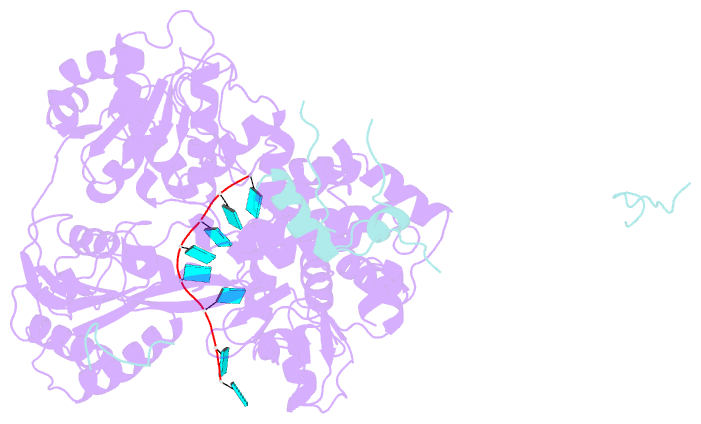
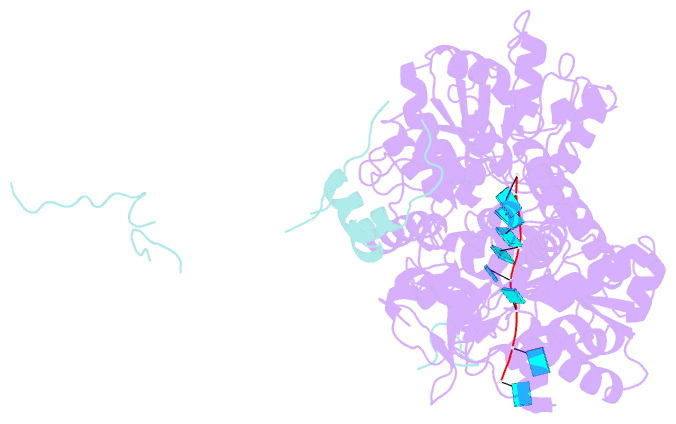
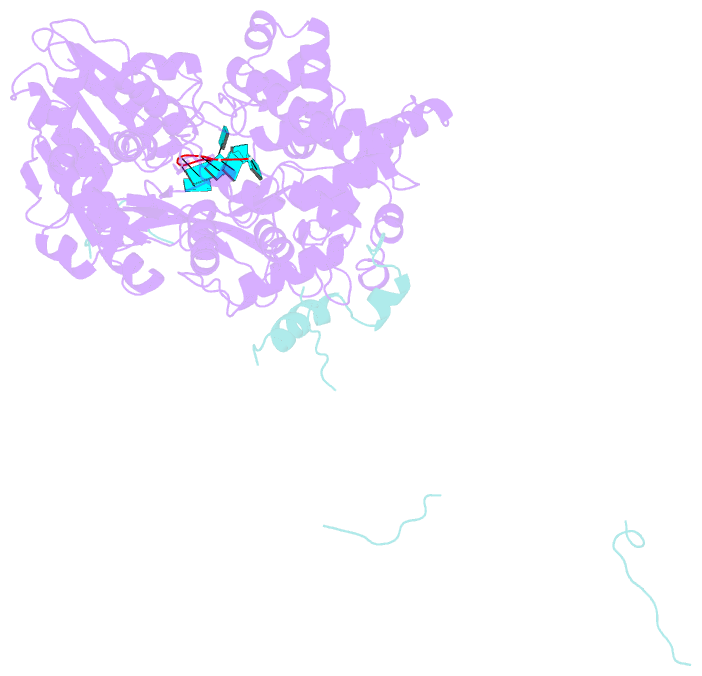
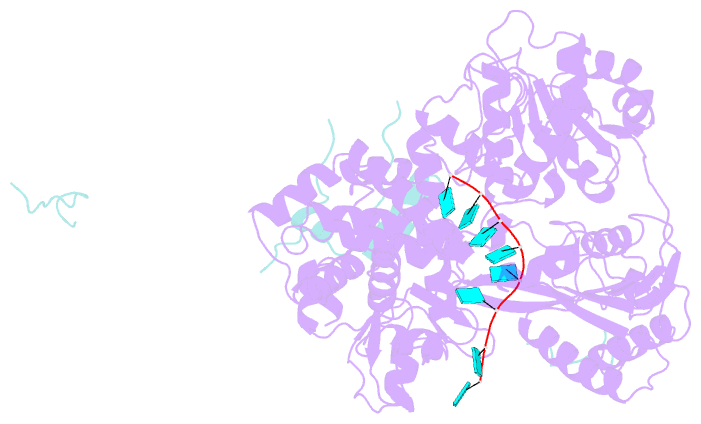
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7dd3; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- splicing
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.2 Å)
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of the pre-mrna-loaded deah-box atpase-helicase prp2 in complex with spp2
- Reference
- Bai R, Wan R, Yan C, Jia Q, Lei J, Shi Y (2021): "Mechanism of spliceosome remodeling by the ATPase/helicase Prp2 and its coactivator Spp2." Science, 371. doi: 10.1126/science.abe8863.
- Abstract
- Spliceosome remodeling, executed by conserved adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase)/helicases including Prp2, enables precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) splicing. However, the structural basis for the function of the ATPase/helicases remains poorly understood. Here, we report atomic structures of Prp2 in isolation, Prp2 complexed with its coactivator Spp2, and Prp2-loaded activated spliceosome and the results of structure-guided biochemical analysis. Prp2 weakly associates with the spliceosome and cannot function without Spp2, which stably associates with Prp2 and anchors on the spliceosome, thus tethering Prp2 to the activated spliceosome and allowing Prp2 to function. Pre-mRNA is loaded into a featured channel between the N and C halves of Prp2, where Leu536 from the N half and Arg844 from the C half prevent backward sliding of pre-mRNA toward its 5'-end. Adenosine 5'-triphosphate binding and hydrolysis trigger interdomain movement in Prp2, which drives unidirectional stepwise translocation of pre-mRNA toward its 3'-end. These conserved mechanisms explain the coupling of spliceosome remodeling to pre-mRNA splicing.