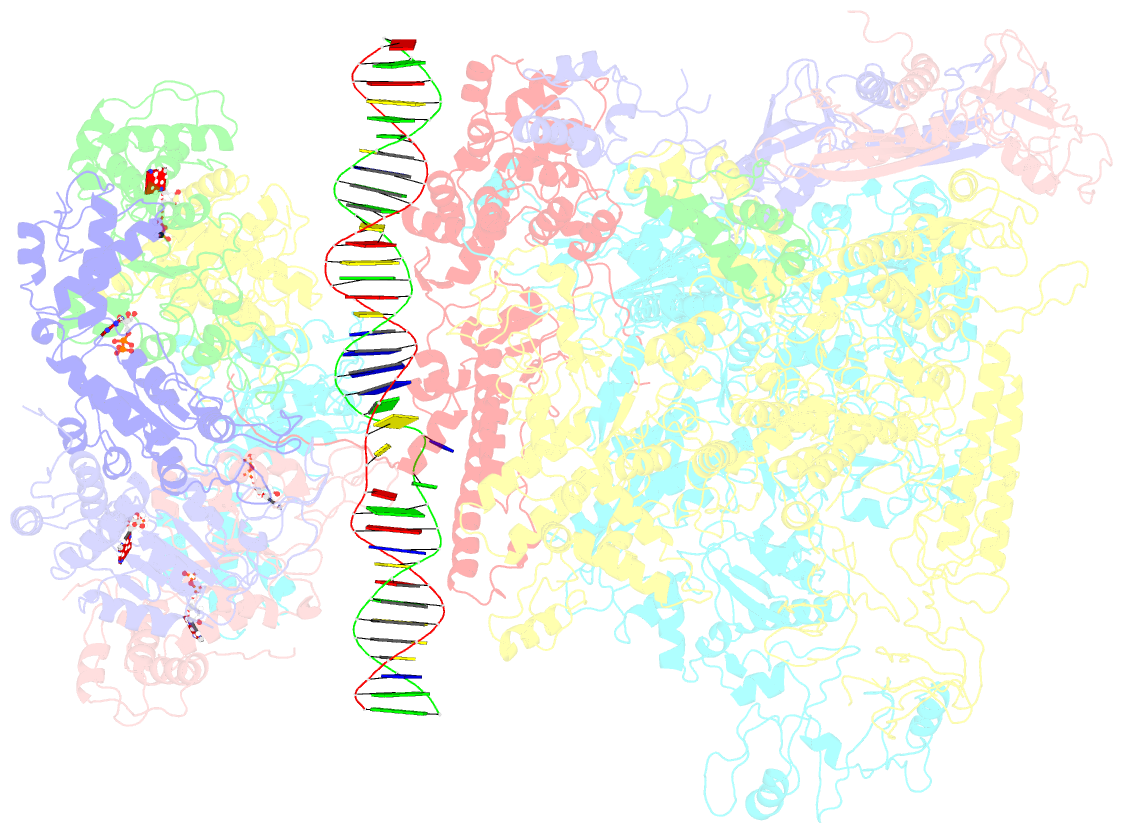
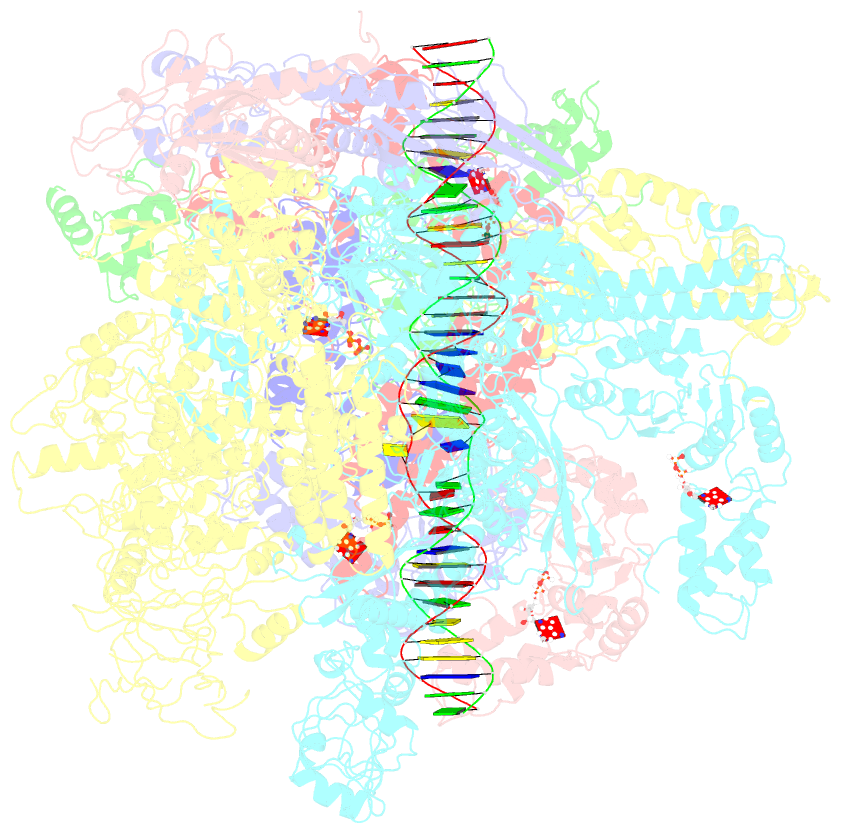
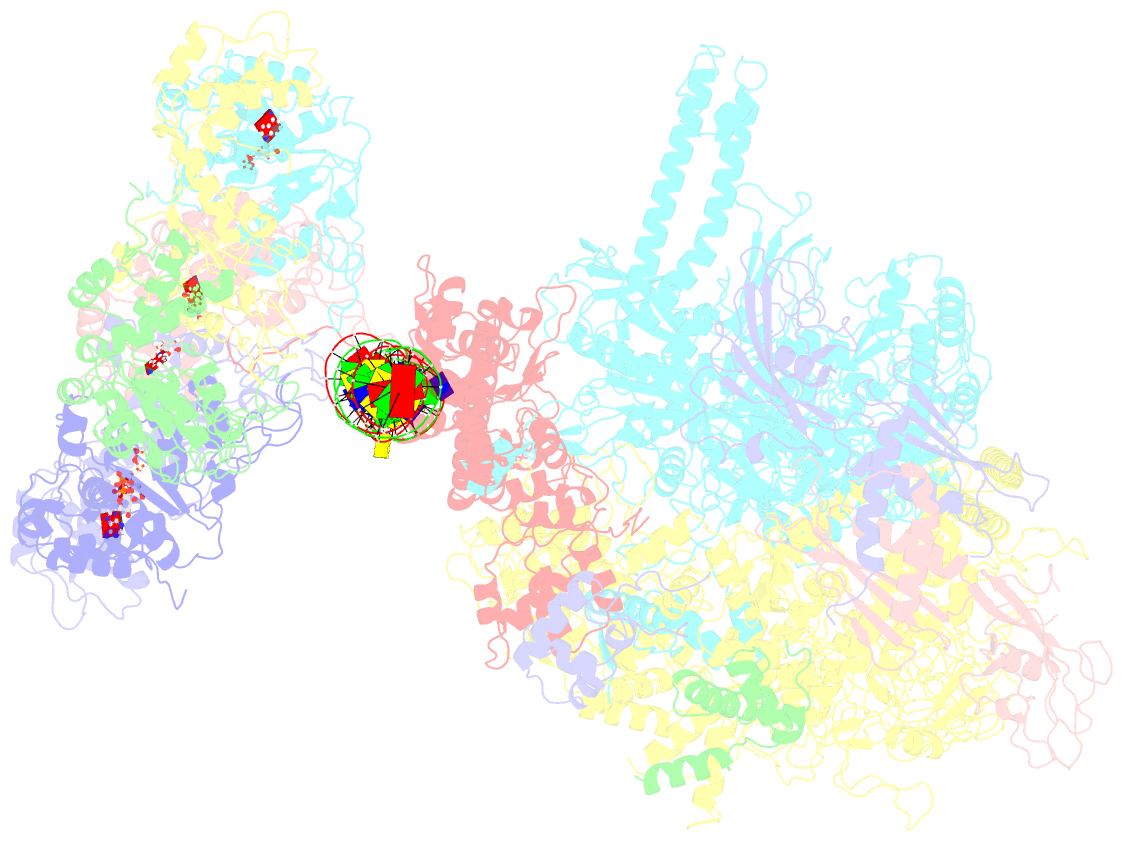
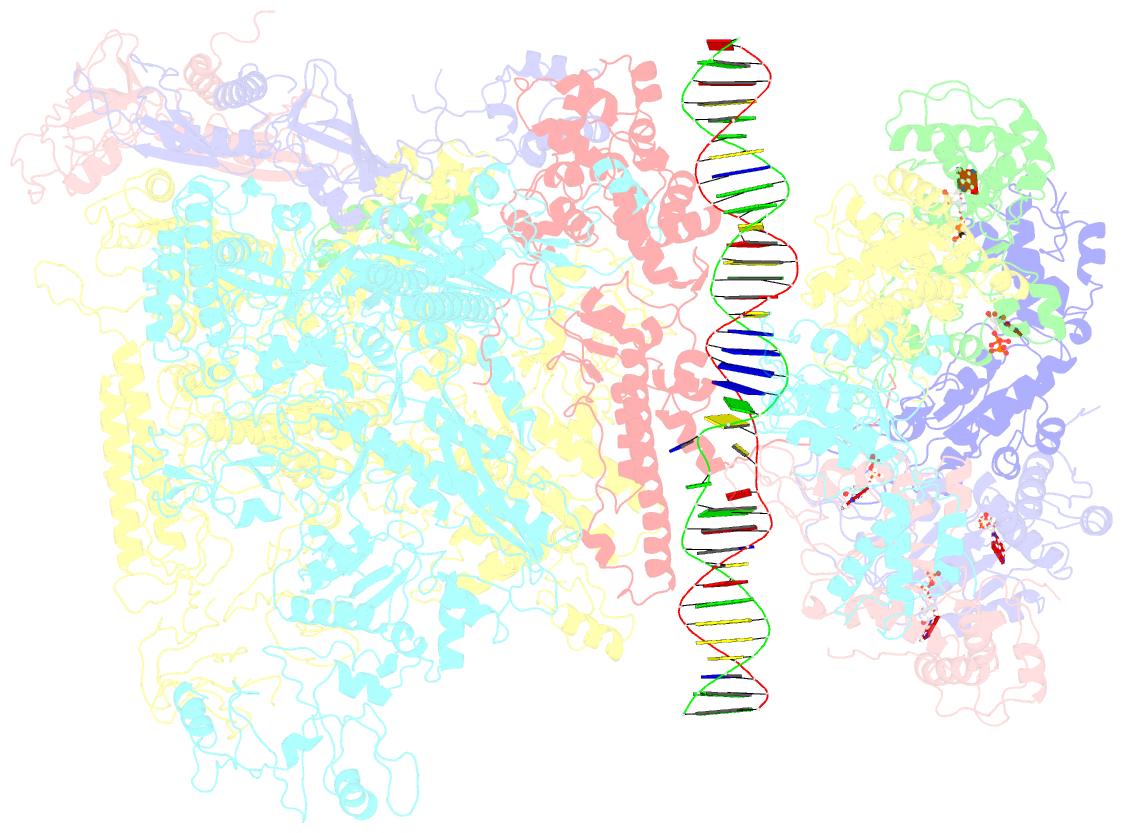
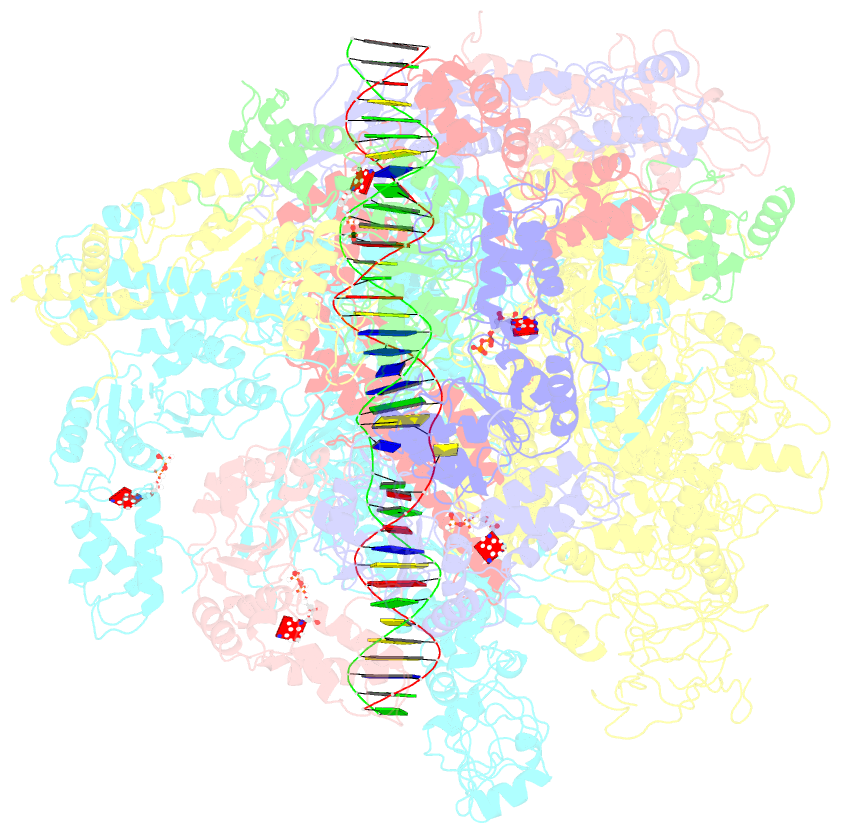
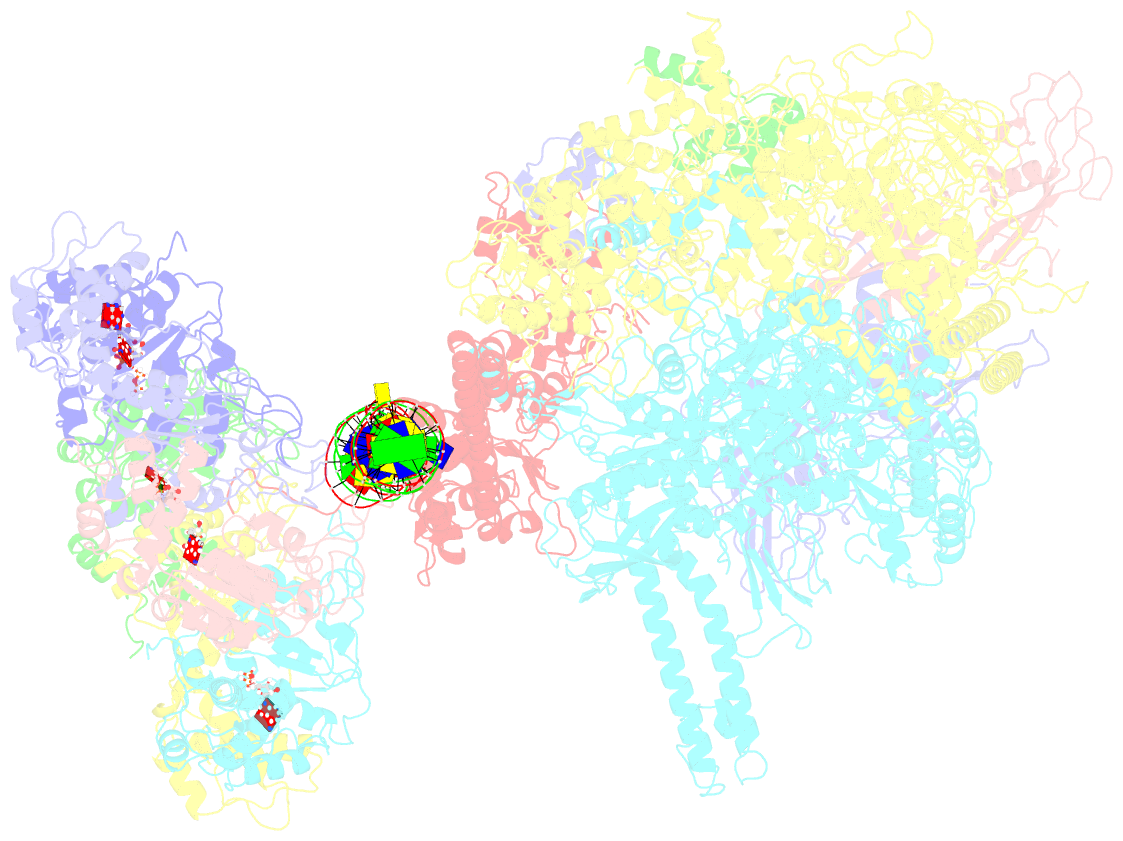
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7qv9; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.5 Å)
- Summary
- Cryoem structure of bacterial transcription intermediate complex mediated by activator pspf
- Reference
- Ye F, Gao F, Liu X, Buck M, Zhang X (2022): "Mechanisms of DNA opening revealed in AAA+ transcription complex structures." Sci Adv, 8, eadd3479. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add3479.
- Abstract
- Gene transcription is carried out by RNA polymerase (RNAP) and requires the conversion of the initial closed promoter complex, where DNA is double stranded, to a transcription-competent open promoter complex, where DNA is opened up. In bacteria, RNAP relies on σ factors for its promoter specificities. Using a special form of sigma factor (σ54), which forms a stable closed complex and requires its activator that belongs to the AAA+ ATPases (ATPases associated with diverse cellular activities), we obtained cryo-electron microscopy structures of transcription initiation complexes that reveal a previously unidentified process of DNA melting opening. The σ54 amino terminus threads through the locally opened up DNA and then becomes enclosed by the AAA+ hexameric ring in the activator-bound intermediate complex. Our structures suggest how ATP hydrolysis by the AAA+ activator could remove the σ54 inhibition while helping to open up DNA, using σ54 amino-terminal peptide as a pry bar.