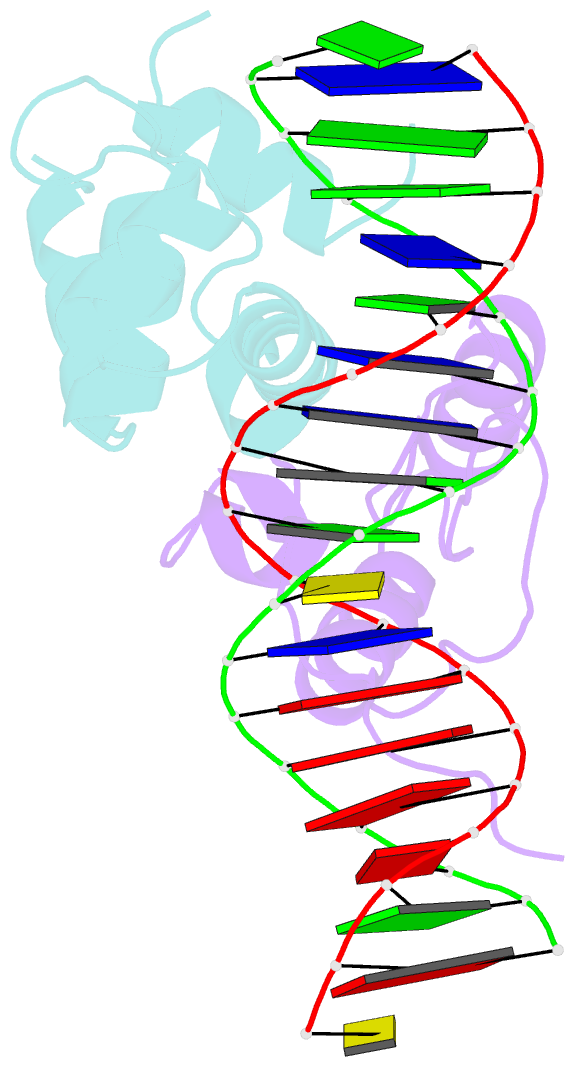
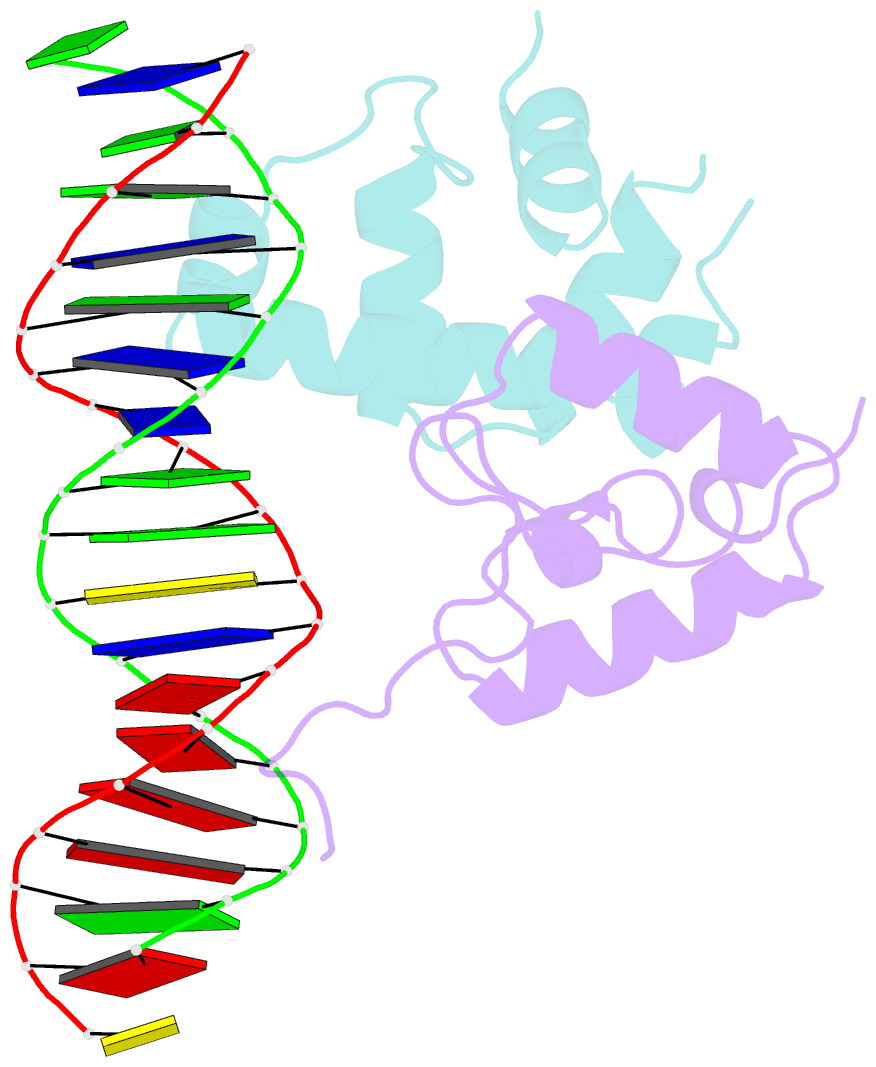
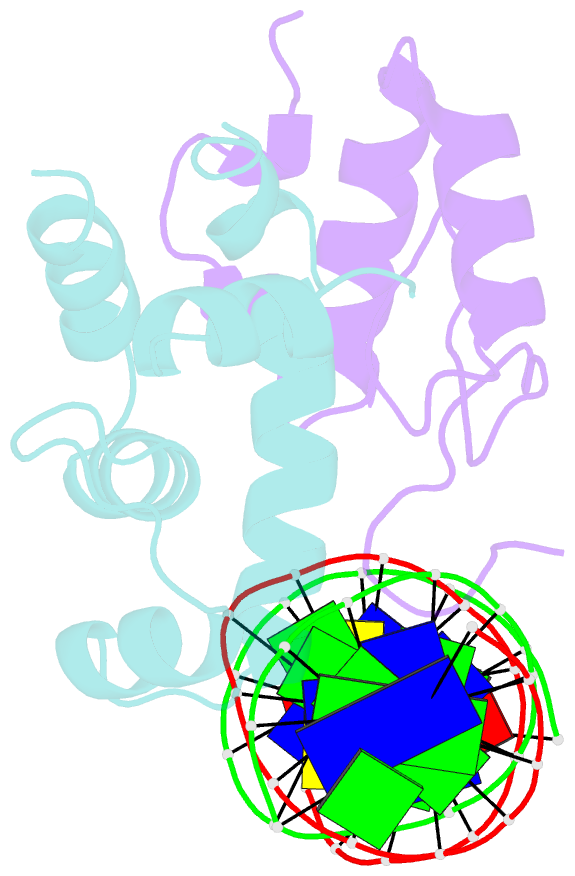
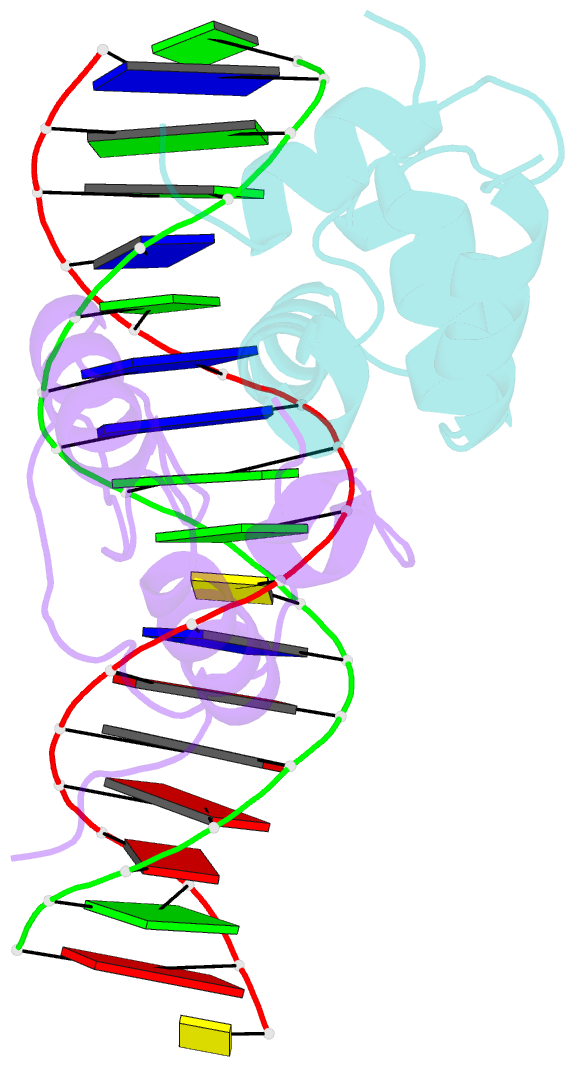
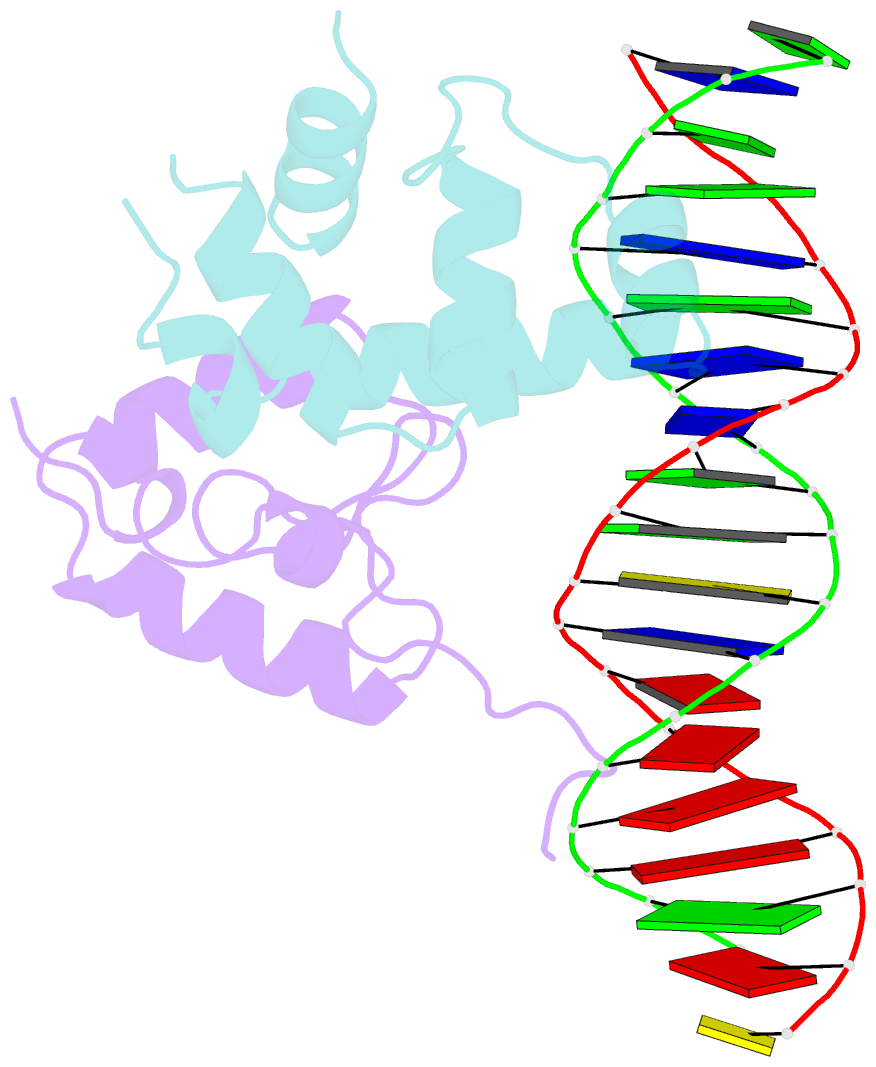
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7kuf; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- X-ray (2.6 Å)
- Summary
- Transcription activation subcomplex with whib7 bound to sigmaar4-rnap beta flap tip chimera and DNA
- Reference
- Wan T, Horova M, Beltran DG, Li S, Wong HX, Zhang LM (2021): "Structural insights into the functional divergence of WhiB-like proteins in Mycobacterium tuberculosis." Mol.Cell, 81, 2887. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2021.06.002.
- Abstract
- WhiB7 represents a distinct subclass of transcription factors in the WhiB-Like (Wbl) family, a unique group of iron-sulfur (4Fe-4S] cluster-containing proteins exclusive to the phylum of Actinobacteria. In Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), WhiB7 interacts with domain 4 of the primary sigma factor (σA4) in the RNA polymerase holoenzyme and activates genes involved in multiple drug resistance and redox homeostasis. Here, we report crystal structures of the WhiB7:σA4 complex alone and bound to its target promoter DNA at 1.55-Å and 2.6-Å resolution, respectively. These structures show how WhiB7 regulates gene expression by interacting with both σA4 and the AT-rich sequence upstream of the -35 promoter DNA via its C-terminal DNA-binding motif, the AT-hook. By combining comparative structural analysis of the two high-resolution σA4-bound Wbl structures with molecular and biochemical approaches, we identify the structural basis of the functional divergence between the two distinct subclasses of Wbl proteins in Mtb.