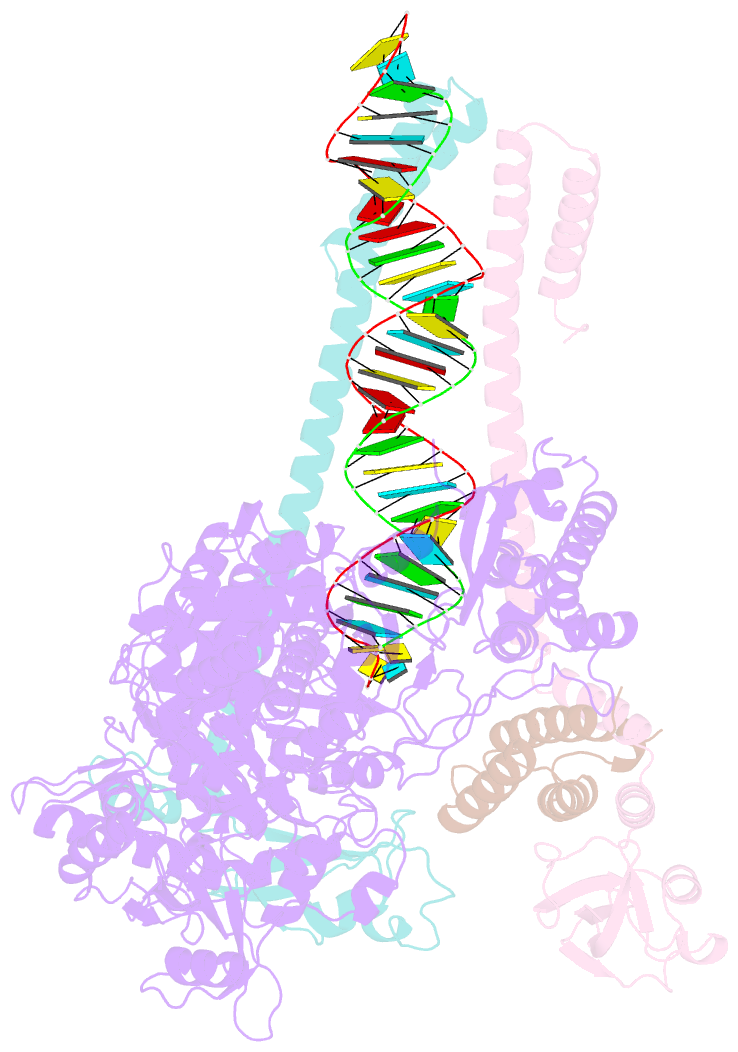
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7dte; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.0 Å)
- Summary
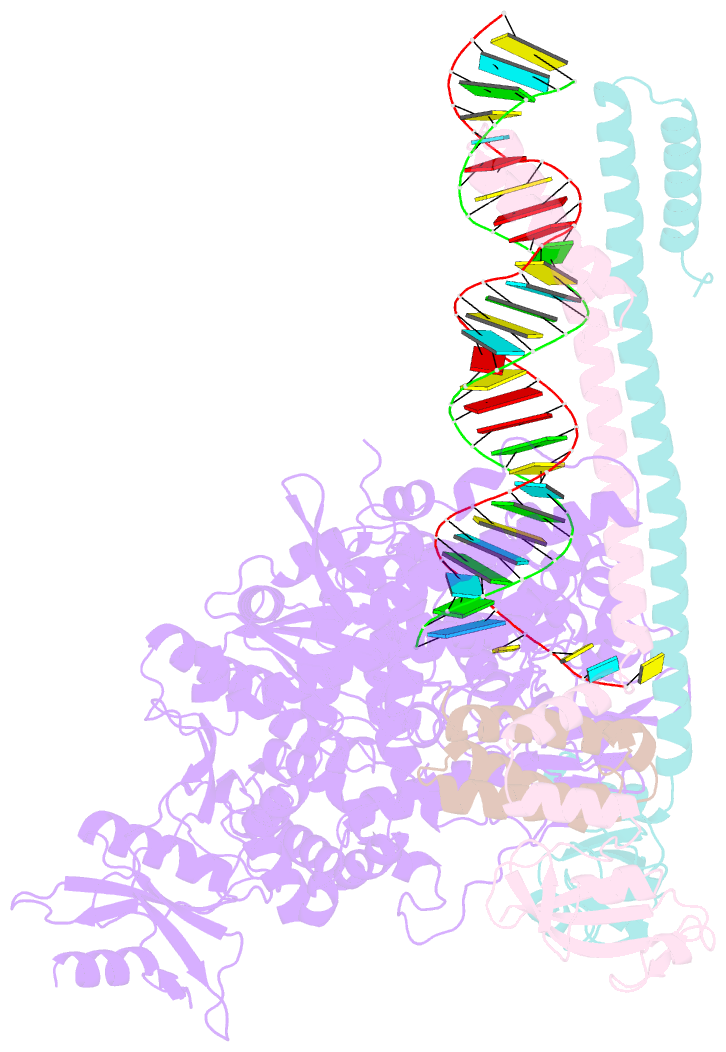
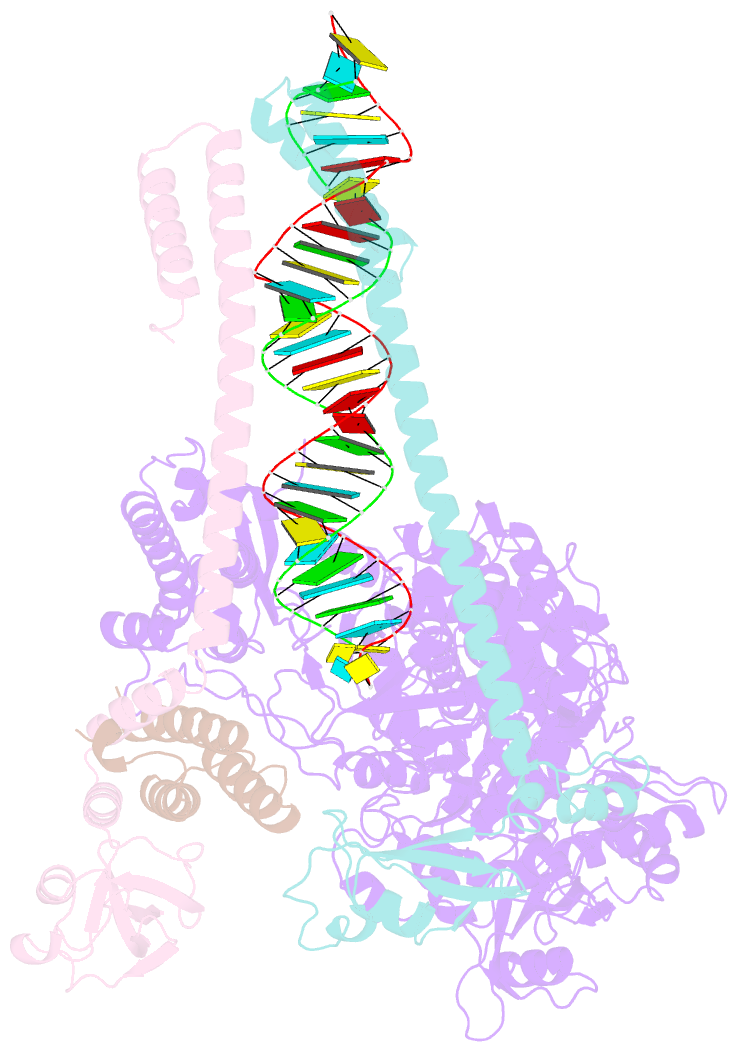
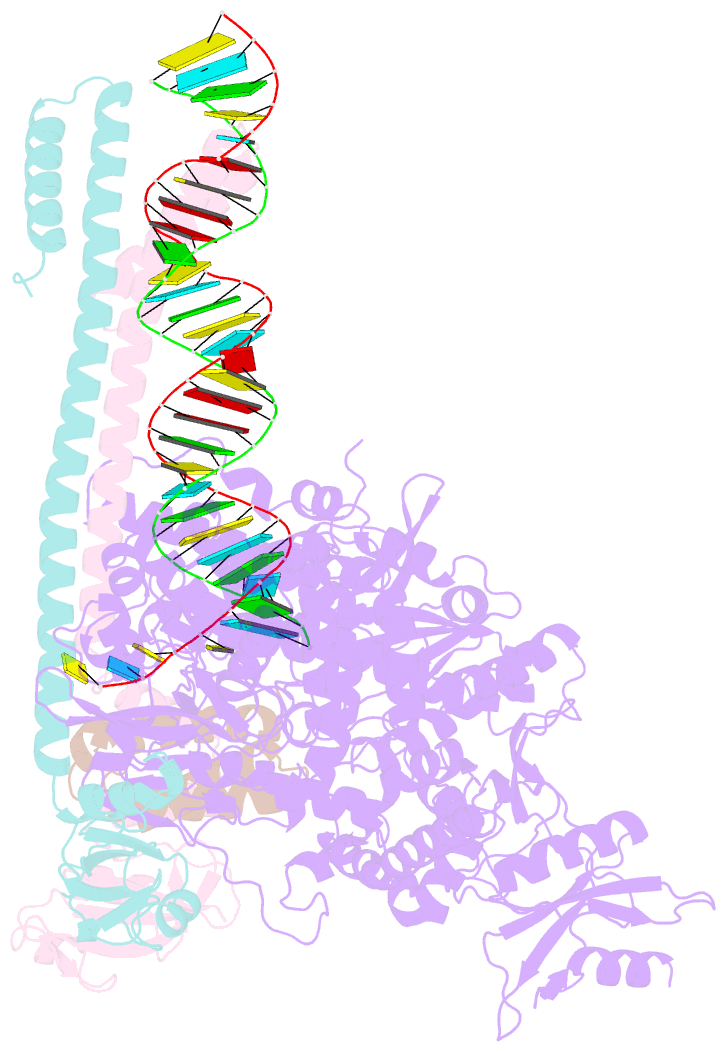
- Sars-cov-2 rdrp catalytic complex with t33-1 RNA
- Reference
- Wu J, Wang H, Liu Q, Li R, Gao Y, Fang X, Zhong Y, Wang M, Wang Q, Rao Z, Gong P (2021): "Remdesivir overcomes the S861 roadblock in SARS-CoV-2 polymerase elongation complex." Cell Rep, 37, 109882. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109882.
- Abstract
- Remdesivir (RDV), a nucleotide analog with broad-spectrum features, has exhibited effectiveness in COVID-19 treatment. However, the precise working mechanism of RDV when targeting the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRP) has not been fully elucidated. Here, we solve a 3.0-Å structure of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) RdRP elongation complex (EC) and assess RDV intervention in polymerase elongation phase. Although RDV could induce an "i+3" delayed termination in meta-stable complexes, only pausing and subsequent elongation are observed in the EC. A comparative investigation using an enterovirus RdRP further confirms similar delayed intervention and demonstrates that steric hindrance of the RDV-characteristic 1'-cyano at the -4 position is responsible for the "i+3" intervention, although two representative Flaviviridae RdRPs do not exhibit similar behavior. A comparison of representative viral RdRP catalytic complex structures indicates that the product RNA backbone encounters highly conserved structural elements, highlighting the broad-spectrum intervention potential of 1'-modified nucleotide analogs in anti-RNA virus drug development.