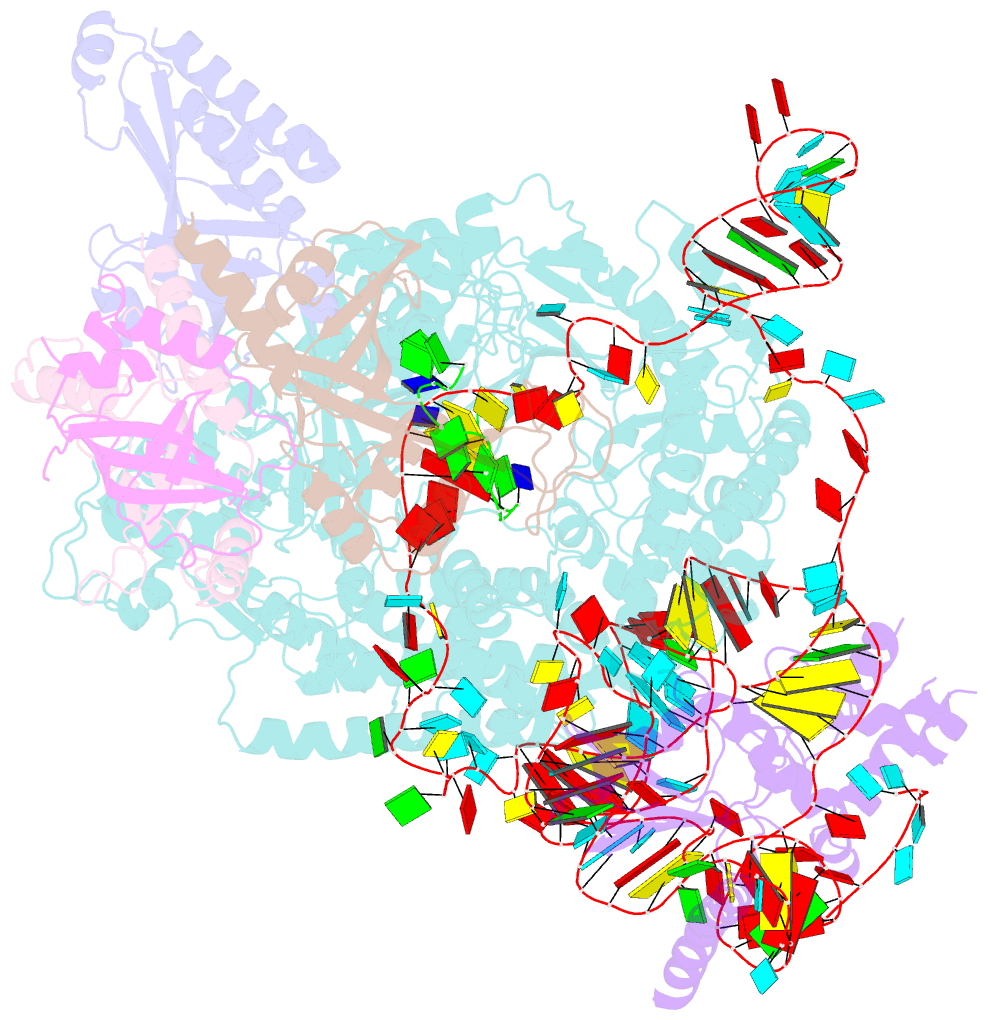
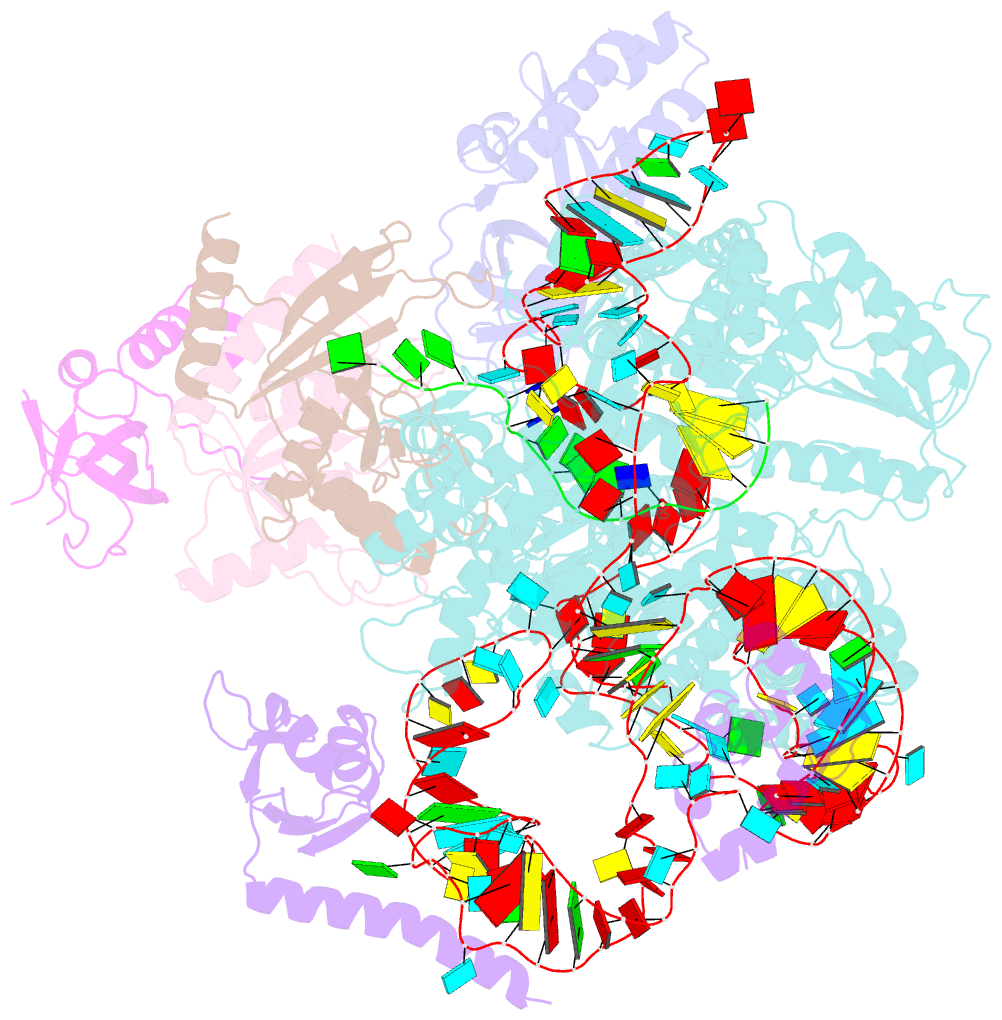
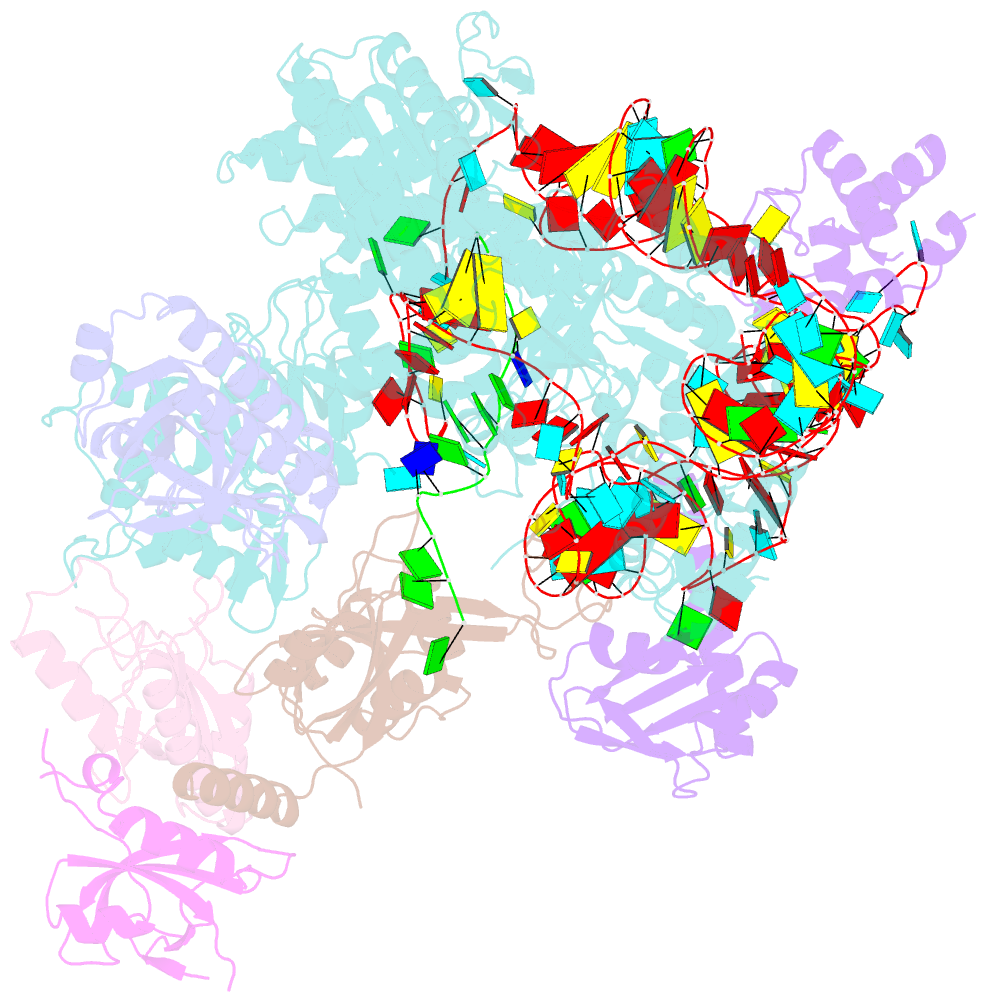
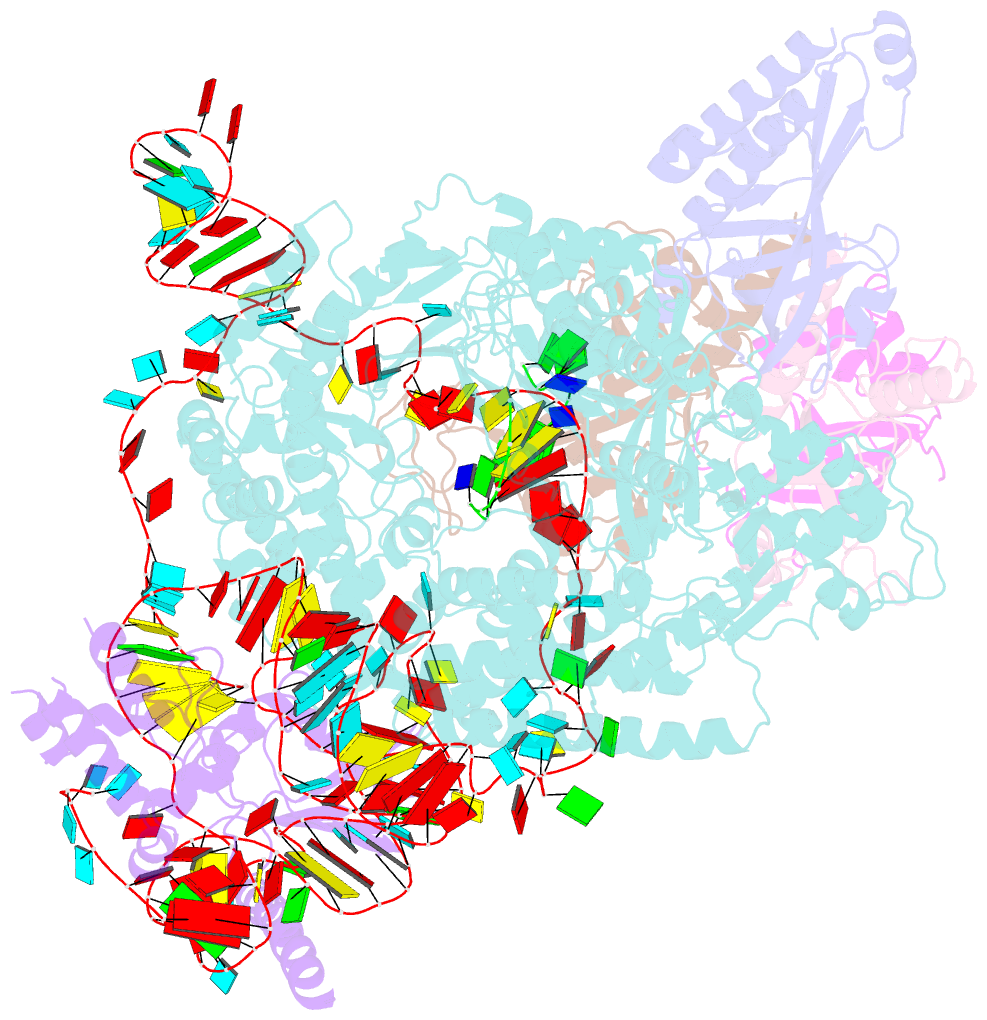
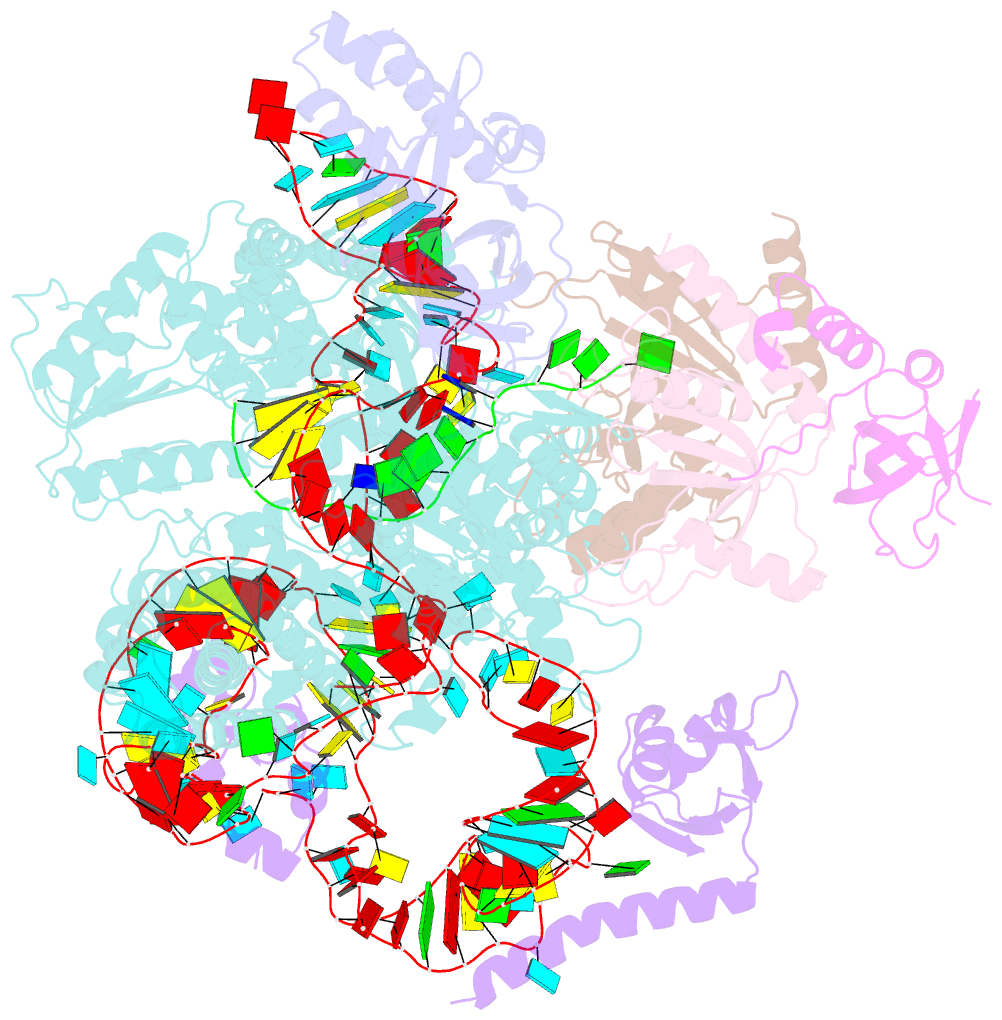
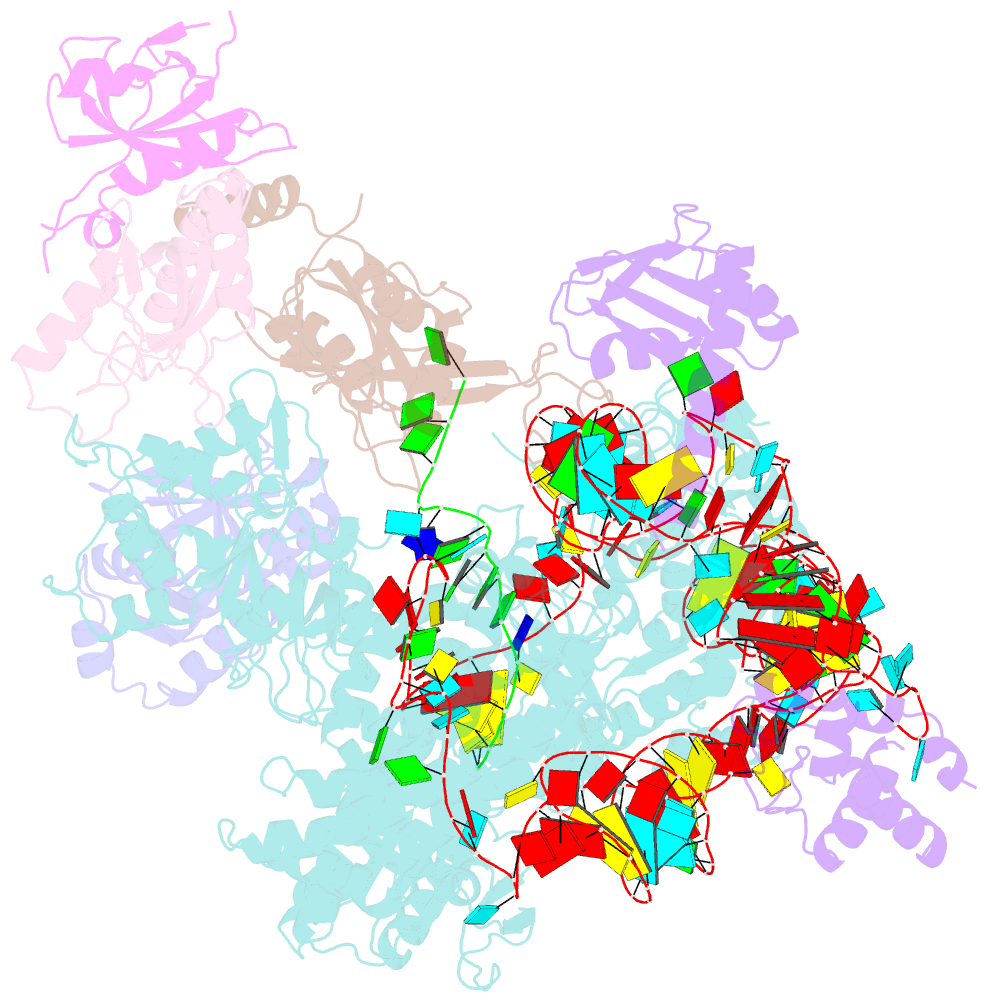
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7lma; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- replication-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.3 Å)
- Summary
- Tetrahymena telomerase t3d2 structure at 3.3 angstrom
- Reference
- He Y, Wang Y, Liu B, Helmling C, Susac L, Cheng R, Zhou ZH, Feigon J (2021): "Structures of telomerase at several steps of telomere repeat synthesis." Nature, 593, 454-459. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-03529-9.
- Abstract
- Telomerase is unique among the reverse transcriptases in containing a noncoding RNA (known as telomerase RNA (TER)) that includes a short template that is used for the processive synthesis of G-rich telomeric DNA repeats at the 3' ends of most eukaryotic chromosomes1. Telomerase maintains genomic integrity, and its activity or dysregulation are critical determinants of human longevity, stem cell renewal and cancer progression2,3. Previous cryo-electron microscopy structures have established the general architecture, protein components and stoichiometries of Tetrahymena and human telomerase, but our understandings of the details of DNA-protein and RNA-protein interactions and of the mechanisms and recruitment involved remain limited4-6. Here we report cryo-electron microscopy structures of active Tetrahymena telomerase with telomeric DNA at different steps of nucleotide addition. Interactions between telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT), TER and DNA reveal the structural basis of the determination of the 5' and 3' template boundaries, handling of the template-DNA duplex and separation of the product strand during nucleotide addition. The structure and binding interface between TERT and telomerase protein p50 (a homologue of human TPP17,8) define conserved interactions that are required for telomerase activation and recruitment to telomeres. Telomerase La-related protein p65 remodels several regions of TER, bridging the 5' and 3' ends and the conserved pseudoknot to facilitate assembly of the TERT-TER catalytic core.