Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7r0e; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.51 Å)
- Summary
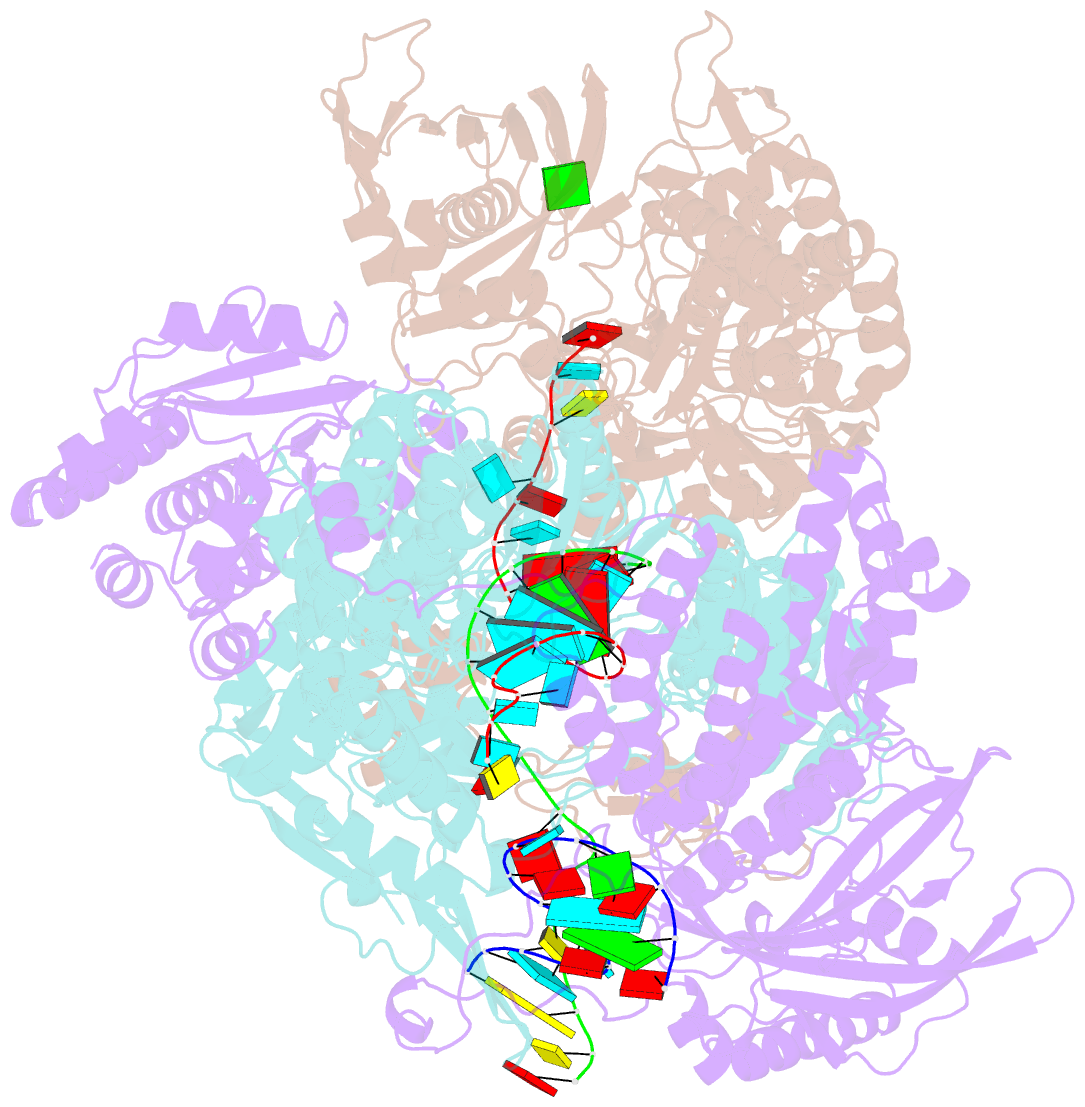
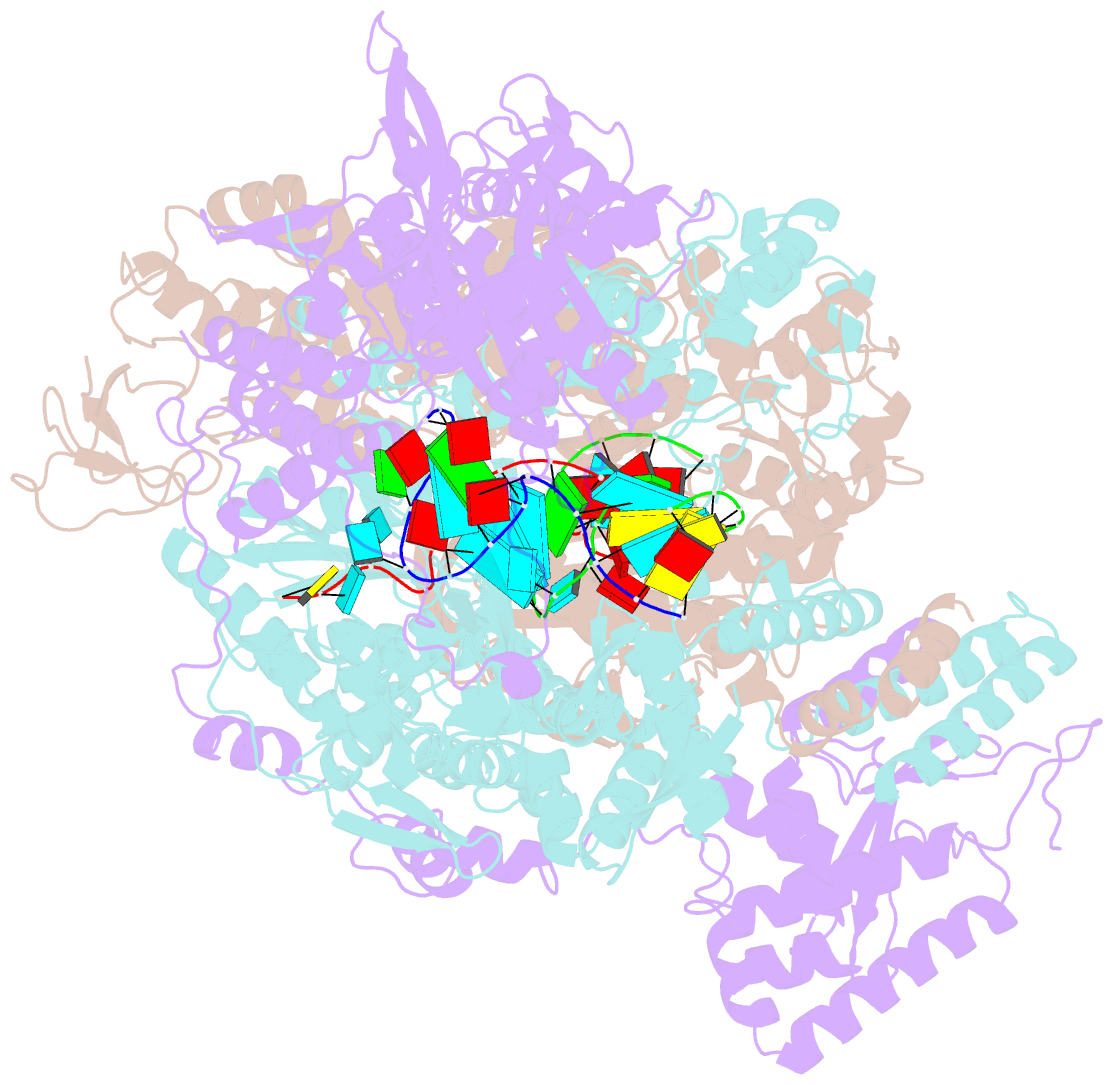
- Early transcription elongation state of influenza a-h7n9 polymerase backtracked due to double incoproation of nucleotide analogue t1106 and with singly incoporated t1106 at the +1 position
- Reference
- Kouba T, Dubankova A, Drncova P, Donati E, Vidossich P, Speranzini V, Pflug A, Huchting J, Meier C, De Vivo M, Cusack S (2023): "Direct observation of backtracking by influenza A and B polymerases upon consecutive incorporation of the nucleoside analog T1106." Cell Rep, 42, 111901. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111901.
- Abstract
- The antiviral pseudo-base T705 and its de-fluoro analog T1106 mimic adenine or guanine and can be competitively incorporated into nascent RNA by viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Although dispersed, single pseudo-base incorporation is mutagenic, consecutive incorporation causes polymerase stalling and chain termination. Using a template encoding single and then consecutive T1106 incorporation four nucleotides later, we obtained a cryogenic electron microscopy structure of stalled influenza A/H7N9 polymerase. This shows that the entire product-template duplex backtracks by 5 nt, bringing the singly incorporated T1106 to the +1 position, where it forms an unexpected T1106:U wobble base pair. Similar structures show that influenza B polymerase also backtracks after consecutive T1106 incorporation, regardless of whether prior single incorporation has occurred. These results give insight into the unusual mechanism of chain termination by pyrazinecarboxamide base analogs. Consecutive incorporation destabilizes the proximal end of the product-template duplex, promoting irreversible backtracking to a more energetically favorable overall configuration.