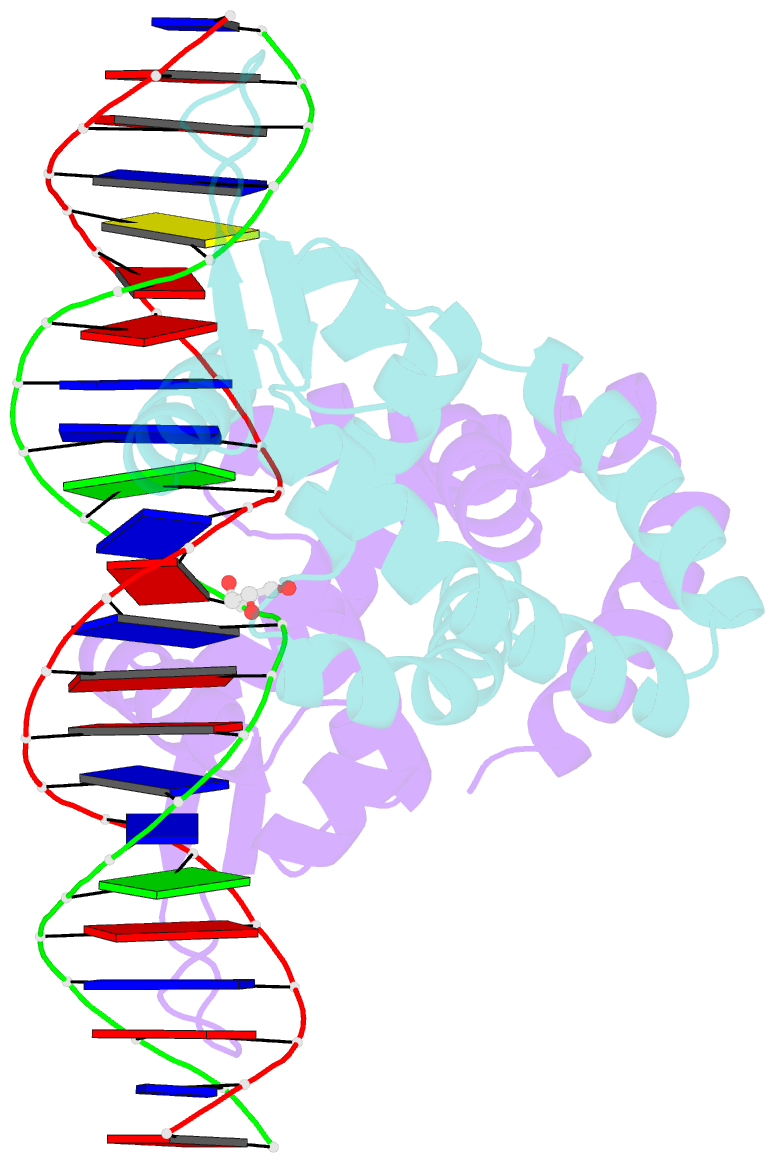
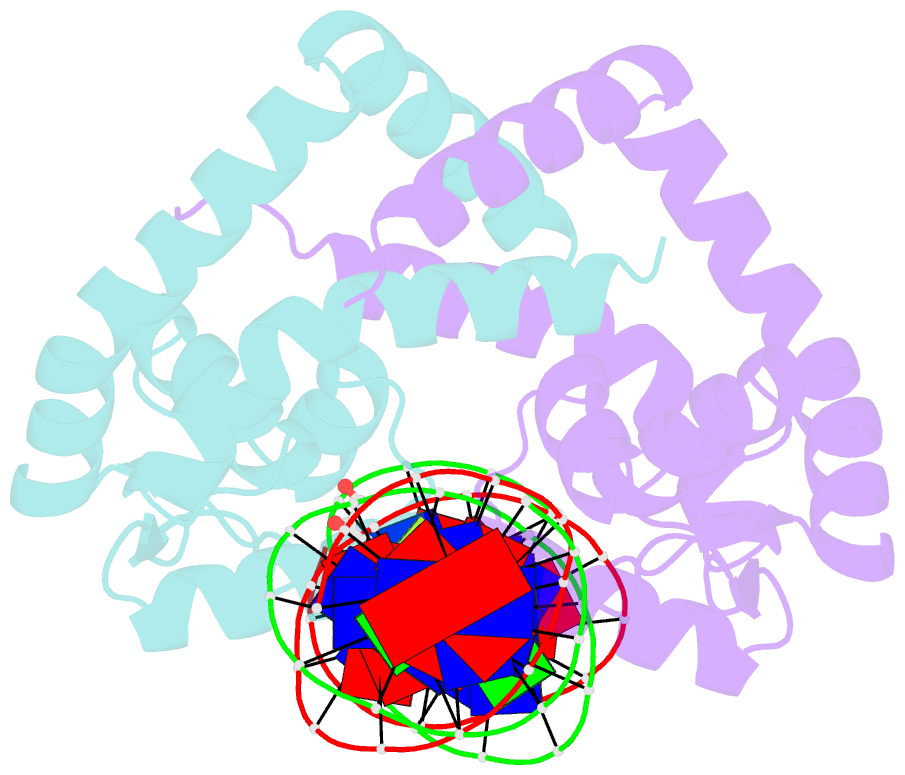
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7el3; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (1.7 Å)
- Summary
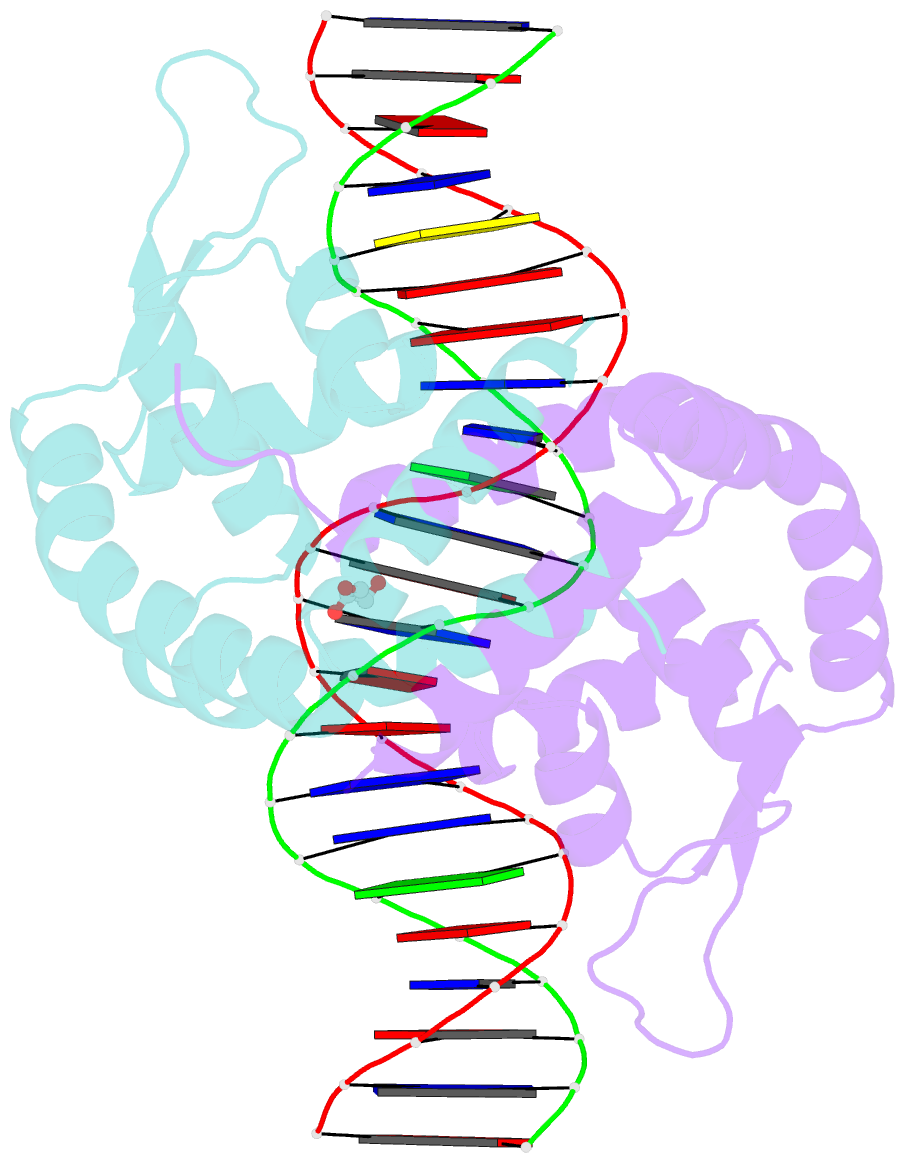
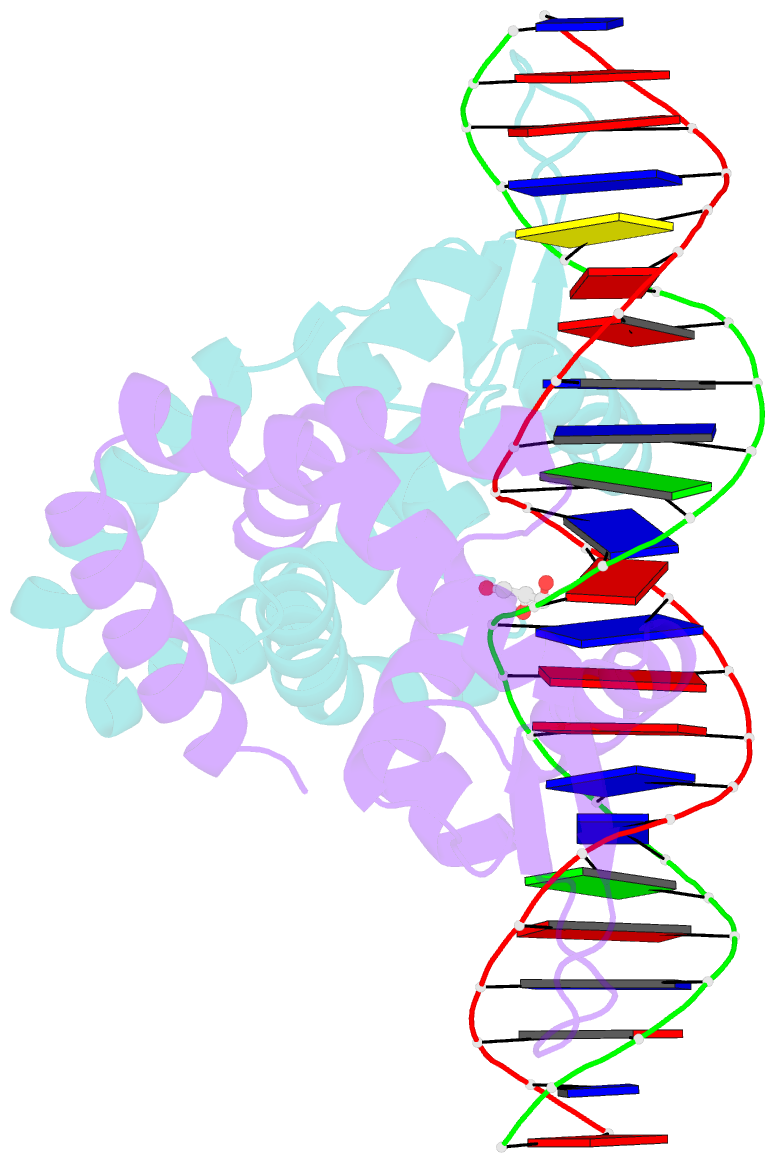
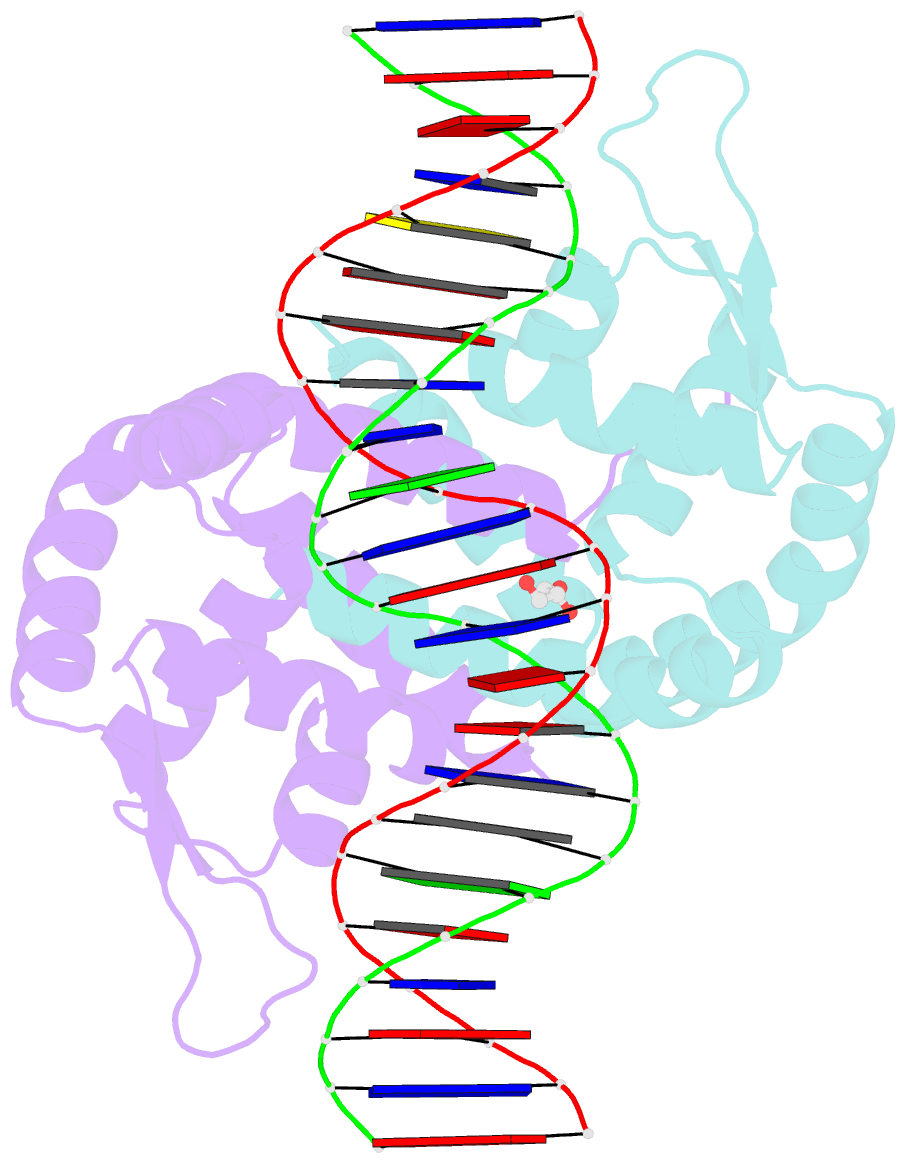
- Crystal structure of hpar-DNA complex from acinetobacter baumannii
- Reference
- Permsirivisarn P, Yuenyao A, Pramanpol N, Charoenwattanasatien R, Suginta W, Chaiyen P, Pakotiprapha D (2022): "Mechanism of transcription regulation by Acinetobacter baumannii HpaR in the catabolism of p-hydroxyphenylacetate." Febs J., 289, 3217-3240. doi: 10.1111/febs.16340.
- Abstract
- HpaR is a transcription regulator in the MarR family that controls the expression of the gene cluster responsible for conversion of p-hydroxyphenylacetate to pyruvate and succinate for cellular metabolism. Here, we report the biochemical and structural characterization of Acinetobacter baumannii HpaR (AbHpaR) and its complex with cognate DNA. Our study revealed that AbHpaR binds upstream of the divergently transcribed hpaA gene and the meta-cleavage operon, as well as the hpaR gene, thereby repressing their transcription by blocking access of RNA polymerase. Structural analysis of AbHpaR-DNA complex revealed that the DNA binding specificity can be achieved via a combination of both direct and indirect DNA sequence readouts. DNA binding of AbHpaR is weakened by 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetate (DHPA), which is the substrate of the meta-cleavage reactions; this likely leads to expression of the target genes. Based on our findings, we propose a model for how A. baumannii controls transcription of HPA-metabolizing genes, which highlights the independence of global catabolite repression and could be beneficial for metabolic engineering toward bioremediation applications. DATABASES: The structural data that support these findings are openly available in the wwPDB at https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb7EL2/pdb and https://doi.org/10.2210/pdb7EL3/pdb for AbHpaR and AbHpaR-DNA complex, respectively.