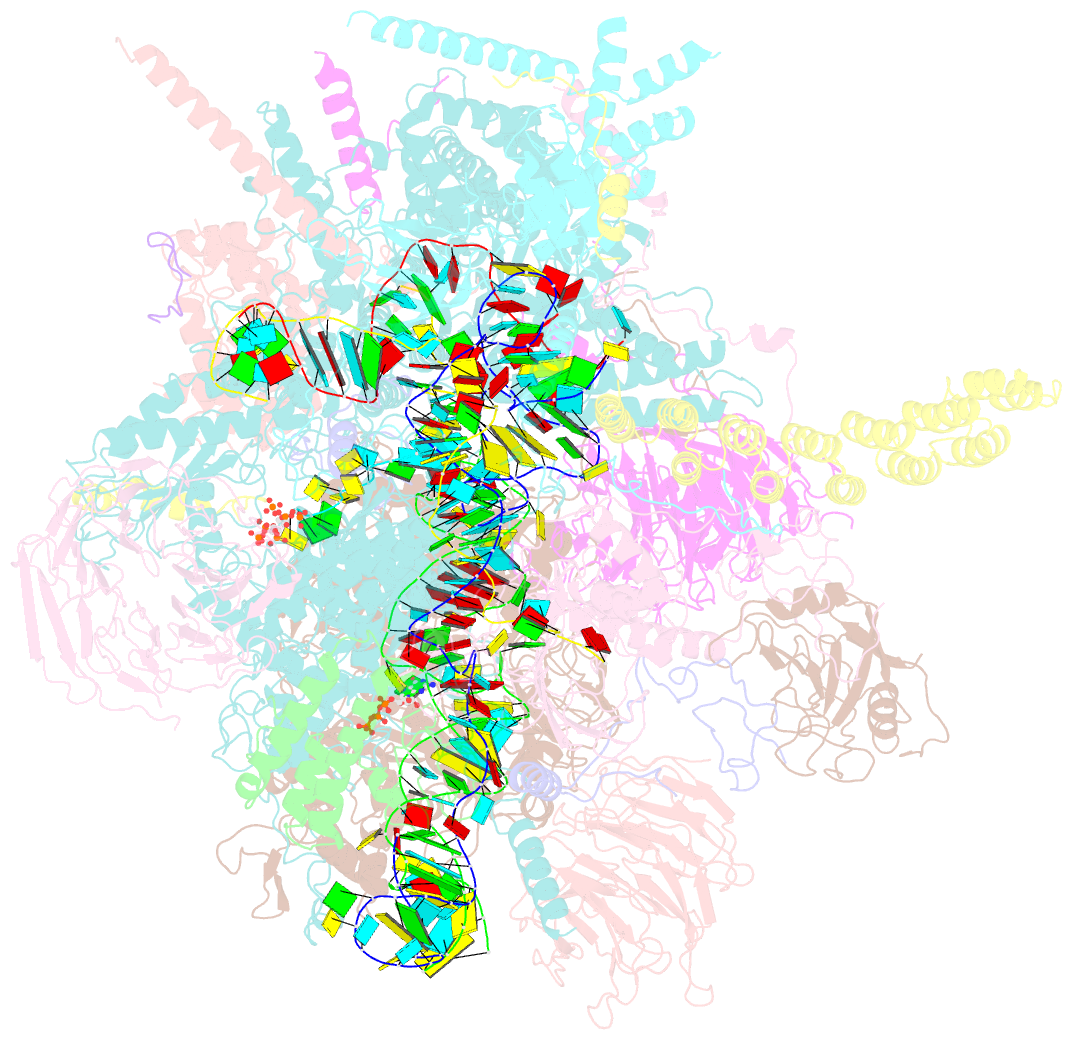
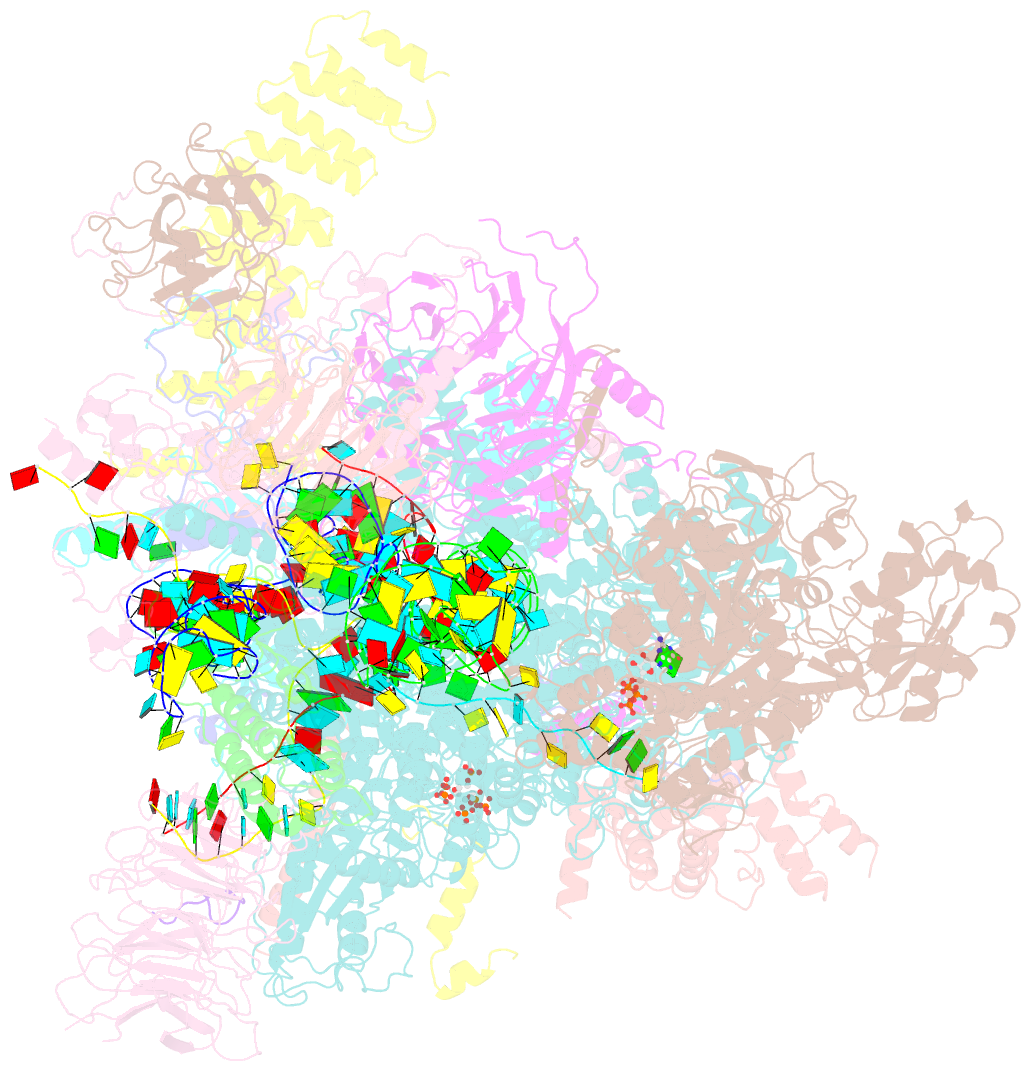
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 6zym; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- splicing
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.4 Å)
- Summary
- Human c complex spliceosome - high-resolution core
- Reference
- Bertram K, El Ayoubi L, Dybkov O, Agafonov DE, Will CL, Hartmuth K, Urlaub H, Kastner B, Stark H, Luhrmann R (2020): "Structural Insights into the Roles of Metazoan-Specific Splicing Factors in the Human Step 1 Spliceosome." Mol.Cell, 80, 127-139.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.09.012.
- Abstract
- Human spliceosomes contain numerous proteins absent in yeast, whose functions remain largely unknown. Here we report a 3D cryo-EM structure of the human spliceosomal C complex at 3.4 Å core resolution and 4.5-5.7 Å at its periphery, and aided by protein crosslinking we determine its molecular architecture. Our structure provides additional insights into the spliceosome's architecture between the catalytic steps of splicing, and how proteins aid formation of the spliceosome's catalytically active RNP (ribonucleoprotein) conformation. It reveals the spatial organization of the metazoan-specific proteins PPWD1, WDR70, FRG1, and CIR1 in human C complexes, indicating they stabilize functionally important protein domains and RNA structures rearranged/repositioned during the Bact to C transition. Structural comparisons with human Bact, C∗, and P complexes reveal an intricate cascade of RNP rearrangements during splicing catalysis, with intermediate RNP conformations not found in yeast, and additionally elucidate the structural basis for the sequential recruitment of metazoan-specific spliceosomal proteins.