Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7rsu; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.1 Å)
- Summary
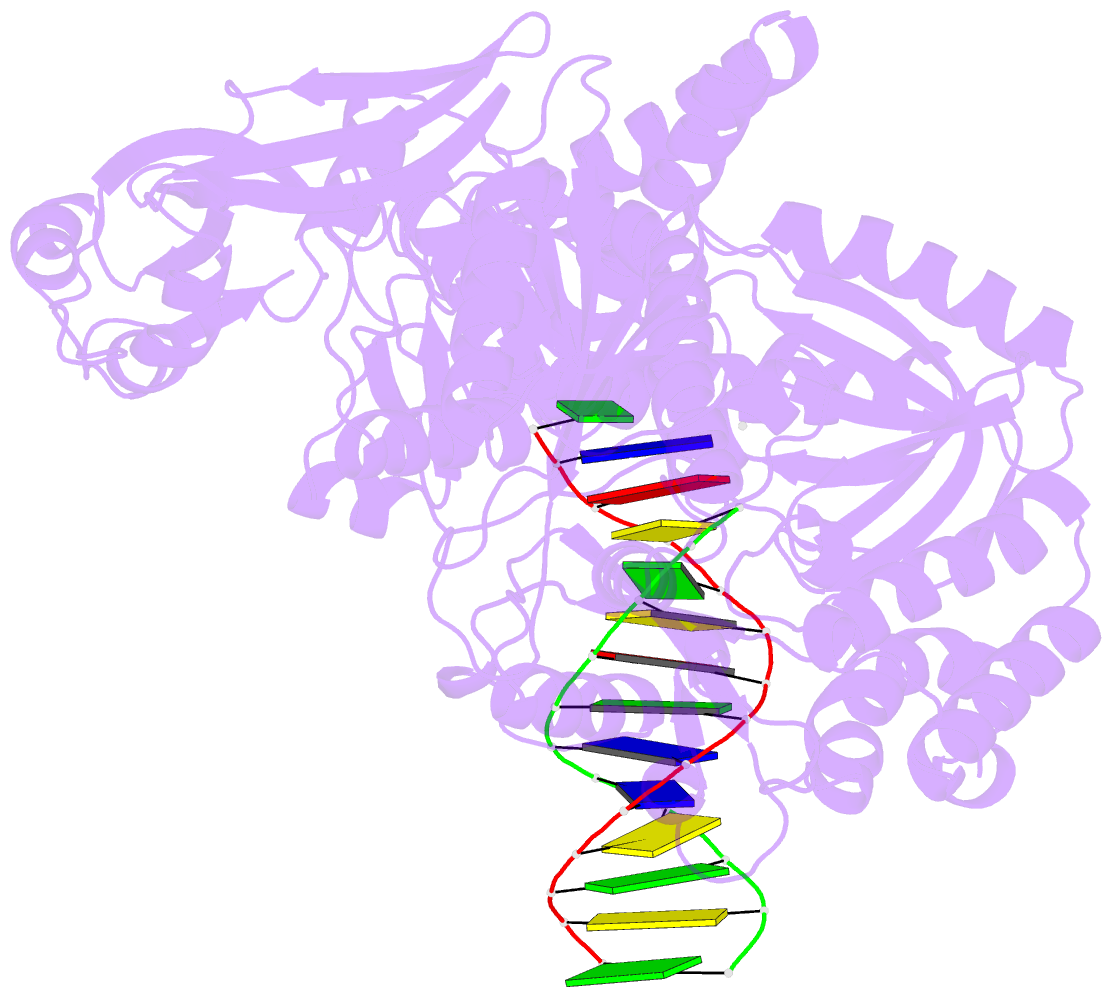
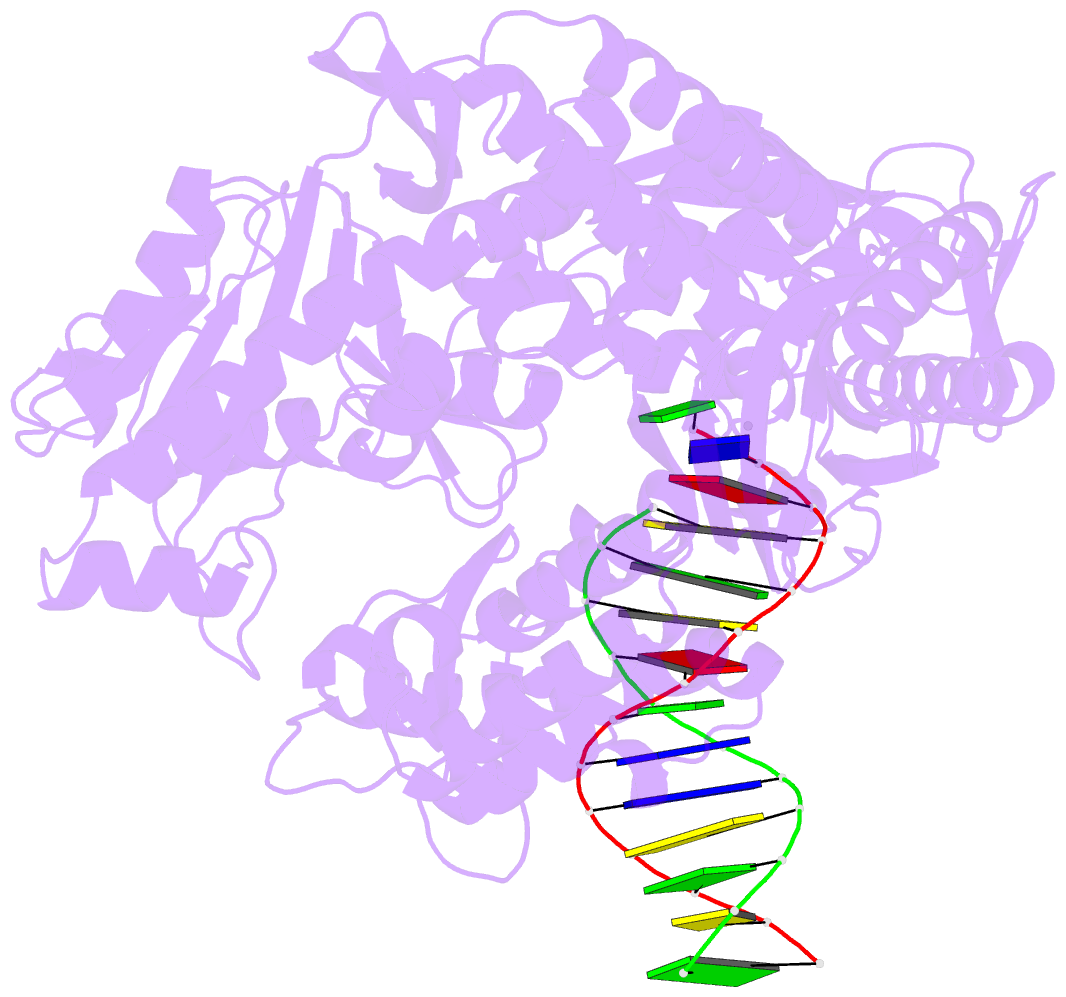
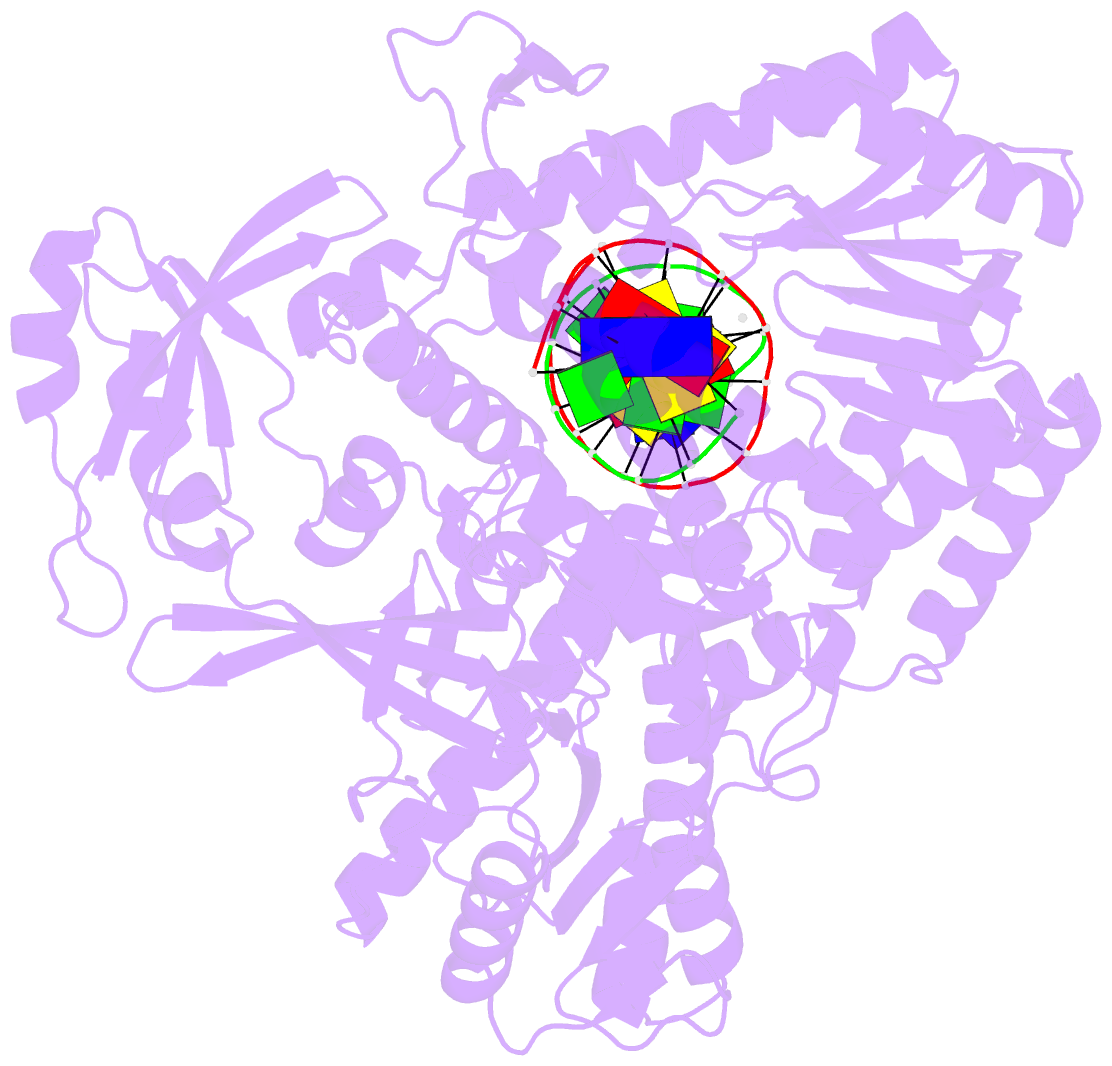
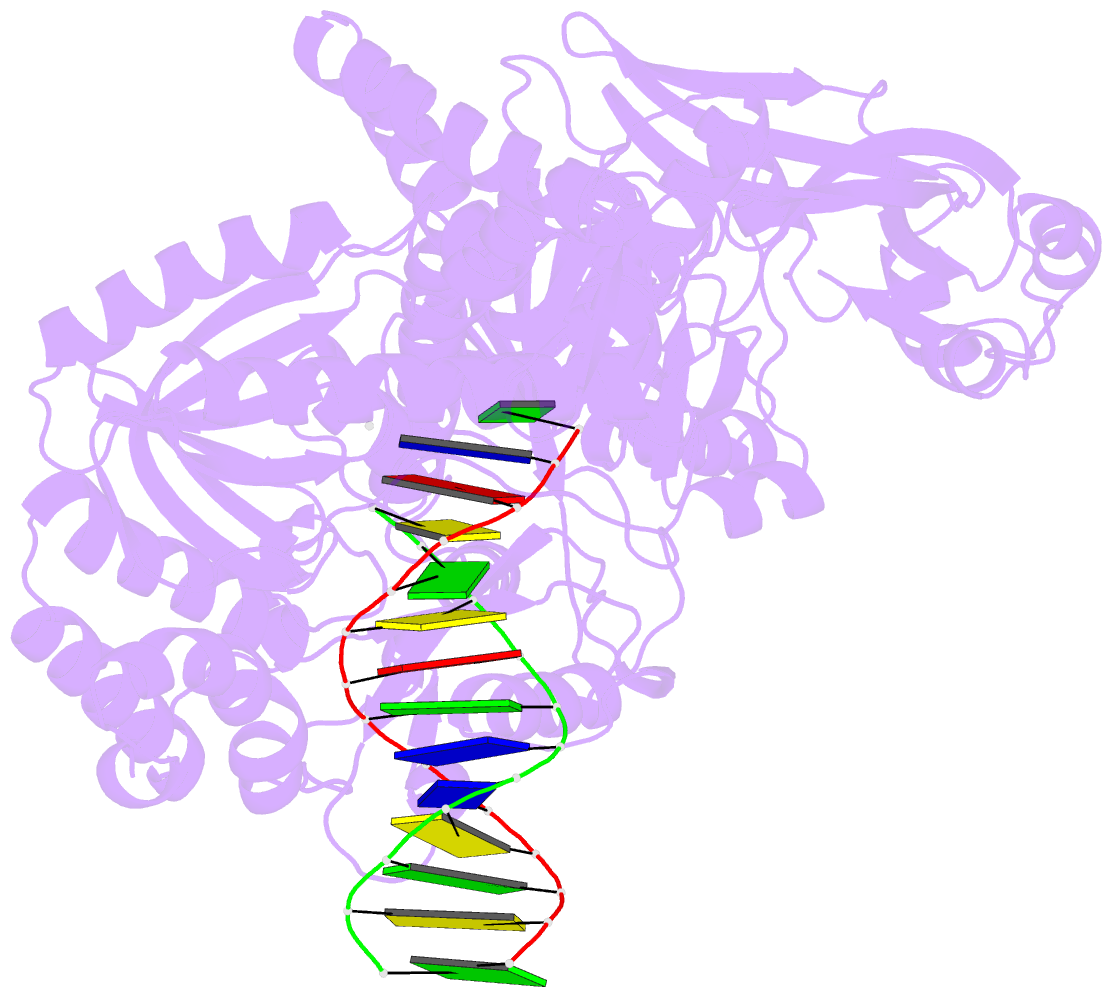
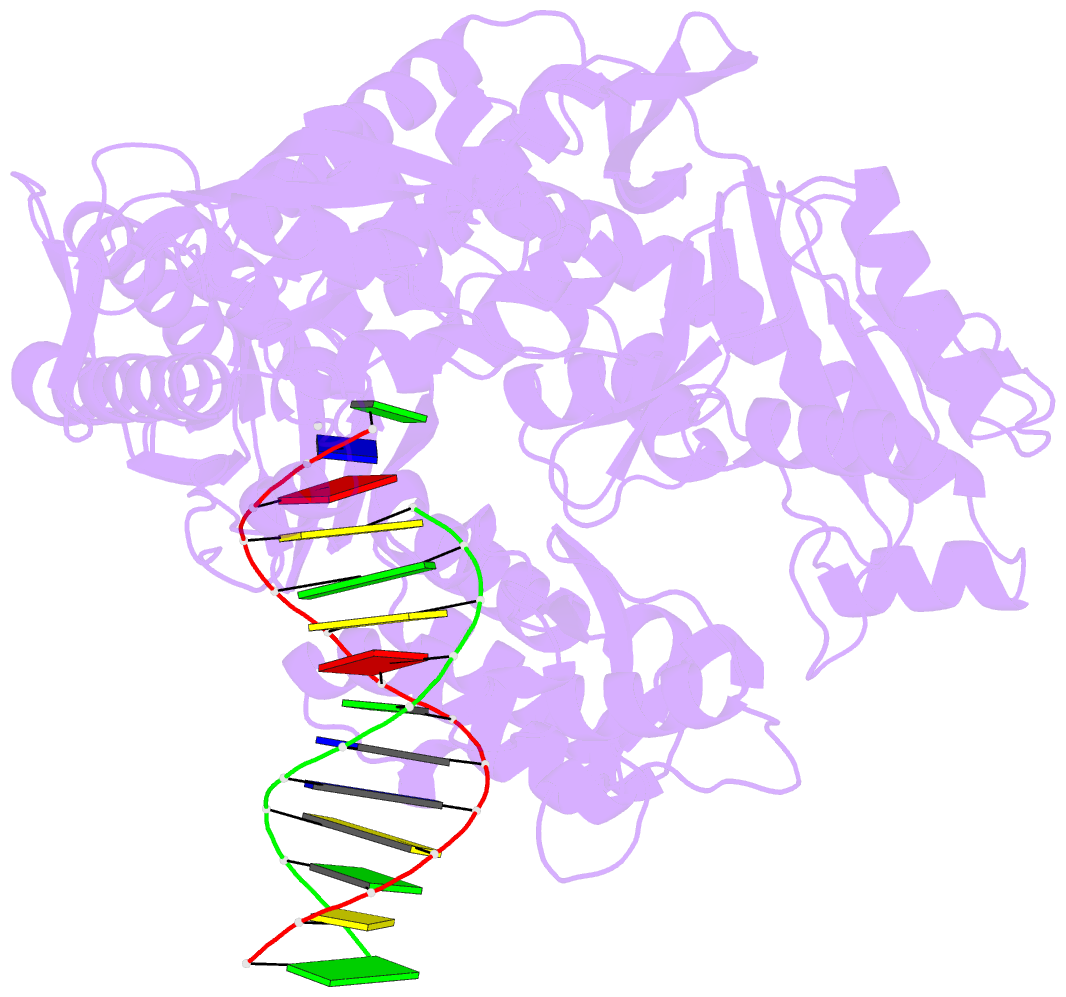
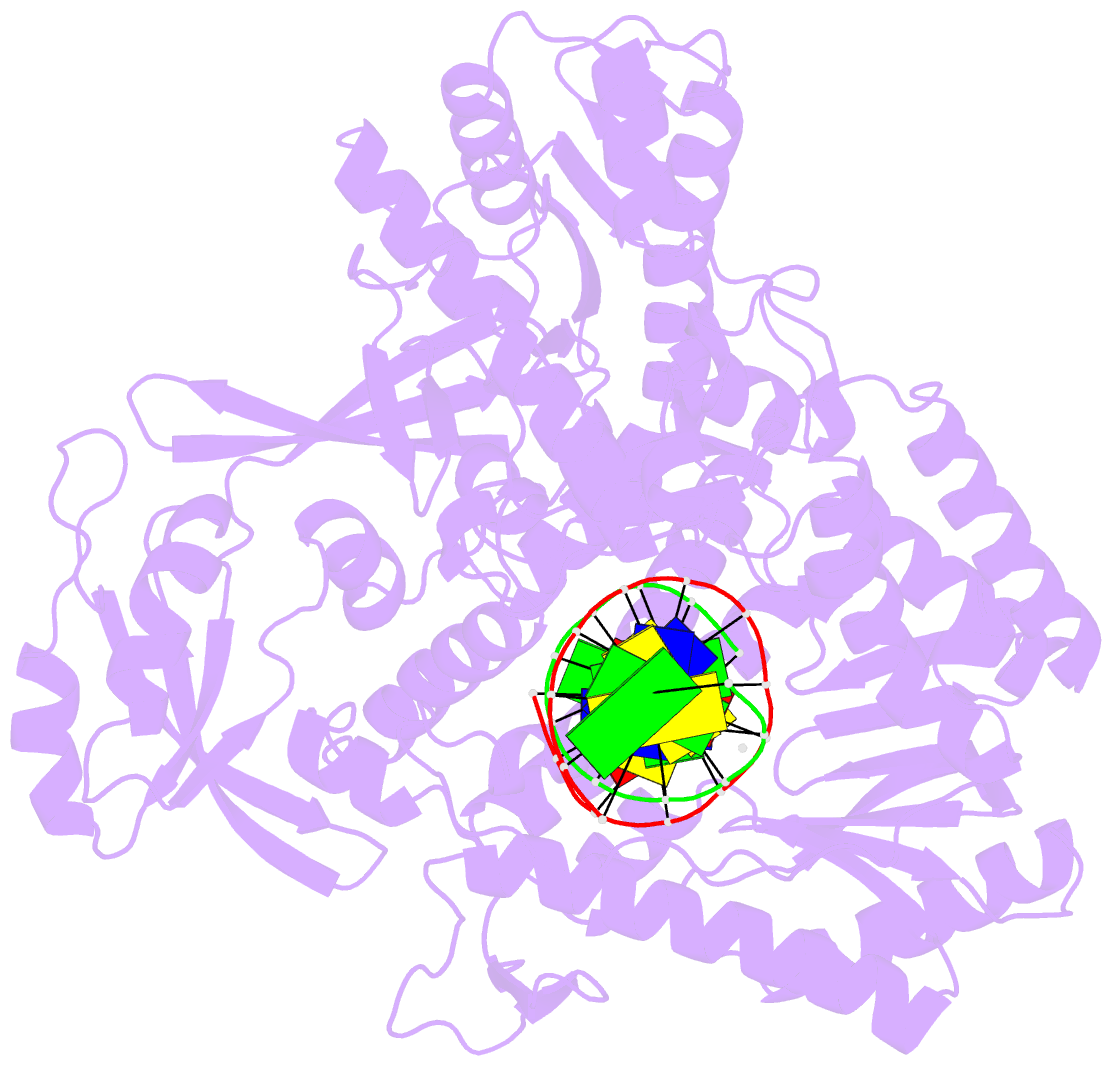
- Tna polymerase, n+2 product
- Reference
- Li Q, Maola VA, Chim N, Hussain J, Lozoya-Colinas A, Chaput JC (2021): "Synthesis and Polymerase Recognition of Threose Nucleic Acid Triphosphates Equipped with Diverse Chemical Functionalities." J.Am.Chem.Soc., 143, 17761-17768. doi: 10.1021/jacs.1c08649.
- Abstract
- Expanding the chemical space of evolvable non-natural genetic polymers (XNAs) to include functional groups that enhance protein target binding affinity offers a promising route to therapeutic aptamers with high biological stability. Here we describe the chemical synthesis and polymerase recognition of 10 chemically diverse functional groups introduced at the C-5 position of α-l-threofuranosyl uridine nucleoside triphosphate (tUTP). We show that the set of tUTP substrates is universally recognized by the laboratory-evolved polymerase Kod-RSGA. Insights into the mechanism of TNA synthesis were obtained from a high-resolution X-ray crystal structure of the postcatalytic complex bound to the primer-template duplex. A structural analysis reveals a large cavity in the enzyme active site that can accommodate the side chain of C-5-modified tUTP substrates. Our findings expand the chemical space of evolvable nucleic acid systems by providing a synthetic route to artificial genetic polymers that are uniformly modified with diversity-enhancing functional groups.