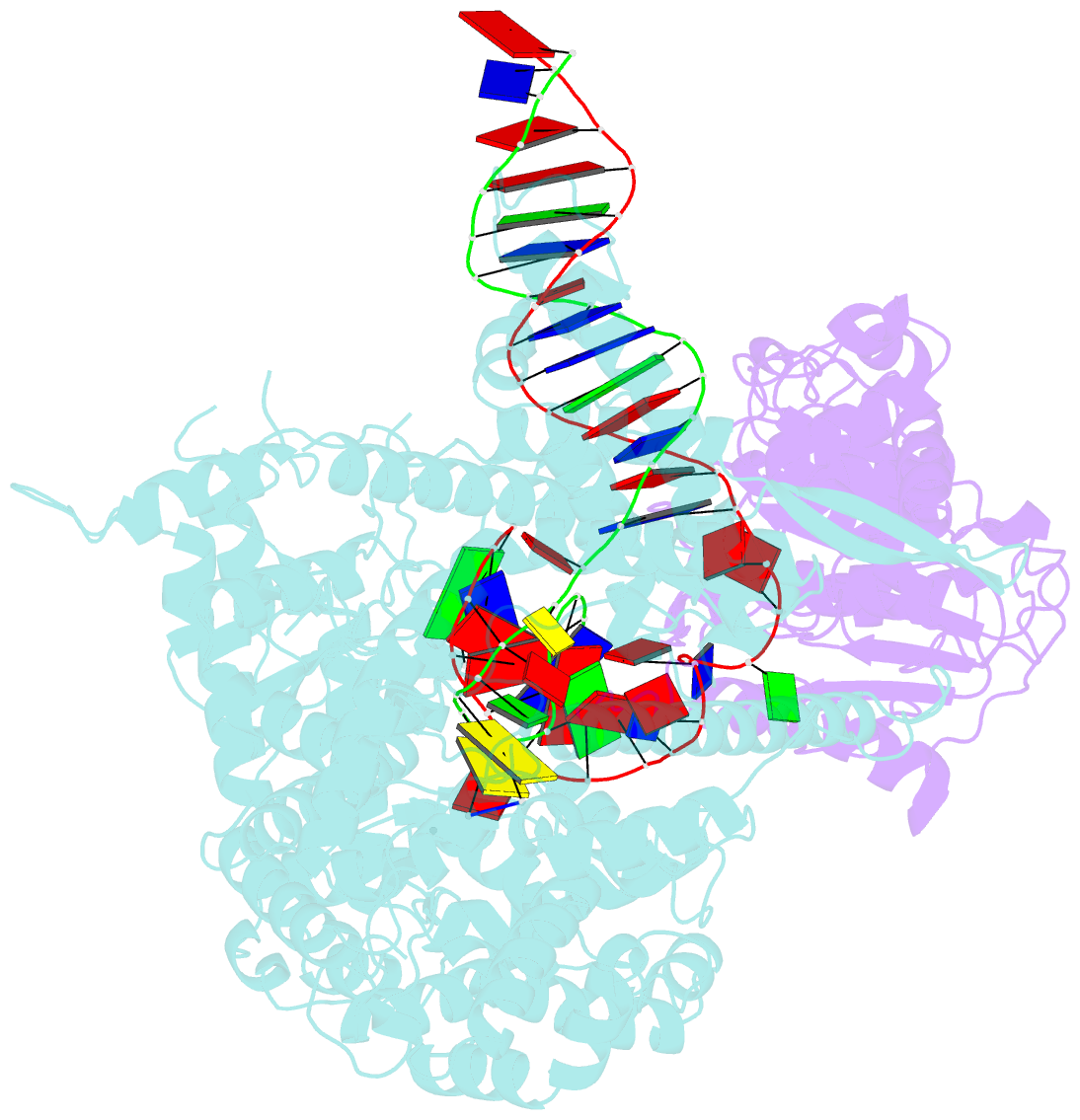
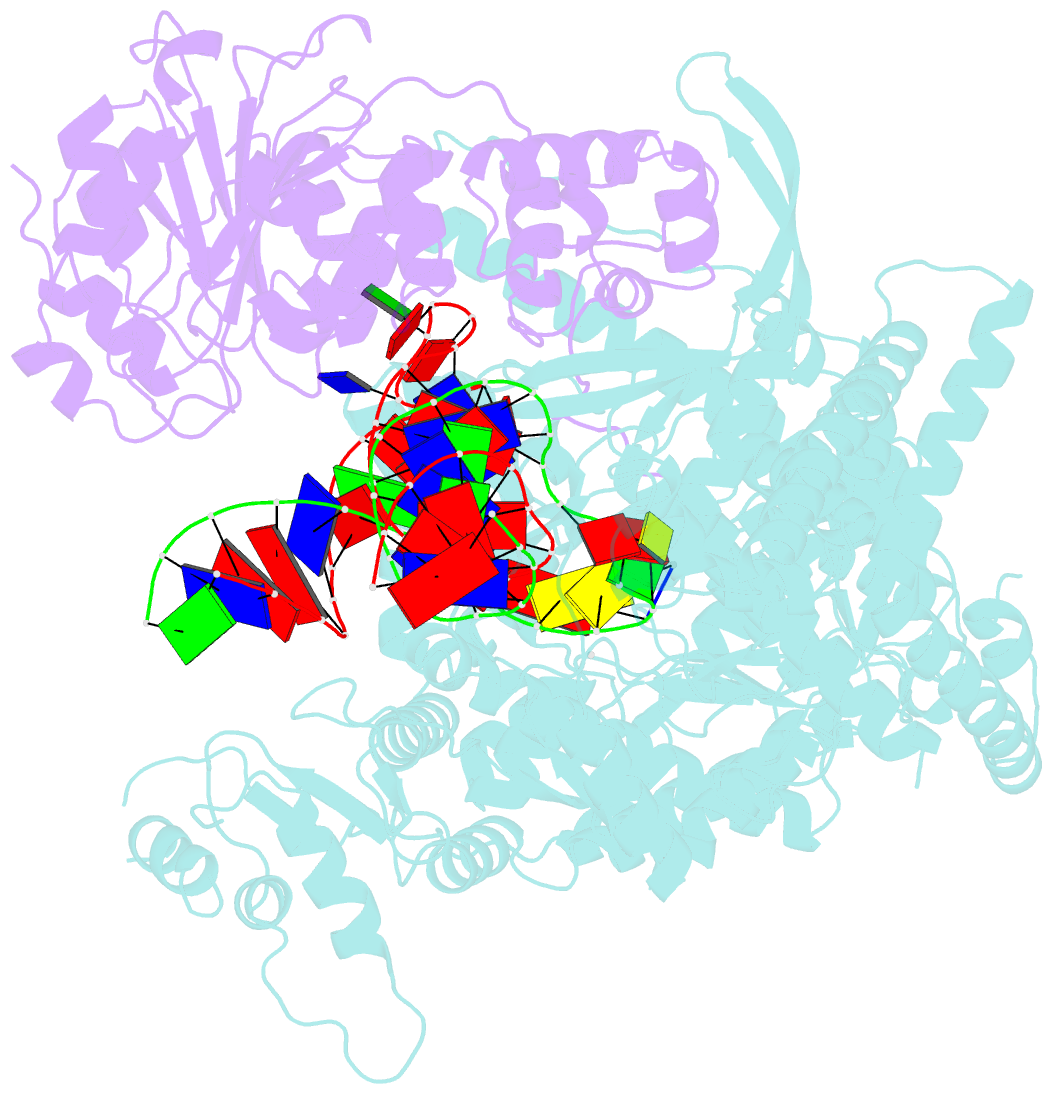
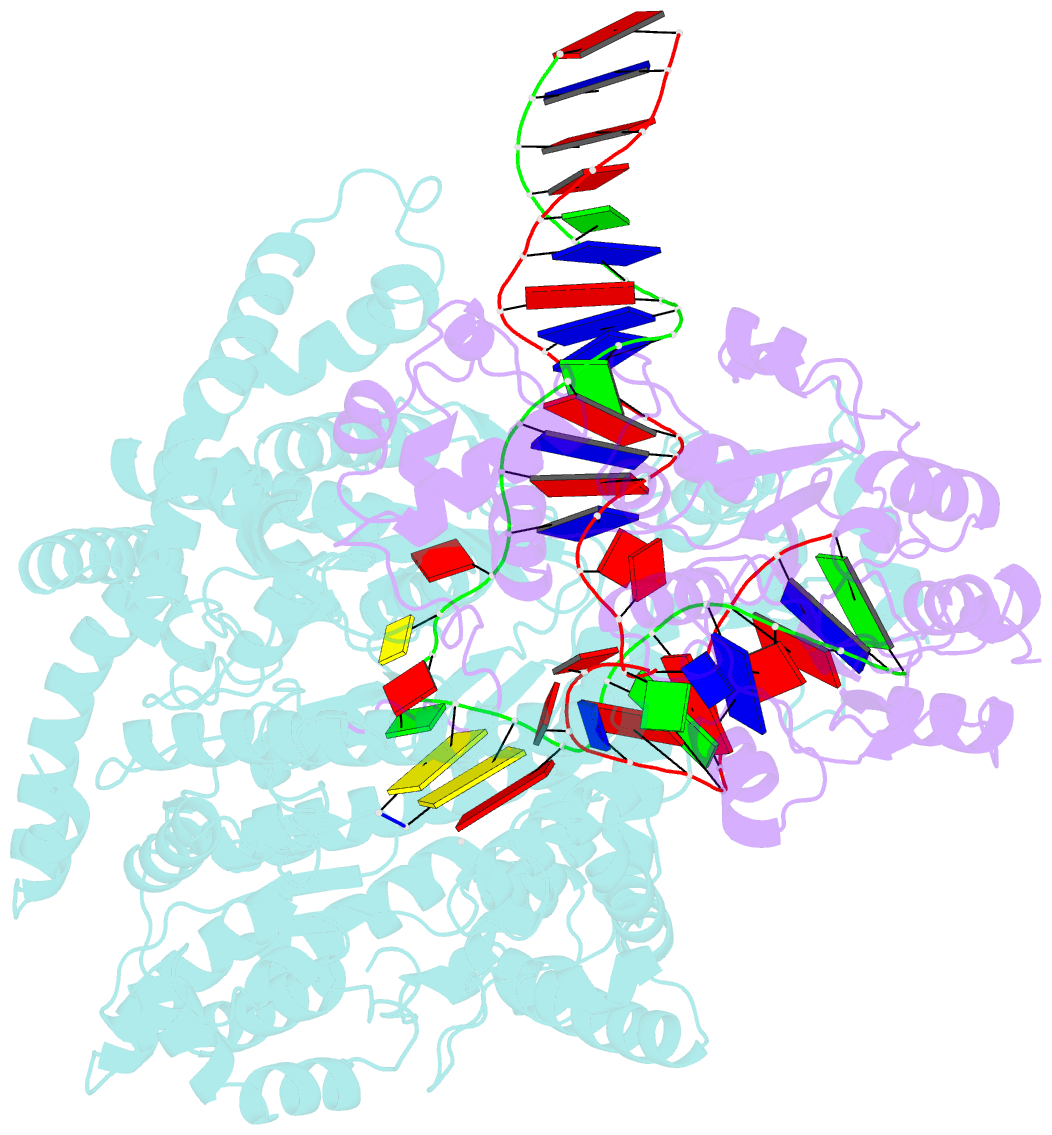
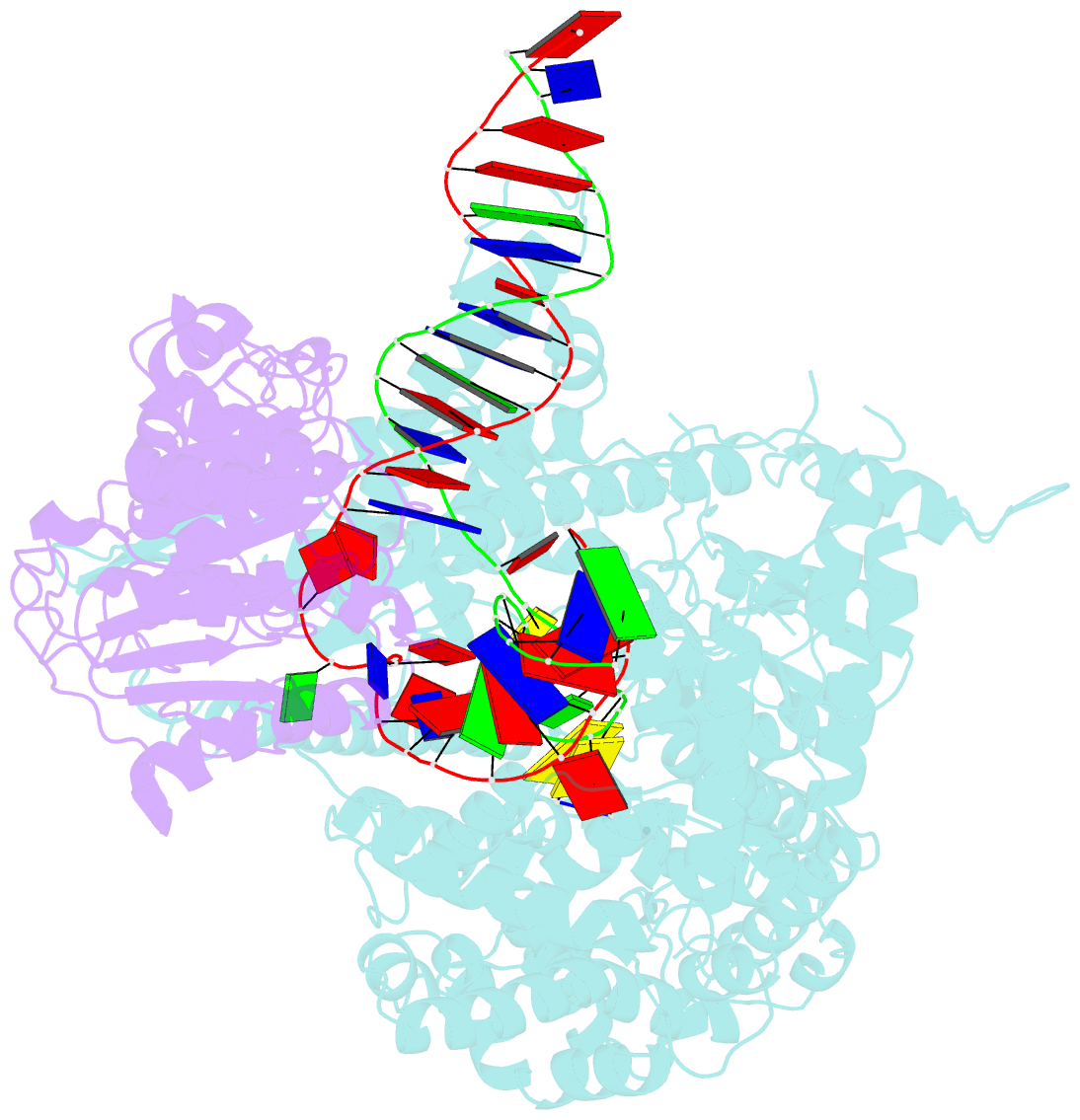
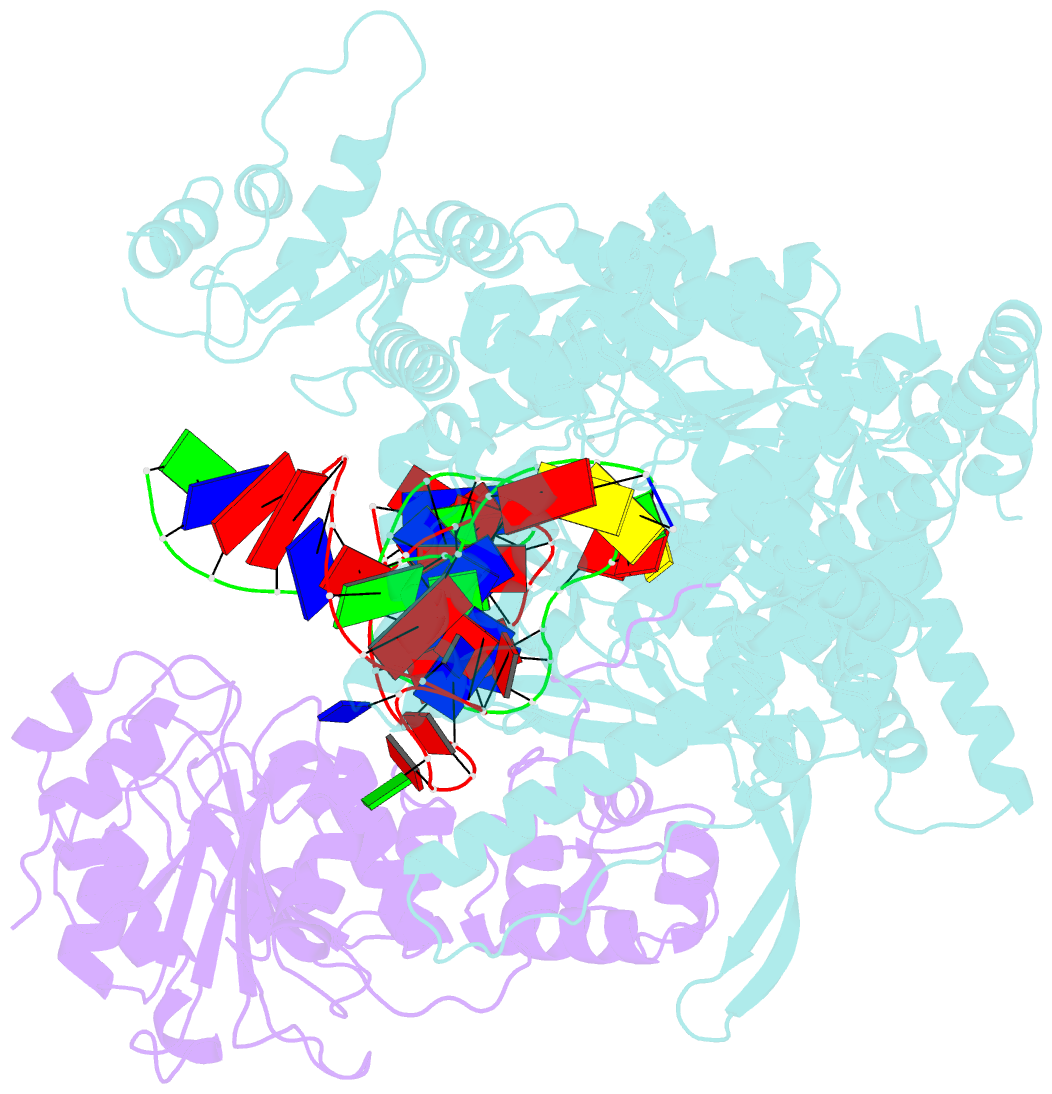
- cryo-EM structure of yeast mitochondrial RNA polymerase transcription initiation complex
- Reference
- De Wijngaert B, Sultana S, Singh A, Dharia C, Vanbuel H, Shen J, Vasilchuk D, Martinez SE, Kandiah E, Patel SS, Das K (2021): "Cryo-EM Structures Reveal Transcription Initiation Steps by Yeast Mitochondrial RNA Polymerase." Mol.Cell, 81, 268. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.016.
- Abstract
- Mitochondrial RNA polymerase (mtRNAP) is crucial in cellular energy production, yet understanding of mitochondrial DNA transcription initiation lags that of bacterial and nuclear DNA transcription. We report structures of two transcription initiation intermediate states of yeast mtRNAP that explain promoter melting, template alignment, DNA scrunching, abortive synthesis, and transition into elongation. In the partially melted initiation complex (PmIC), transcription factor MTF1 makes base-specific interactions with flipped non-template (NT) nucleotides "AAGT" at -4 to -1 positions of the DNA promoter. In the initiation complex (IC), the template in the expanded 7-mer bubble positions the RNA and NTP analog UTPαS, while NT scrunches into an NT loop. The scrunched NT loop is stabilized by the centrally positioned MTF1 C-tail. The IC and PmIC states coexist in solution, revealing a dynamic equilibrium between two functional states. Frequent scrunching/unscruching transitions and the imminent steric clashes of the inflating NT loop and growing RNA:DNA with the C-tail explain abortive synthesis and transition into elongation.