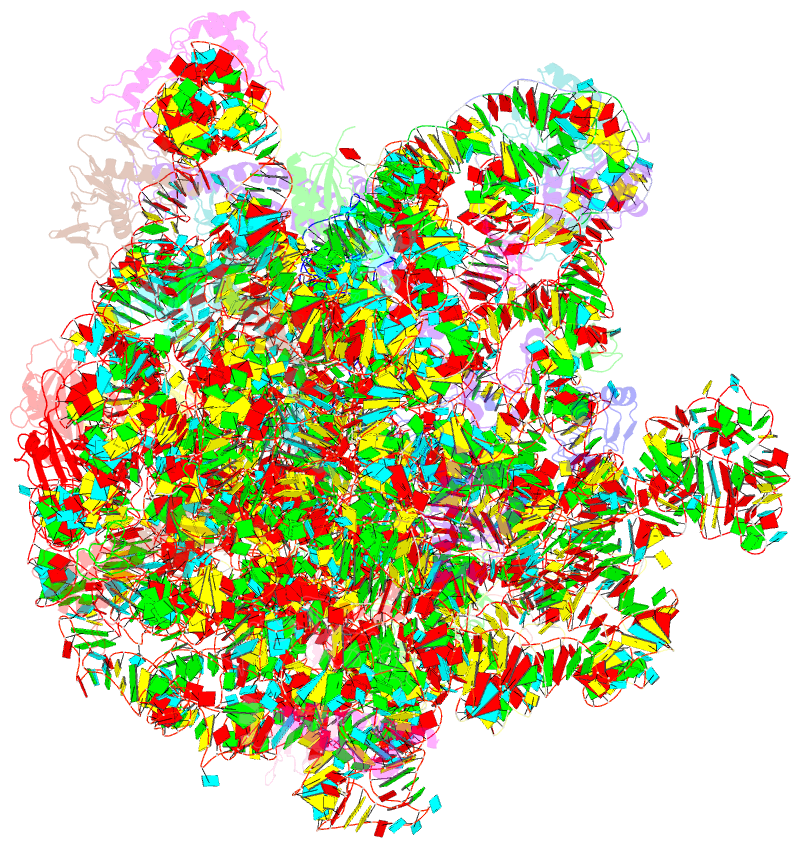
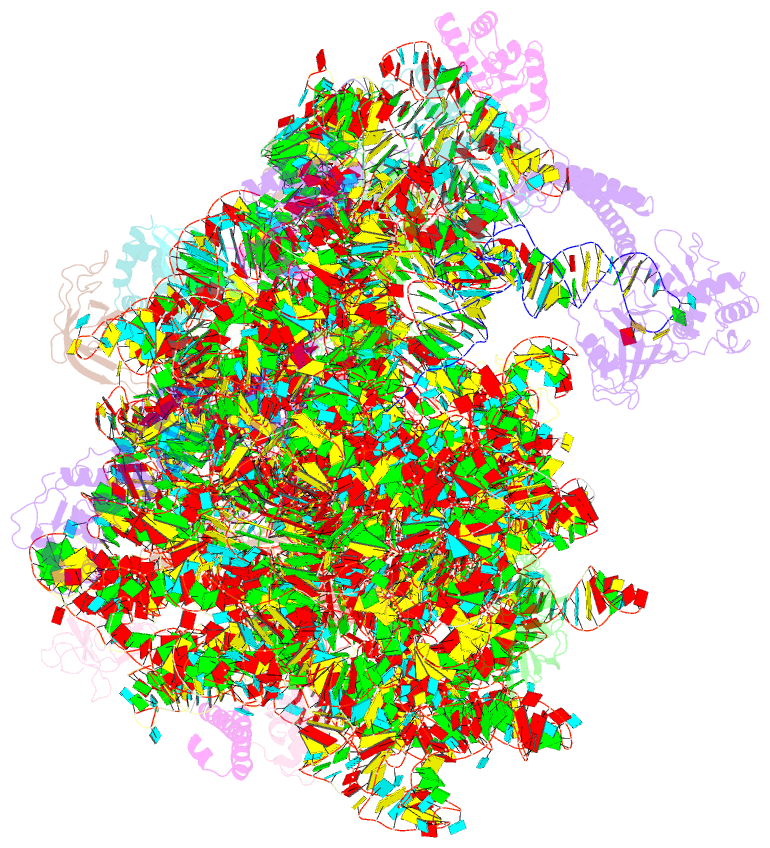
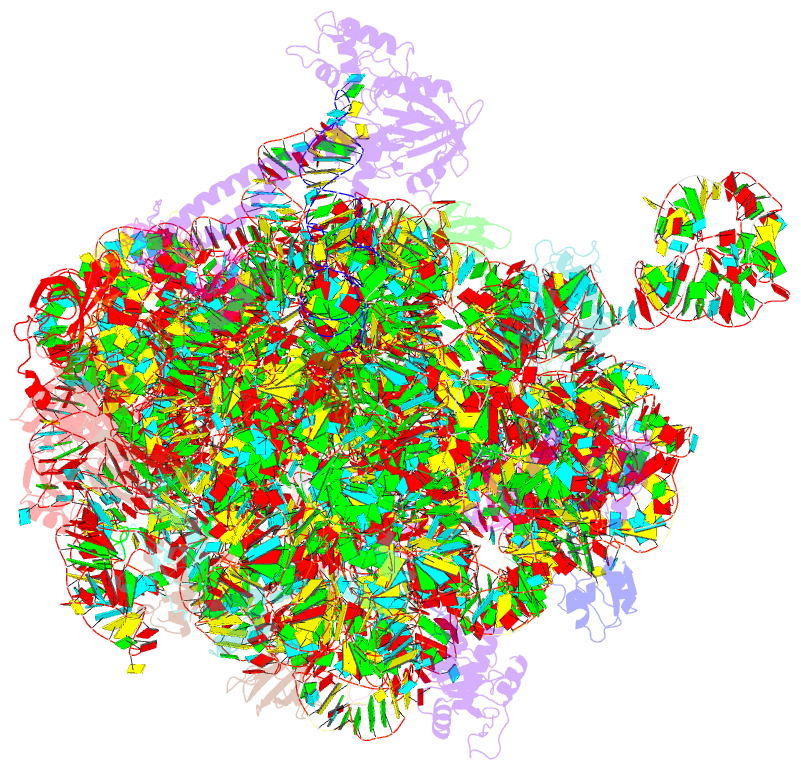
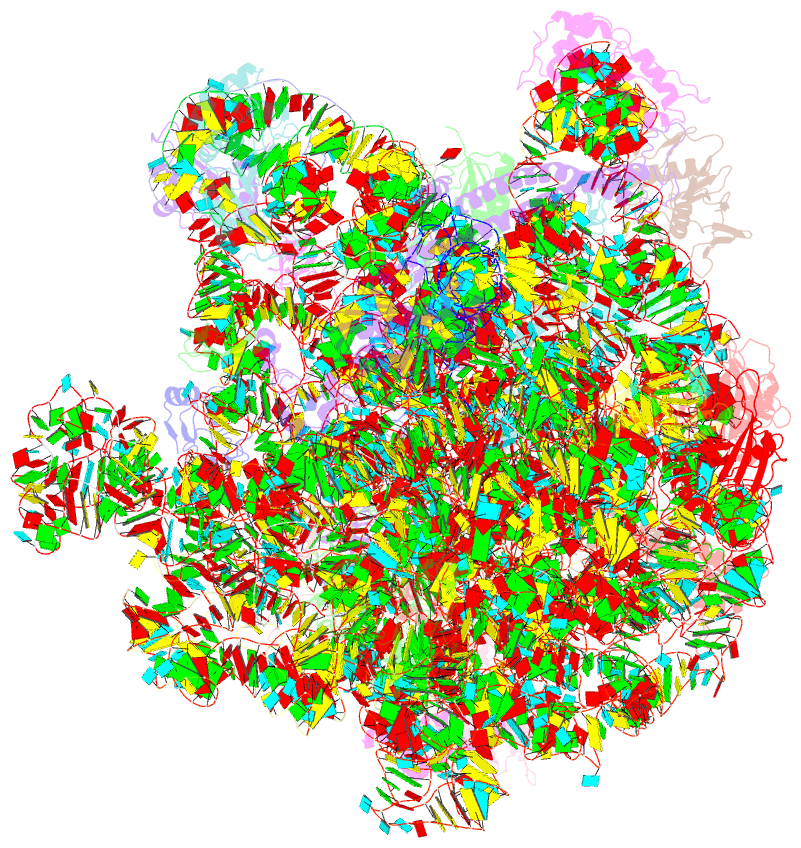
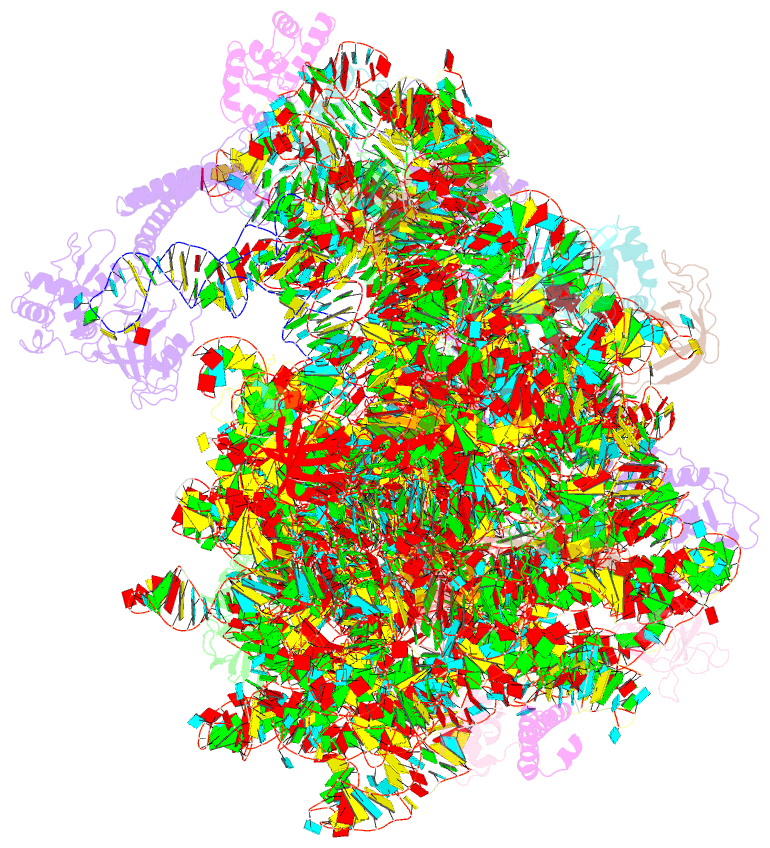
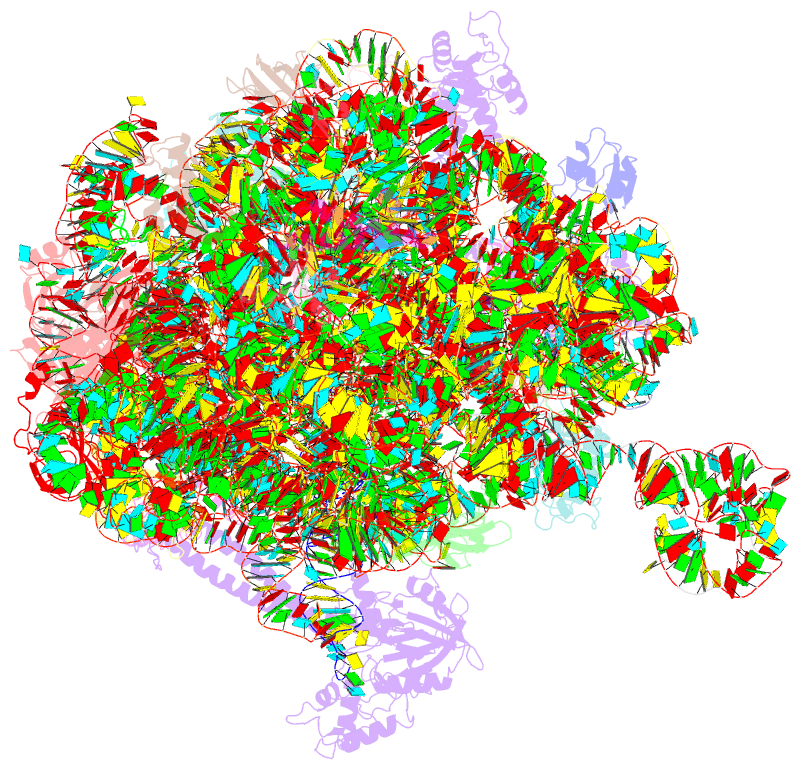
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7aqd; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- ribosome
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.1 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of the bacterial rqc complex (translocating state)
- Reference
- Filbeck S, Cerullo F, Paternoga H, Tsaprailis G, Joazeiro CAP, Pfeffer S (2021): "Mimicry of Canonical Translation Elongation Underlies Alanine Tail Synthesis in RQC." Mol.Cell, 81, 104. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.001.
- Abstract
- Aborted translation produces large ribosomal subunits obstructed with tRNA-linked nascent chains, which are substrates of ribosome-associated quality control (RQC). Bacterial RqcH, a widely conserved RQC factor, senses the obstruction and recruits tRNAAla(UGC) to modify nascent-chain C termini with a polyalanine degron. However, how RqcH and its eukaryotic homologs (Rqc2 and NEMF), despite their relatively simple architecture, synthesize such C-terminal tails in the absence of a small ribosomal subunit and mRNA has remained unknown. Here, we present cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of Bacillus subtilis RQC complexes representing different Ala tail synthesis steps. The structures explain how tRNAAla is selected via anticodon reading during recruitment to the A-site and uncover striking hinge-like movements in RqcH leading tRNAAla into a hybrid A/P-state associated with peptidyl-transfer. Finally, we provide structural, biochemical, and molecular genetic evidence identifying the Hsp15 homolog (encoded by rqcP) as a novel RQC component that completes the cycle by stabilizing the P-site tRNA conformation. Ala tailing thus follows mechanistic principles surprisingly similar to canonical translation elongation.