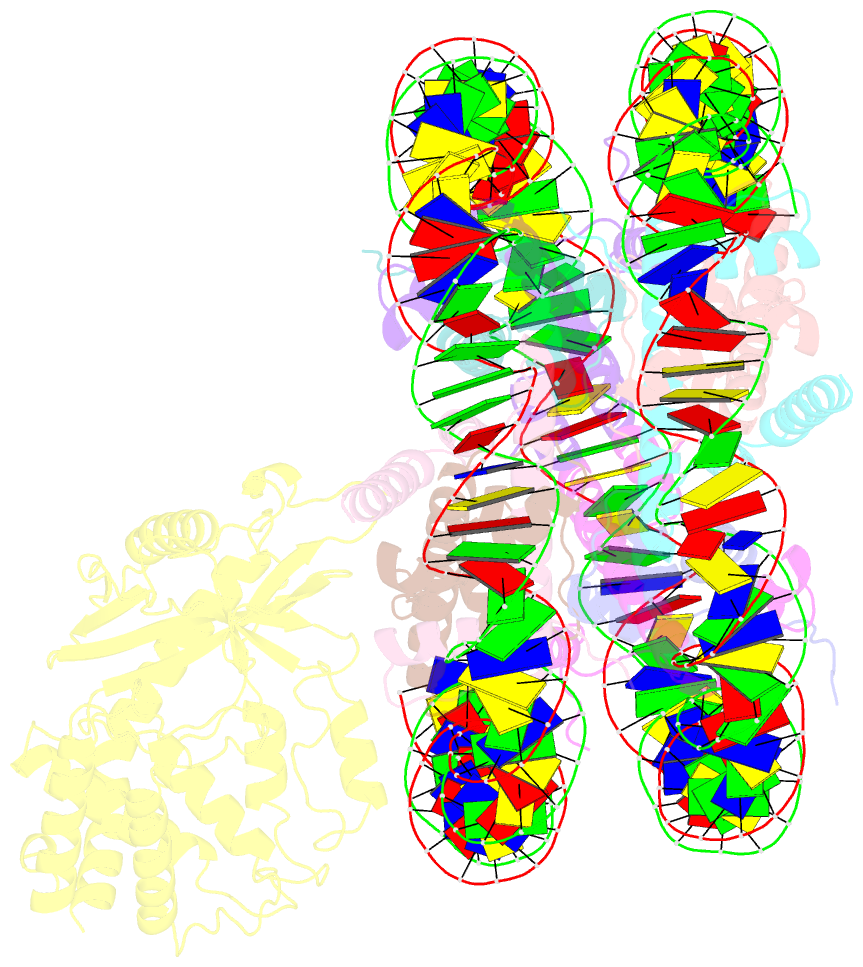
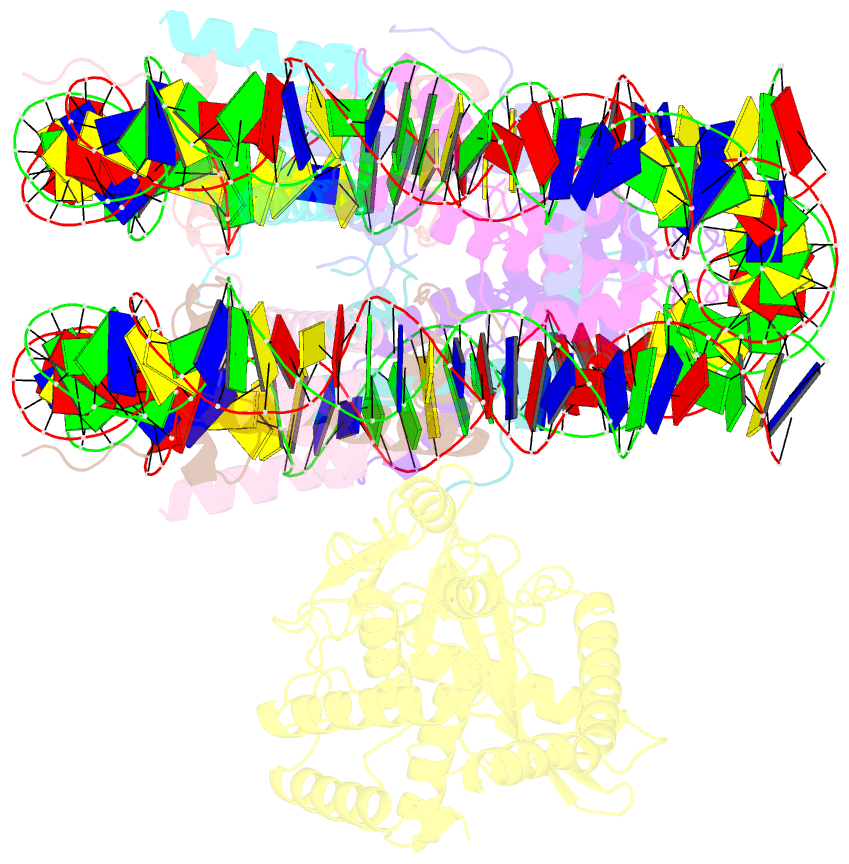
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7joa; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA-transferase
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.3 Å)
- Summary
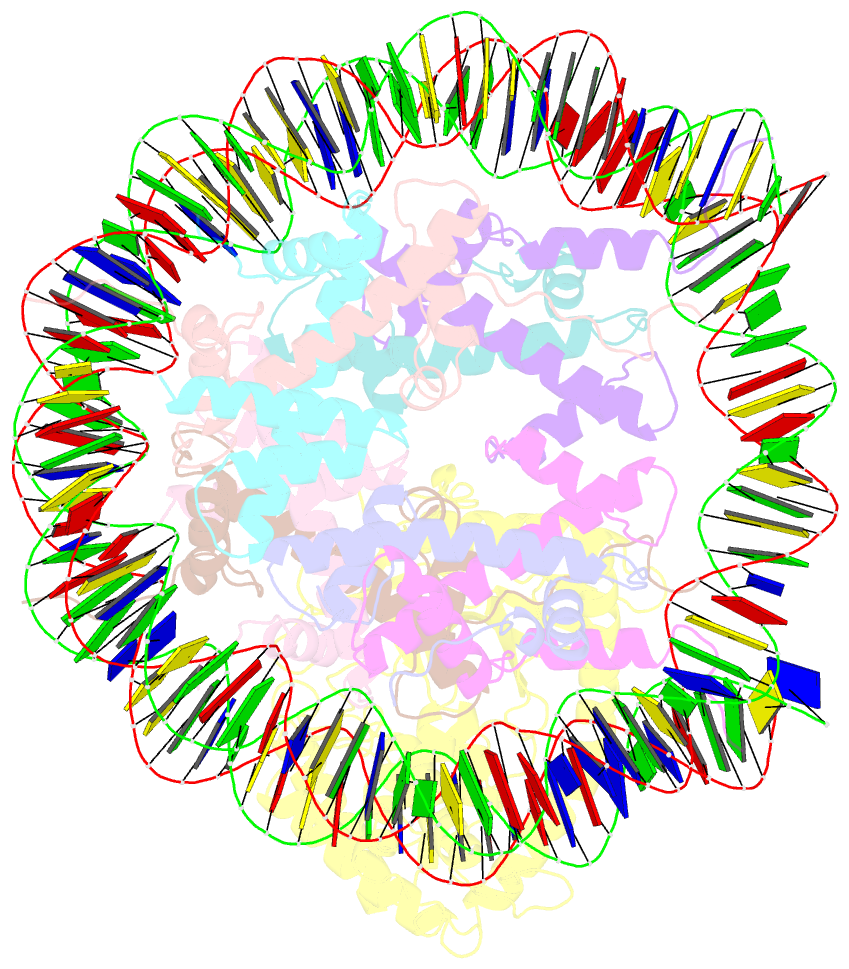
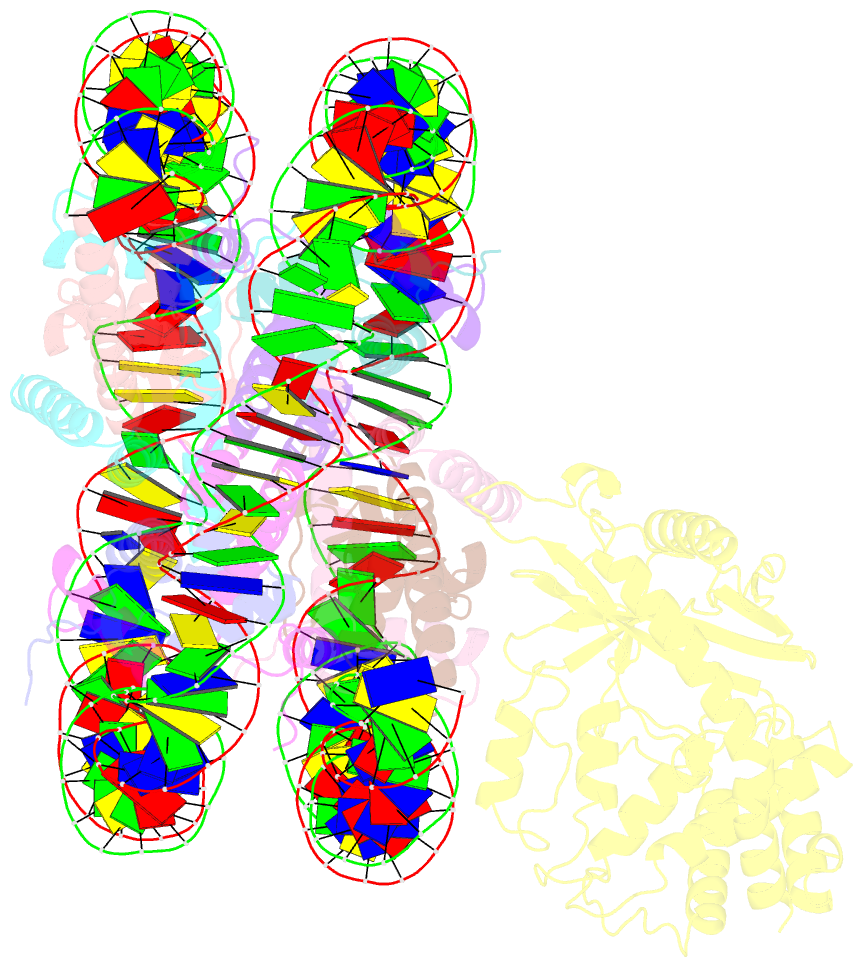
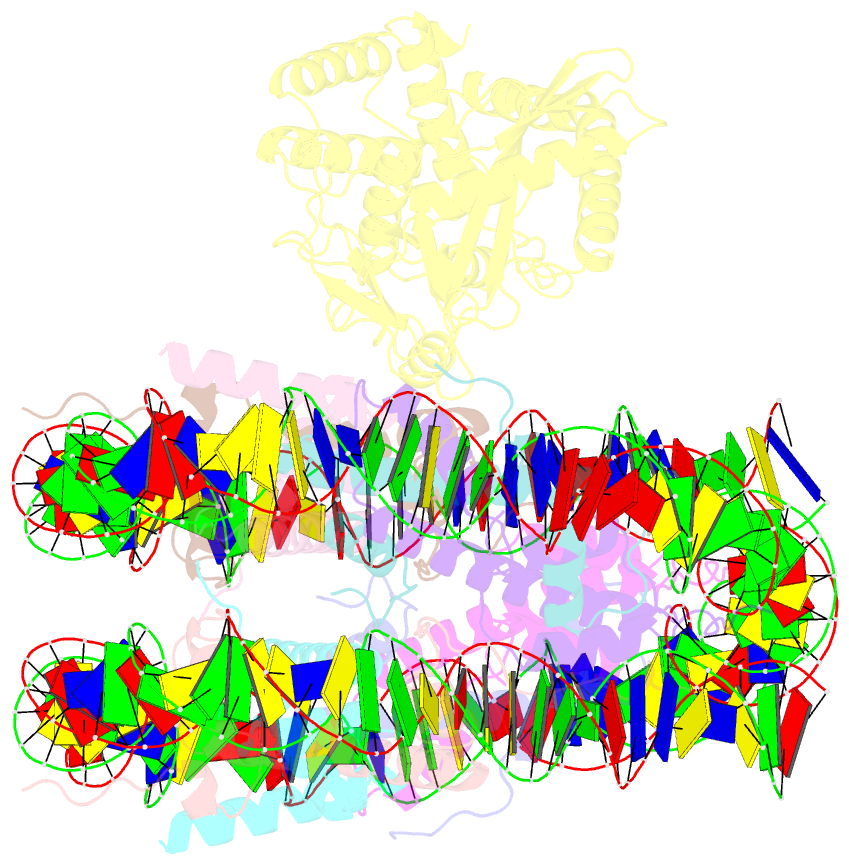
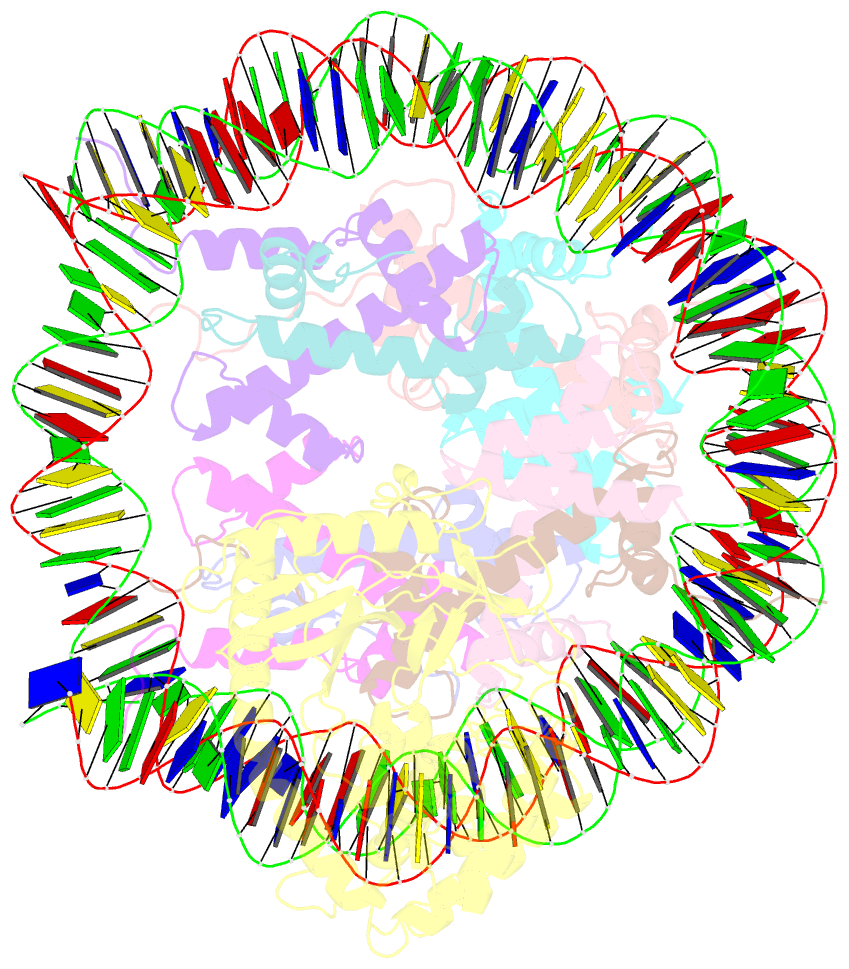
- 2:1 cgas-nucleosome complex
- Reference
- Boyer JA, Spangler CJ, Strauss JD, Cesmat AP, Liu P, McGinty RK, Zhang Q (2020): "Structural basis of nucleosome-dependent cGAS inhibition." Science, 370, 450-454. doi: 10.1126/science.abd0609.
- Abstract
- Cyclic guanosine monophosphate (GMP)-adenosine monophosphate (AMP) synthase (cGAS) recognizes cytosolic foreign or damaged DNA to activate the innate immune response to infection, inflammatory diseases, and cancer. By contrast, cGAS reactivity against self-DNA in the nucleus is suppressed by chromatin tethering. We report a 3.3-angstrom-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of cGAS in complex with the nucleosome core particle. The structure reveals that cGAS uses two conserved arginines to anchor to the nucleosome acidic patch. The nucleosome-binding interface exclusively occupies the strong double-stranded DNA (dsDNA)-binding surface on cGAS and sterically prevents cGAS from oligomerizing into the functionally active 2:2 cGAS-dsDNA state. These findings provide a structural basis for how cGAS maintains an inhibited state in the nucleus and further exemplify the role of the nucleosome in regulating diverse nuclear protein functions.