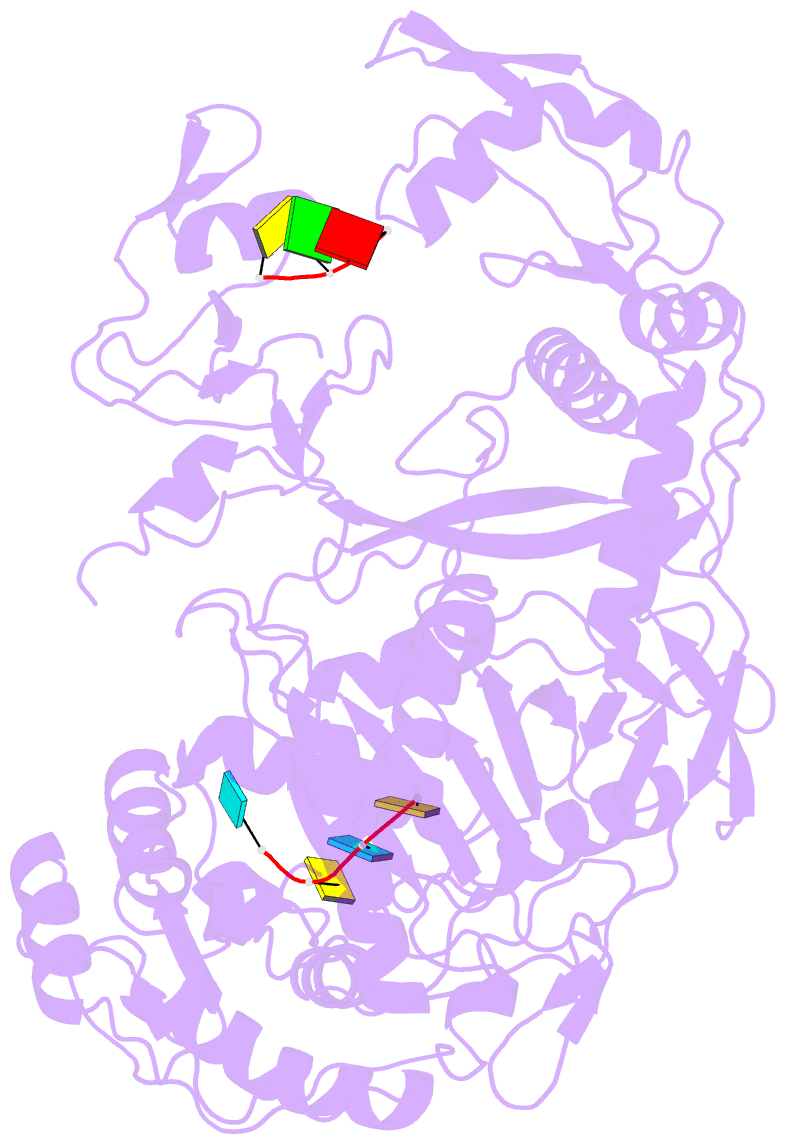
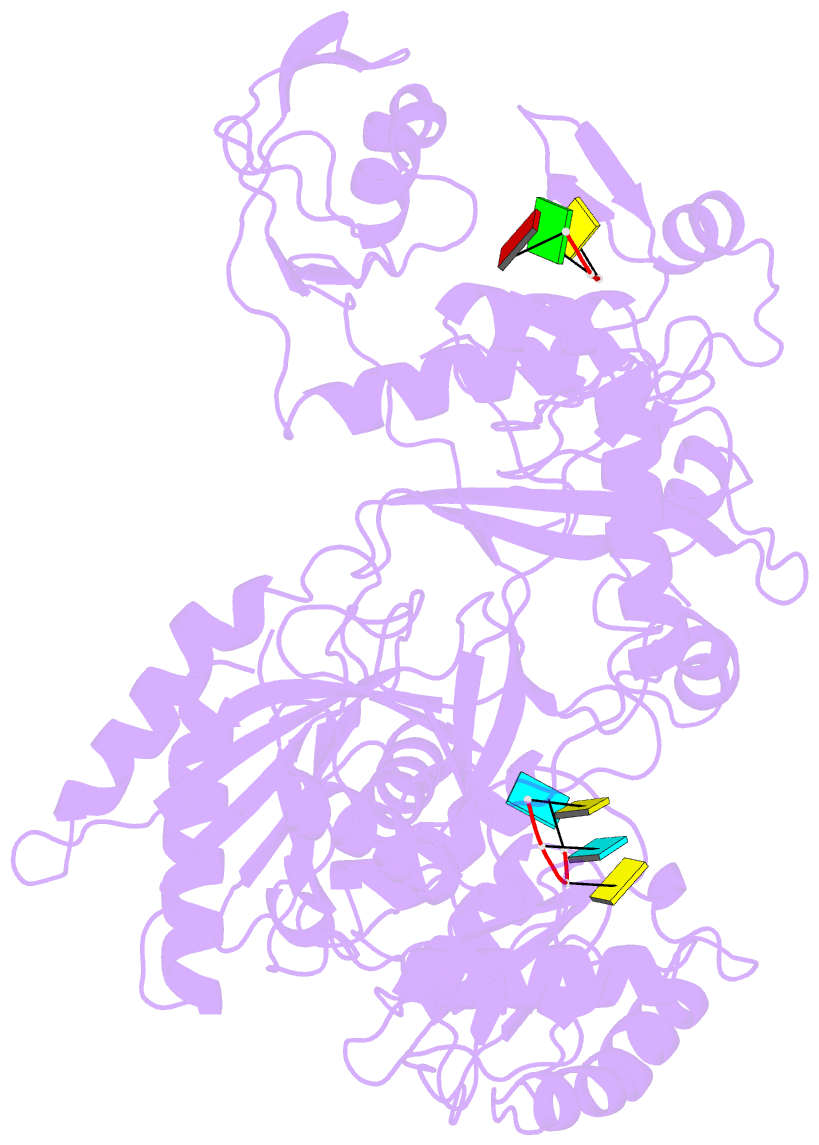
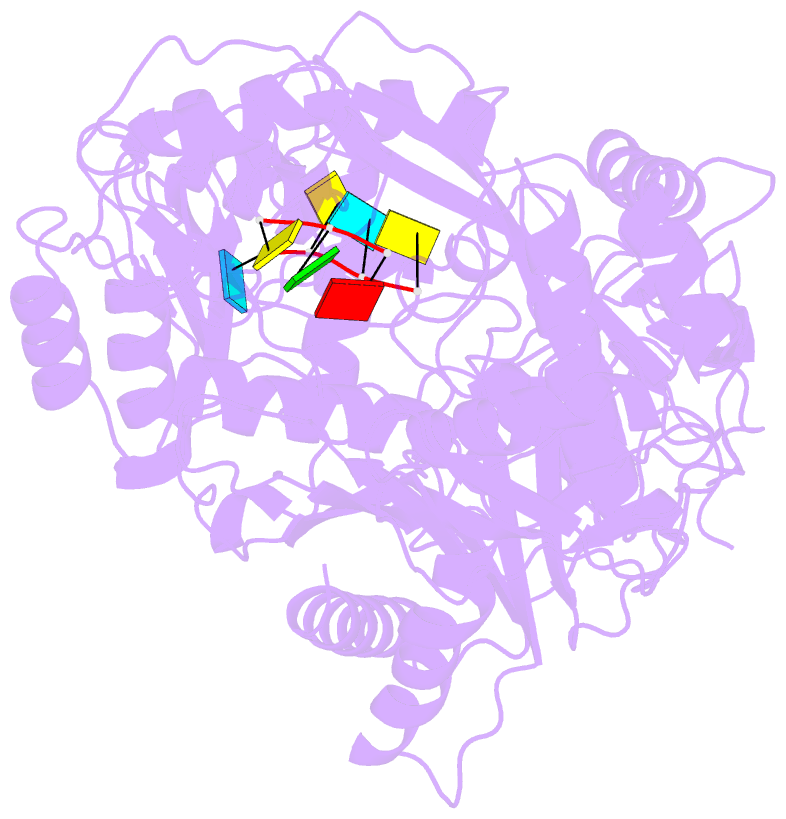
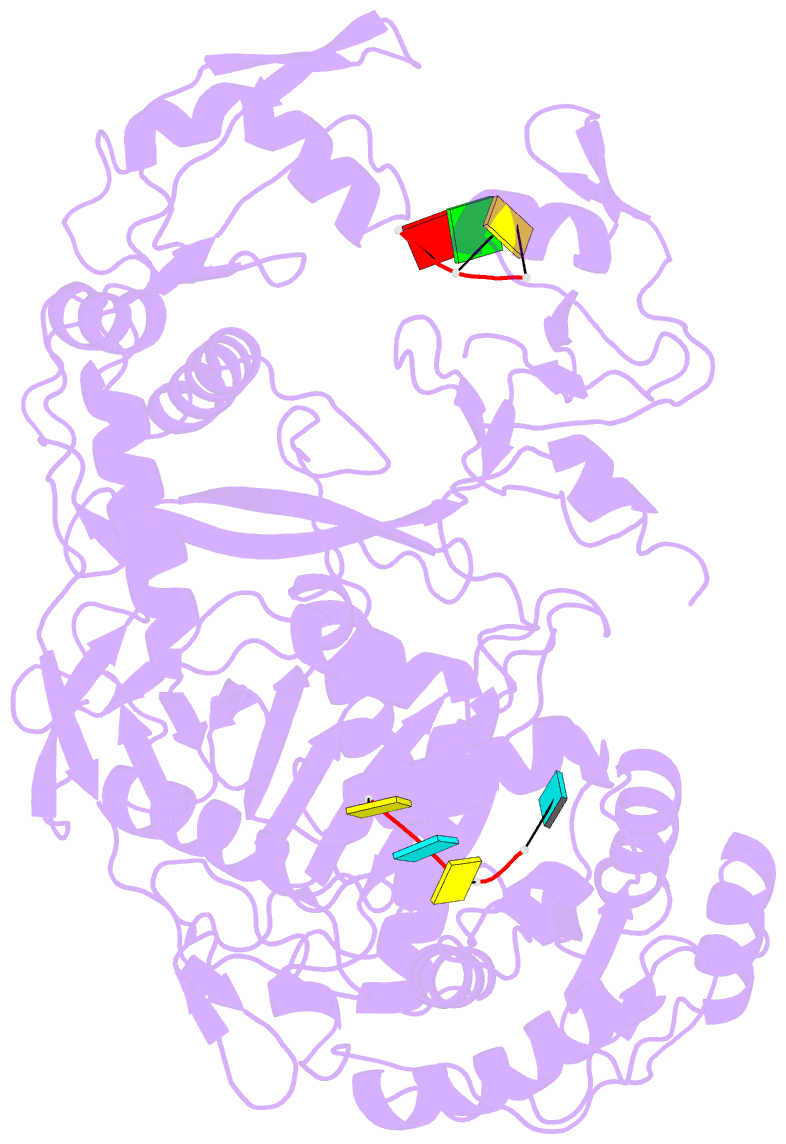
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7kx7; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase,RNA binding protein-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.8 Å)
- Summary
- cryo-EM structure of ephydatia fluviatilis piwia-pirna complex
- Reference
- Anzelon TA, Chowdhury S, Hughes SM, Xiao Y, Lander GC, MacRae IJ (2021): "Structural basis for piRNA targeting." Nature, 597, 285-289. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03856-x.
- Abstract
- PIWI proteins use PIWI-interacting RNAs (piRNAs) to identify and silence transposable elements and thereby maintain genome integrity between metazoan generations1. The targeting of transposable elements by PIWI has been compared to mRNA target recognition by Argonaute proteins2,3, which use microRNA (miRNA) guides, but the extent to which piRNAs resemble miRNAs is not known. Here we present cryo-electron microscopy structures of a PIWI-piRNA complex from the sponge Ephydatia fluviatilis with and without target RNAs, and a biochemical analysis of target recognition. Mirroring Argonaute, PIWI identifies targets using the piRNA seed region. However, PIWI creates a much weaker seed so that stable target association requires further piRNA-target pairing, making piRNAs less promiscuous than miRNAs. Beyond the seed, the structure of PIWI facilitates piRNA-target pairing in a manner that is tolerant of mismatches, leading to long-lived PIWI-piRNA-target interactions that may accumulate on transposable-element transcripts. PIWI ensures targeting fidelity by physically blocking the propagation of piRNA-target interactions in the absence of faithful seed pairing, and by requiring an extended piRNA-target duplex to reach an endonucleolytically active conformation. PIWI proteins thereby minimize off-targeting cellular mRNAs while defending against evolving genomic threats.