Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7eqg; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- immune system-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.2 Å)
- Summary
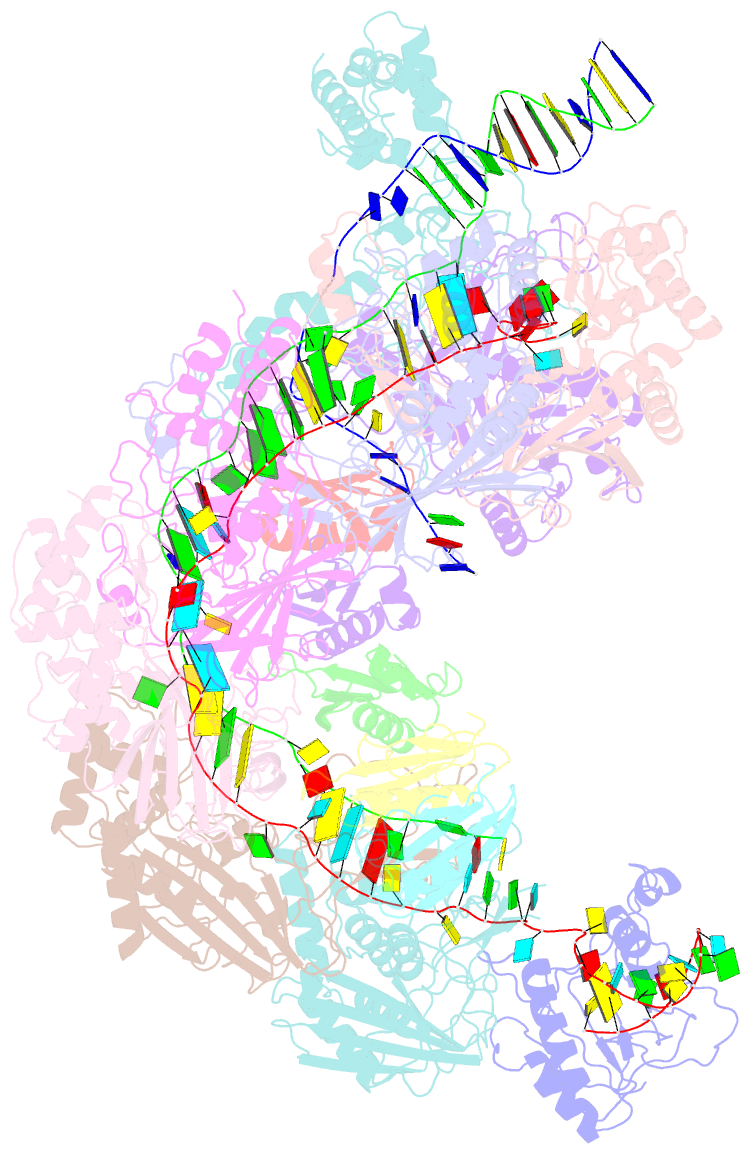
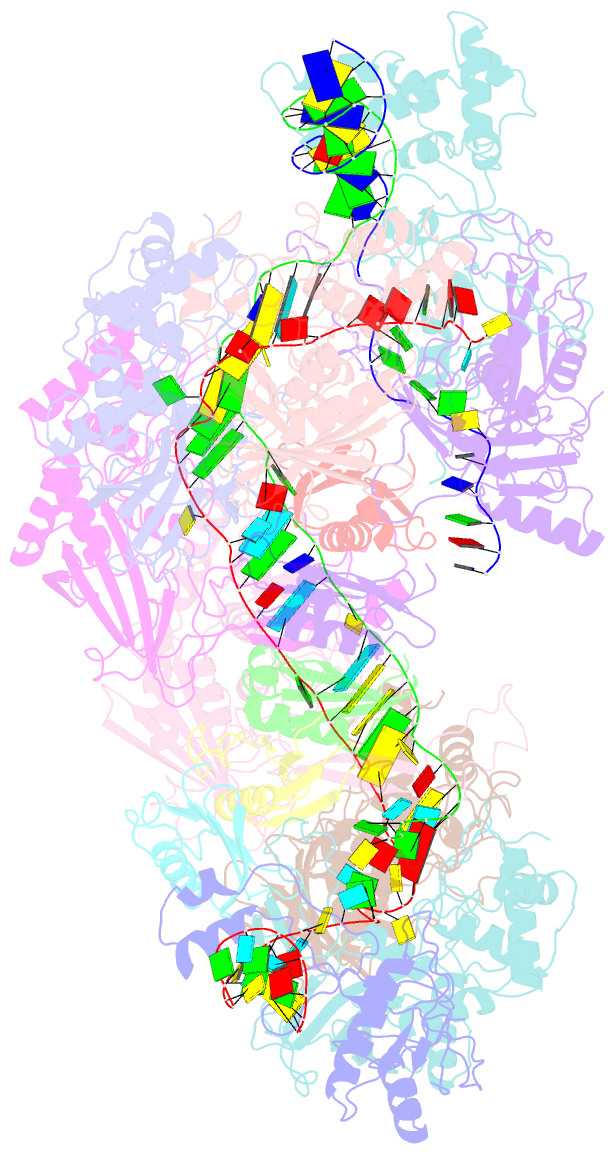
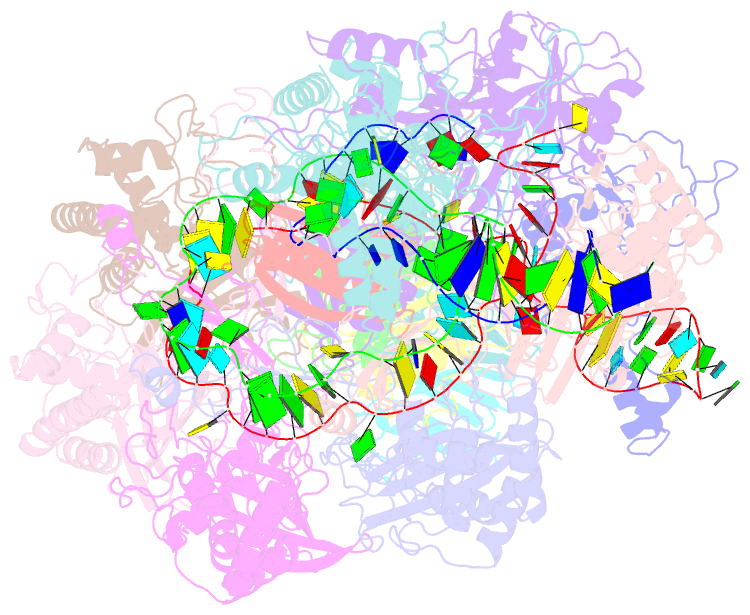
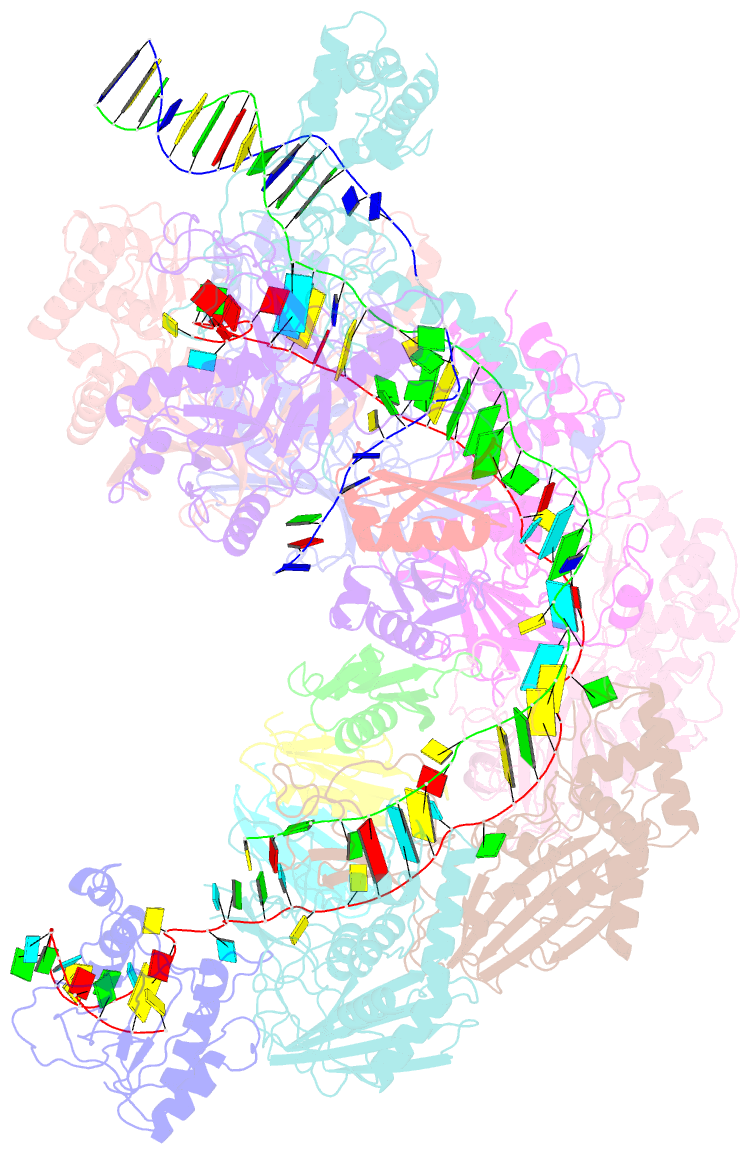
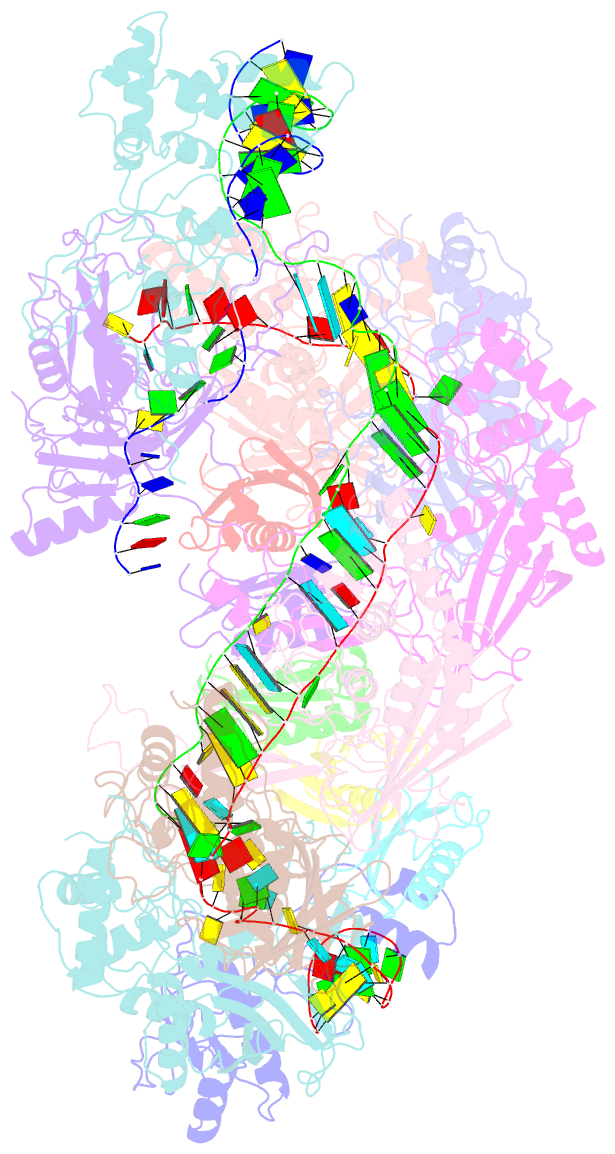
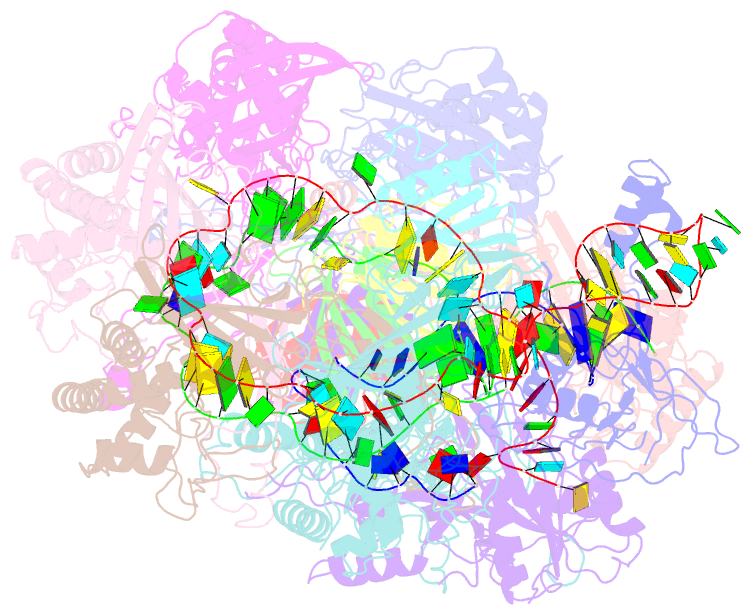
- Structure of csy-acrif5
- Reference
- Xie Y, Zhang L, Gao Z, Yin P, Wang H, Li H, Chen Z, Zhang Y, Yang M, Feng Y (2022): "AcrIF5 specifically targets DNA-bound CRISPR-Cas surveillance complex for inhibition." Nat.Chem.Biol., 18, 670-677. doi: 10.1038/s41589-022-00995-8.
- Abstract
- CRISPR-Cas systems are prokaryotic antiviral systems, and phages use anti-CRISPR proteins (Acrs) to inactivate these systems. Here we present structural and functional analyses of AcrIF5, exploring its unique anti-CRISPR mechanism. AcrIF5 shows binding specificity only for the target DNA-bound form of the crRNA-guided surveillance (Csy) complex, but not the apo Csy complex from the type I-F CRISPR-Cas system. We solved the structure of the Csy-dsDNA-AcrIF5 complex, revealing that the conformational changes of the Csy complex caused by dsDNA binding dictate the binding specificity for the Csy-dsDNA complex by AcrIF5. Mechanistically, five AcrIF5 molecules bind one Csy-dsDNA complex, which destabilizes the helical bundle domain of Cas8f, thus preventing subsequent Cas2/3 recruitment. AcrIF5 exists in symbiosis with AcrIF3, which blocks Cas2/3 recruitment. This attack on the recruitment event stands in contrast to the conventional mechanisms of blocking binding of target DNA. Overall, our study reveals an unprecedented mechanism of CRISPR-Cas inhibition by AcrIF5.