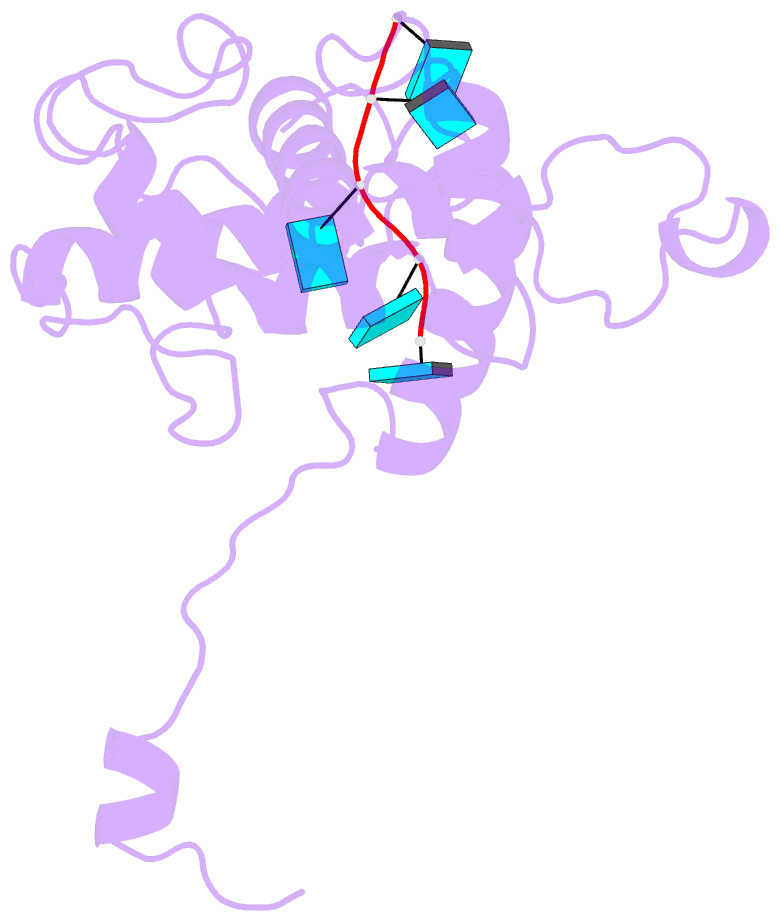
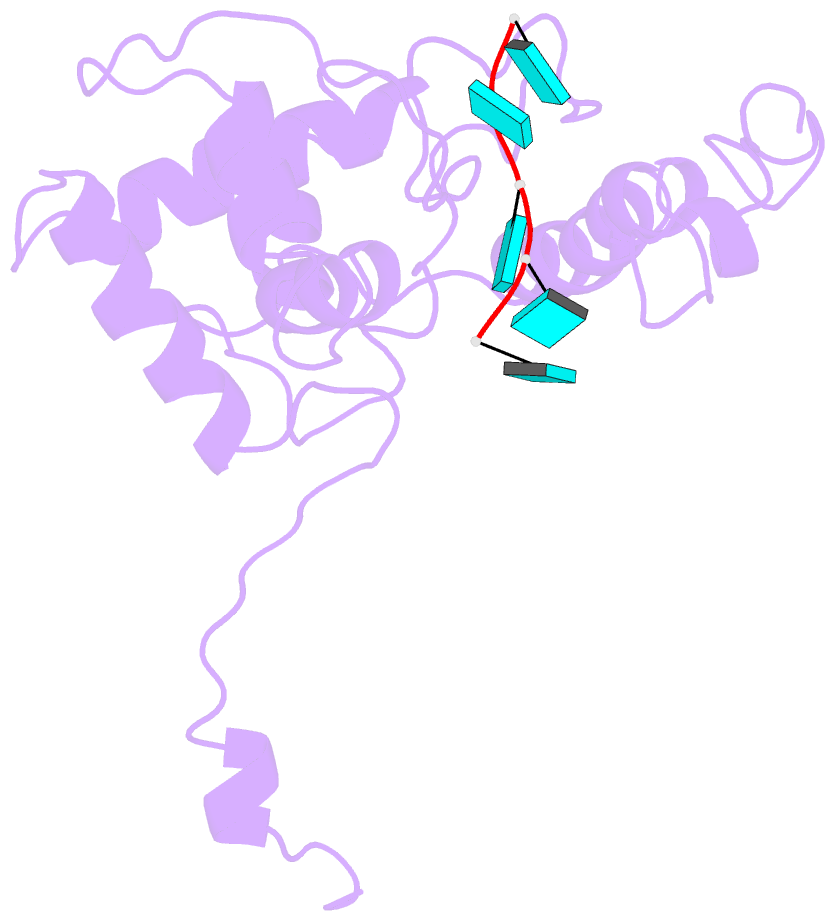
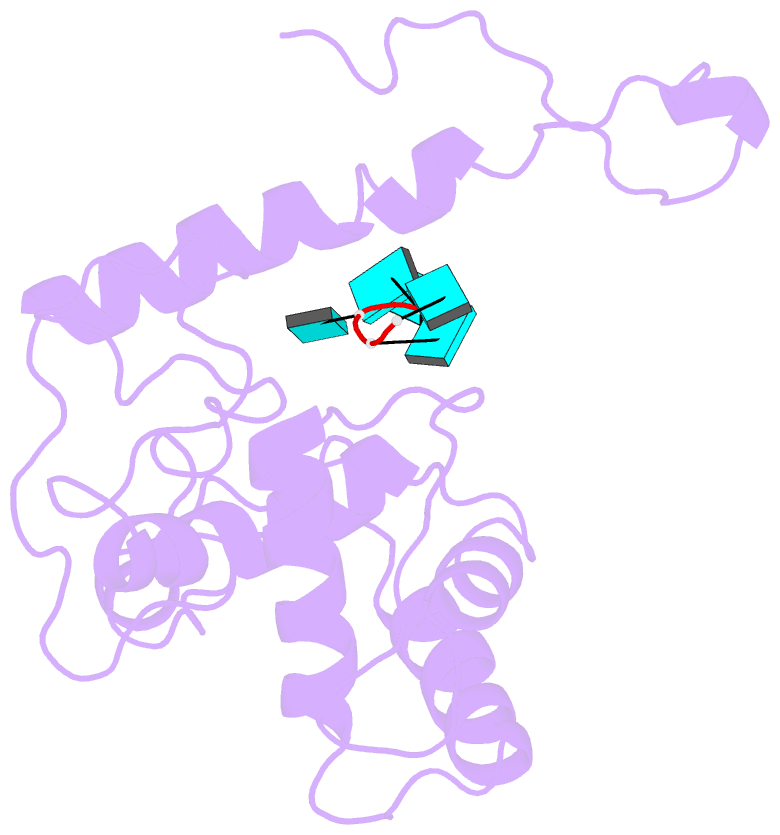
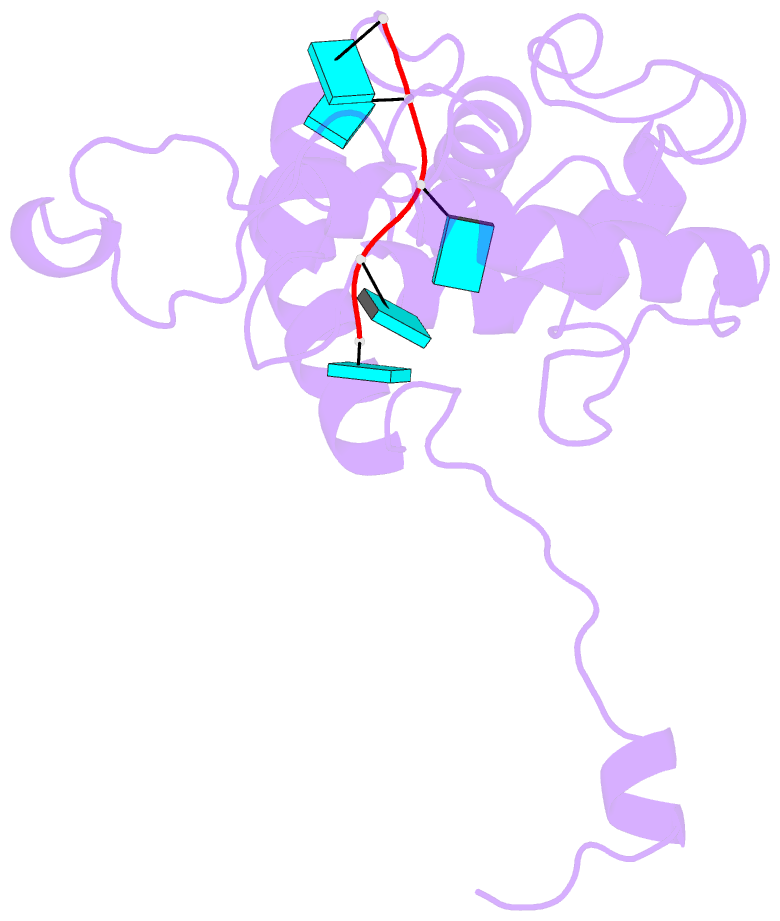
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7og6; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- virus like particle
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.3 Å)
- Summary
- Structure of alternanthera mosaic vlp by cryoem
- Reference
- Thuenemann EC, Byrne MJ, Peyret H, Saunders K, Castells-Graells R, Ferriol I, Santoni M, Steele JFC, Ranson NA, Avesani L, Lopez-Moya JJ, Lomonossoff GP (2021): "A Replicating Viral Vector Greatly Enhances Accumulation of Helical Virus-Like Particles in Plants." Viruses, 13. doi: 10.3390/v13050885.
- Abstract
- The production of plant helical virus-like particles (VLPs) via plant-based expression has been problematic with previous studies suggesting that an RNA scaffold may be necessary for their efficient production. To examine this, we compared the accumulation of VLPs from two potexviruses, papaya mosaic virus and alternanthera mosaic virus (AltMV), when the coat proteins were expressed from a replicating potato virus X- based vector (pEff) and a non-replicating vector (pEAQ-HT). Significantly greater quantities of VLPs could be purified when pEff was used. The pEff system was also very efficient at producing VLPs of helical viruses from different virus families. Examination of the RNA content of AltMV and tobacco mosaic virus VLPs produced from pEff revealed the presence of vector-derived RNA sequences, suggesting that the replicating RNA acts as a scaffold for VLP assembly. Cryo-EM analysis of the AltMV VLPs showed they had a structure very similar to that of authentic potexvirus particles. Thus, we conclude that vectors generating replicating forms of RNA, such as pEff, are very efficient for producing helical VLPs.