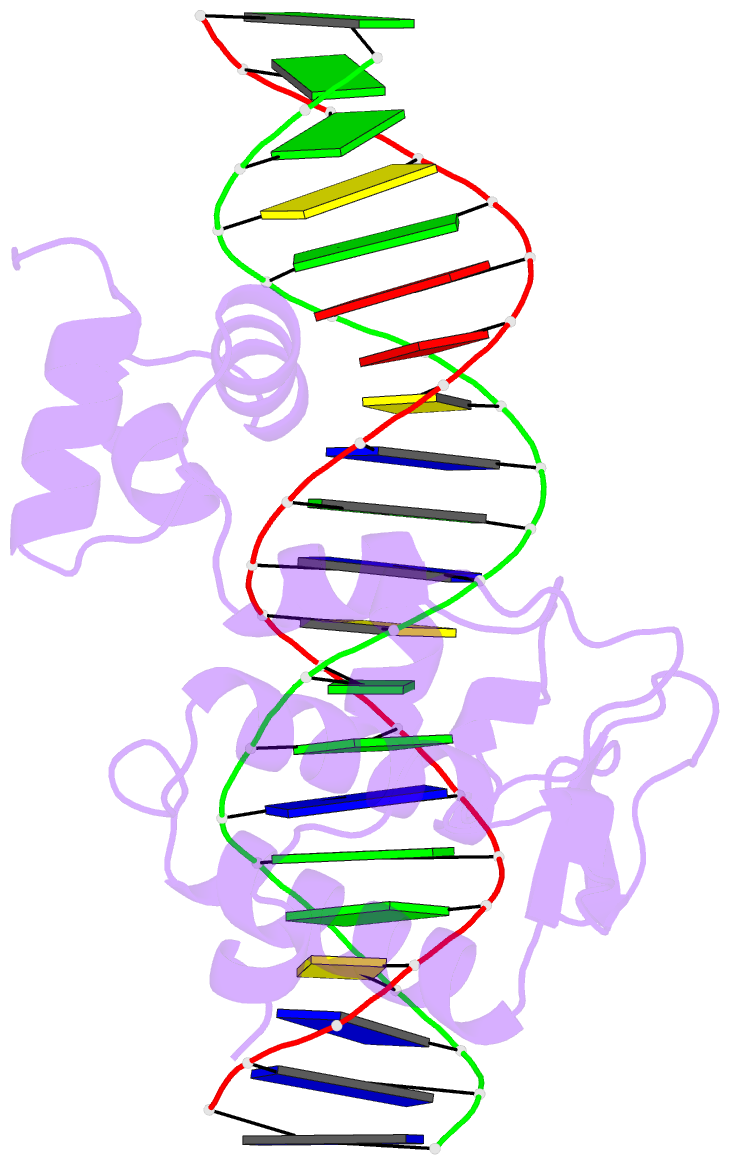
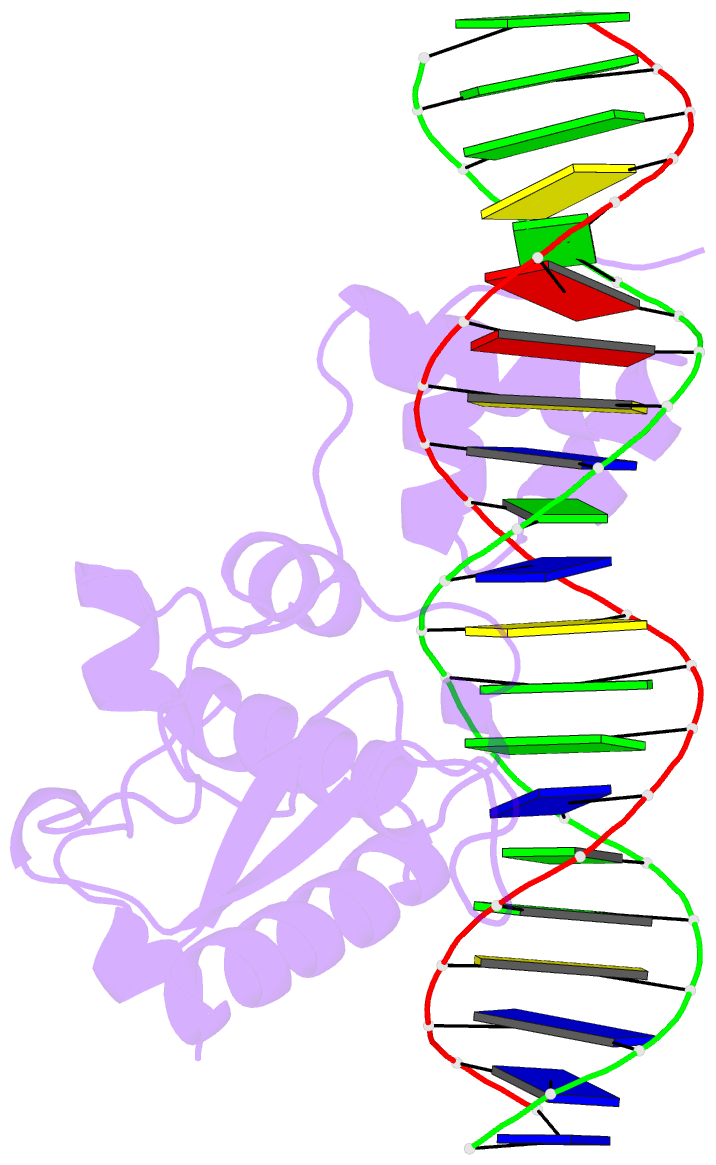
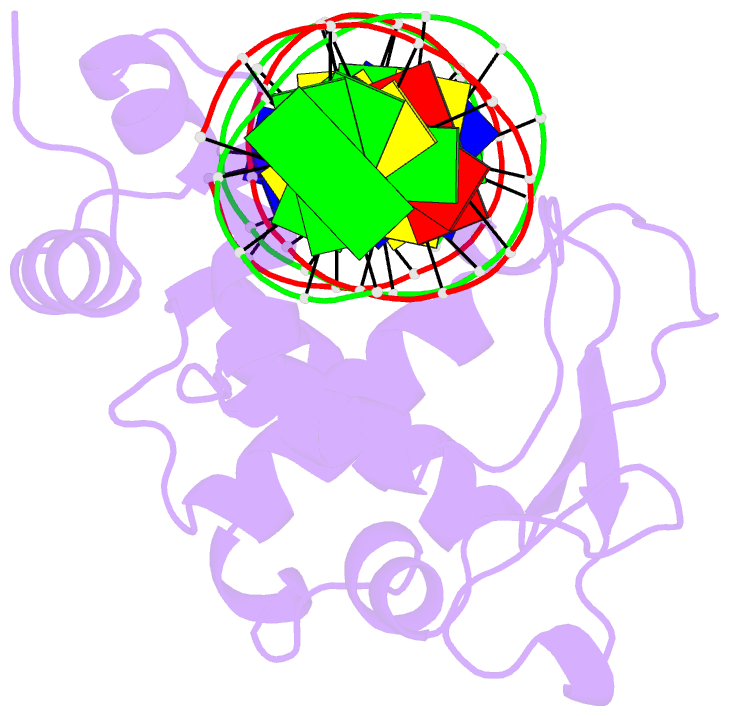
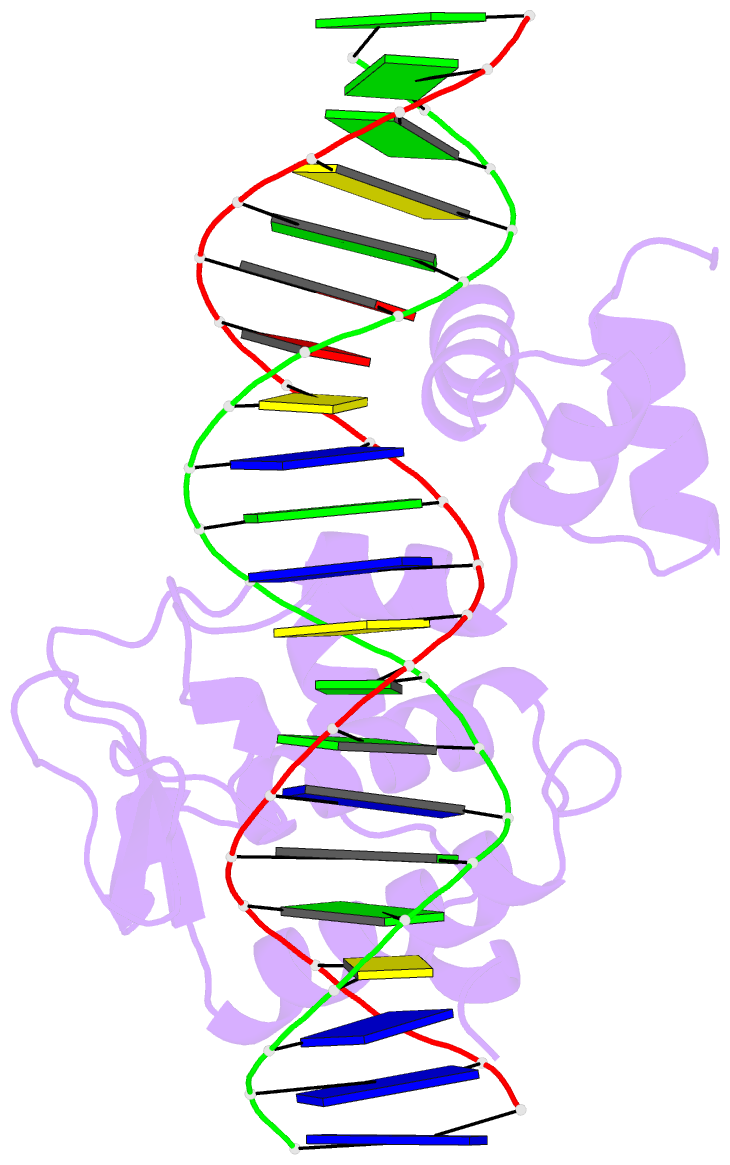
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7r6r; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (3.13 Å)
- Summary
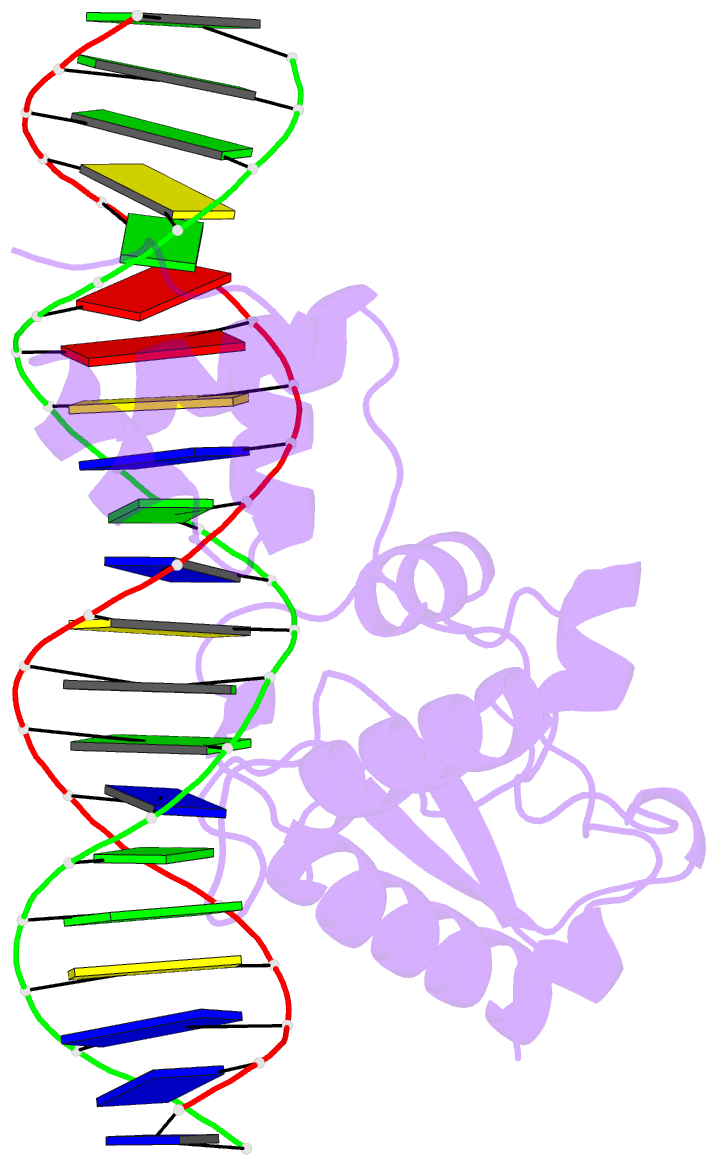
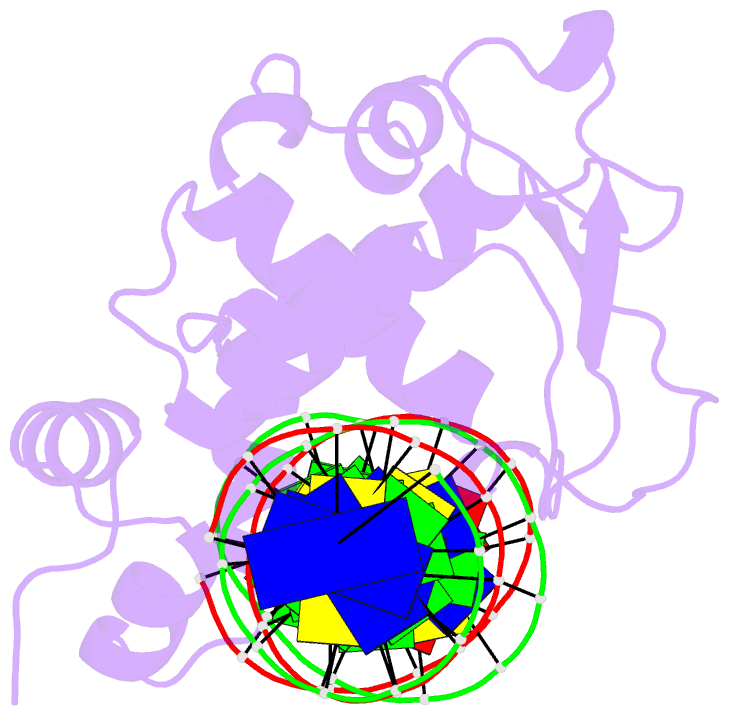
- Crystal structure of a mycobacteriophage cluster a2 immunity repressor:DNA complex
- Reference
- McGinnis RJ, Brambley CA, Stamey B, Green WC, Gragg KN, Cafferty ER, Terwilliger TC, Hammel M, Hollis TJ, Miller JM, Gainey MD, Wallen JR (2022): "A monomeric mycobacteriophage immunity repressor utilizes two domains to recognize an asymmetric DNA sequence." Nat Commun, 13, 4105. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-31678-6.
- Abstract
- Regulation of bacteriophage gene expression involves repressor proteins that bind and downregulate early lytic promoters. A large group of mycobacteriophages code for repressors that are unusual in also terminating transcription elongation at numerous binding sites (stoperators) distributed across the phage genome. Here we provide the X-ray crystal structure of a mycobacteriophage immunity repressor bound to DNA, which reveals the binding of a monomer to an asymmetric DNA sequence using two independent DNA binding domains. The structure is supported by small-angle X-ray scattering, DNA binding, molecular dynamics, and in vivo immunity assays. We propose a model for how dual DNA binding domains facilitate regulation of both transcription initiation and elongation, while enabling evolution of other superinfection immune specificities.