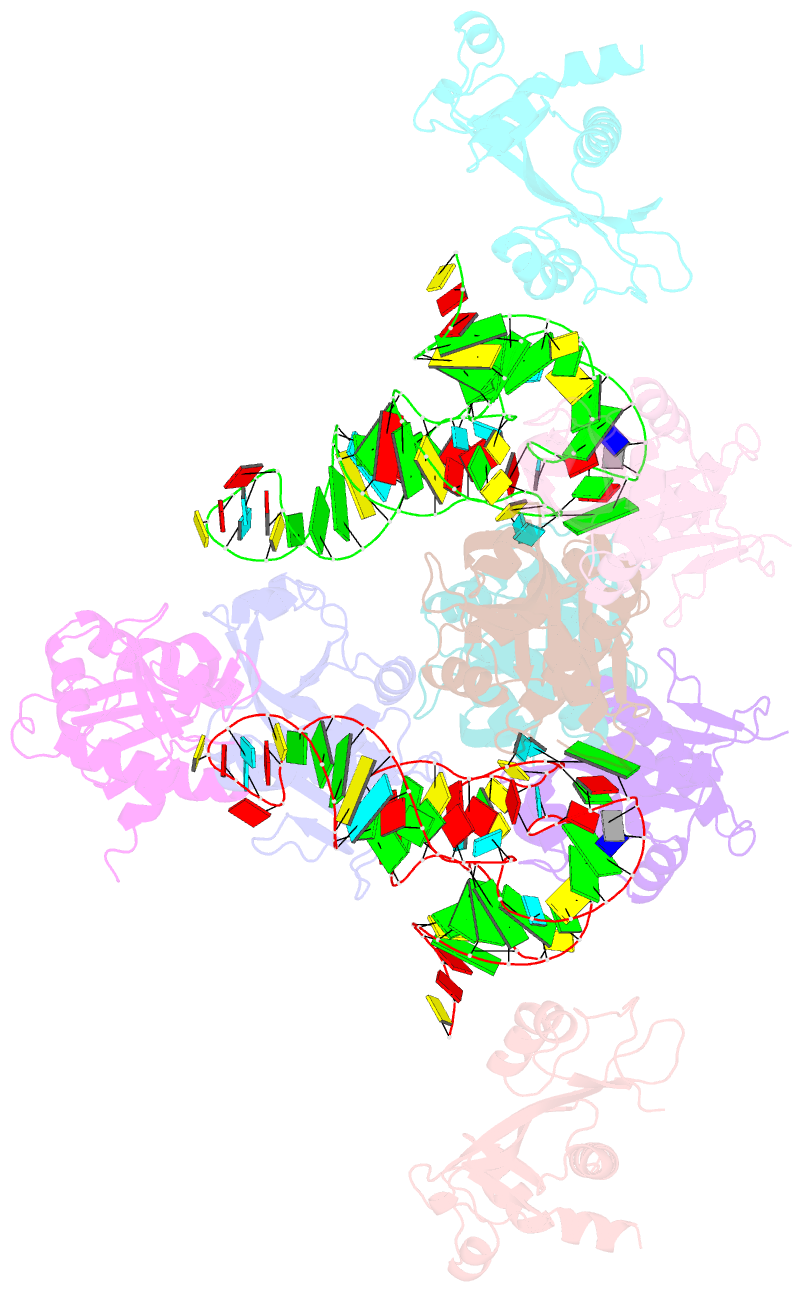
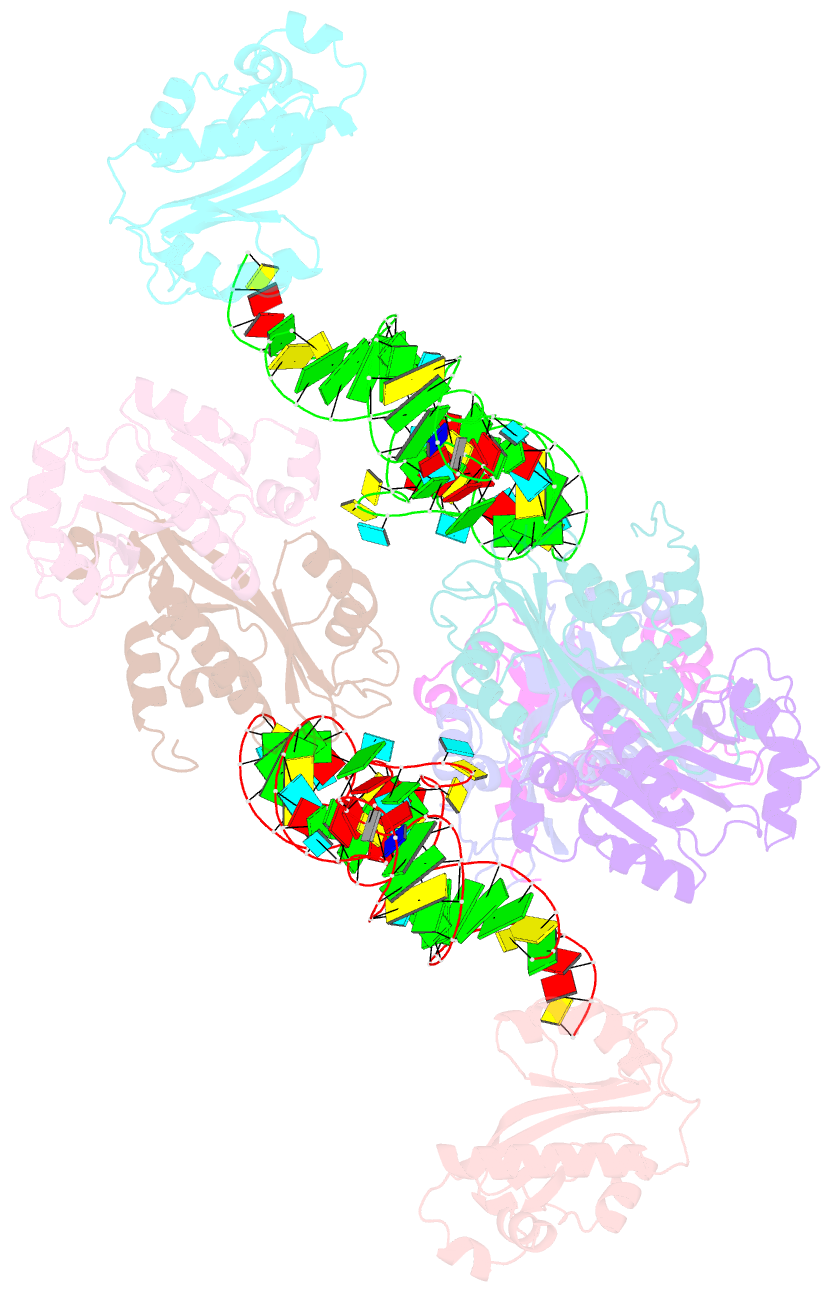
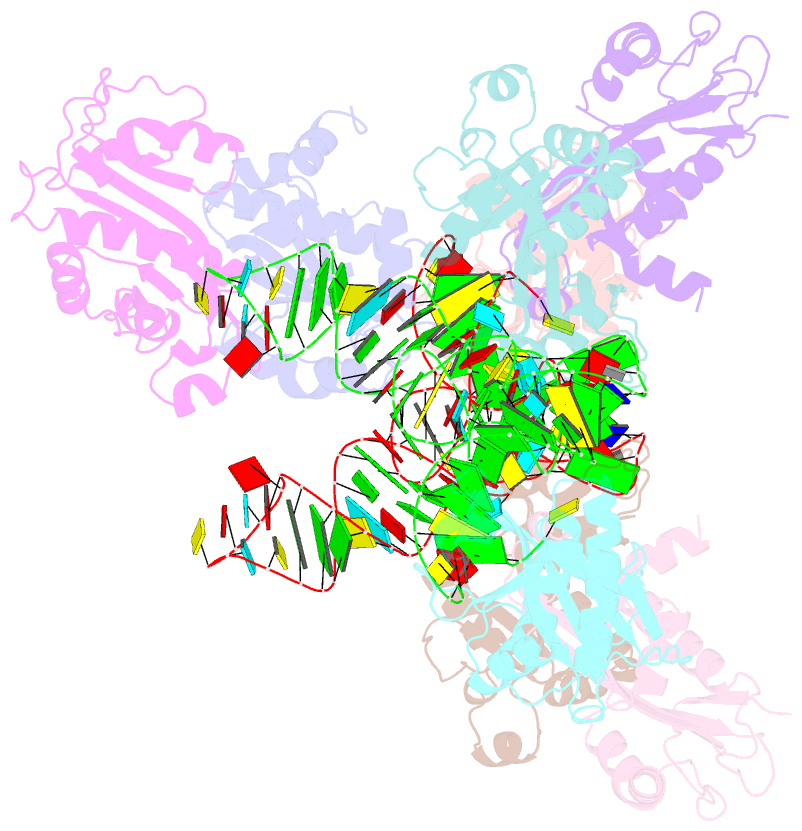
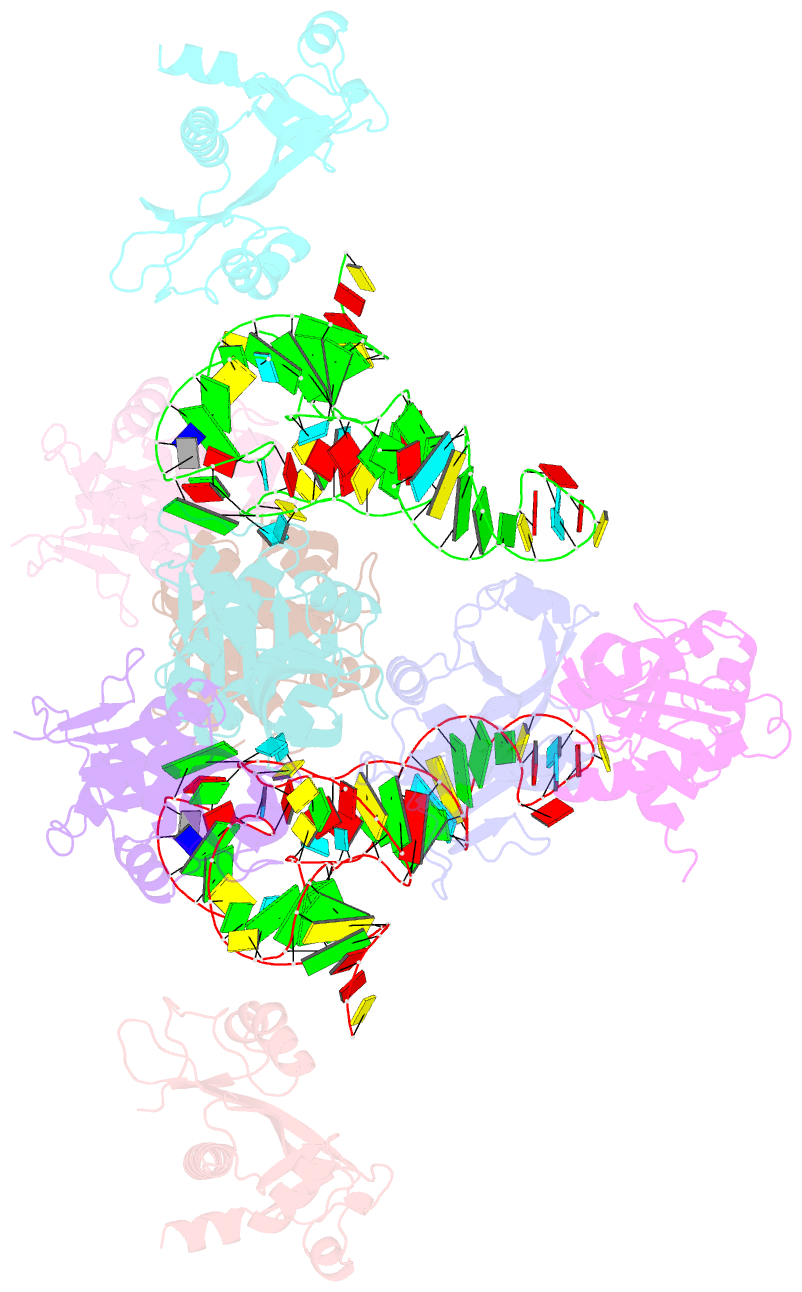
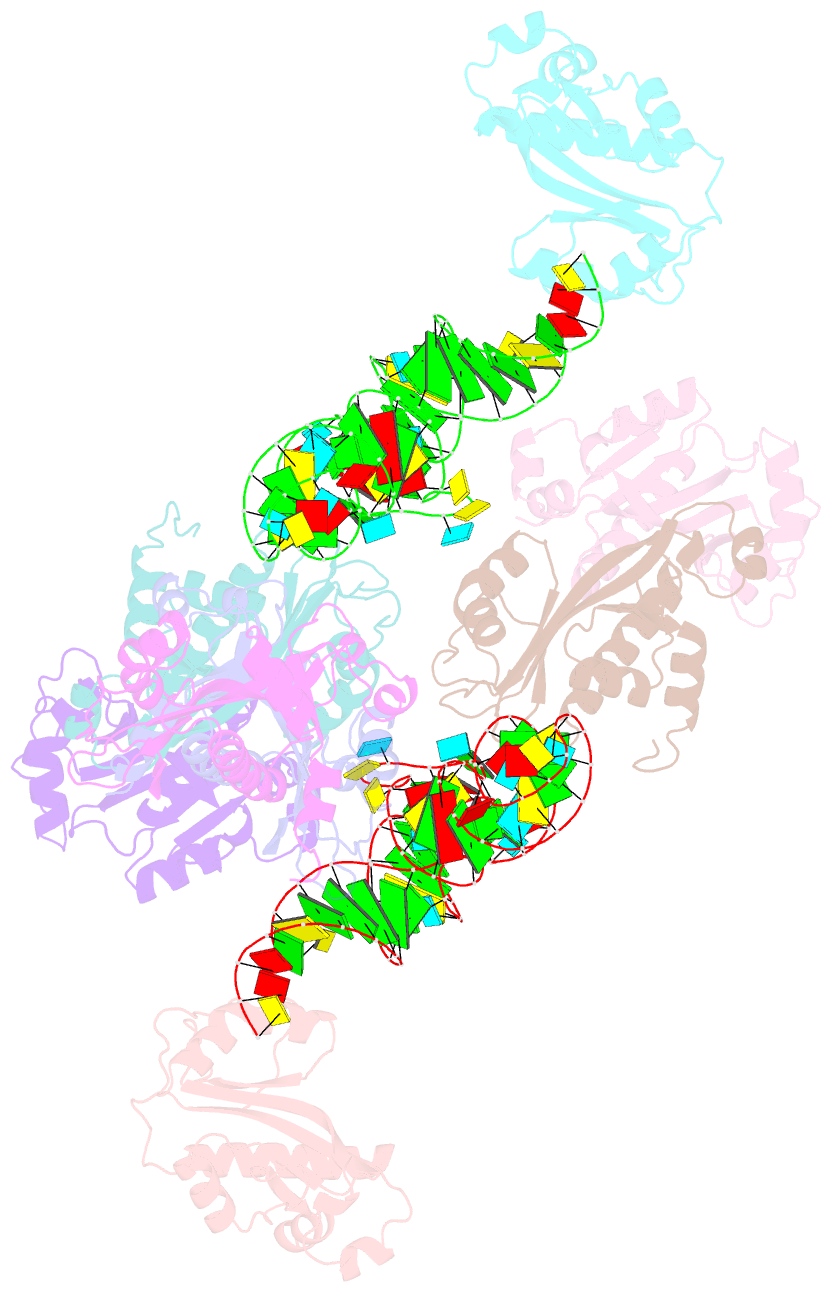
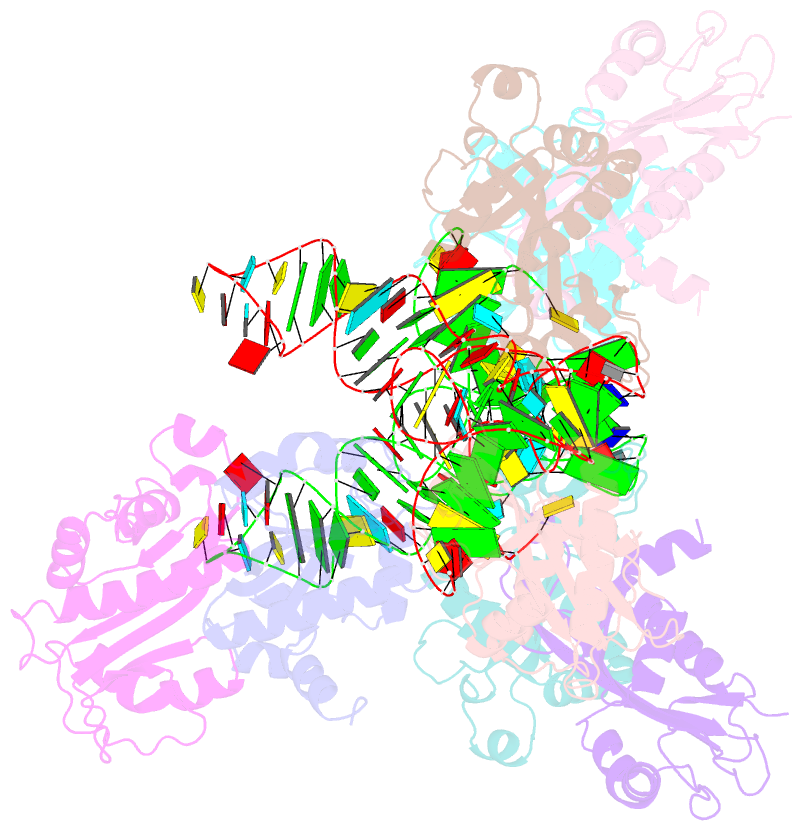
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7chd; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase
- Method
- X-ray (3.804 Å)
- Summary
- Atat complexed with acetyl-methionyl-trnafmet
- Reference
- Yashiro Y, Sakaguchi Y, Suzuki T, Tomita K (2020): "Mechanism of aminoacyl-tRNA acetylation by an aminoacyl-tRNA acetyltransferase AtaT from enterohemorrhagic E. coli." Nat Commun, 11, 5438. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19281-z.
- Abstract
- Toxin-antitoxin systems in bacteria contribute to stress adaptation, dormancy, and persistence. AtaT, a type-II toxin in enterohemorrhagic E. coli, reportedly acetylates the α-amino group of the aminoacyl-moiety of initiator Met-tRNAfMet, thus inhibiting translation initiation. Here, we show that AtaT has a broader specificity for aminoacyl-tRNAs than initially claimed. AtaT efficiently acetylates Gly-tRNAGly, Trp-tRNATrp, Tyr-tRNATyr and Phe-tRNAPhe isoacceptors, in addition to Met-tRNAfMet, and inhibits global translation. AtaT interacts with the acceptor stem of tRNAfMet, and the consecutive G-C pairs in the bottom-half of the acceptor stem are required for acetylation. Consistently, tRNAGly, tRNATrp, tRNATyr and tRNAPhe also possess consecutive G-C base-pairs in the bottom halves of their acceptor stems. Furthermore, misaminoacylated valyl-tRNAfMet and isoleucyl-tRNAfMet are not acetylated by AtaT. Therefore, the substrate selection by AtaT is governed by the specific acceptor stem sequence and the properties of the aminoacyl-moiety of aminoacyl-tRNAs.