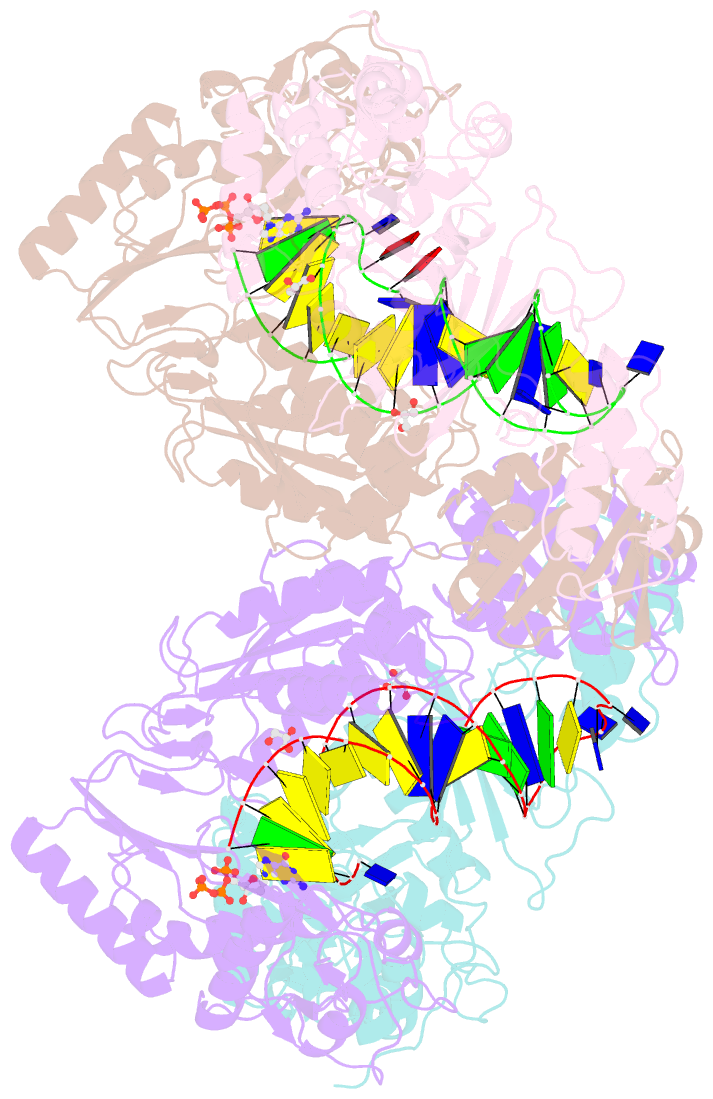
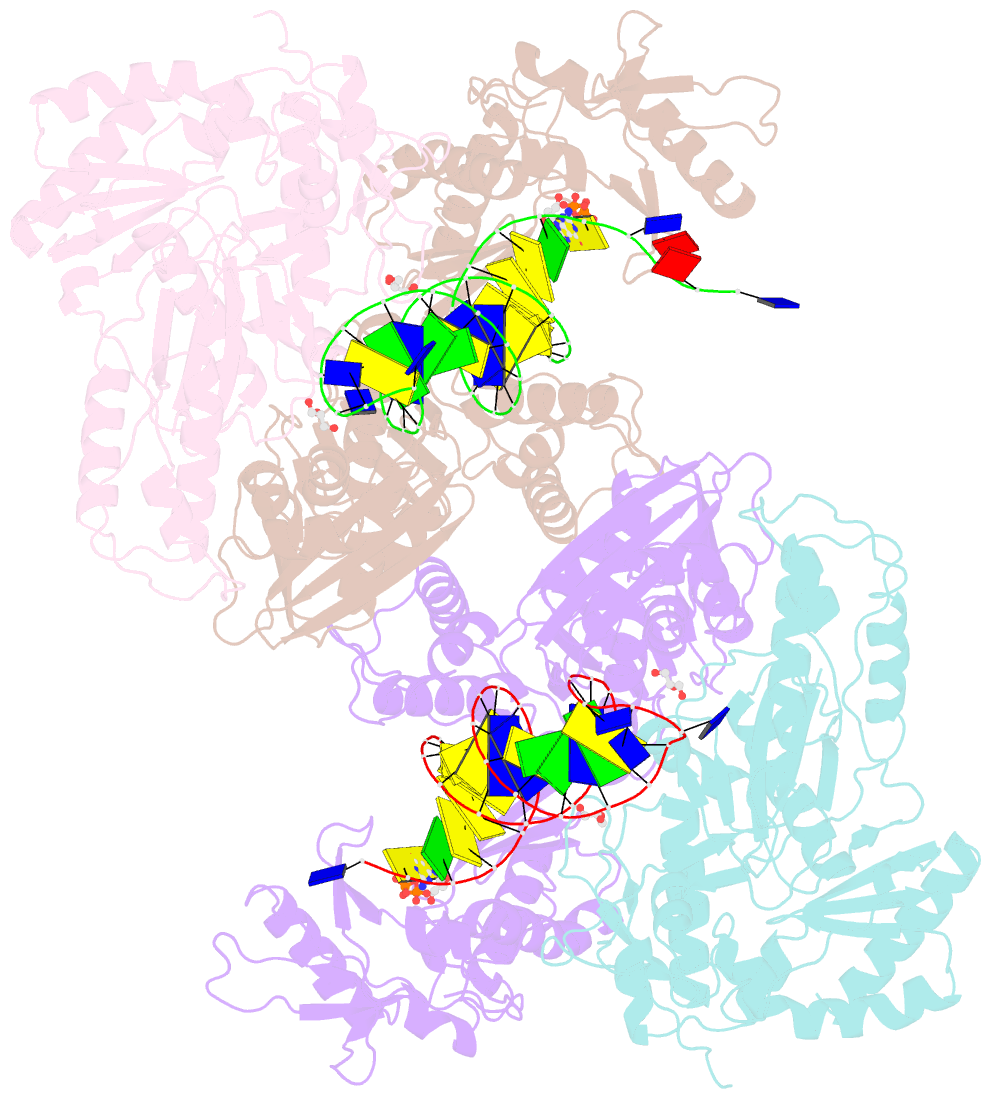
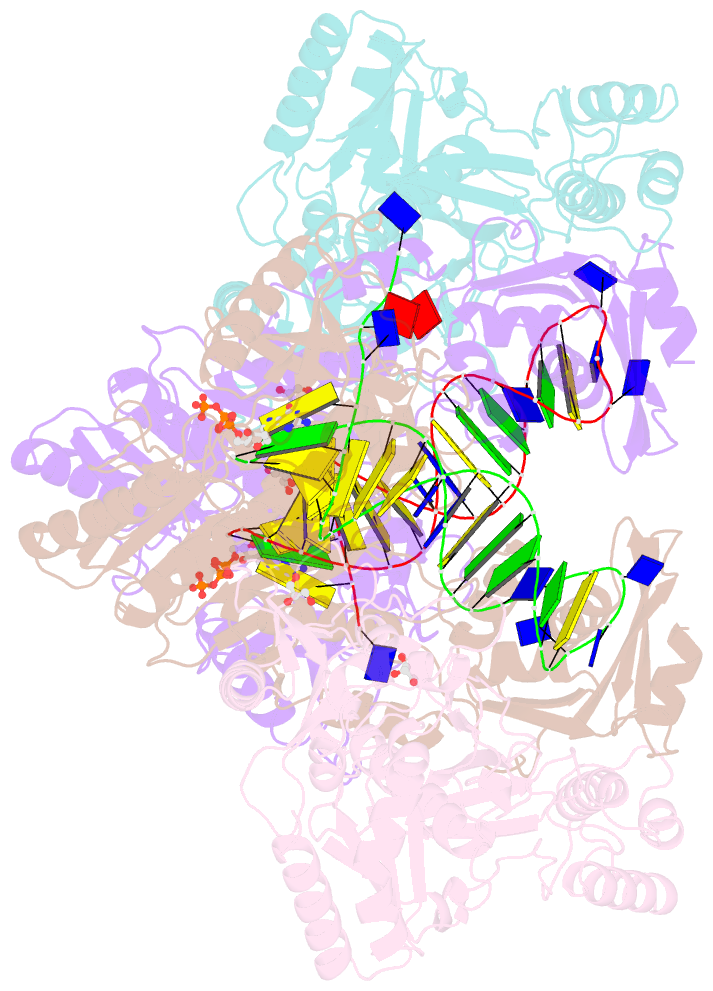
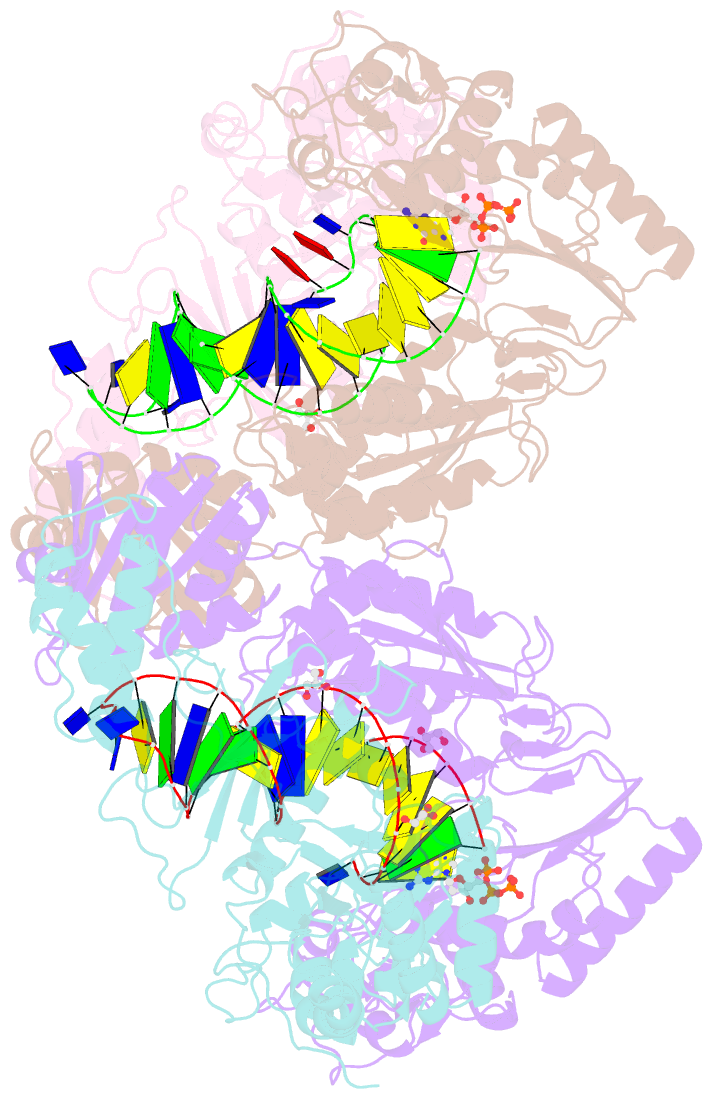
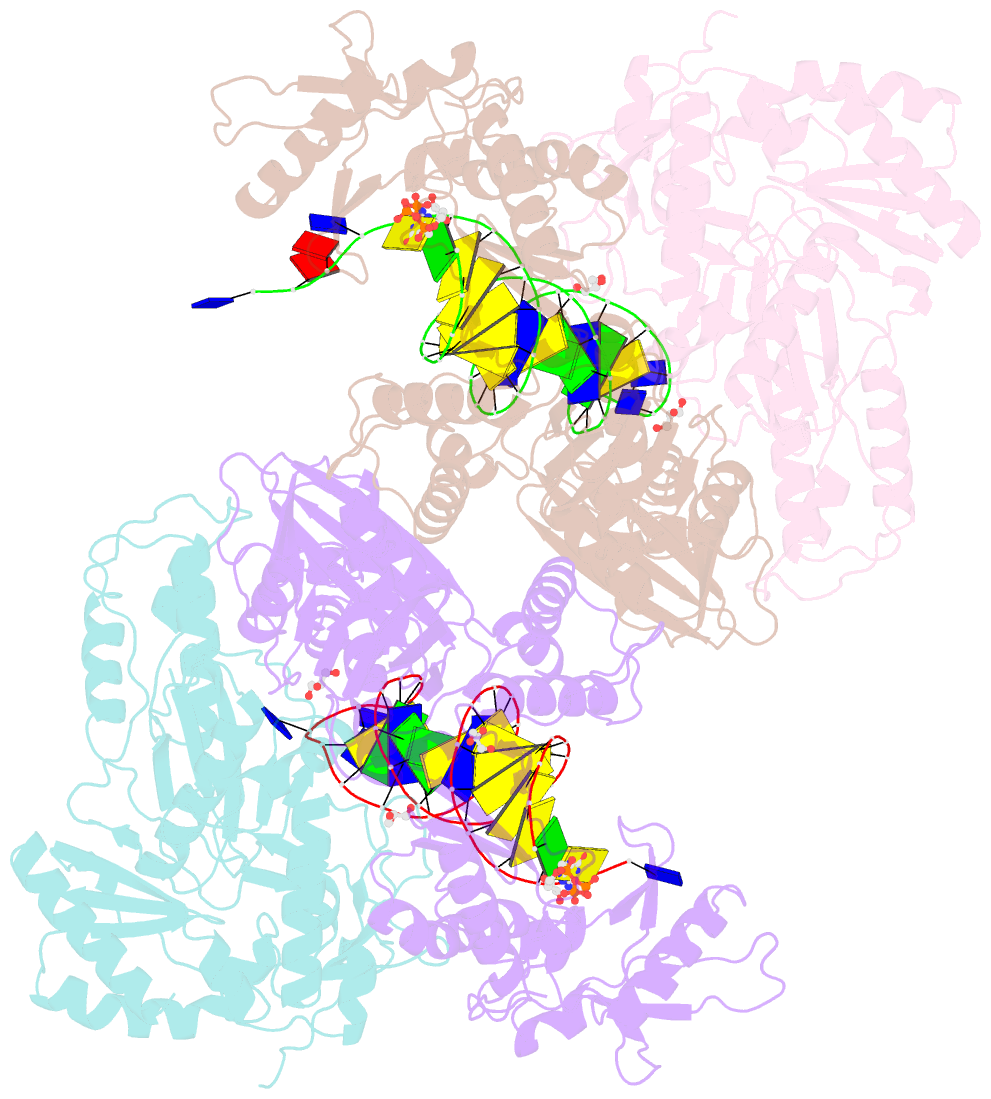
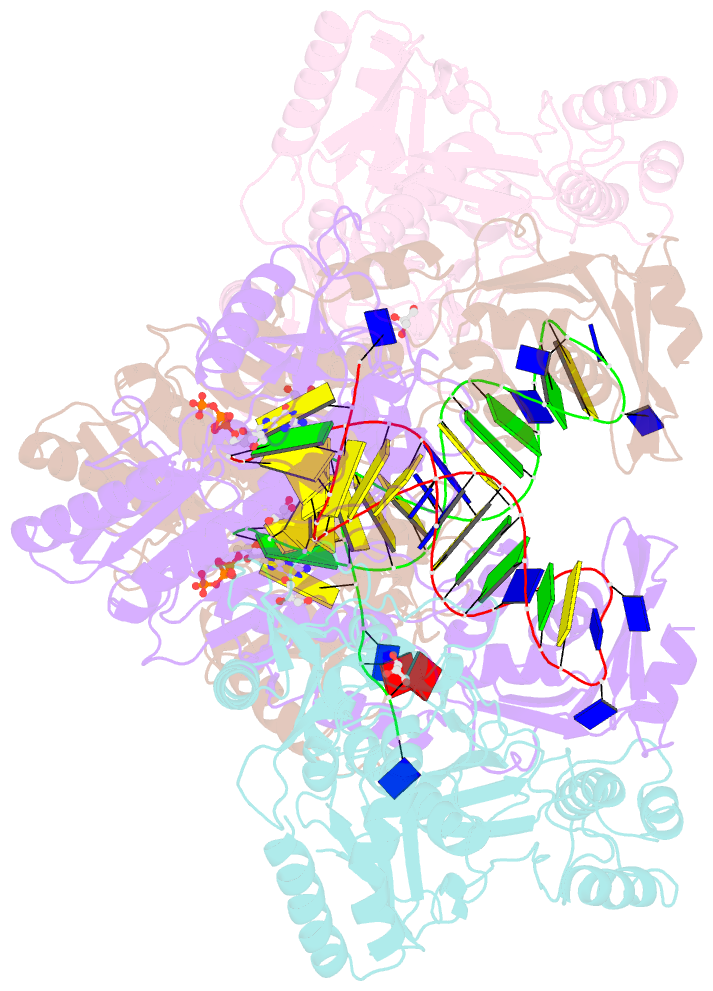
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7dbm; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.43 Å)
- Summary
- Hiv-1 reverse transcriptase mutant q151m-y115f-f116y-m184v:DNA:dgtp ternary complex
- Reference
- Nakajima S, Watashi K, Kato T, Muramatsu M, Wakita T, Tamura N, Hattori SI, Maeda K, Mitsuya H, Yasutake Y, Toyoda T (2021): "Biochemical and Structural Properties of Entecavir-Resistant Hepatitis B Virus Polymerase with L180M/M204V Mutations." J.Virol., 95, e0240120. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02401-20.
- Abstract
- Entecavir (ETV) is a widely used anti-hepatitis B virus (HBV) drug. However, the emergence of resistant mutations in HBV reverse transcriptase (RT) results in treatment failure. To understand the mechanism underlying the development of ETV resistance by HBV RT, we analyzed the L180M, M204V, and L180M/M204V mutants using a combination of biochemical and structural techniques. ETV-triphosphate (ETV-TP) exhibited competitive inhibition with dGTP in both wild-type (wt) RT and M204V RT, as observed using Lineweaver-Burk plots. In contrast, RT L180M or L180M/M204V did not fit either competitive, uncompetitive, noncompetitive, or typical mixed inhibition, although ETV-TP was a competitive inhibitor of dGTP. Crystallography of HIV RTY115F/F116Y/Q151M/F160M/M184V, mimicking HBV RT L180M/M204V, showed that the F115 bulge (F88 in HBV RT) caused by the F160M mutation induced deviated binding of dCTP from its normal tight binding position. Modeling of ETV-TP on the deviated dCTP indicated that a steric clash could occur between ETV-TP methylene and the 3'-end nucleoside ribose. ETV-TP is likely to interact primarily with HBV RT M171 prior to final accommodation at the deoxynucleoside triphosphate (dNTP) binding site (Y. Yasutake, S. Hattori, H. Hayashi, K. Matsuda, et al., Sci Rep 8:1624, 2018, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19602-9). Therefore, in HBV RT L180M/M204V, ETV-TP may be stuck at M171, a residue that is conserved in almost all HBV isolates, leading to the strange inhibition pattern observed in the kinetic analysis. Collectively, our results provide novel insights into the mechanism of ETV resistance of HBV RT caused by L180M and M204V mutations.