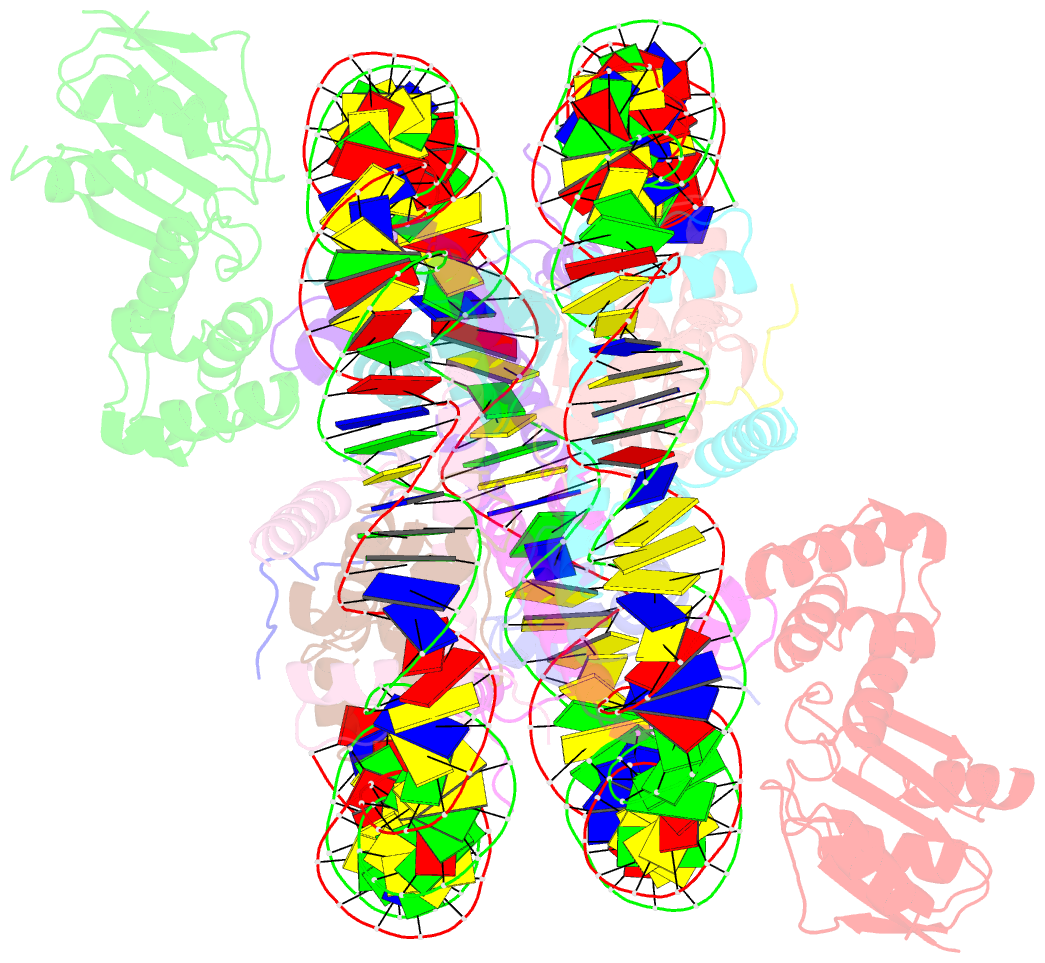
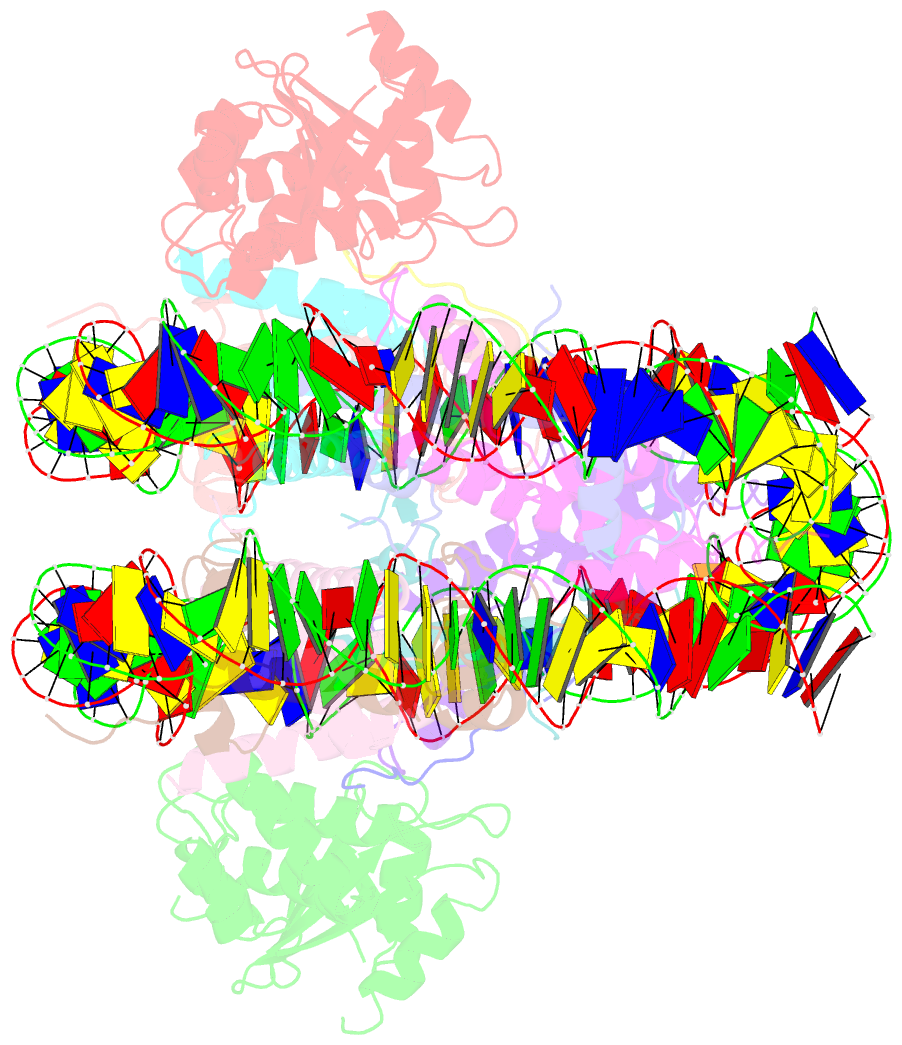
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7bxt; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- cell cycle-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (4.2 Å)
- Summary
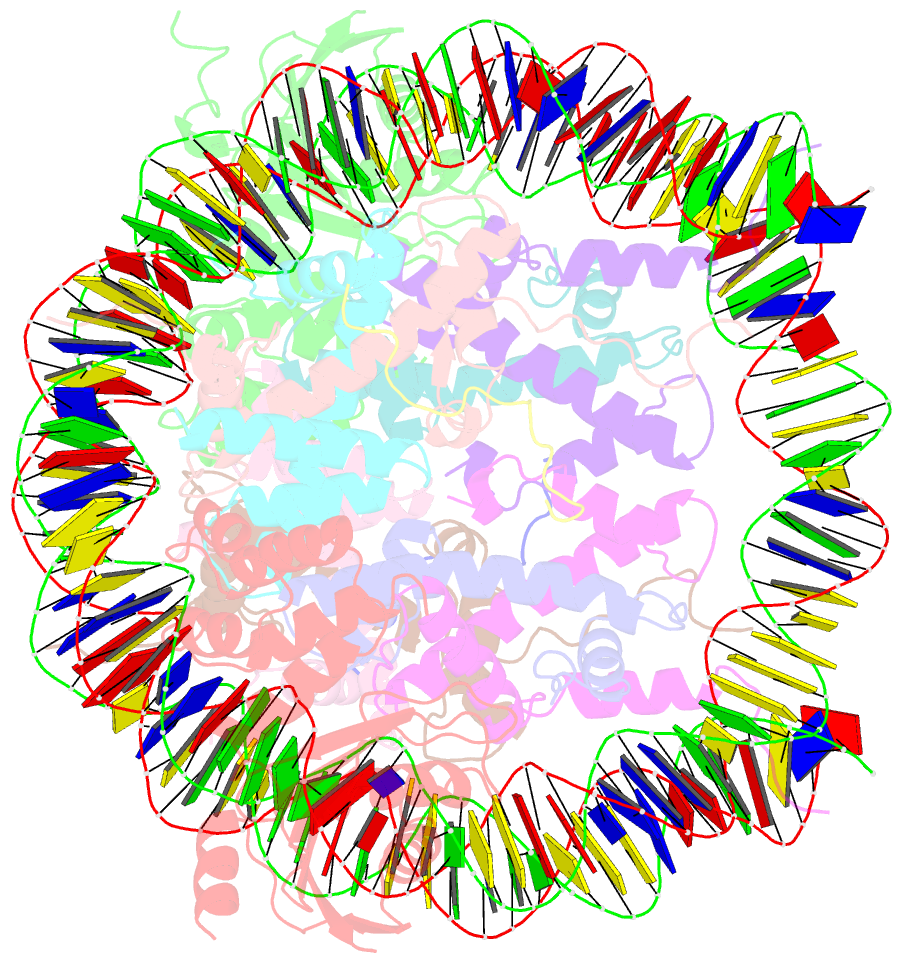
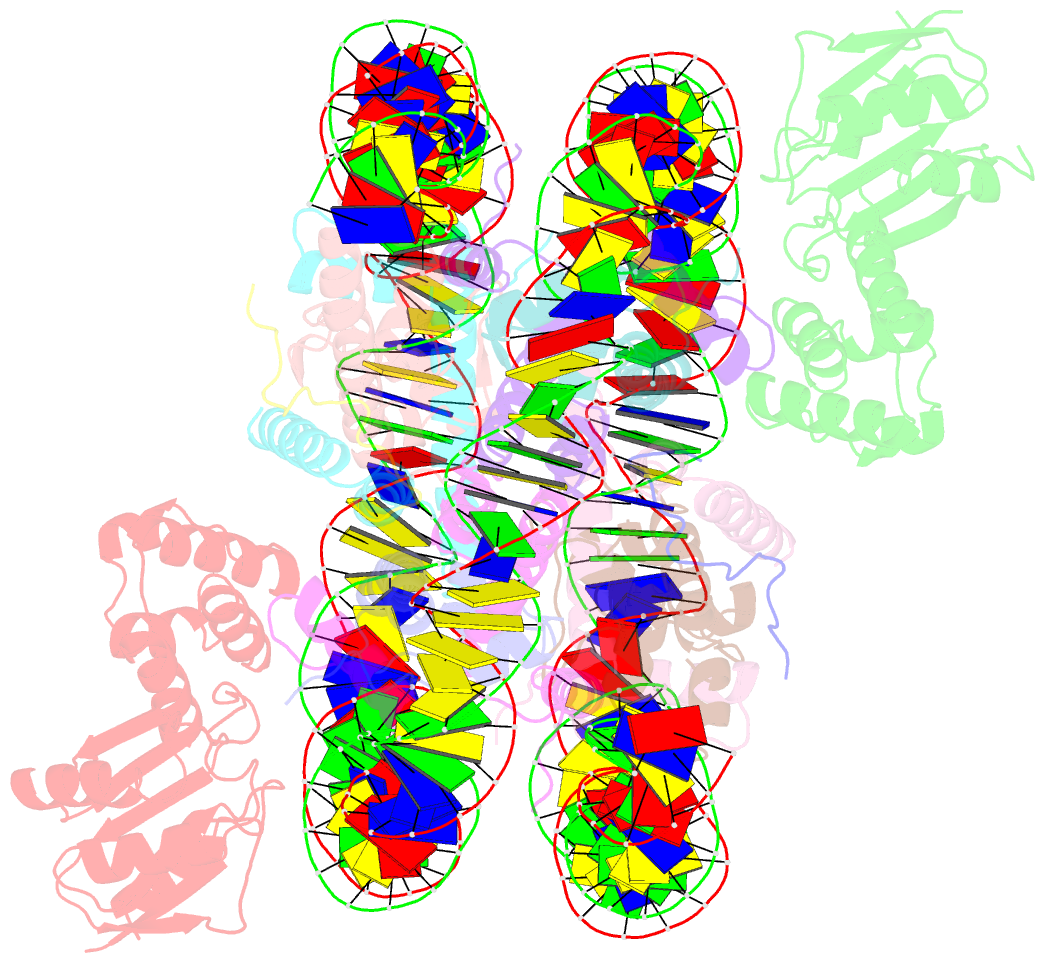
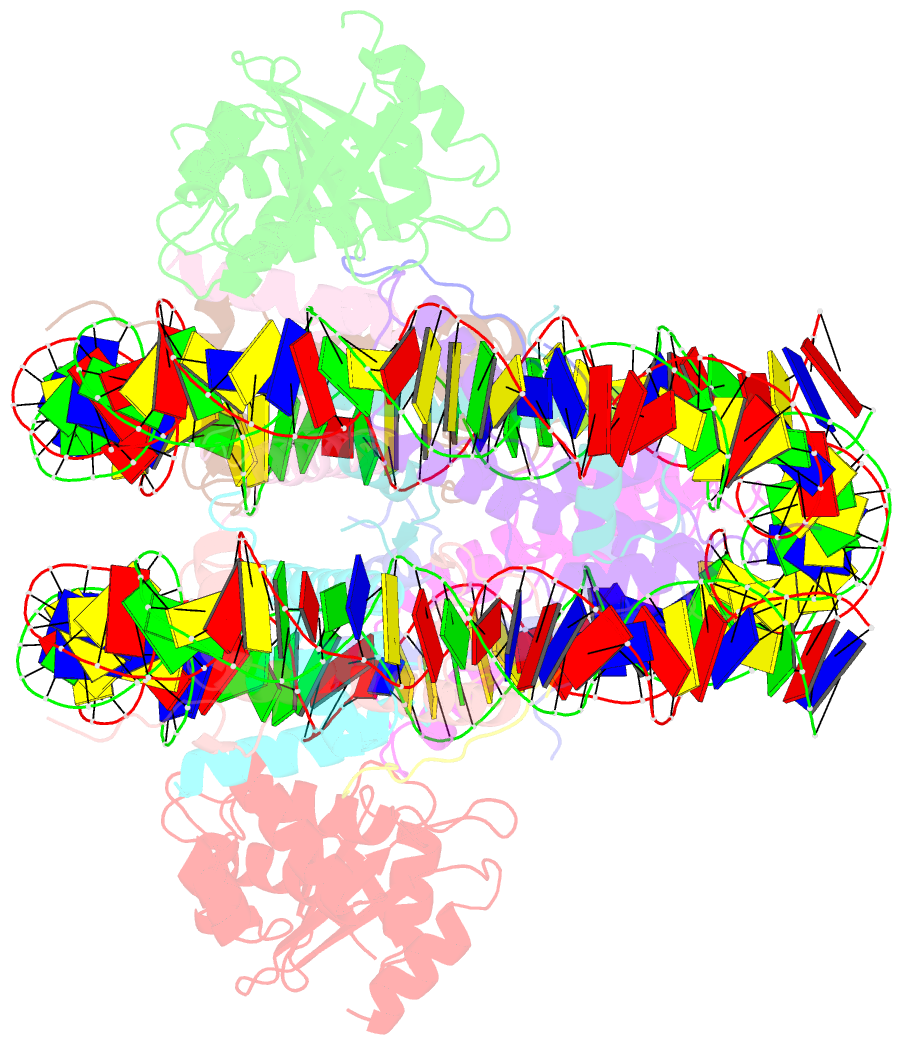
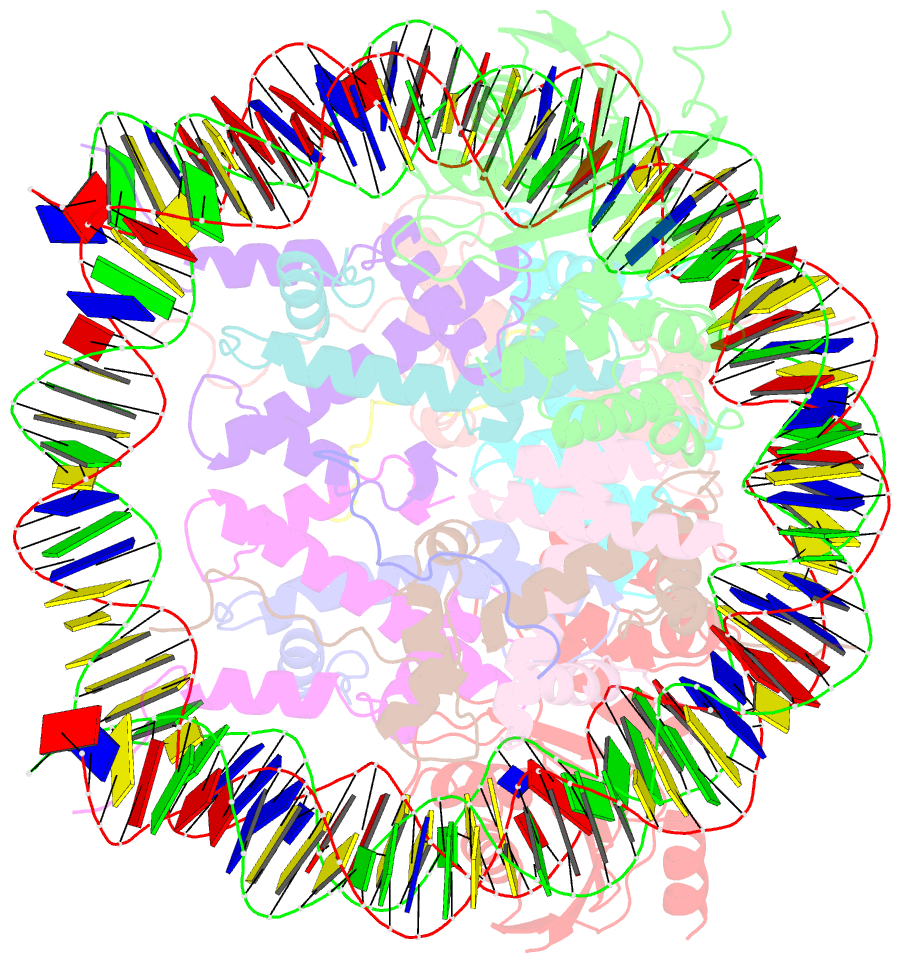
- The cryo-EM structure of cenp-a nucleosome in complex with cenp-c peptide and cenp-n n-terminal domain
- Reference
- Ariyoshi M, Makino F, Watanabe R, Nakagawa R, Kato T, Namba K, Arimura Y, Fujita R, Kurumizaka H, Okumura EI, Hara M, Fukagawa T (2021): "Cryo-EM structure of the CENP-A nucleosome in complex with phosphorylated CENP-C." Embo J., 40, e105671. doi: 10.15252/embj.2020105671.
- Abstract
- The CENP-A nucleosome is a key structure for kinetochore assembly. Once the CENP-A nucleosome is established in the centromere, additional proteins recognize the CENP-A nucleosome to form a kinetochore. CENP-C and CENP-N are CENP-A binding proteins. We previously demonstrated that vertebrate CENP-C binding to the CENP-A nucleosome is regulated by CDK1-mediated CENP-C phosphorylation. However, it is still unknown how the phosphorylation of CENP-C regulates its binding to CENP-A. It is also not completely understood how and whether CENP-C and CENP-N act together on the CENP-A nucleosome. Here, using cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) in combination with biochemical approaches, we reveal a stable CENP-A nucleosome-binding mode of CENP-C through unique regions. The chicken CENP-C structure bound to the CENP-A nucleosome is stabilized by an intramolecular link through the phosphorylated CENP-C residue. The stable CENP-A-CENP-C complex excludes CENP-N from the CENP-A nucleosome. These findings provide mechanistic insights into the dynamic kinetochore assembly regulated by CDK1-mediated CENP-C phosphorylation.