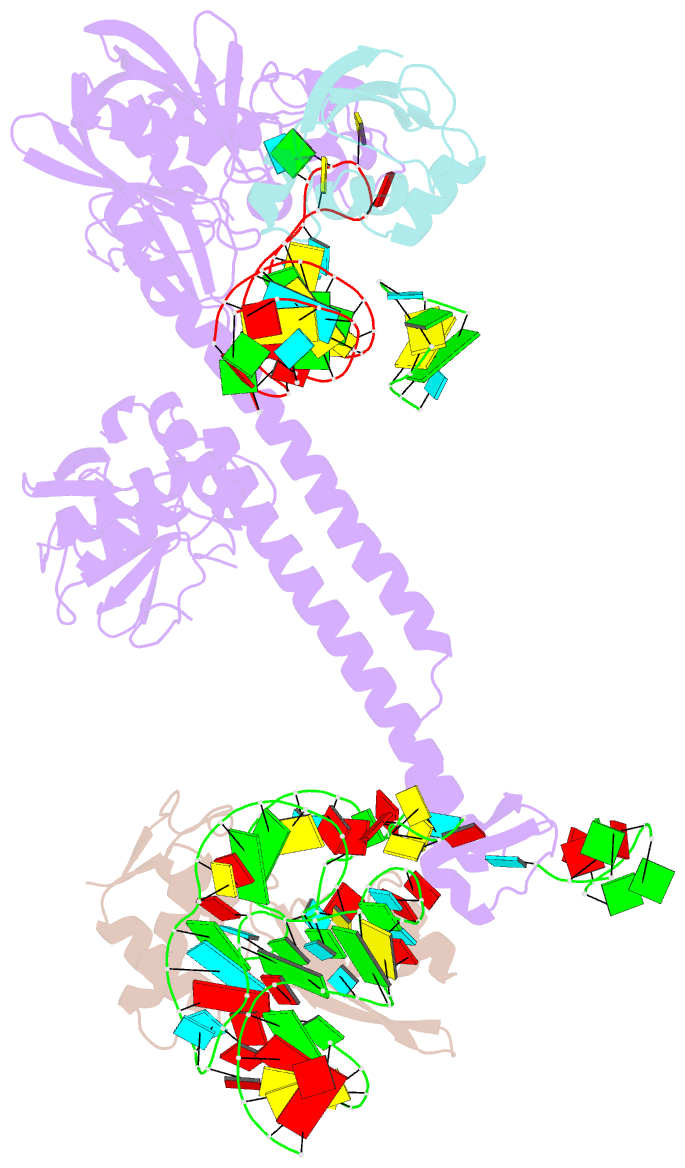
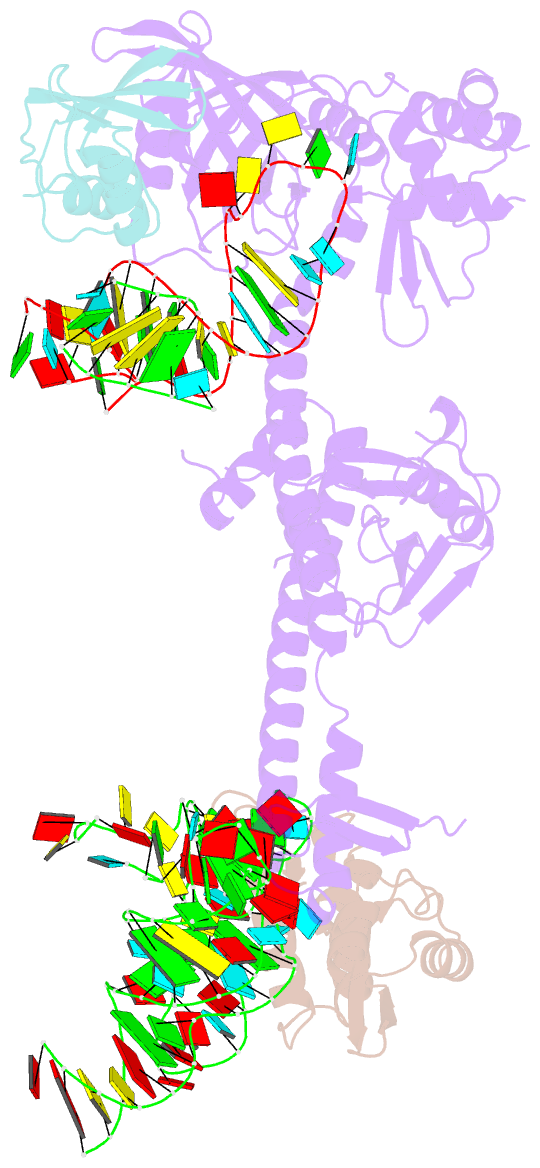
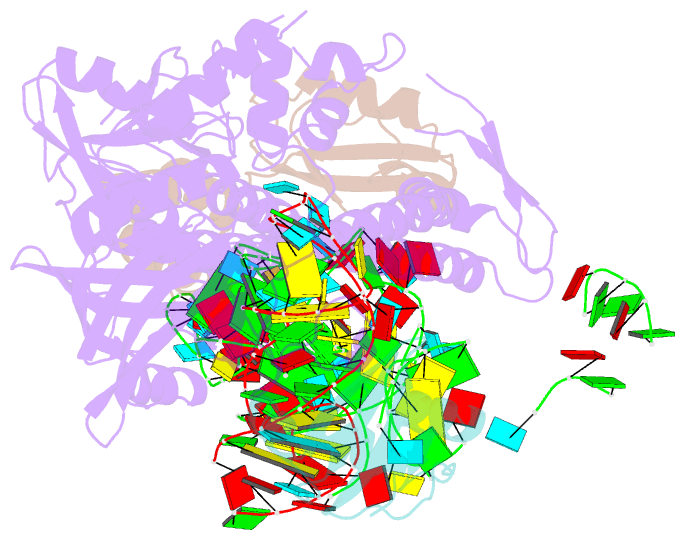
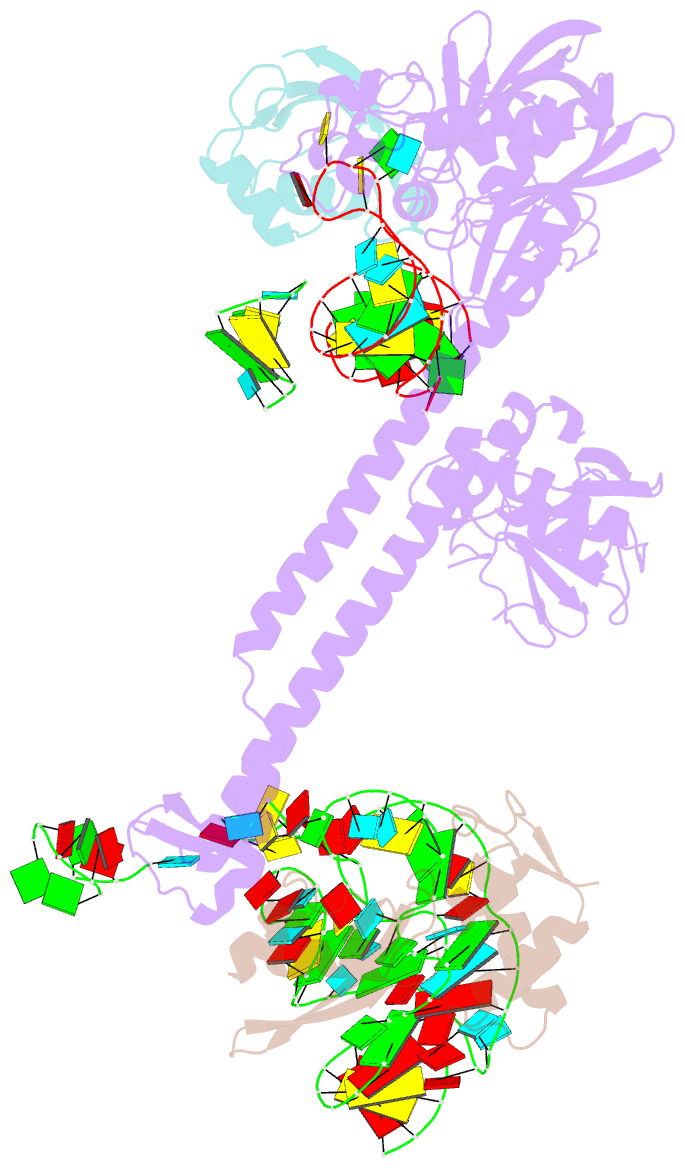
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7asa; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- translation
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.5 Å)
- Summary
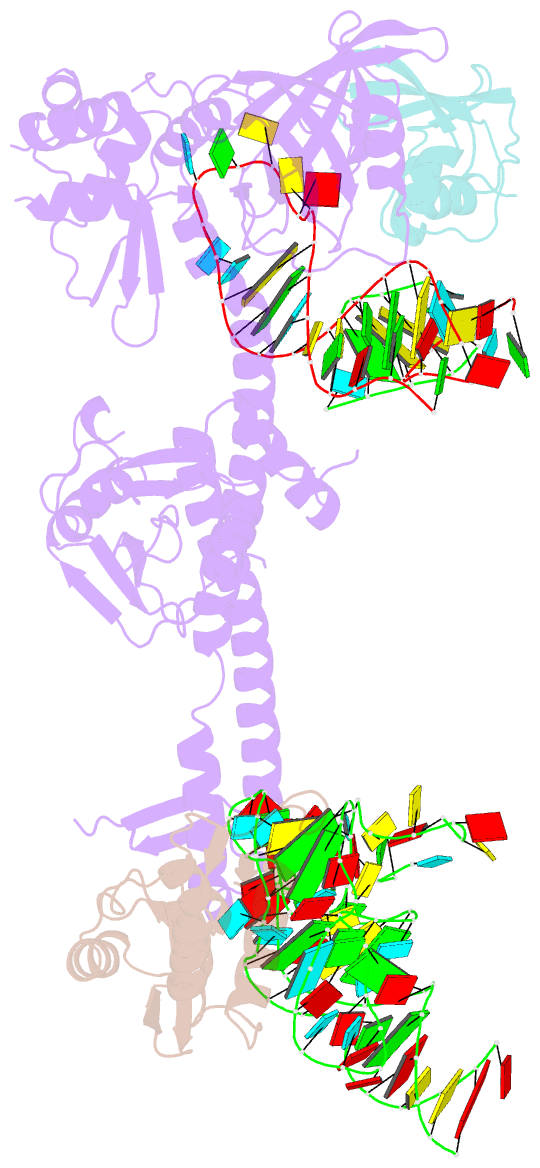
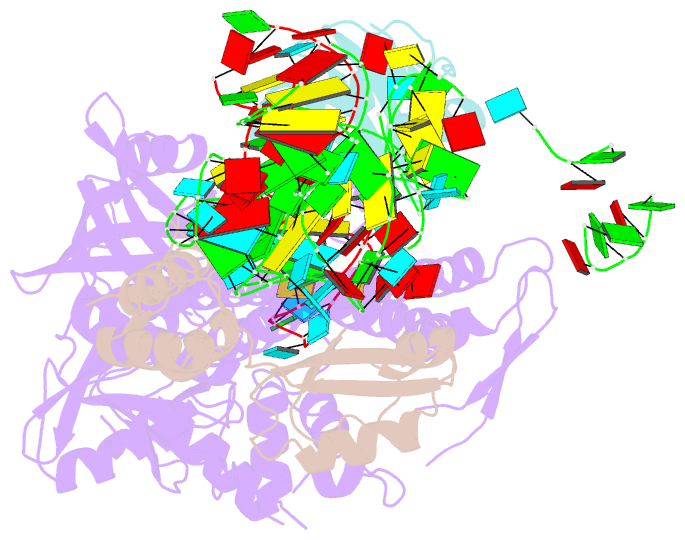
- Bacillus subtilis ribosome-associated quality control complex state b, multibody refinement focussed on rqch. ribosomal 50s subunit with p-trna, rqch, and rqcp-yabo
- Reference
- Crowe-McAuliffe C, Takada H, Murina V, Polte C, Kasvandik S, Tenson T, Ignatova Z, Atkinson GC, Wilson DN, Hauryliuk V (2021): "Structural Basis for Bacterial Ribosome-Associated Quality Control by RqcH and RqcP." Mol.Cell, 81, 115. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2020.11.002.
- Abstract
- In all branches of life, stalled translation intermediates are recognized and processed by ribosome-associated quality control (RQC) pathways. RQC begins with the splitting of stalled ribosomes, leaving an unfinished polypeptide still attached to the large subunit. Ancient and conserved NEMF family RQC proteins target these incomplete proteins for degradation by the addition of C-terminal "tails." How such tailing can occur without the regular suite of translational components is, however, unclear. Using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy (EM) of native complexes, we show that C-terminal tailing in Bacillus subtilis is mediated by NEMF protein RqcH in concert with RqcP, an Hsp15 family protein. Our structures reveal how these factors mediate tRNA movement across the ribosomal 50S subunit to synthesize polypeptides in the absence of mRNA or the small subunit.