Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7eh1; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-DNA-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.9 Å)
- Summary
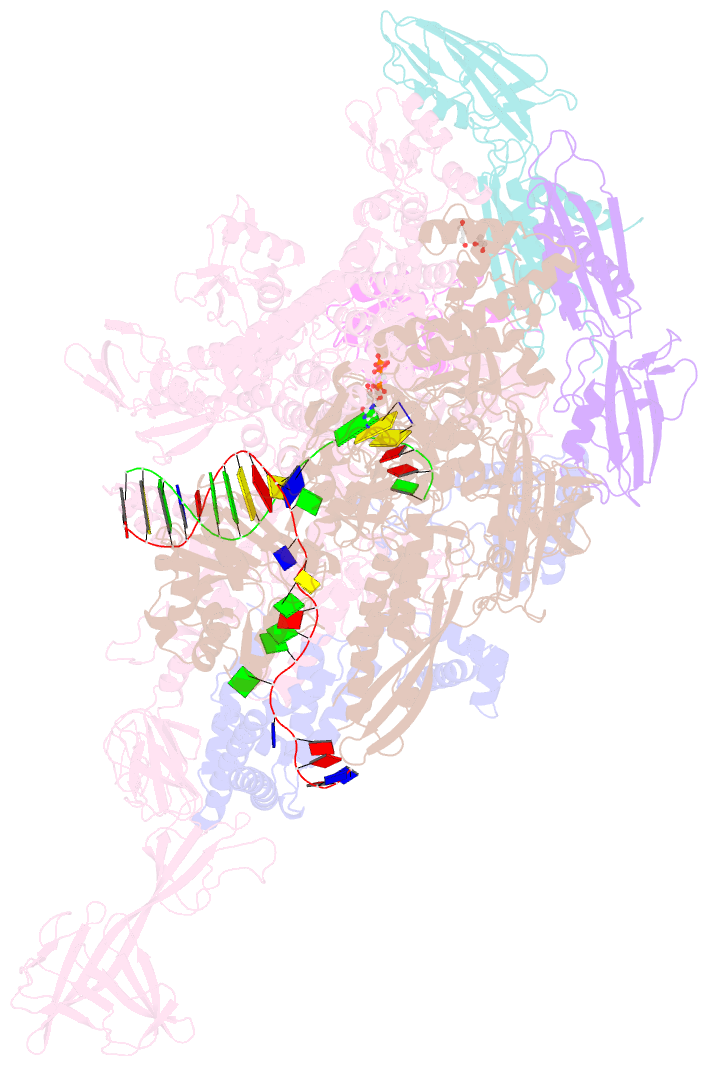
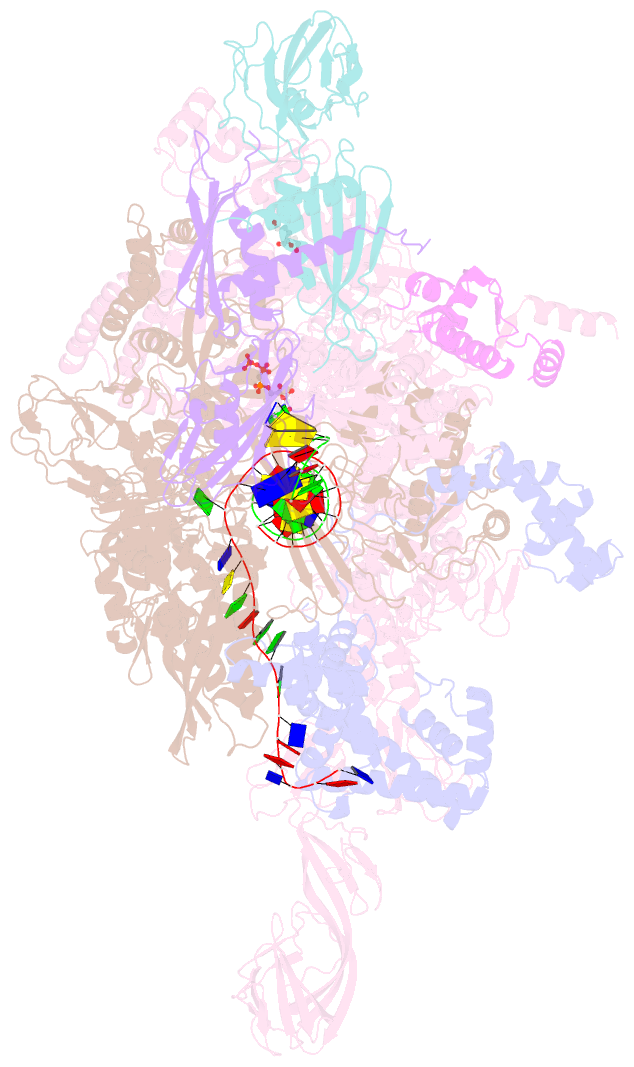
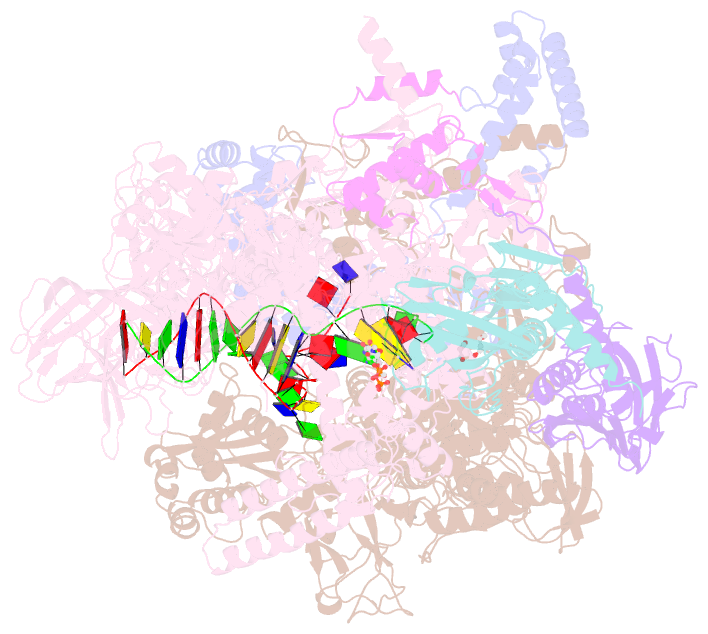
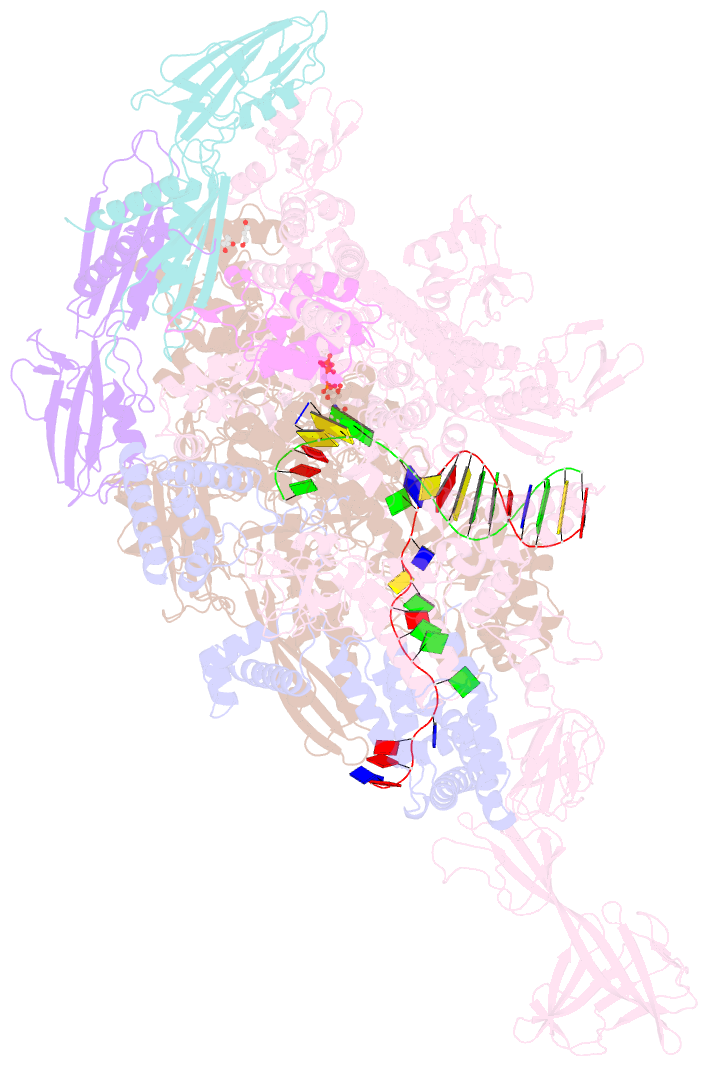
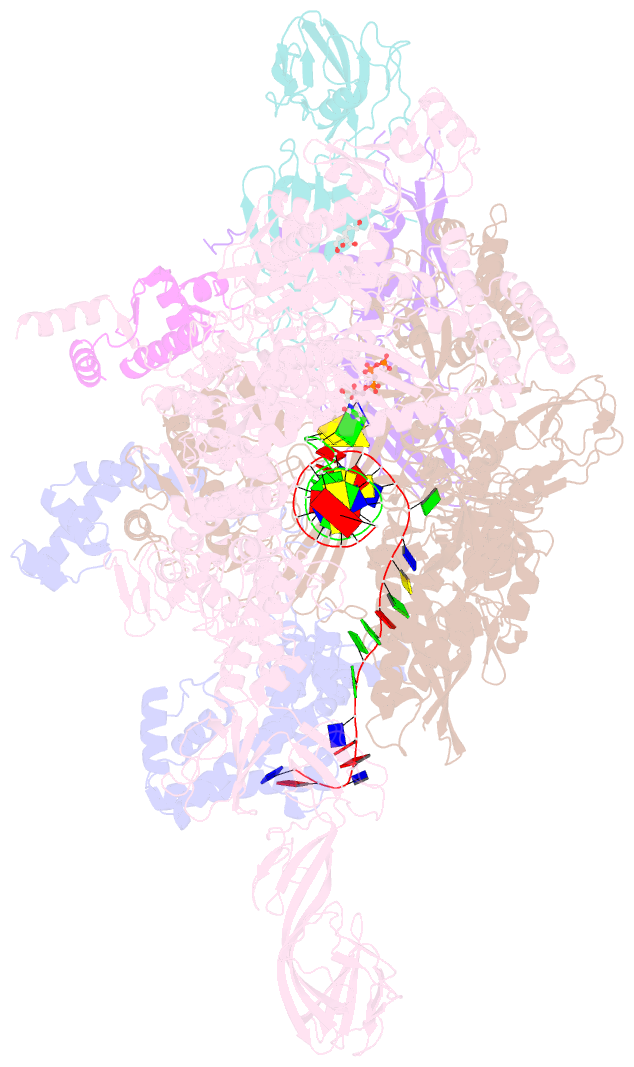
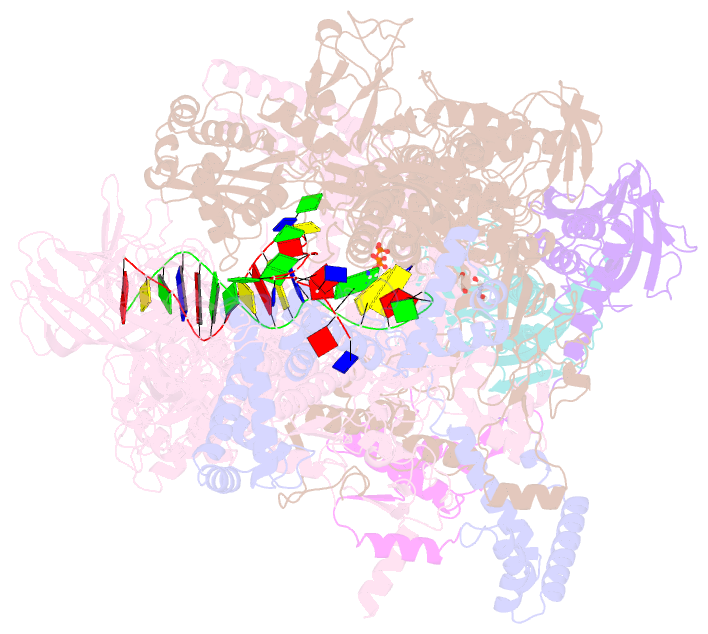
- Thermus thermophilus transcription initiation complex containing a template-strand purine at position tss-2, gpg RNA primer, and cmpcpp
- Reference
- Skalenko KS, Li L, Zhang Y, Vvedenskaya IO, Winkelman JT, Cope AL, Taylor DM, Shah P, Ebright RH, Kinney JB, Zhang Y, Nickels BE (2021): "Promoter-sequence determinants and structural basis of primer-dependent transcription initiation in Escherichia coli ." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2106388118.
- Abstract
- Chemical modifications of RNA 5'-ends enable "epitranscriptomic" regulation, influencing multiple aspects of RNA fate. In transcription initiation, a large inventory of substrates compete with nucleoside triphosphates for use as initiating entities, providing an ab initio mechanism for altering the RNA 5'-end. In Escherichia coli cells, RNAs with a 5'-end hydroxyl are generated by use of dinucleotide RNAs as primers for transcription initiation, "primer-dependent initiation." Here, we use massively systematic transcript end readout (MASTER) to detect and quantify RNA 5'-ends generated by primer-dependent initiation for ∼410 (∼1,000,000) promoter sequences in E. coli The results show primer-dependent initiation in E. coli involves any of the 16 possible dinucleotide primers and depends on promoter sequences in, upstream, and downstream of the primer binding site. The results yield a consensus sequence for primer-dependent initiation, YTSS-2NTSS-1NTSSWTSS+1, where TSS is the transcription start site, NTSS-1NTSS is the primer binding site, Y is pyrimidine, and W is A or T. Biochemical and structure-determination studies show that the base pair (nontemplate-strand base:template-strand base) immediately upstream of the primer binding site (Y:RTSS-2, where R is purine) exerts its effect through the base on the DNA template strand (RTSS-2) through interchain base stacking with the RNA primer. Results from analysis of a large set of natural, chromosomally encoded E coli promoters support the conclusions from MASTER. Our findings provide a mechanistic and structural description of how TSS-region sequence hard-codes not only the TSS position but also the potential for epitranscriptomic regulation through primer-dependent transcription initiation.