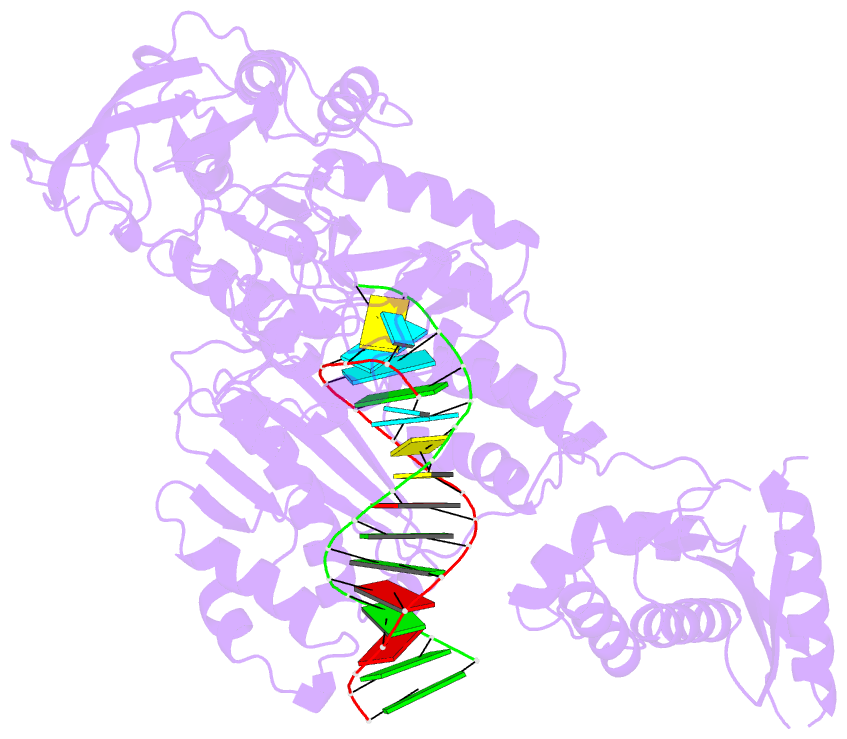
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7o0g; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein
- Method
- X-ray (3.1 Å)
- Summary
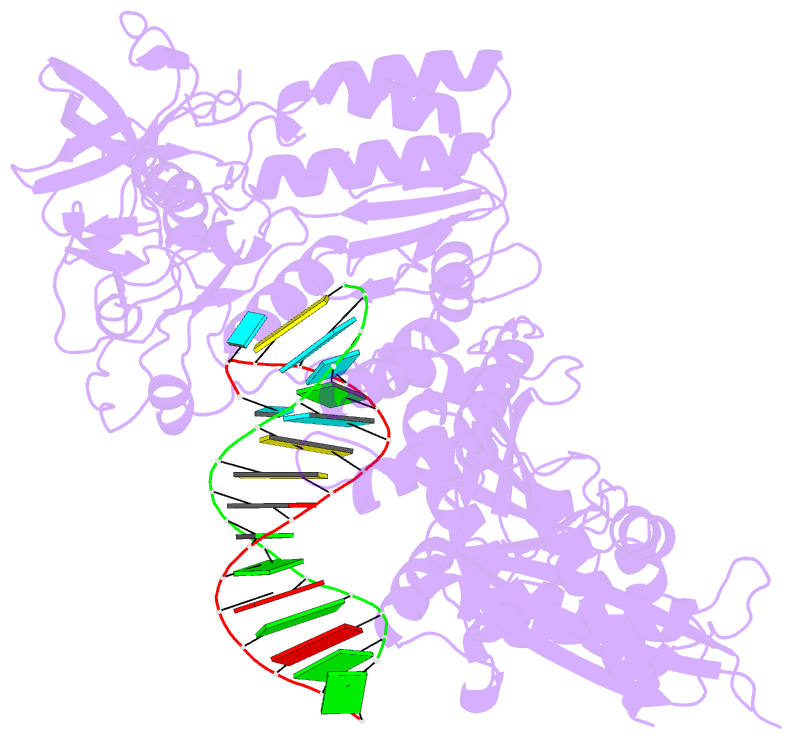
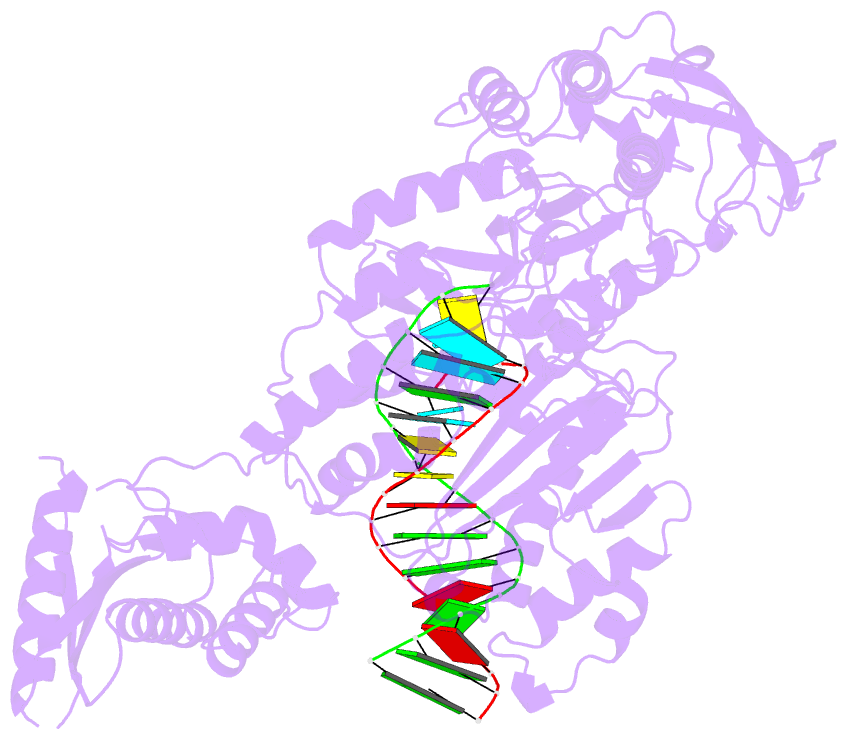
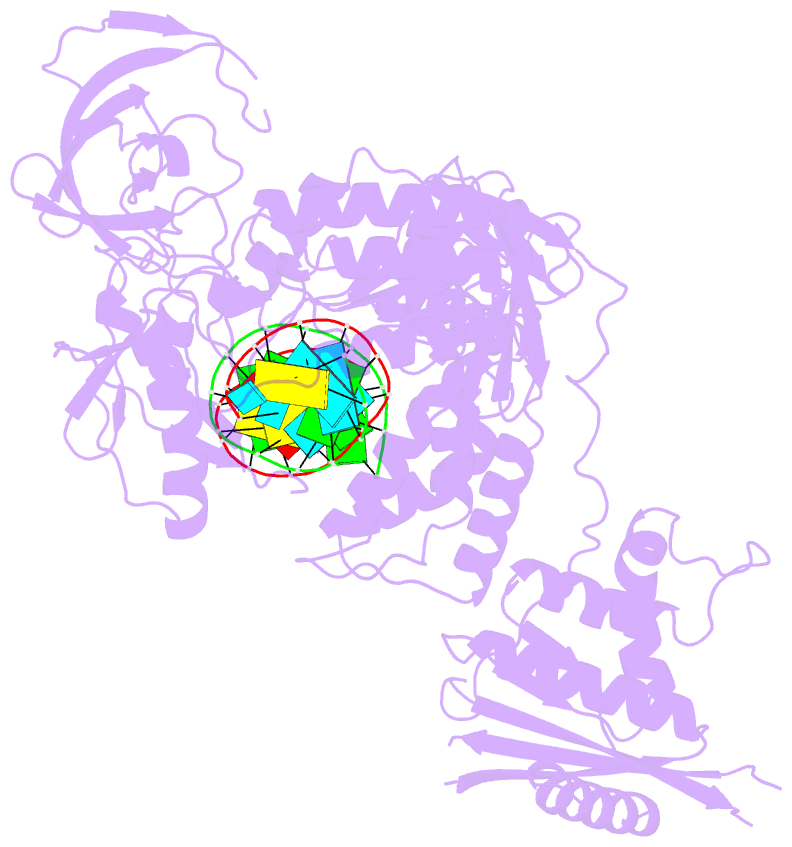
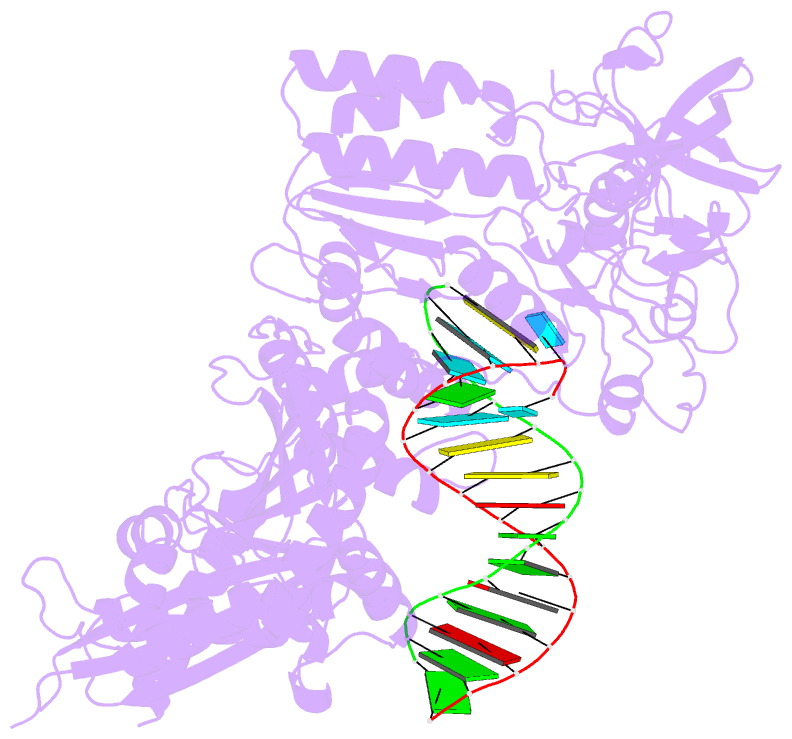
- Structure of the foamy viral protease-reverse transcriptase in complex with RNA-DNA hybrid.
- Reference
- Nowacka M, Nowak E, Czarnocki-Cieciura M, Jackiewicz J, Skowronek K, Szczepanowski RH, Wohrl BM, Nowotny M (2021): "Structures of Substrate Complexes of Foamy Viral Protease-Reverse Transcriptase." J.Virol., 95, e0084821. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00848-21.
- Abstract
- Reverse transcriptases (RTs) use their DNA polymerase and RNase H activities to catalyze the conversion of single-stranded RNA to double-stranded DNA (dsDNA), a crucial process for the replication of retroviruses. Foamy viruses (FVs) possess a unique RT, which is a fusion with the protease (PR) domain. The mechanism of substrate binding by this enzyme has been unknown. Here, we report a crystal structure of monomeric full-length marmoset FV (MFV) PR-RT in complex with an RNA/DNA hybrid substrate. We also describe a structure of MFV PR-RT with an RNase H deletion in complex with a dsDNA substrate in which the enzyme forms an asymmetric homodimer. Cryo-electron microscopy reconstruction of the full-length MFV PR-RT-dsDNA complex confirmed the dimeric architecture. These findings represent the first structural description of nucleic acid binding by a foamy viral RT and demonstrate its ability to change its oligomeric state depending on the type of bound nucleic acid.