Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7aoh; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.7 Å)
- Summary
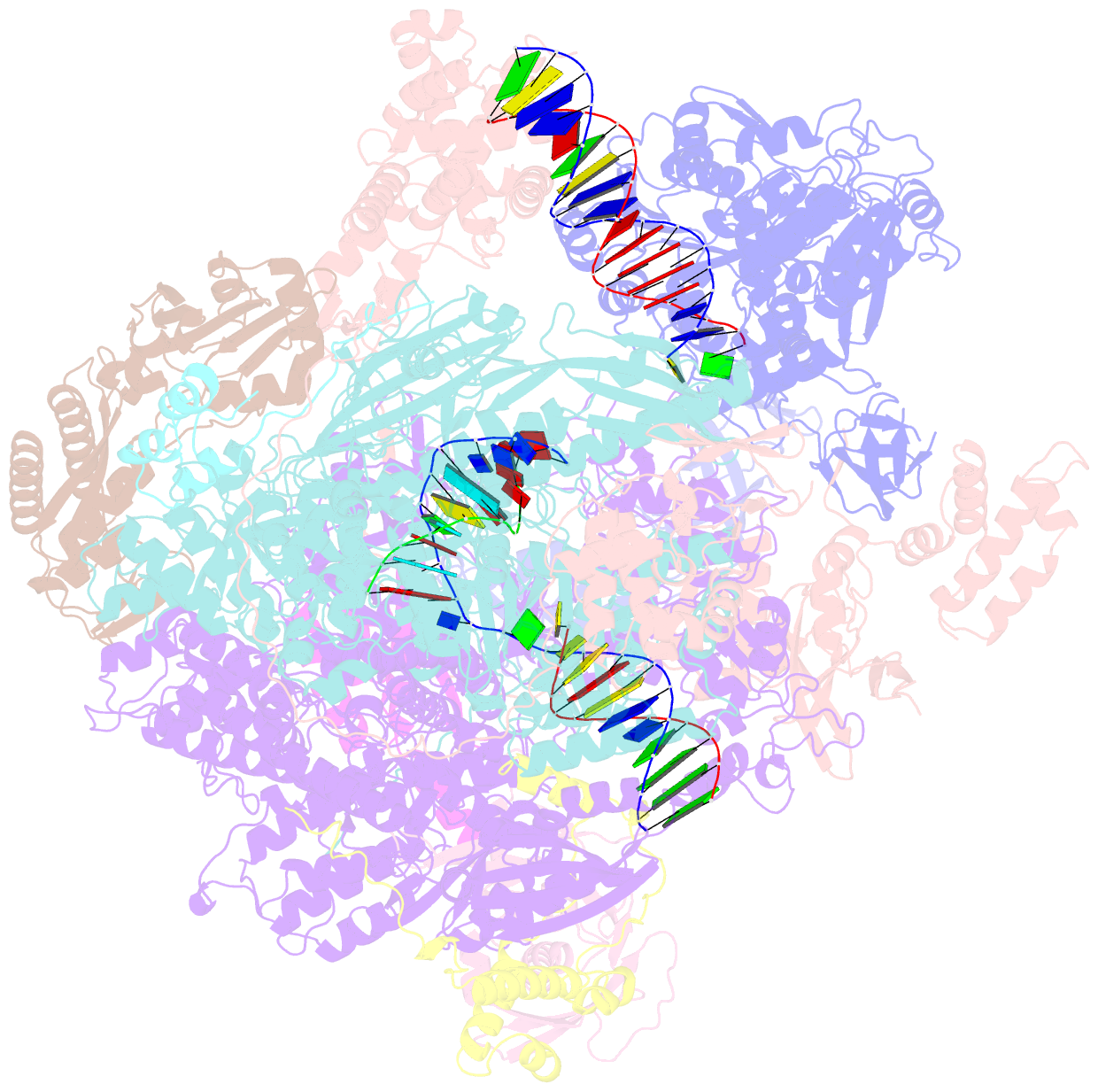
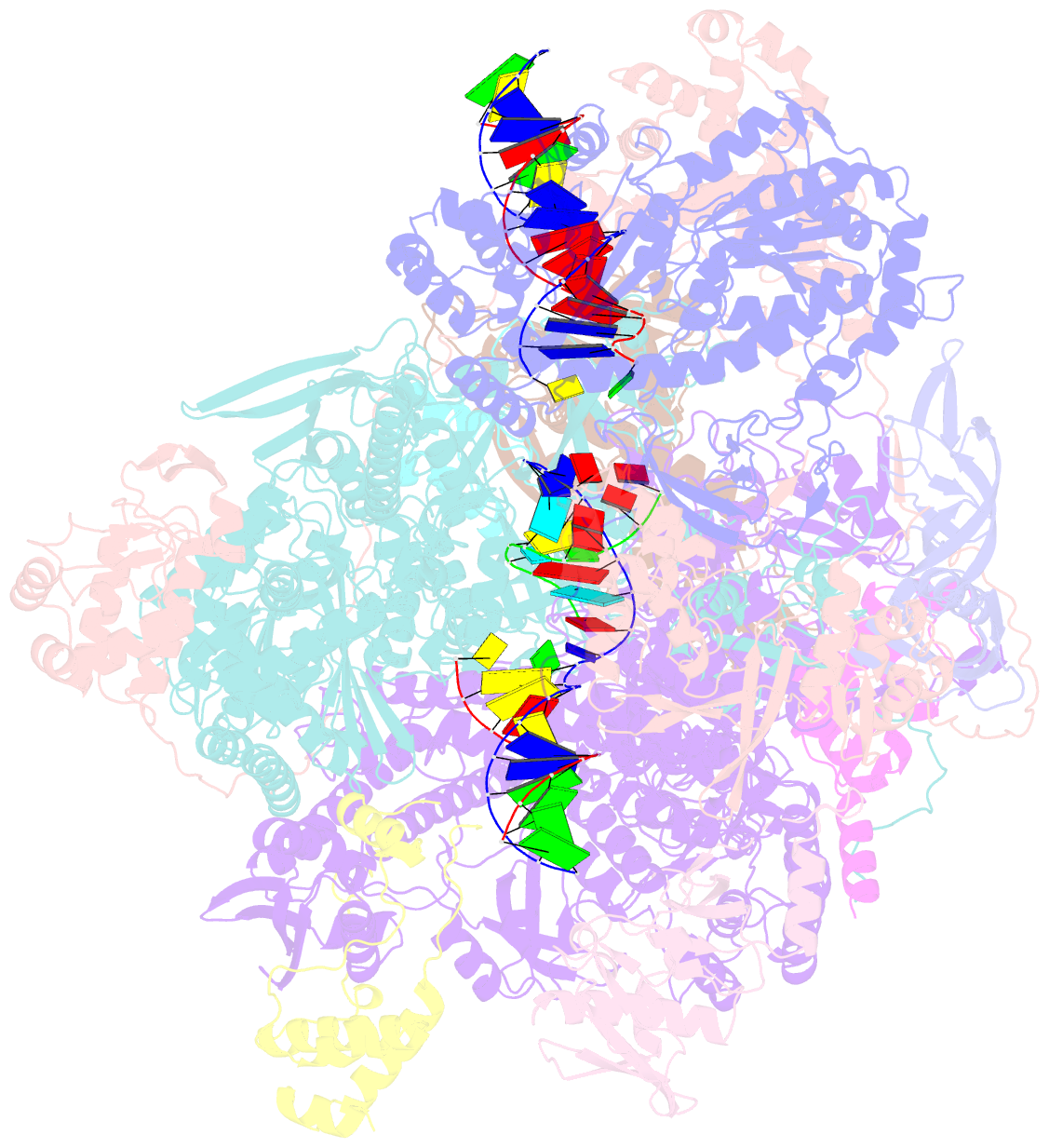
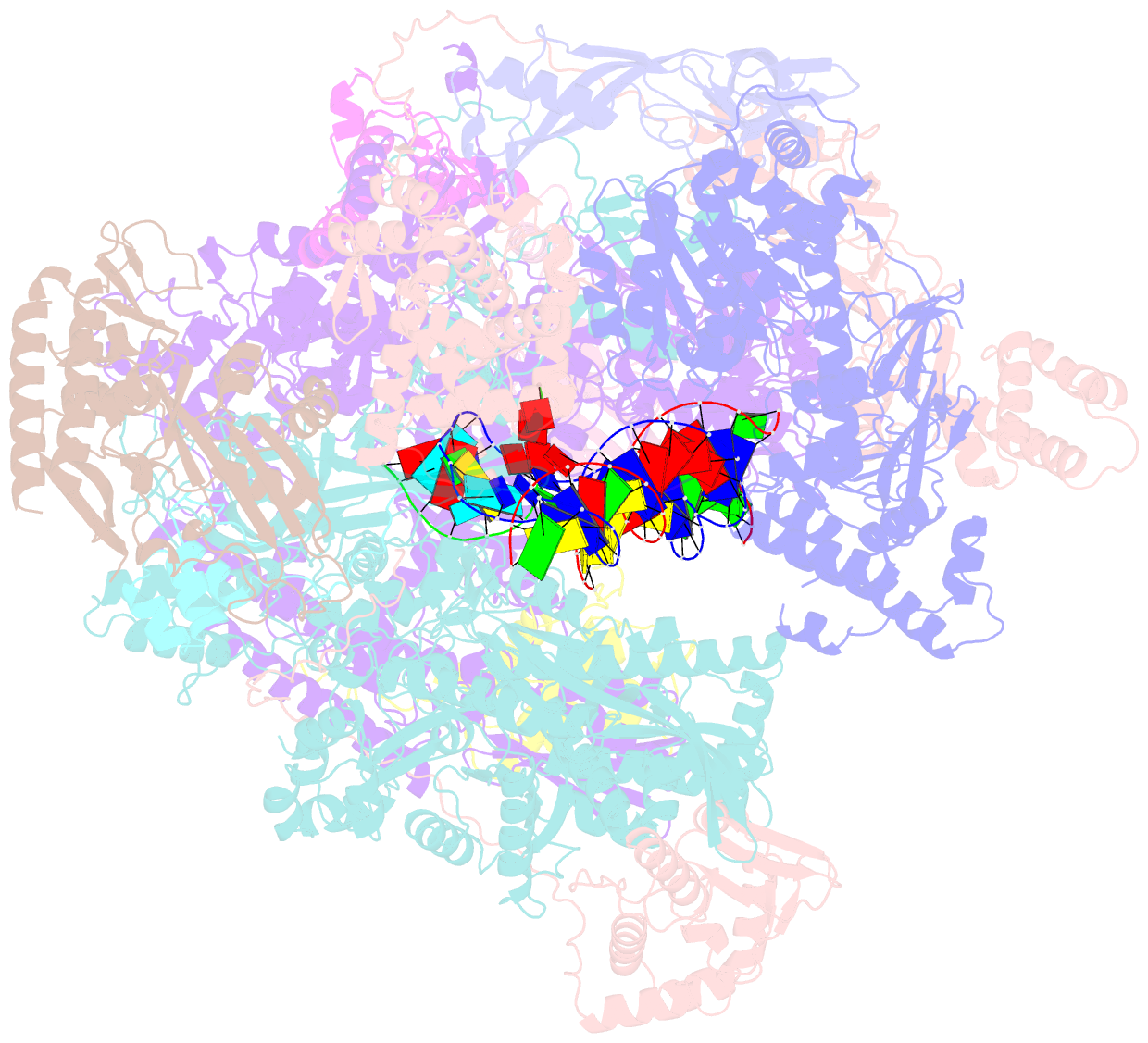
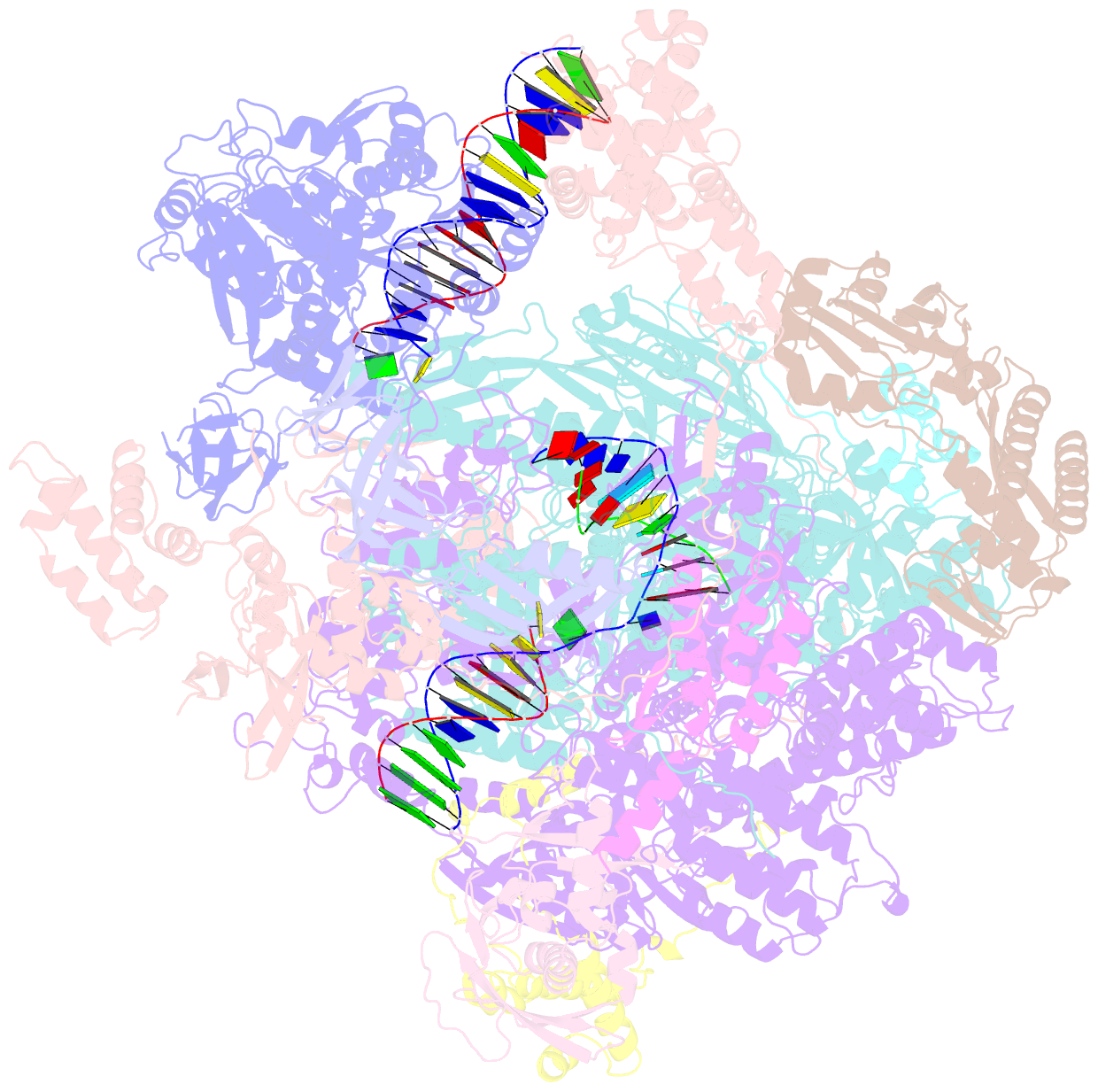
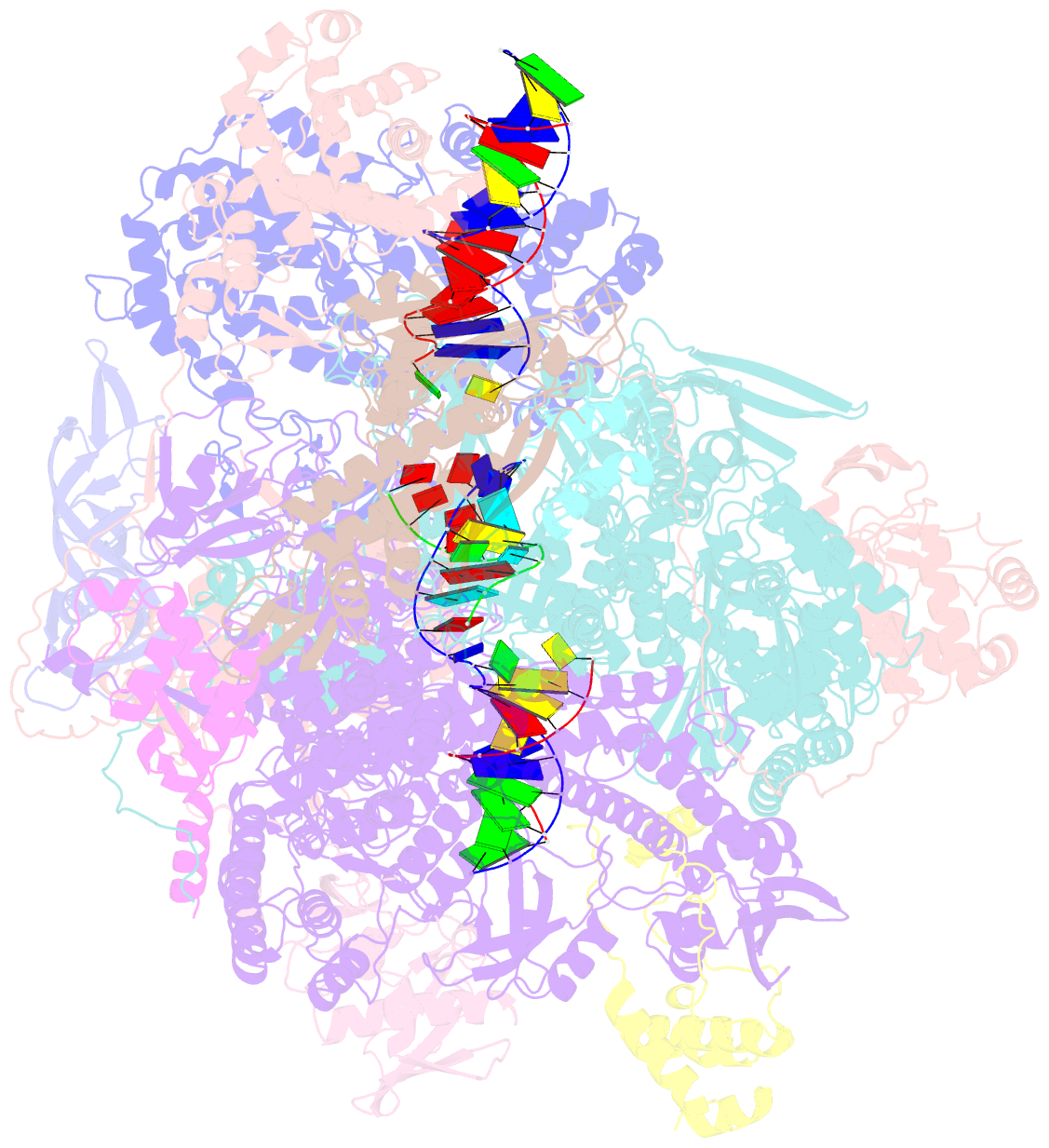
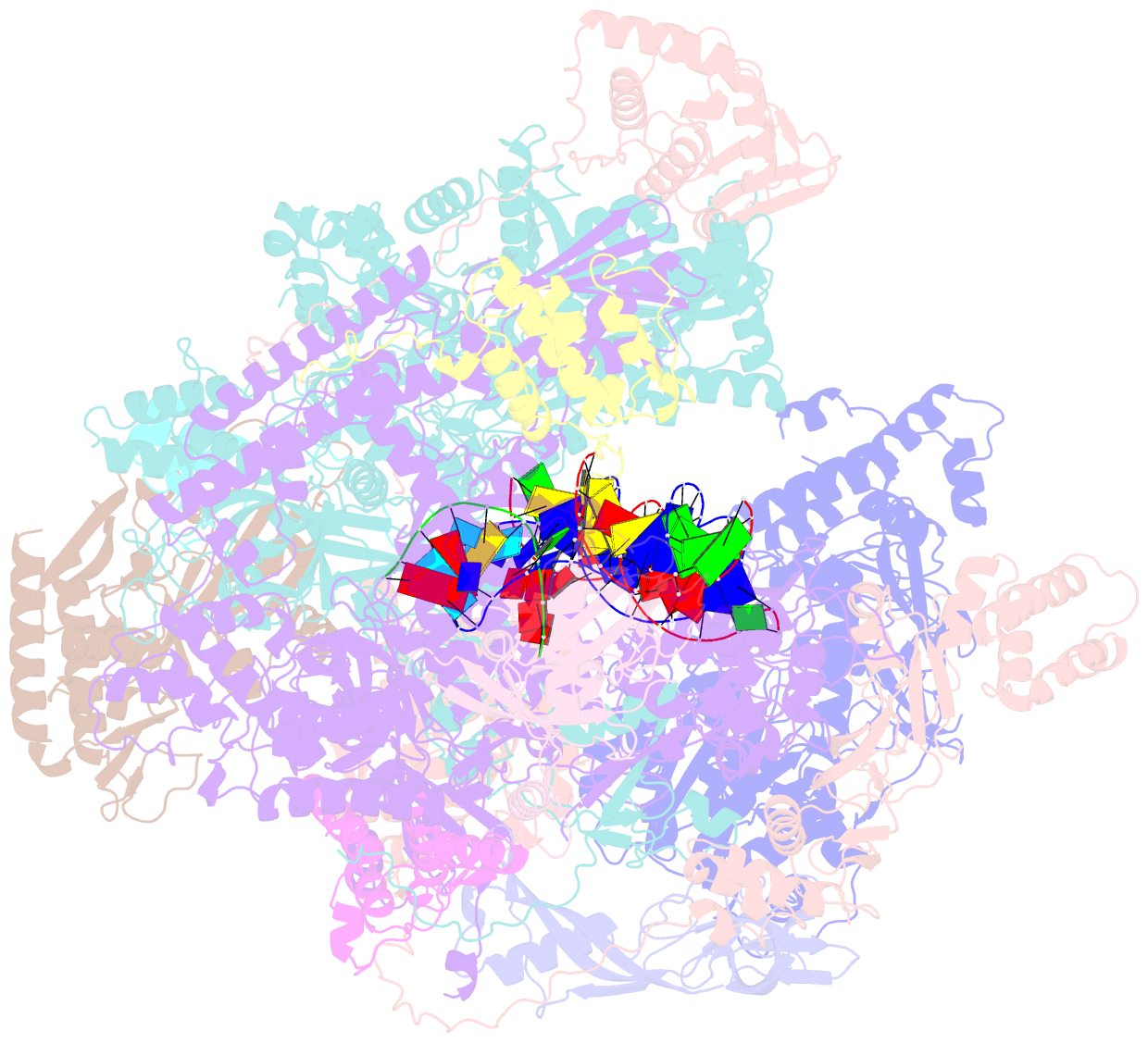
- Atomic structure of the poxvirus late initially transcribing complex
- Reference
- Grimm C, Bartuli J, Boettcher B, Szalay AA, Fischer U (2021): "Structural basis of the complete poxvirus transcription initiation process." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 28, 779-788. doi: 10.1038/s41594-021-00655-w.
- Abstract
- Poxviruses express their genes in the cytoplasm of infected cells using a virus-encoded multi-subunit polymerase (vRNAP) and unique transcription factors. We present cryo-EM structures that uncover the complete transcription initiation phase of the poxvirus vaccinia. In the pre-initiation complex, the heterodimeric early transcription factor VETFs/l adopts an arc-like shape spanning the polymerase cleft and anchoring upstream and downstream promoter elements. VETFI emerges as a TBP-like protein that inserts asymmetrically into the DNA major groove, triggers DNA melting, ensures promoter recognition and enforces transcription directionality. The helicase VETFs fosters promoter melting and the phospho-peptide domain (PPD) of vRNAP subunit Rpo30 enables transcription initiation. An unprecedented upstream promoter scrunching mechanism assisted by the helicase NPH-I probably fosters promoter escape and transition into elongation. Our structures shed light on unique mechanisms of poxviral gene expression and aid the understanding of thus far unexplained universal principles in transcription.