Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7cby; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- X-ray (1.646 Å)
- Summary
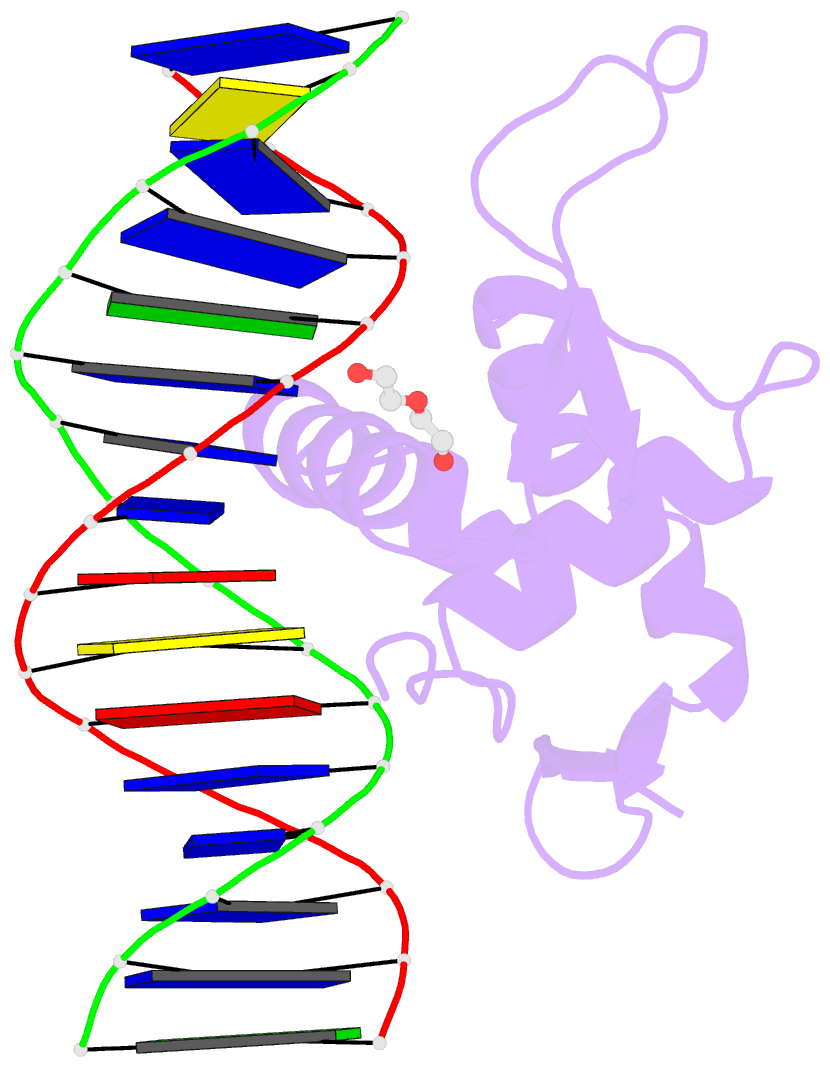
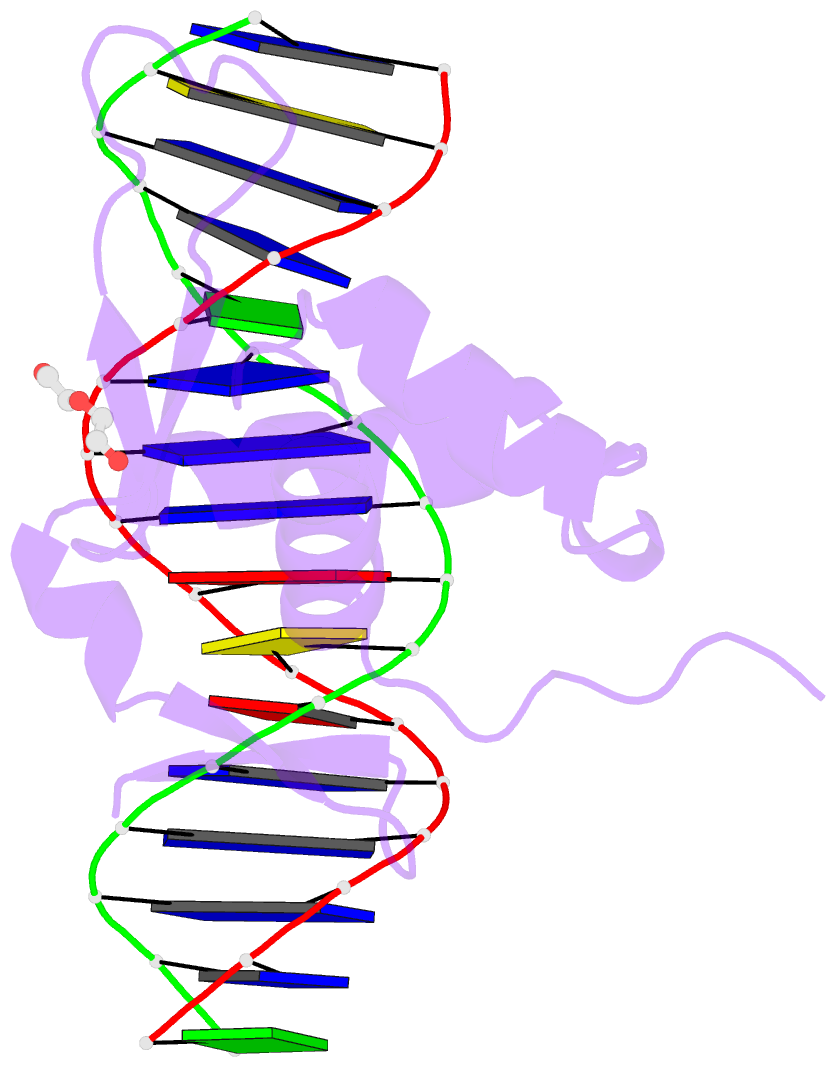
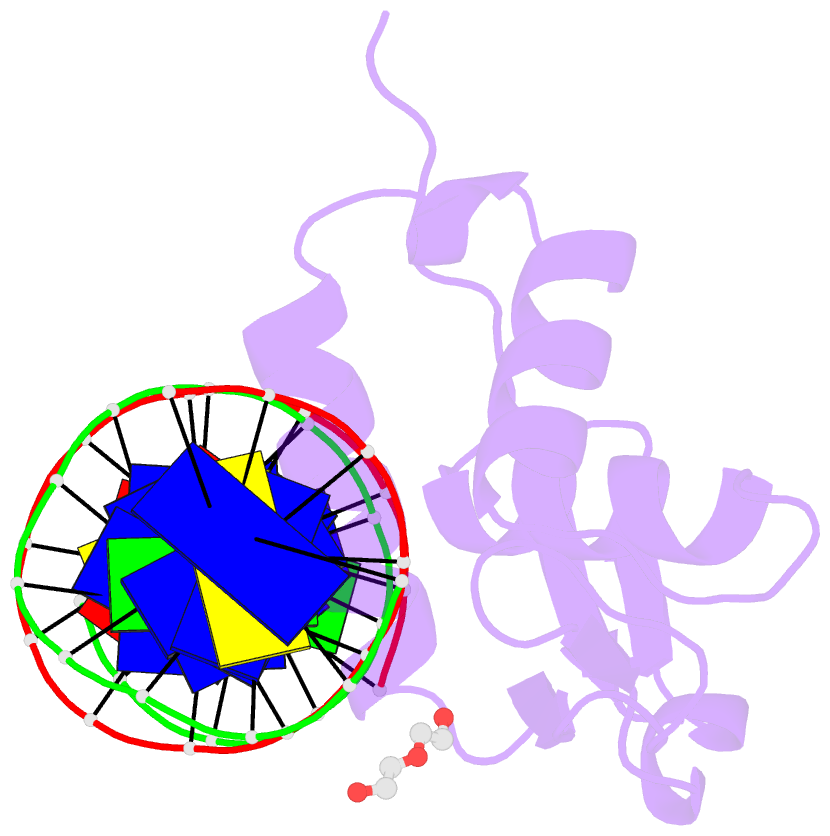
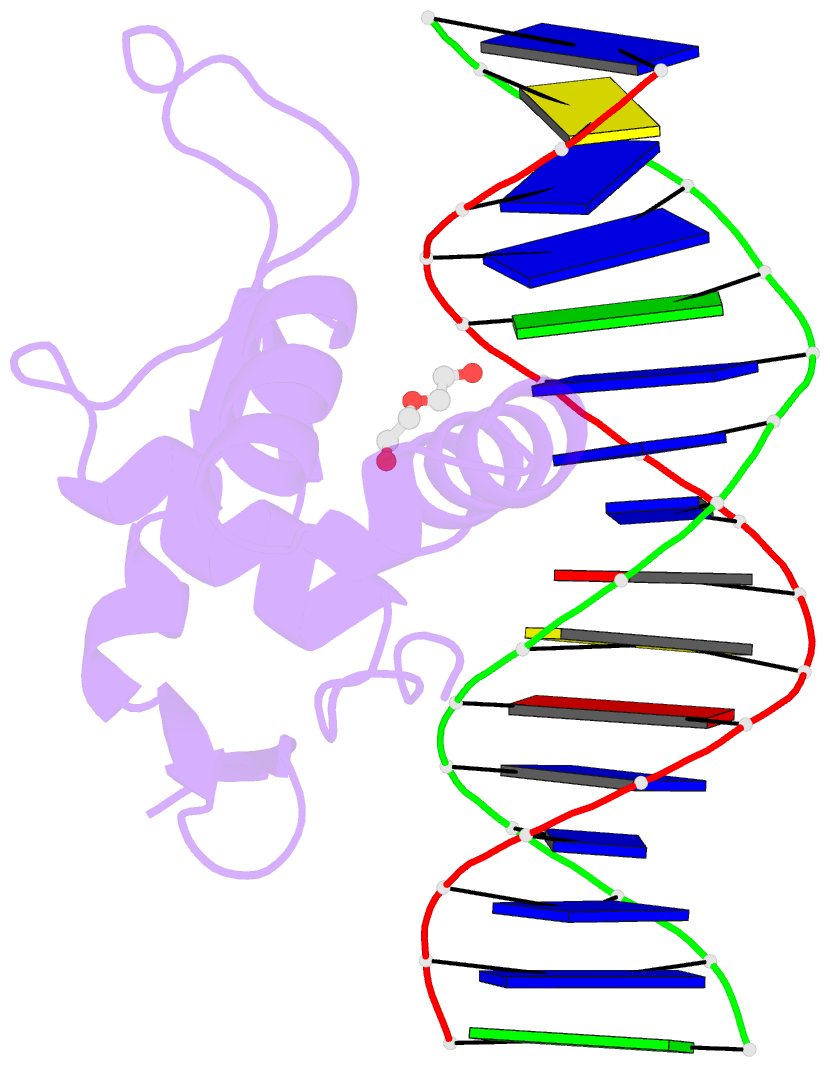
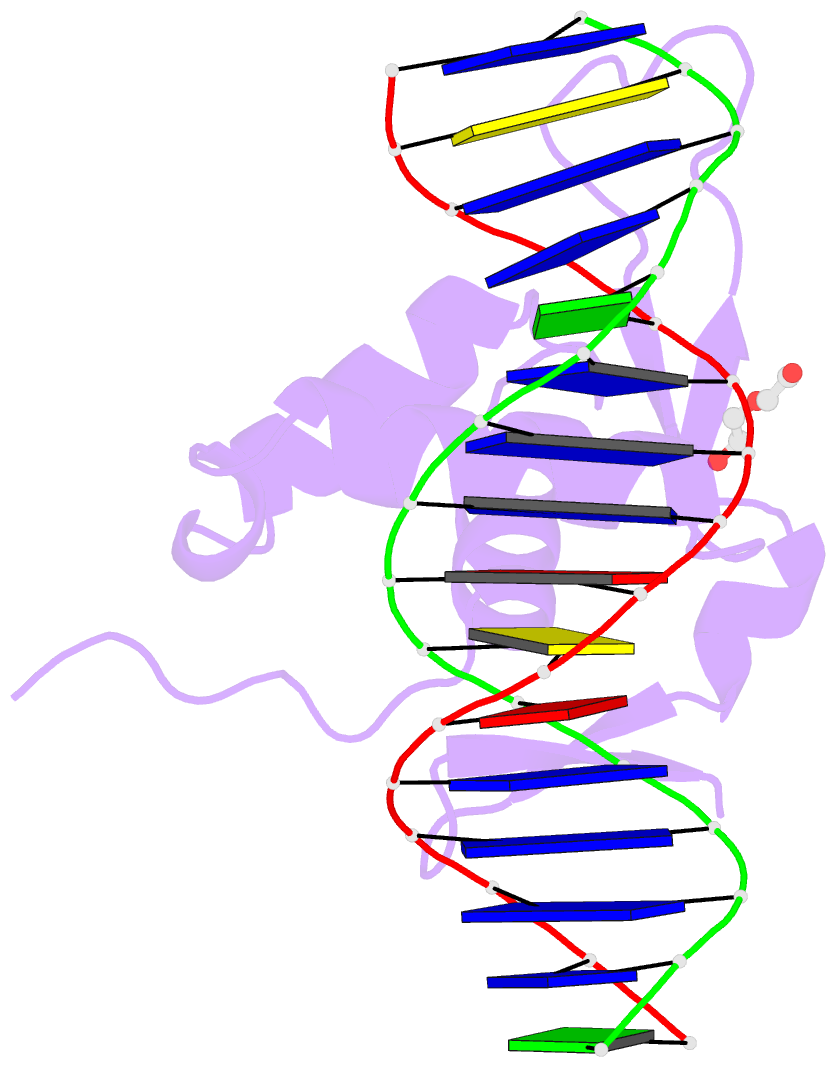
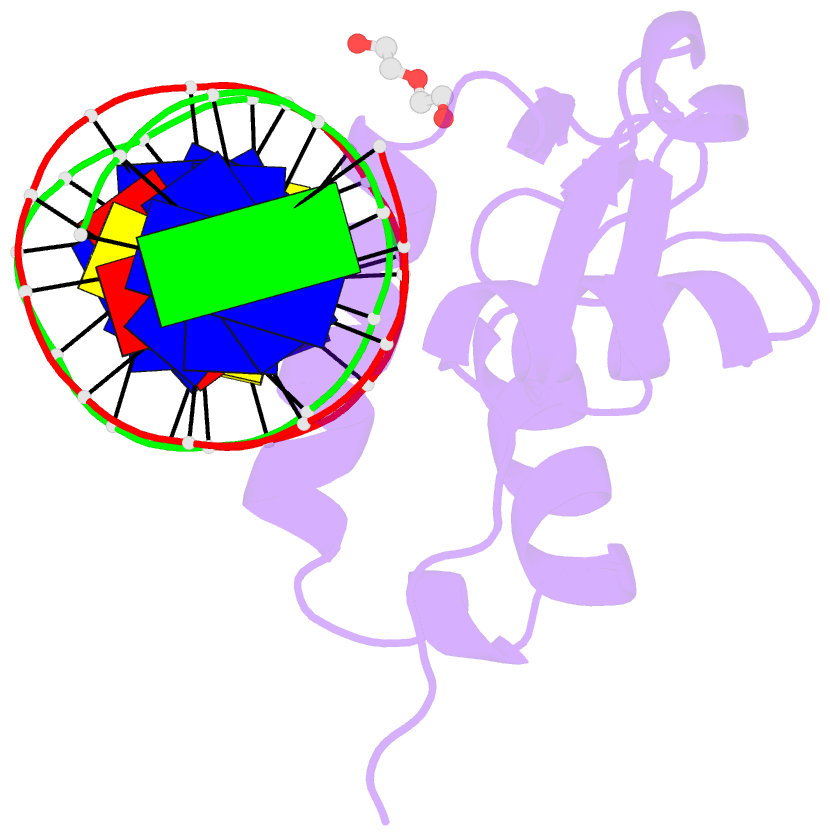
- Structure of foxg1 DNA binding domain bound to dbe2 DNA site
- Reference
- Dai S, Li J, Zhang H, Chen X, Guo M, Chen Z, Chen Y (2020): "Structural Basis for DNA Recognition by FOXG1 and the Characterization of Disease-causing FOXG1 Mutations." J.Mol.Biol., 432, 6146-6156. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2020.10.007.
- Abstract
- Forkhead box G1 (FOXG1) is a transcription factor mainly expressed in the brain that plays a critical role in the development and regionalization of the forebrain. Aberrant expression of FOXG1 has implications in FOXG1 syndrome, a serious neurodevelopmental disorder. Here, we report the crystal structure of the FOXG1 DNA-binding domain (DBD) in complex with the forkhead consensus DNA site DBE2 at the resolution of 1.6 Å. FOXG1-DBD adopts a typical winged helix fold. Compared to those of other FOX-DBD/DBE2 structures, the N terminus, H3 helix and wing2 region of FOXG1-DBD exhibit differences in DNA recognition. The FOXG1-DBD wing2 region adopts a unique architecture composed of two β-strands that differs from all other known FOX-DBD wing2 folds. Mutation assays revealed that the disease-causing mutations within the FOXG1-DBD affect DNA binding, protein thermal stability, or both. Our report provides initial insight into how FOXG1 binds DNA and sheds light on how disease-causing mutations in FOXG1-DBD affect its DNA-binding ability.