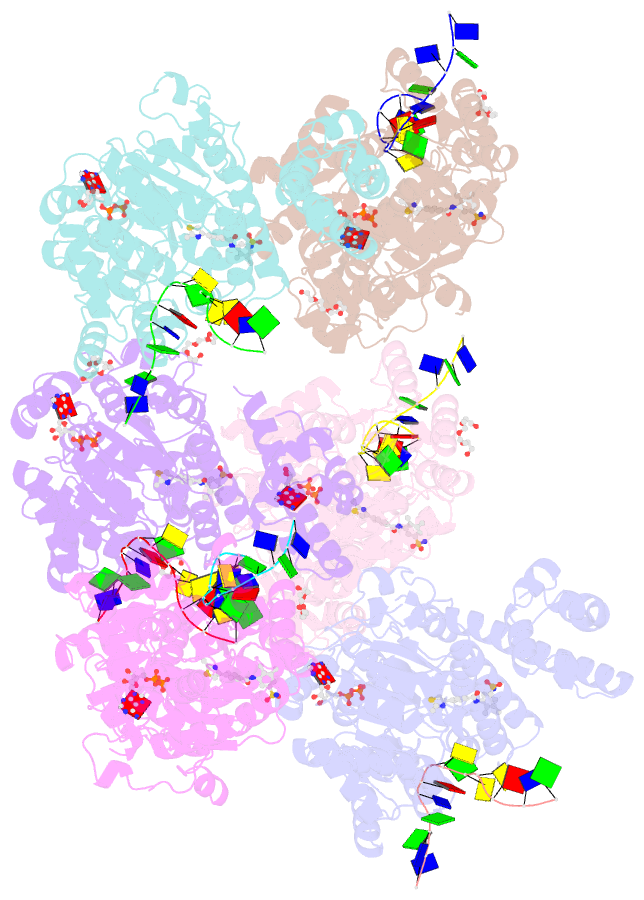
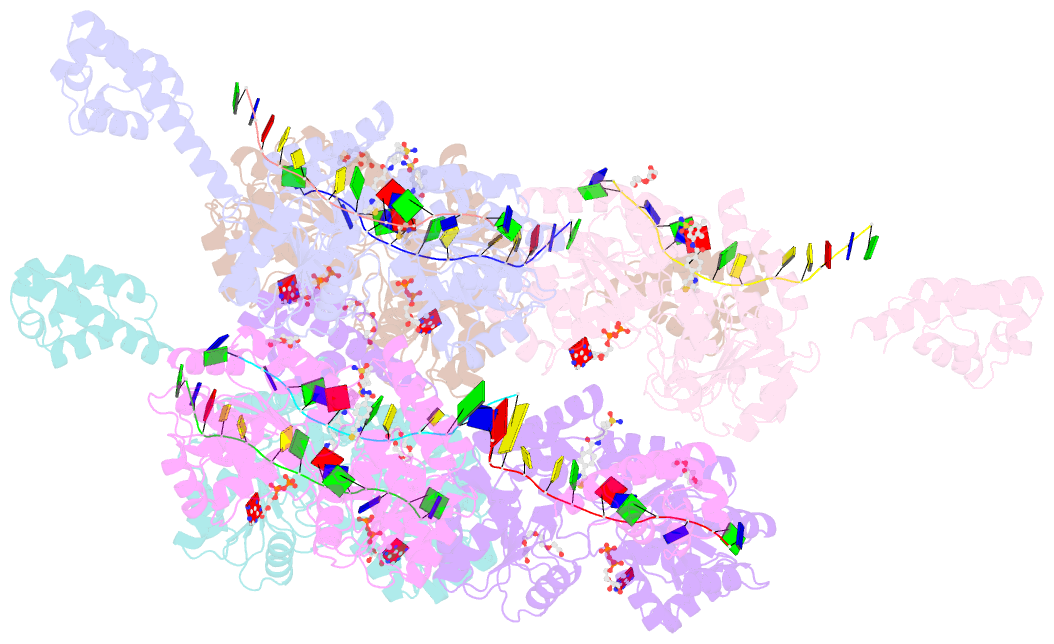
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7aud; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- nuclear protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.96 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of an engineered helicase domain construct for human bloom syndrome protein (blm)
- Reference
- Chen X, Ali YI, Fisher CE, Arribas-Bosacoma R, Rajasekaran MB, Williams G, Walker S, Booth JR, Hudson JJ, Roe SM, Pearl LH, Ward SE, Pearl FM, Oliver AW (2021): "Uncovering an allosteric mode of action for a selective inhibitor of human Bloom syndrome protein." Elife, 10. doi: 10.7554/eLife.65339.
- Abstract
- BLM (Bloom syndrome protein) is a RECQ-family helicase involved in the dissolution of complex DNA structures and repair intermediates. Synthetic lethality analysis implicates BLM as a promising target in a range of cancers with defects in the DNA damage response; however, selective small molecule inhibitors of defined mechanism are currently lacking. Here, we identify and characterise a specific inhibitor of BLM's ATPase-coupled DNA helicase activity, by allosteric trapping of a DNA-bound translocation intermediate. Crystallographic structures of BLM-DNA-ADP-inhibitor complexes identify a hitherto unknown interdomain interface, whose opening and closing are integral to translocation of ssDNA, and which provides a highly selective pocket for drug discovery. Comparison with structures of other RECQ helicases provides a model for branch migration of Holliday junctions by BLM.