Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7cvq; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.3 Å)
- Summary
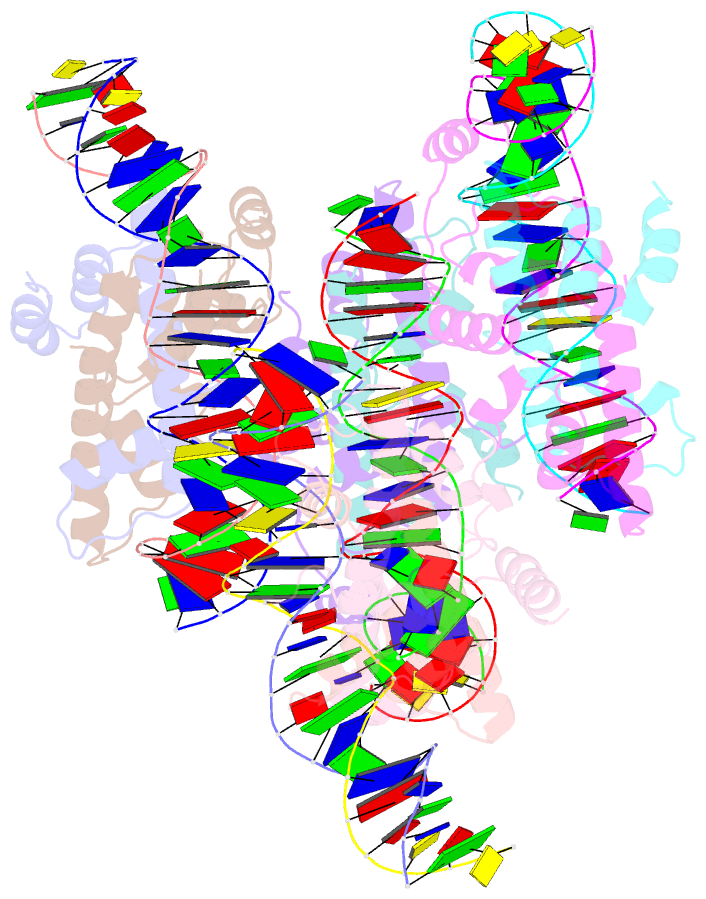
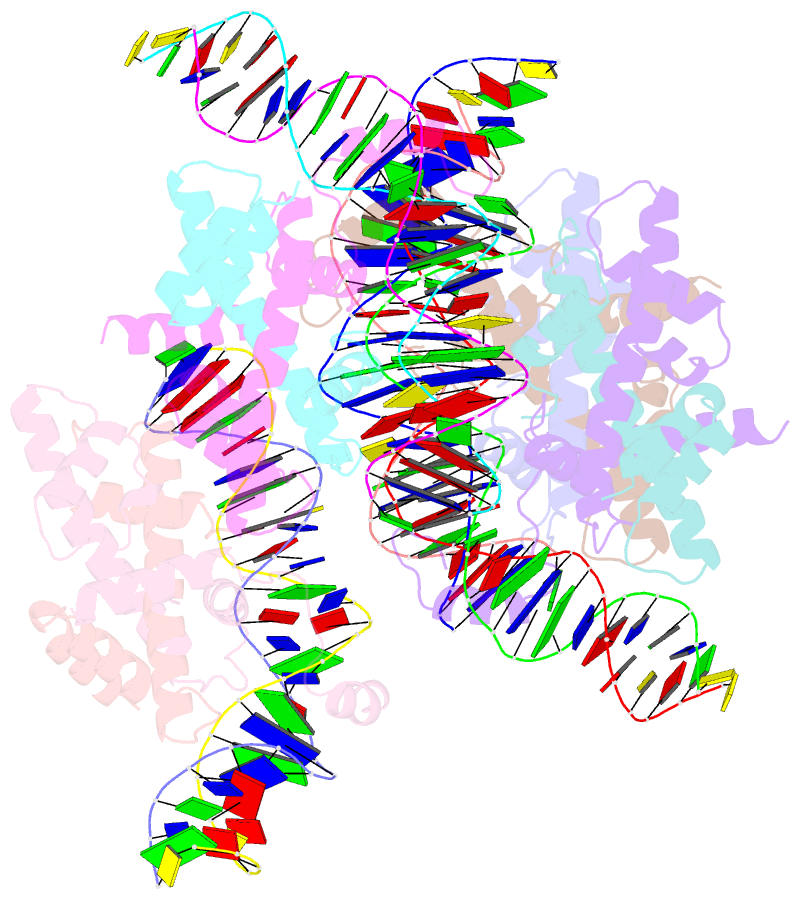
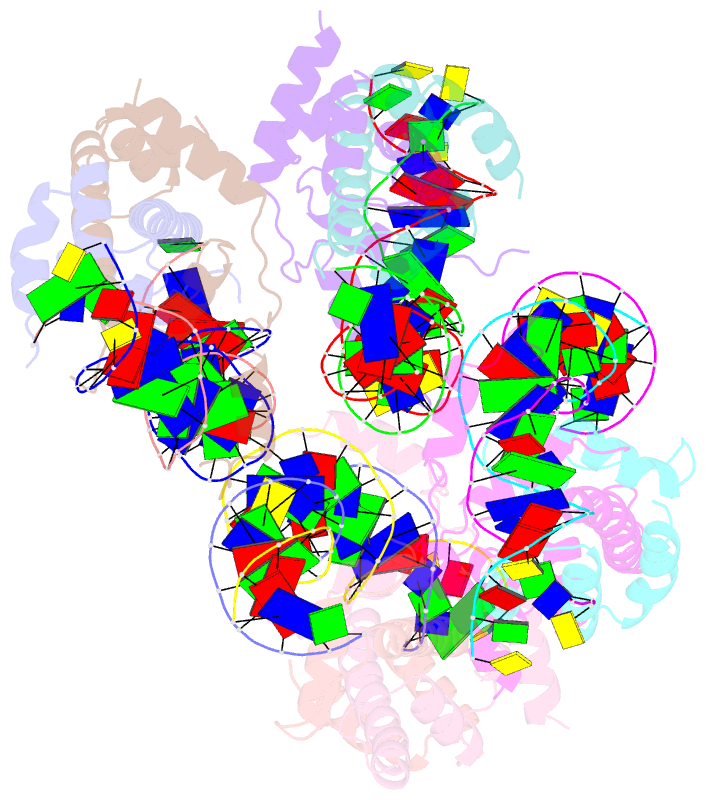
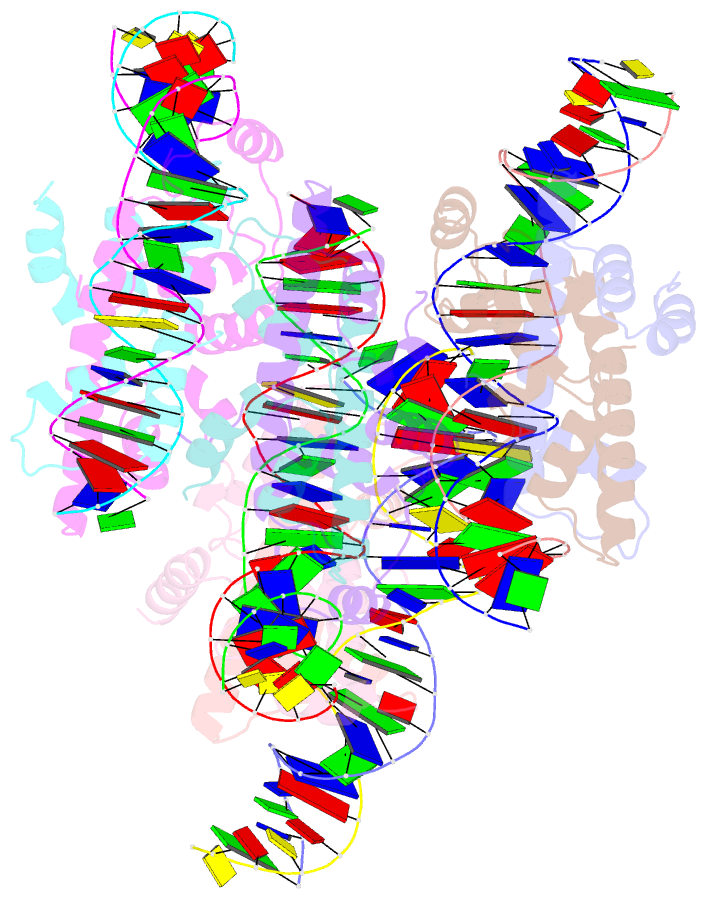
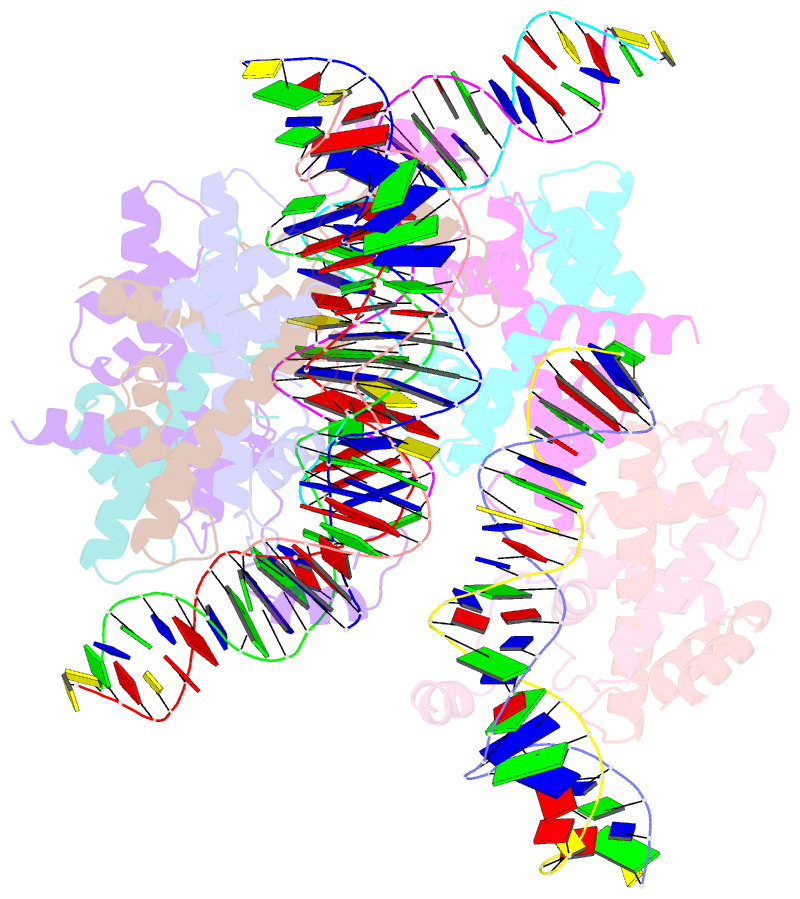
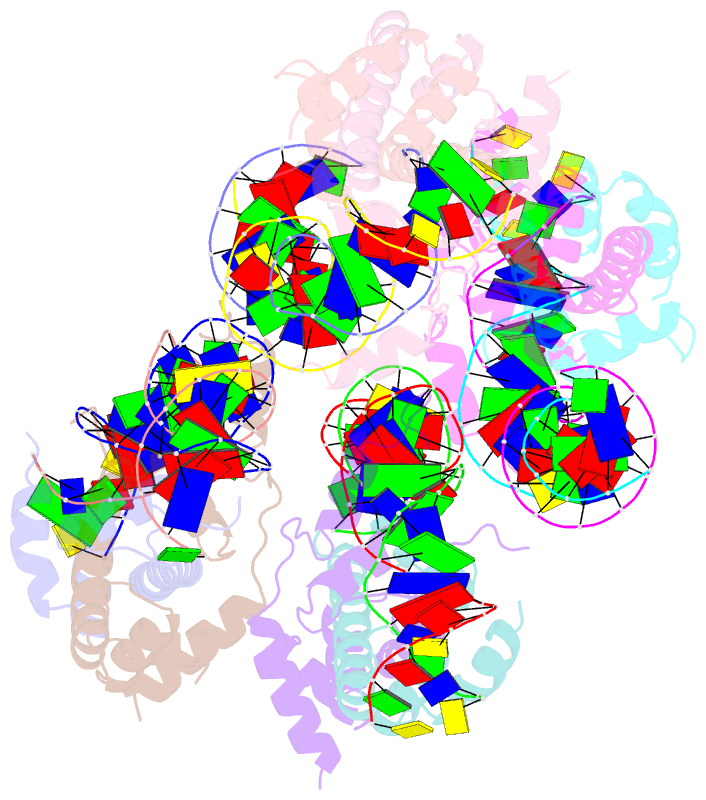
- Crystal structure of arabidopsis co cct domain in complex with nf-yb2-yc3 and ft core1 DNA
- Reference
- Lv X, Zeng X, Hu H, Chen L, Zhang F, Liu R, Liu Y, Zhou X, Wang C, Wu Z, Kim C, He Y, Du J (2021): "Structural insights into the multivalent binding of the Arabidopsis FLOWERING LOCUS T promoter by the CO-NF-Y master transcription factor complex." Plant Cell, 33, 1182-1195. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koab016.
- Abstract
- Flowering plants sense various environmental and endogenous signals to trigger the floral transition and start the reproductive growth cycle. CONSTANS (CO) is a master transcription factor in the photoperiod floral pathway that integrates upstream signals and activates the florigen gene FLOWERING LOCUS T (FT). Here, we performed comprehensive structural and biochemical analyses to study the molecular mechanism underlying the regulation of FT by CO in Arabidopsis thaliana. We show that the four previously characterized cis-elements in the FT promoter proximal region, CORE1, CORE2, P1, and P2, are all direct CO binding sites. Structural analysis of CO in complex with NUCLEAR FACTOR-YB/YC (NF-YB/YC) and the CORE2 or CORE1 elements revealed the molecular basis for the specific recognition of the shared TGTG motifs. Biochemical analysis suggested that CO might form a homomultimeric assembly via its N-terminal B-Box domain and simultaneously occupy multiple cis-elements within the FT promoter. We suggest that this multivalent binding gives the CO-NF-Y complex high affinity and specificity for FT promoter binding. Overall, our data provide a detailed molecular model for the regulation of FT by the master transcription factor complex CO-NF-Y during the floral transition.