Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7kc0; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- replication
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.2 Å)
- Summary
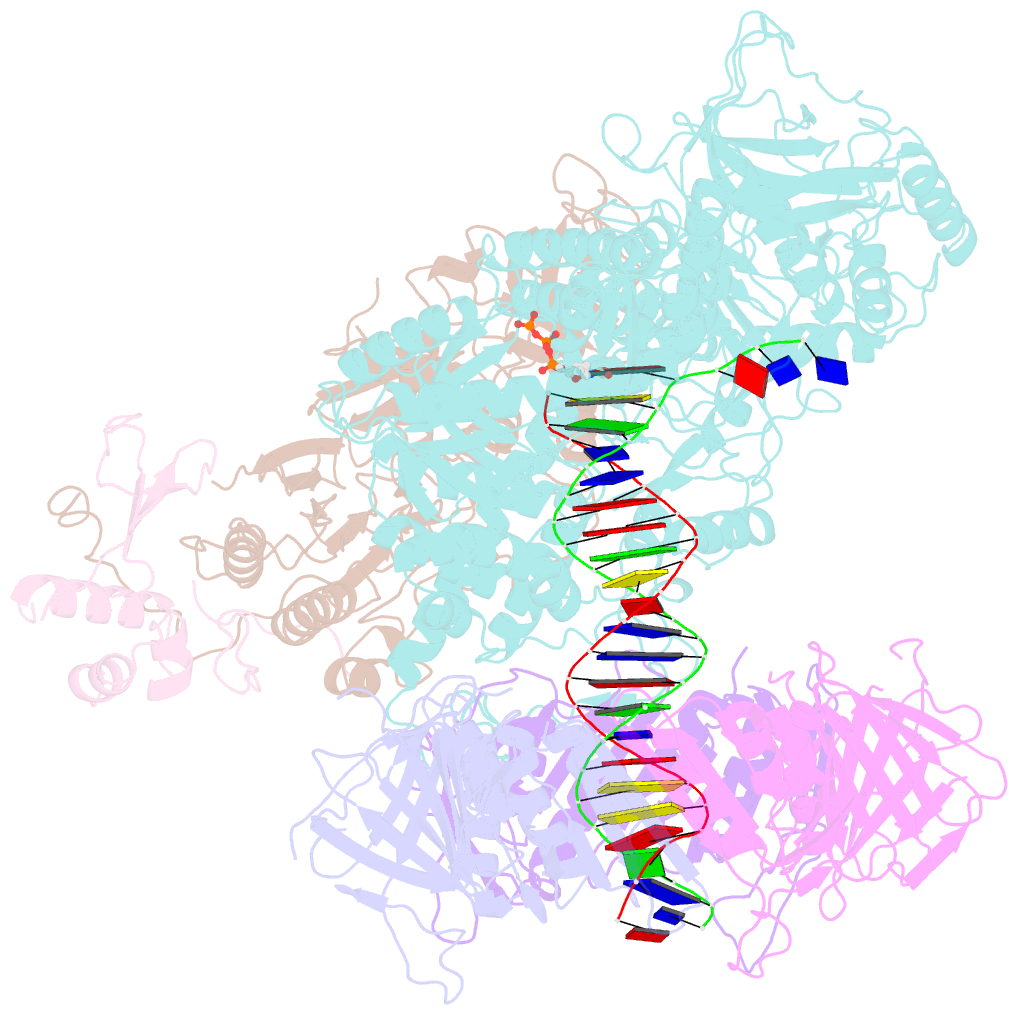
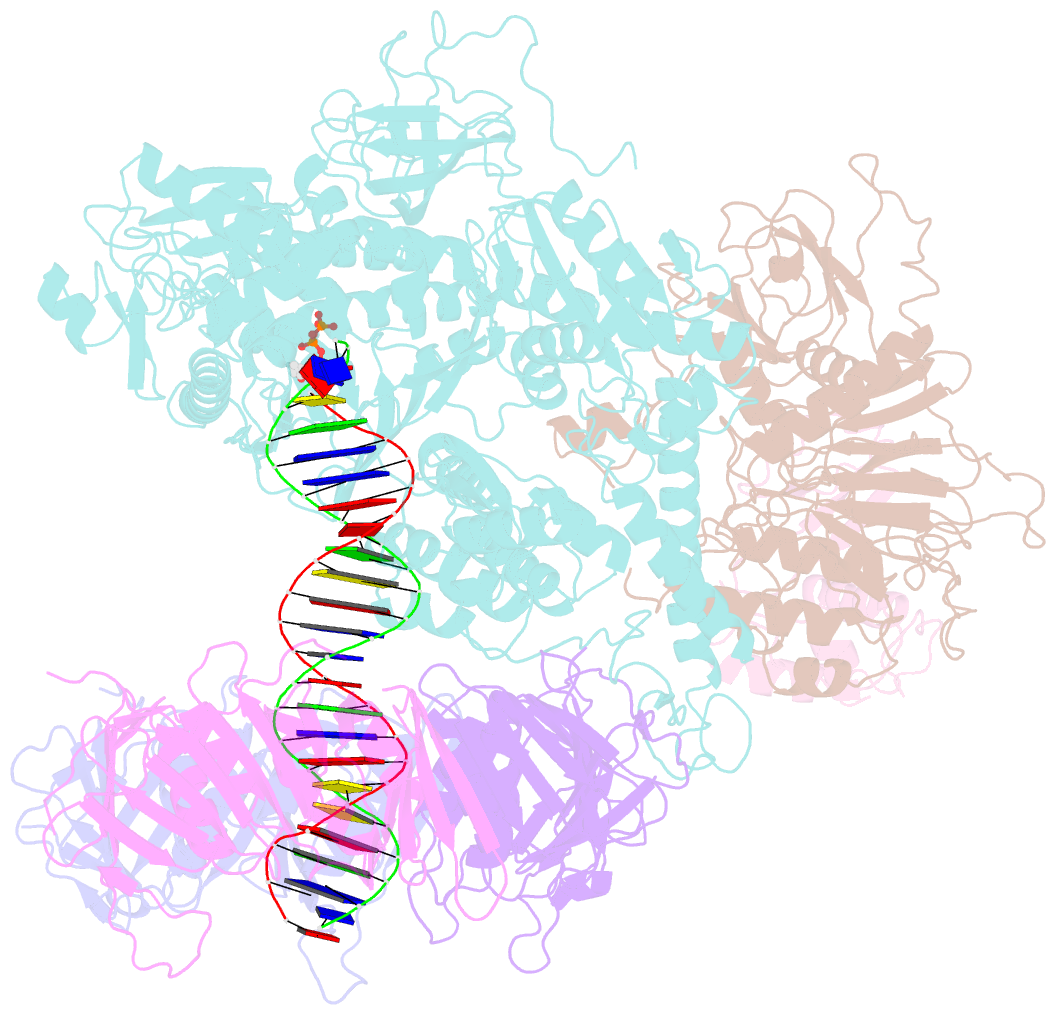
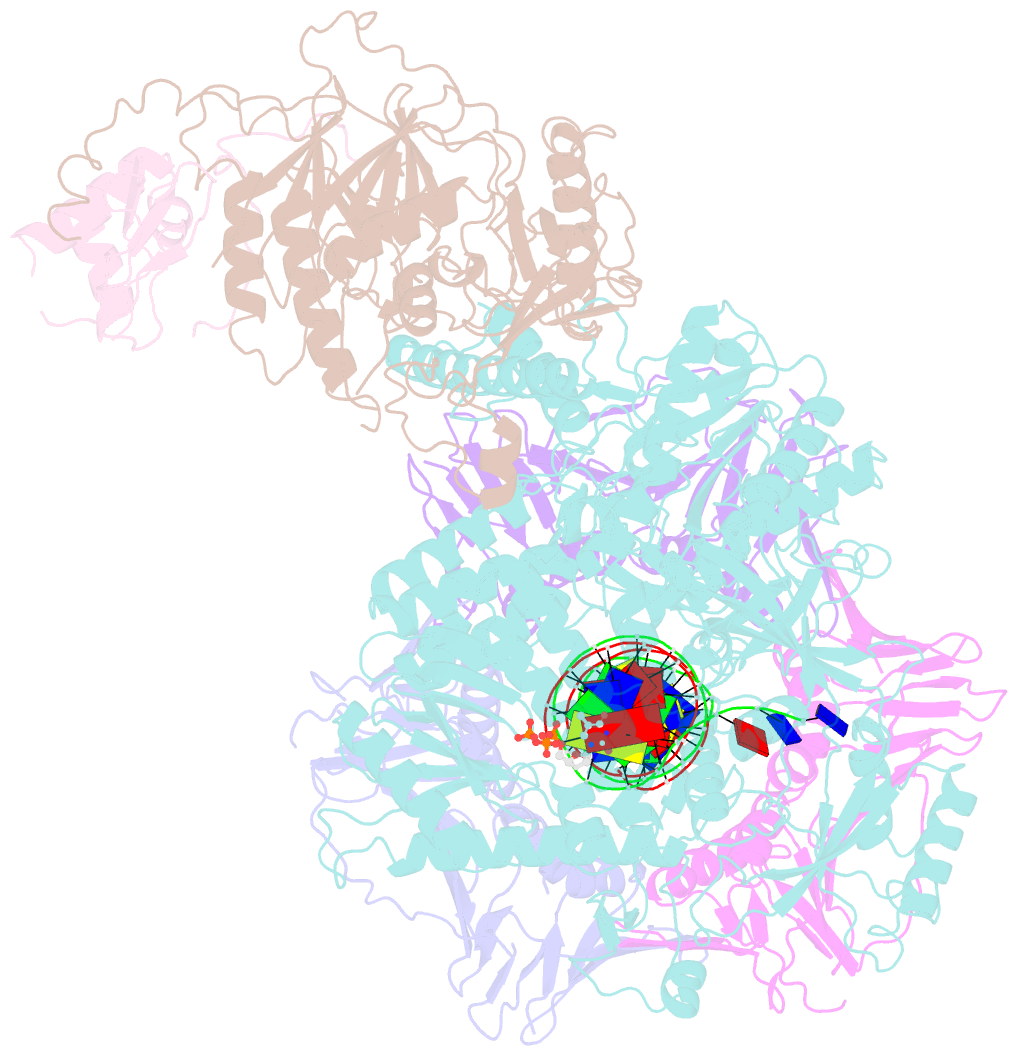
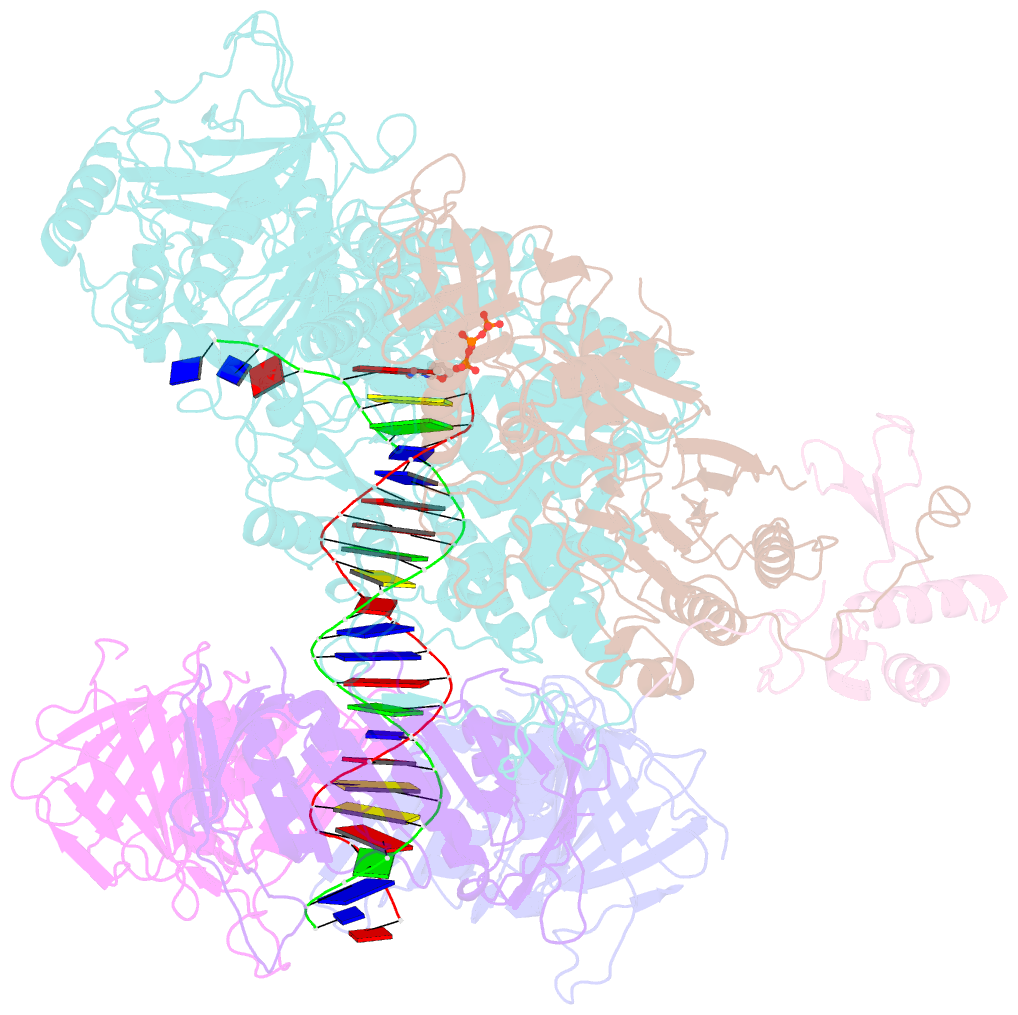
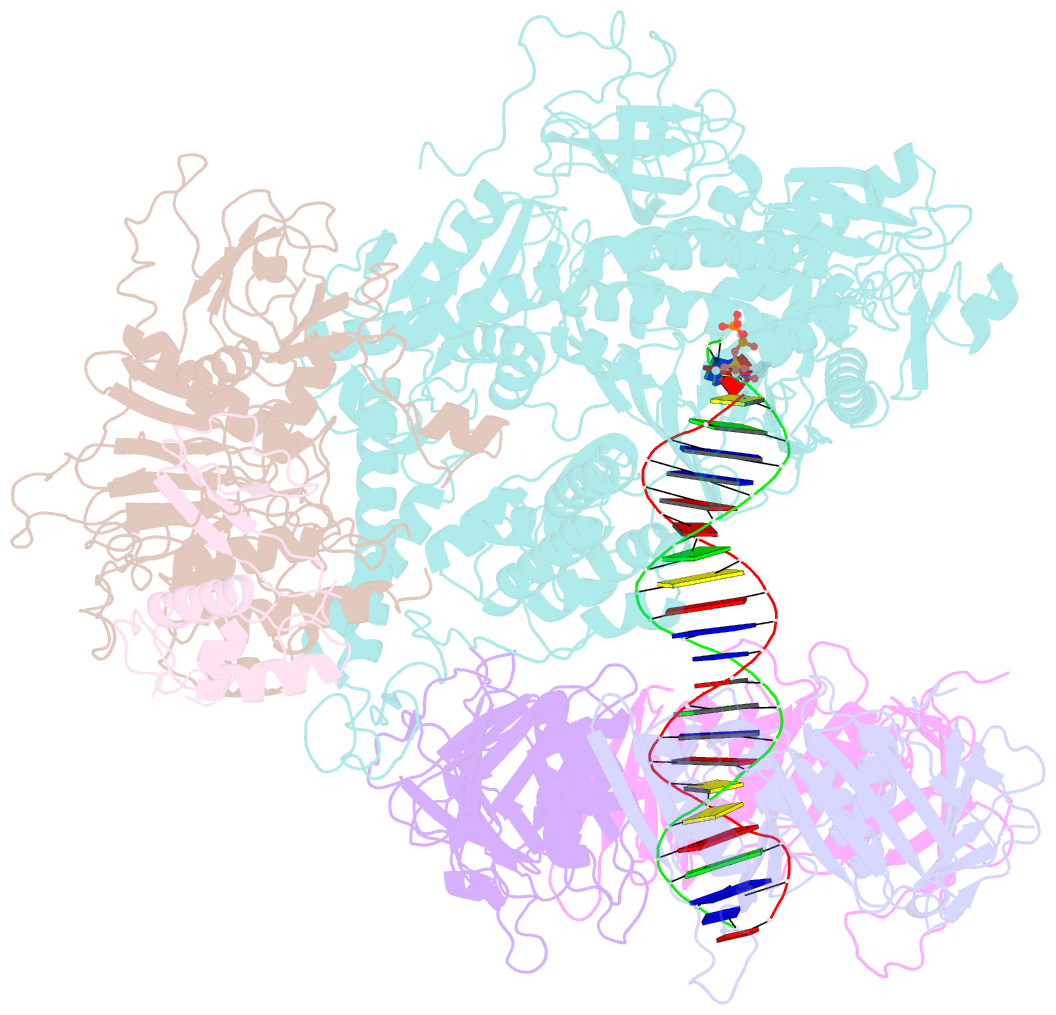
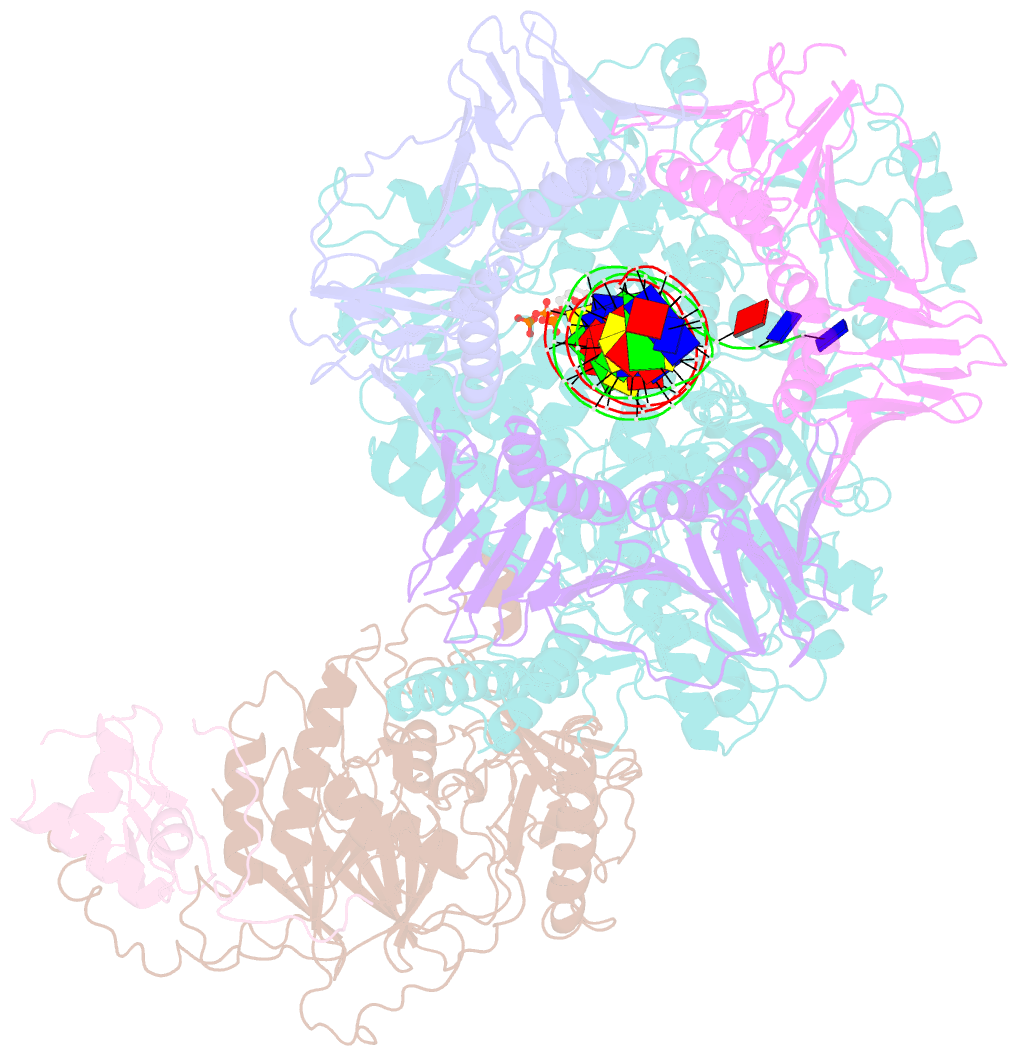
- Structure of the saccharomyces cerevisiae replicative polymerase delta in complex with a primer-template and the pcna clamp
- Reference
- Zheng F, Georgescu RE, Li H, O'Donnell ME (2020): "Structure of eukaryotic DNA polymerase delta bound to the PCNA clamp while encircling DNA." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 117, 30344-30353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2017637117.
- Abstract
- The DNA polymerase (Pol) δ of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (S.c.) is composed of the catalytic subunit Pol3 along with two regulatory subunits, Pol31 and Pol32. Pol δ binds to proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) and functions in genome replication, repair, and recombination. Unique among DNA polymerases, the Pol3 catalytic subunit contains a 4Fe-4S cluster that may sense the cellular redox state. Here we report the 3.2-Å cryo-EM structure of S.c. Pol δ in complex with primed DNA, an incoming ddTTP, and the PCNA clamp. Unexpectedly, Pol δ binds only one subunit of the PCNA trimer. This singular yet extensive interaction holds DNA such that the 2-nm-wide DNA threads through the center of the 3-nm interior channel of the clamp without directly contacting the protein. Thus, a water-mediated clamp and DNA interface enables the PCNA clamp to "waterskate" along the duplex with minimum drag. Pol31 and Pol32 are positioned off to the side of the catalytic Pol3-PCNA-DNA axis. We show here that Pol31-Pol32 binds single-stranded DNA that we propose underlies polymerase recycling during lagging strand synthesis, in analogy to Escherichia coli replicase. Interestingly, the 4Fe-4S cluster in the C-terminal CysB domain of Pol3 forms the central interface to Pol31-Pol32, and this strategic location may explain the regulation of the oxidation state on Pol δ activity, possibly useful during cellular oxidative stress. Importantly, human cancer and other disease mutations map to nearly every domain of Pol3, suggesting that all aspects of Pol δ replication are important to human health and disease.