Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7fji; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.6 Å)
- Summary
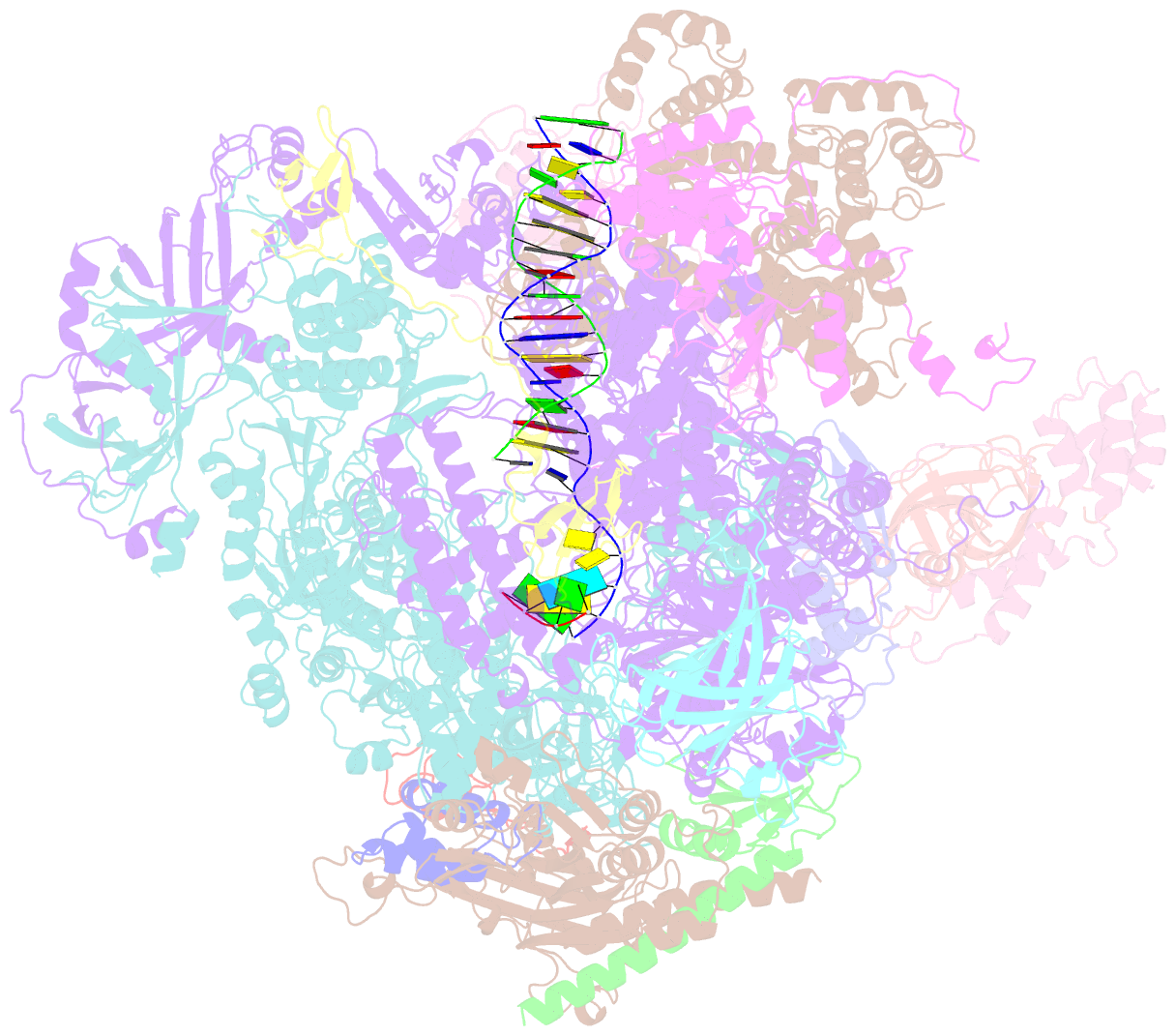
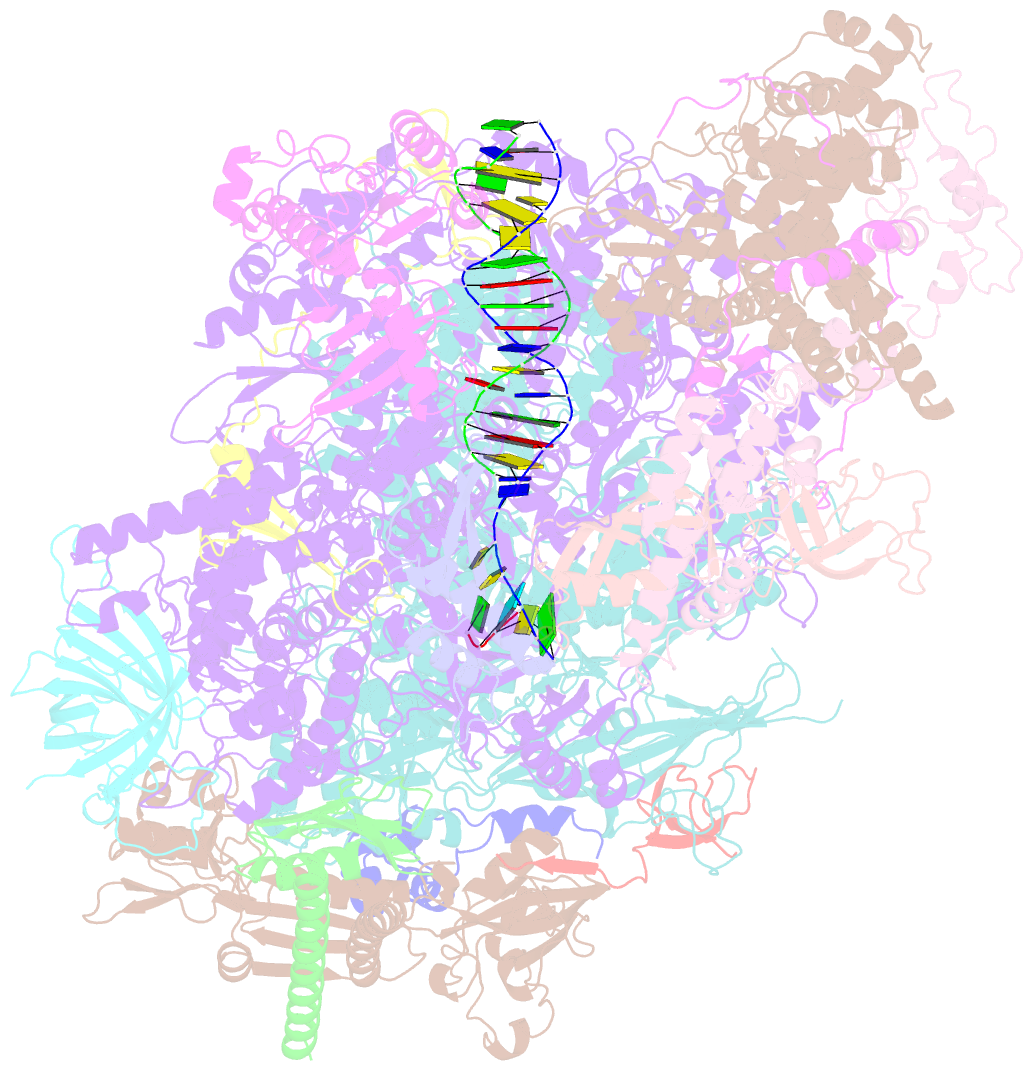
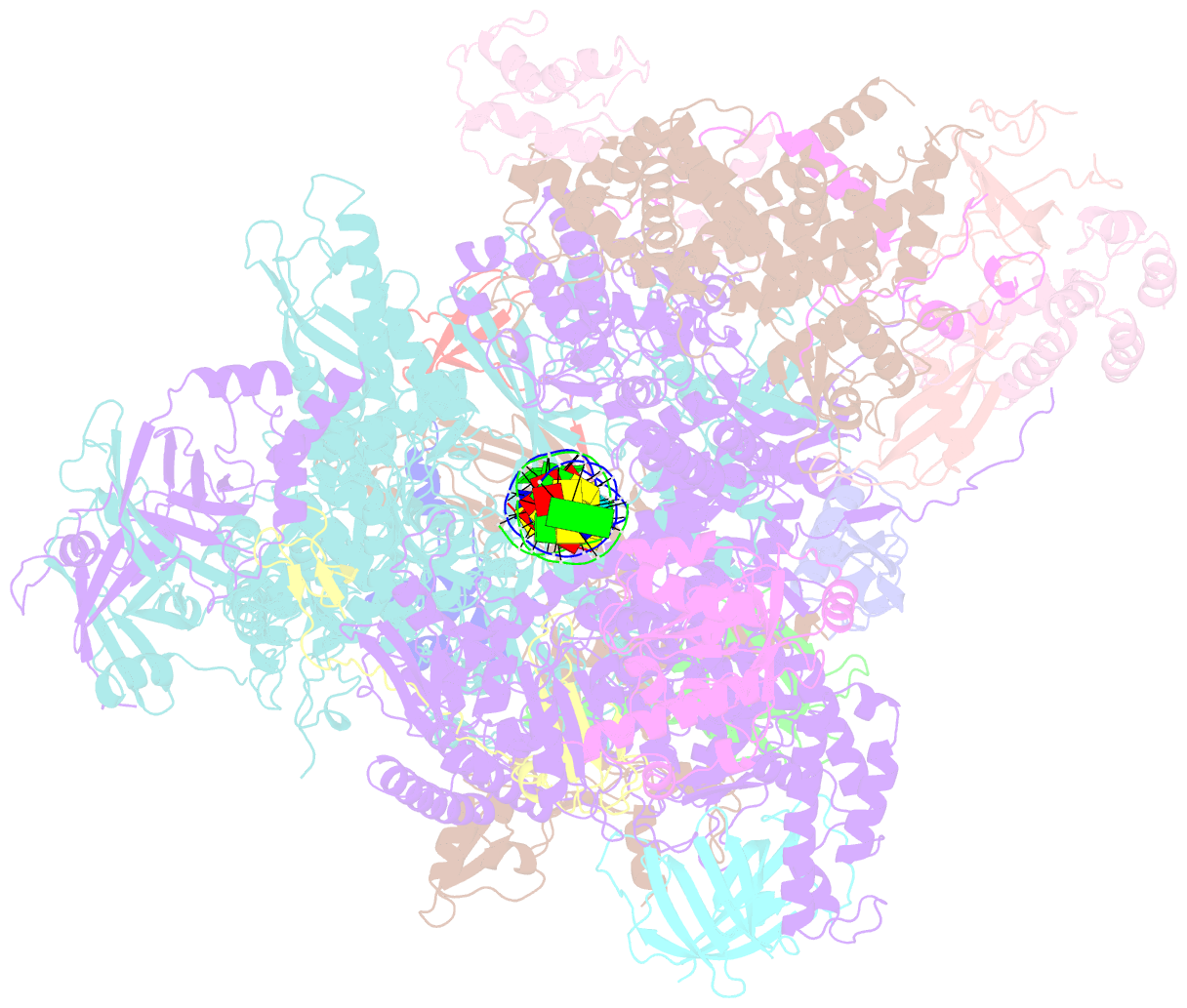
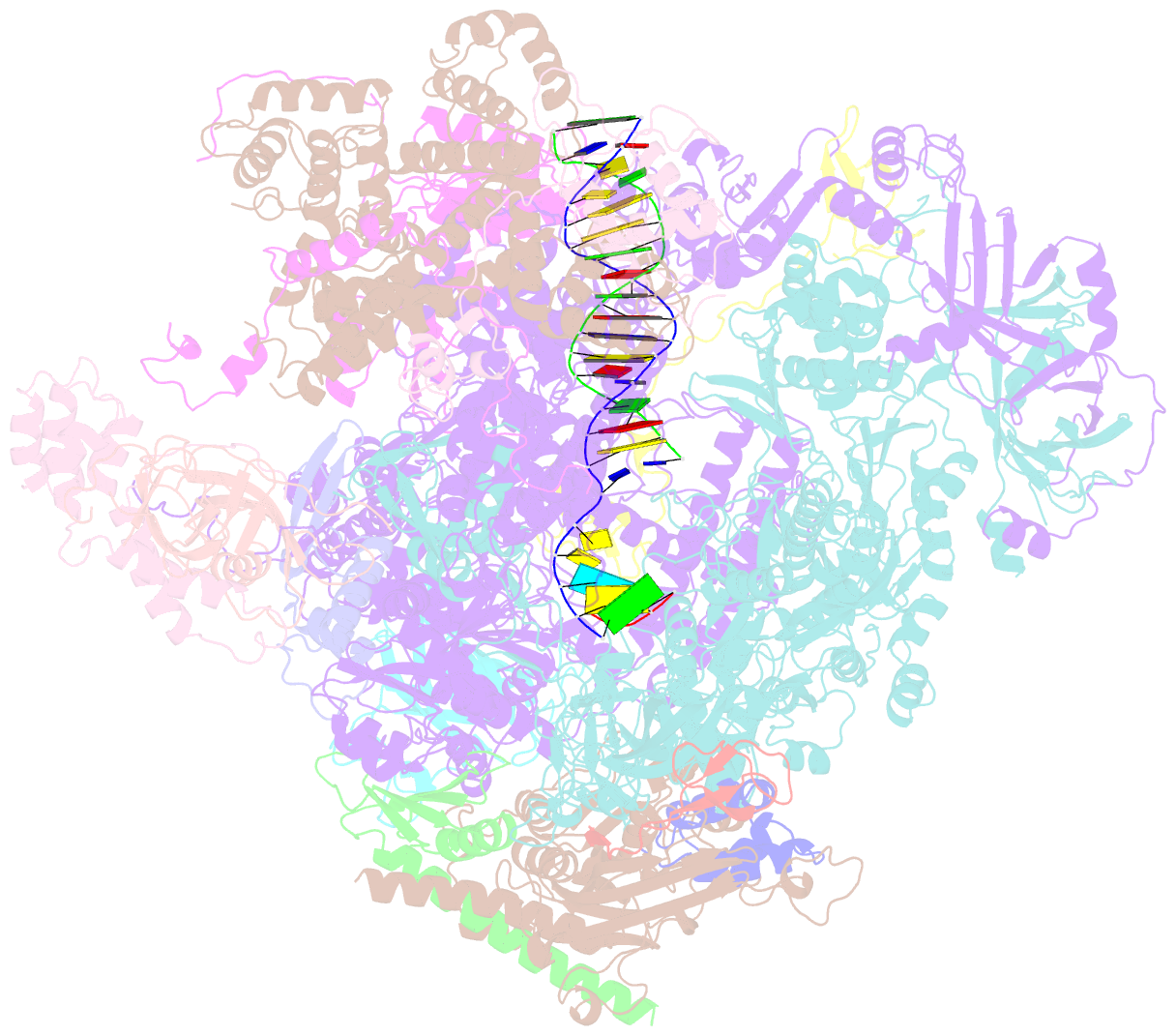
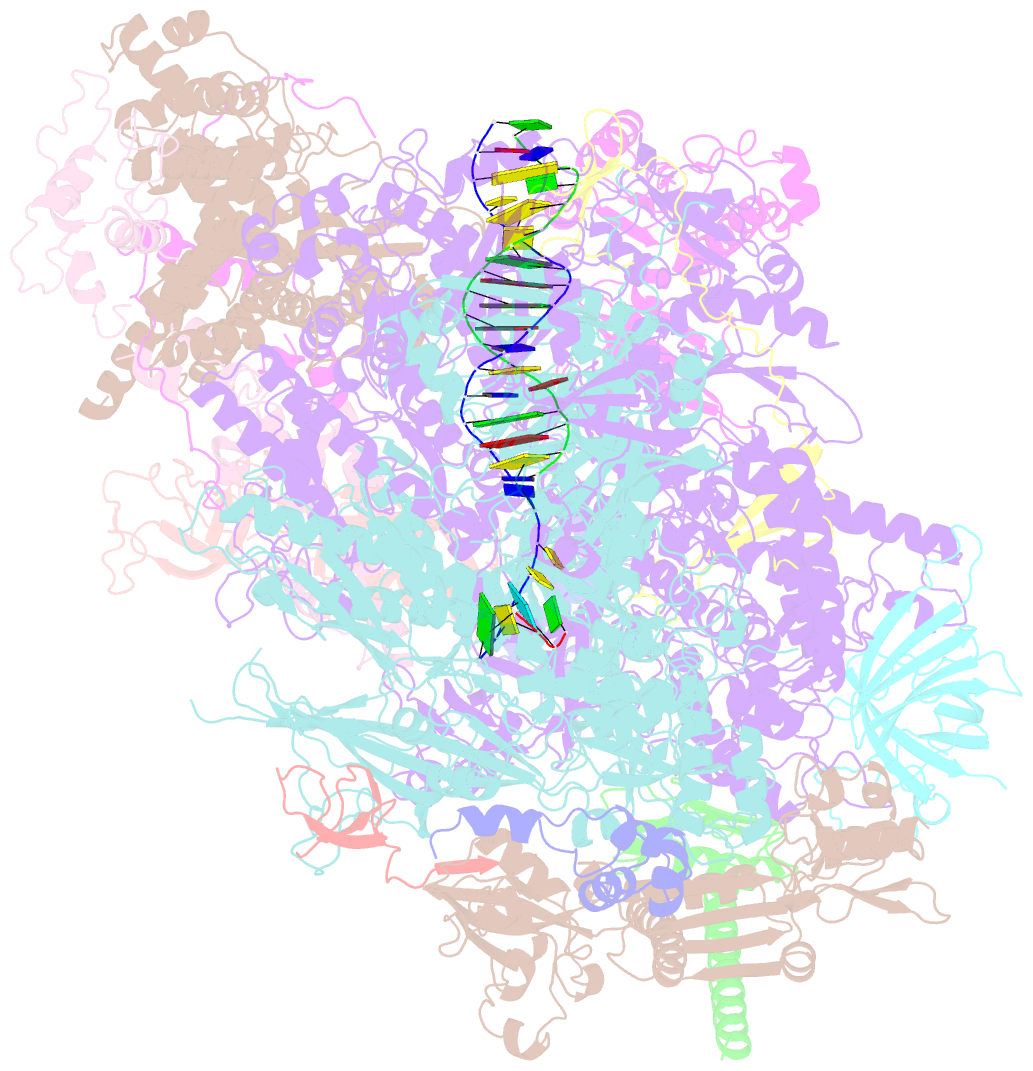
- Human pol iii elongation complex
- Reference
- Hou H, Li Y, Wang M, Liu A, Yu Z, Chen K, Zhao D, Xu Y (2021): "Structural insights into RNA polymerase III-mediated transcription termination through trapping poly-deoxythymidine." Nat Commun, 12, 6135. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-26402-9.
- Abstract
- Termination of the RNA polymerase III (Pol III)-mediated transcription requires the conversion of an elongation complex (EC) to a pre-termination complex (PTC) on poly-deoxythymidine (dT)-containing non-template strand, a mechanism distinct from Pol I and Pol II. Here, our in vitro transcription elongation assay showed that 5-7 dT-containing DNA template led to transcription termination of Pol III, but not Pol I or Pol II. We assembled human Pol III PTC on a 7 dT-containing DNA template and determined the structure at 3.6 Å resolution. The structure reveals that poly-dT are trapped in a narrow exit tunnel formed by RPC2. A hydrophobic gate of the exit tunnel separates the bases of two connected deoxythymidines and may prevent translocation of the non-template strand. The fork loop 2 stabilizes both template and non-template strands around the transcription fork, and may further prevent strand translocation. Our study shows that the Pol III-specific exit tunnel and FL2 allow for efficient translocation of non-poly-dT sequence during transcription elongation but trap poly-dT to promote DNA retention of Pol III, revealing molecular mechanism of poly-dT-dependent transcription termination of Pol III.