Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7c0m; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.9 Å)
- Summary
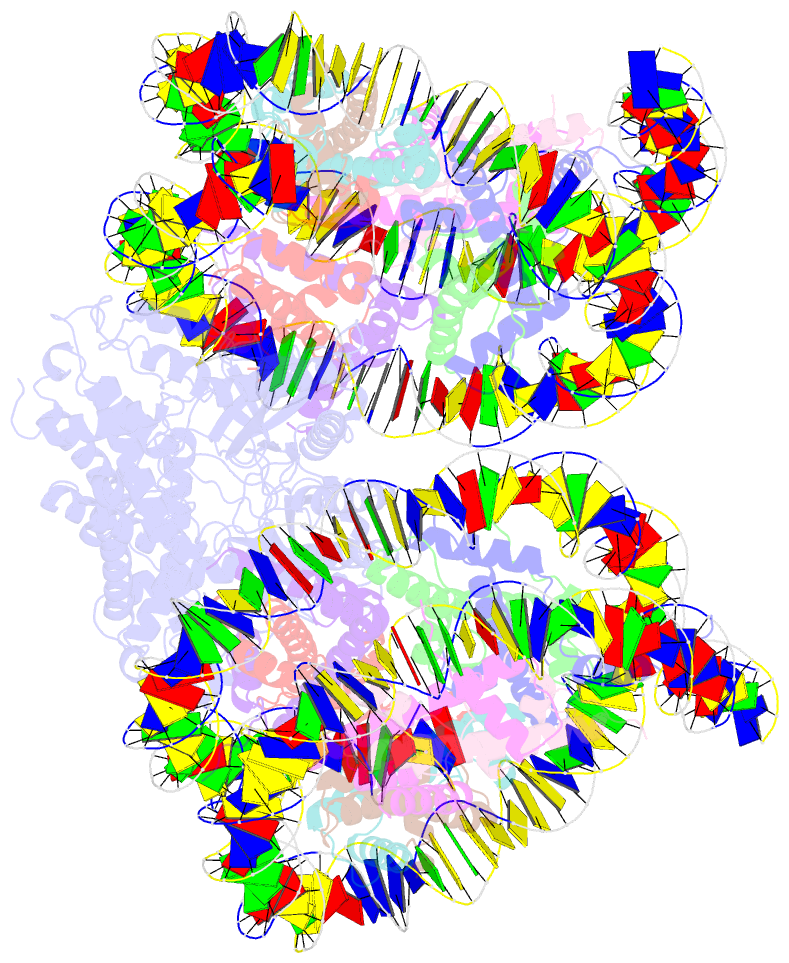
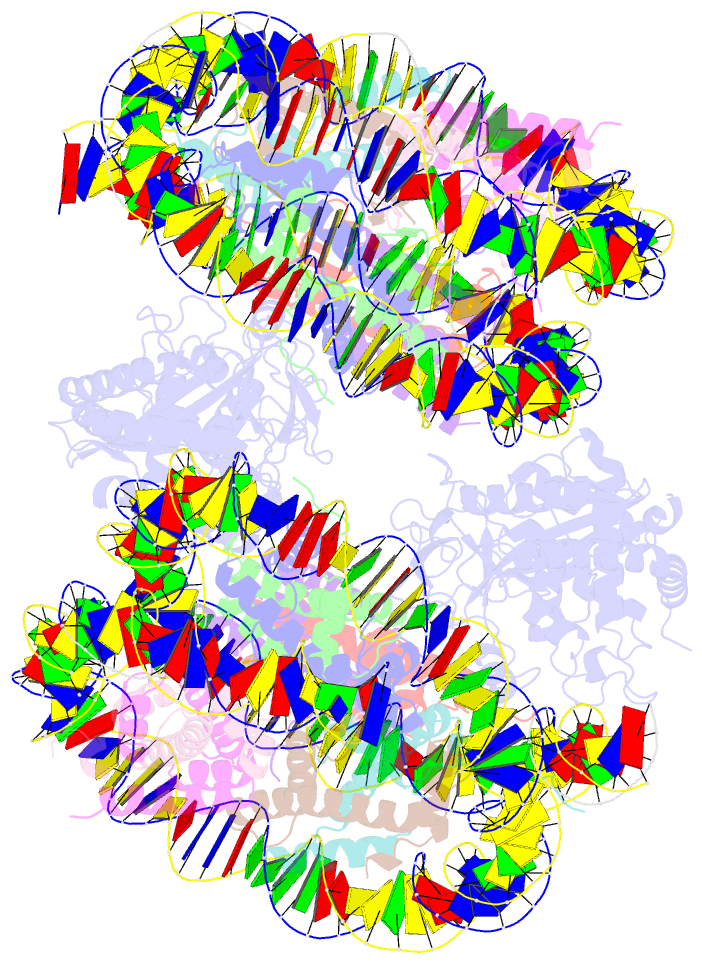
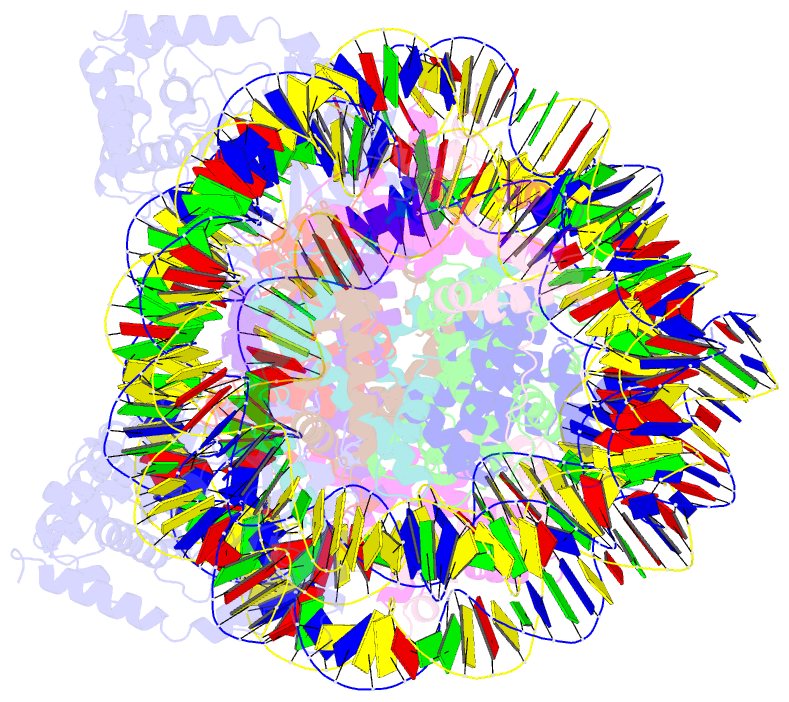
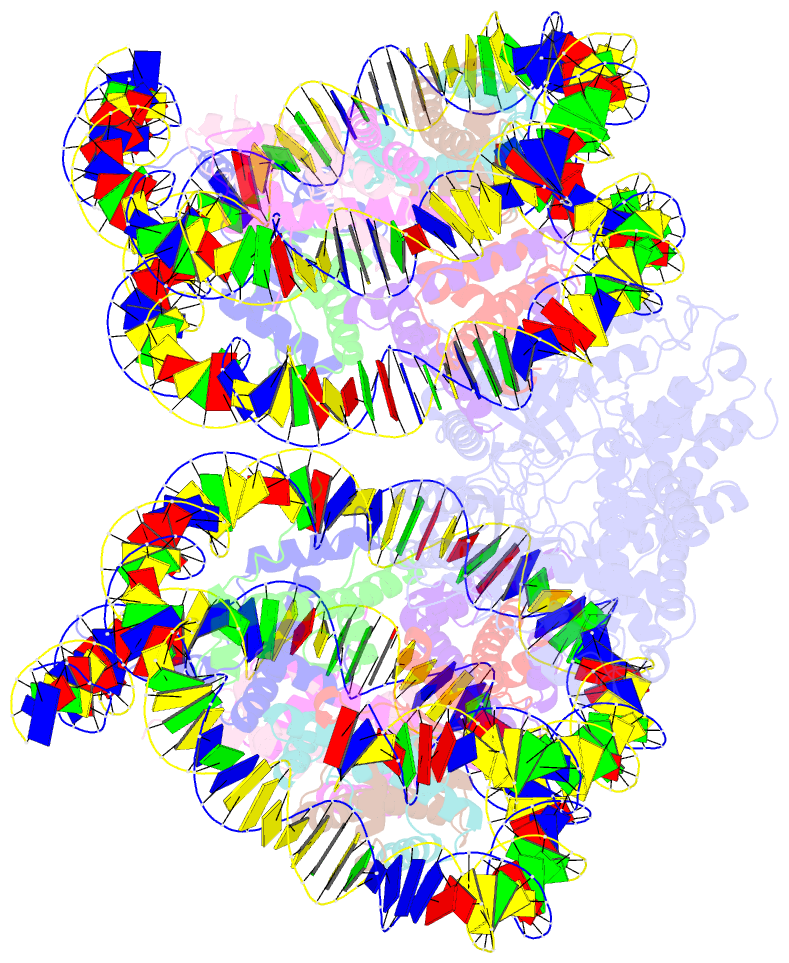
- Human cgas-nucleosome complex
- Reference
- Kujirai T, Zierhut C, Takizawa Y, Kim R, Negishi L, Uruma N, Hirai S, Funabiki H, Kurumizaka H (2020): "Structural basis for the inhibition of cGAS by nucleosomes." Science, 370, 455-458. doi: 10.1126/science.abd0237.
- Abstract
- The cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate synthase (cGAS) senses invasion of pathogenic DNA and stimulates inflammatory signaling, autophagy, and apoptosis. Organization of host DNA into nucleosomes was proposed to limit cGAS autoinduction, but the underlying mechanism was unknown. Here, we report the structural basis for this inhibition. In the cryo-electron microscopy structure of the human cGAS-nucleosome core particle (NCP) complex, two cGAS monomers bridge two NCPs by binding the acidic patch of the histone H2A-H2B dimer and nucleosomal DNA. In this configuration, all three known cGAS DNA binding sites, required for cGAS activation, are repurposed or become inaccessible, and cGAS dimerization, another prerequisite for activation, is inhibited. Mutating key residues linking cGAS and the acidic patch alleviates nucleosomal inhibition. This study establishes a structural framework for why cGAS is silenced on chromatinized self-DNA.