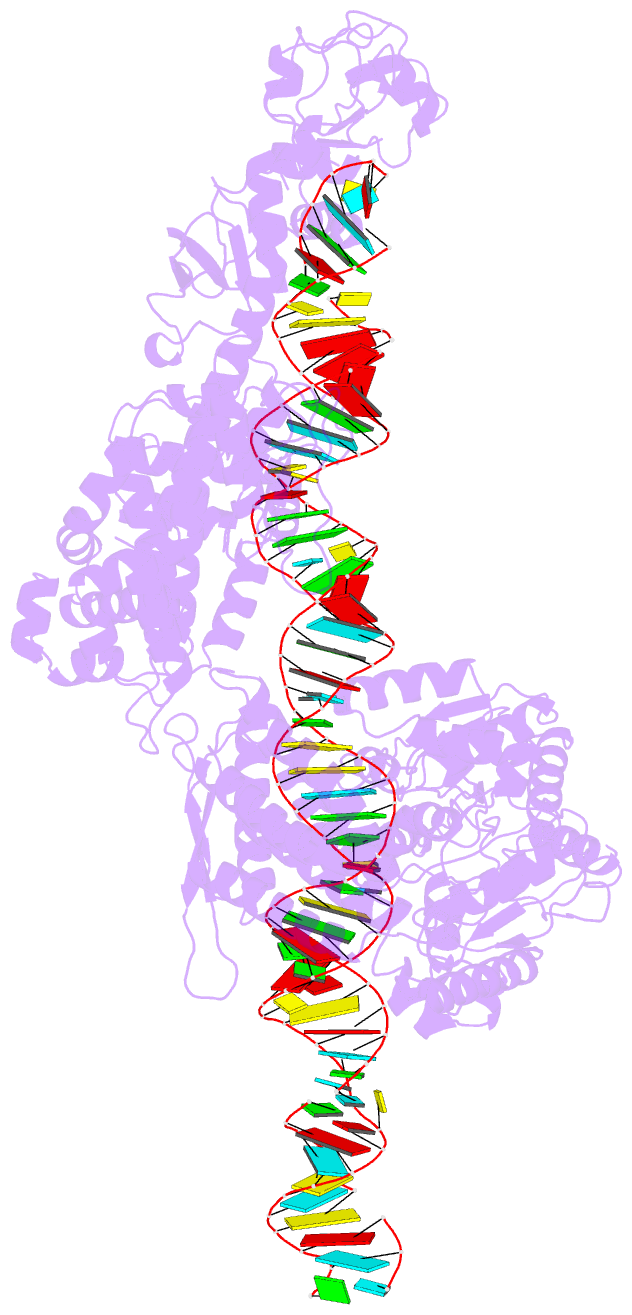
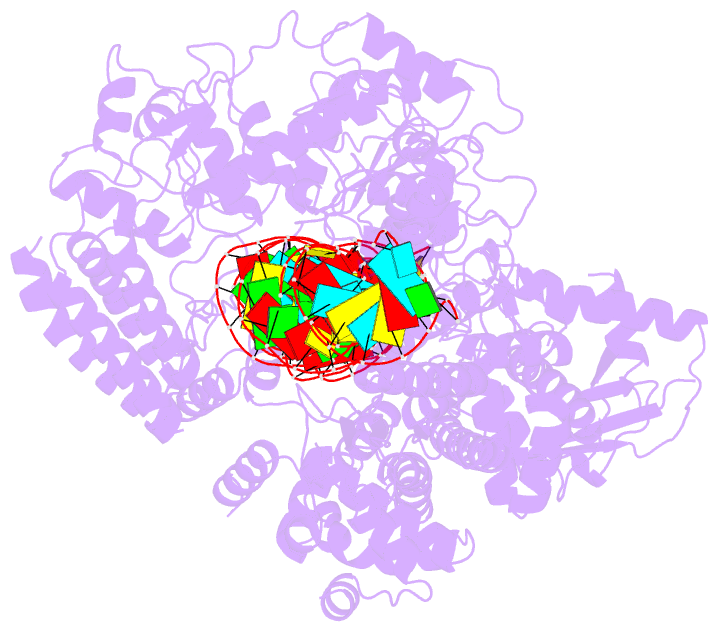
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7eld; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase
- Method
- cryo-EM (4.6 Å)
- Summary
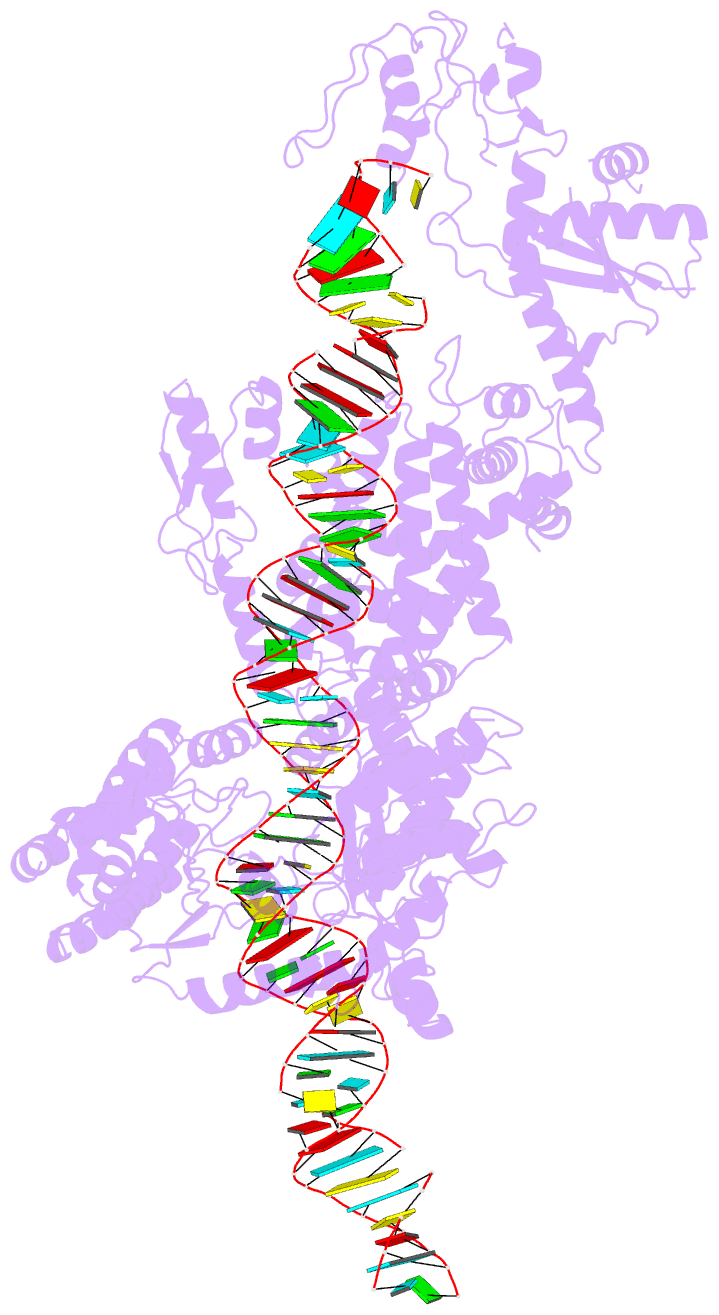
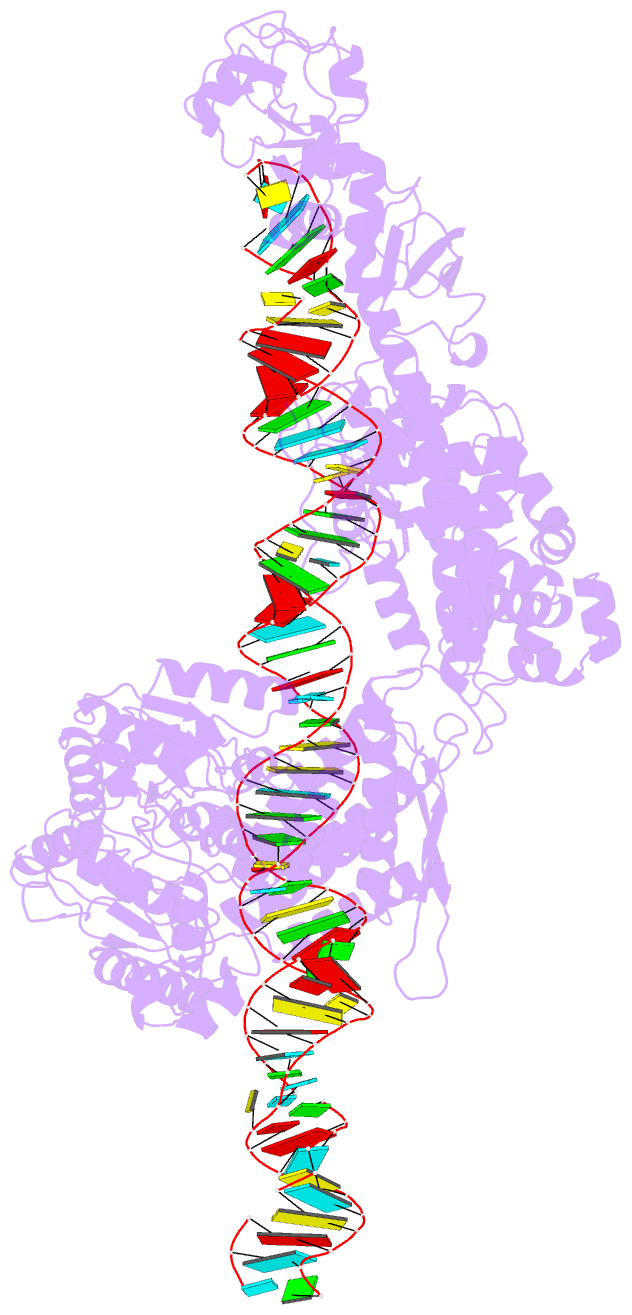
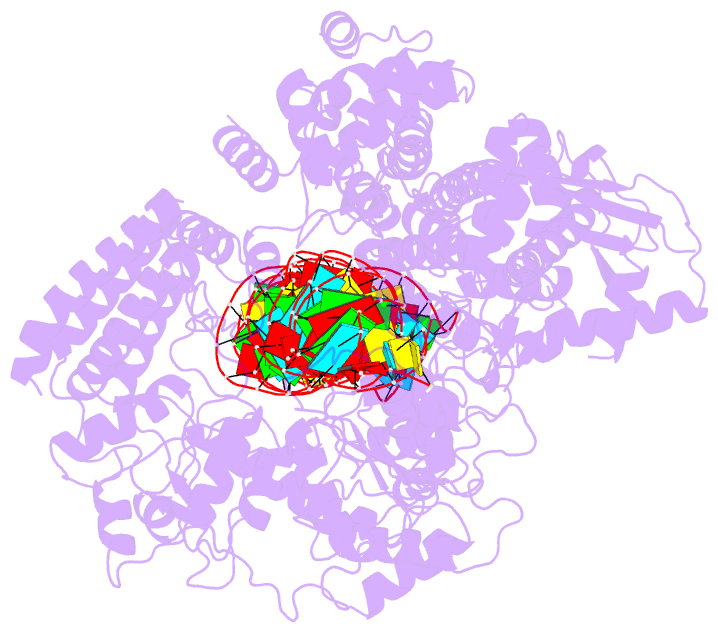
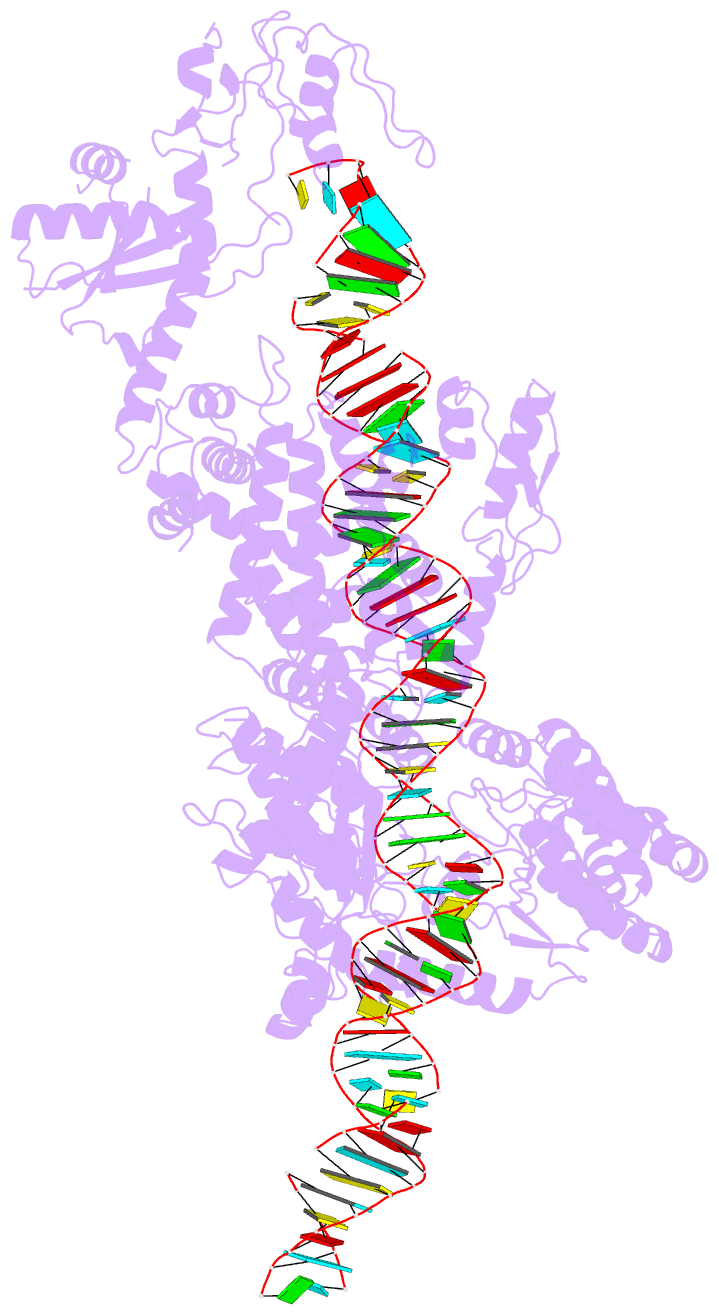
- cryo-EM structure of arabidopsis dcl1 in complex with pri-mirna 166f
- Reference
- Wei X, Ke H, Wen A, Gao B, Shi J, Feng Y (2021): "Structural basis of microRNA processing by Dicer-like 1." Nat.Plants, 7, 1389-1396. doi: 10.1038/s41477-021-01000-1.
- Abstract
- MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are short non-coding RNAs that inhibit the expression of target genes by directly binding to their mRNAs. In animals, pri-miRNAs are cleaved by Drosha to generate pre-miRNAs, which are subsequently cleaved by Dicer to generate mature miRNAs. Instead of being cleaved by two different enzymes, both cleavages in plants are performed by Dicer-like 1 (DCL1). With a similar domain architecture as human Dicer, it is mysterious how DCL1 recognizes pri-miRNAs and performs two cleavages sequentially. Here, we report the single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structures of Arabidopsis DCL1 complexed with a pri-miRNA and a pre-miRNA, respectively, in cleavage-competent states. These structures uncover the plasticity of the PAZ domain, which is critical for the recognition of both pri-miRNA and pre-miRNA. These structures suggest that the helicase module serves as an engine that transfers the substrate between two sequential cleavage events. This study lays a foundation for dissecting the regulation mechanism of miRNA biogenesis in plants and provides insights into the dicing state of human Dicer.