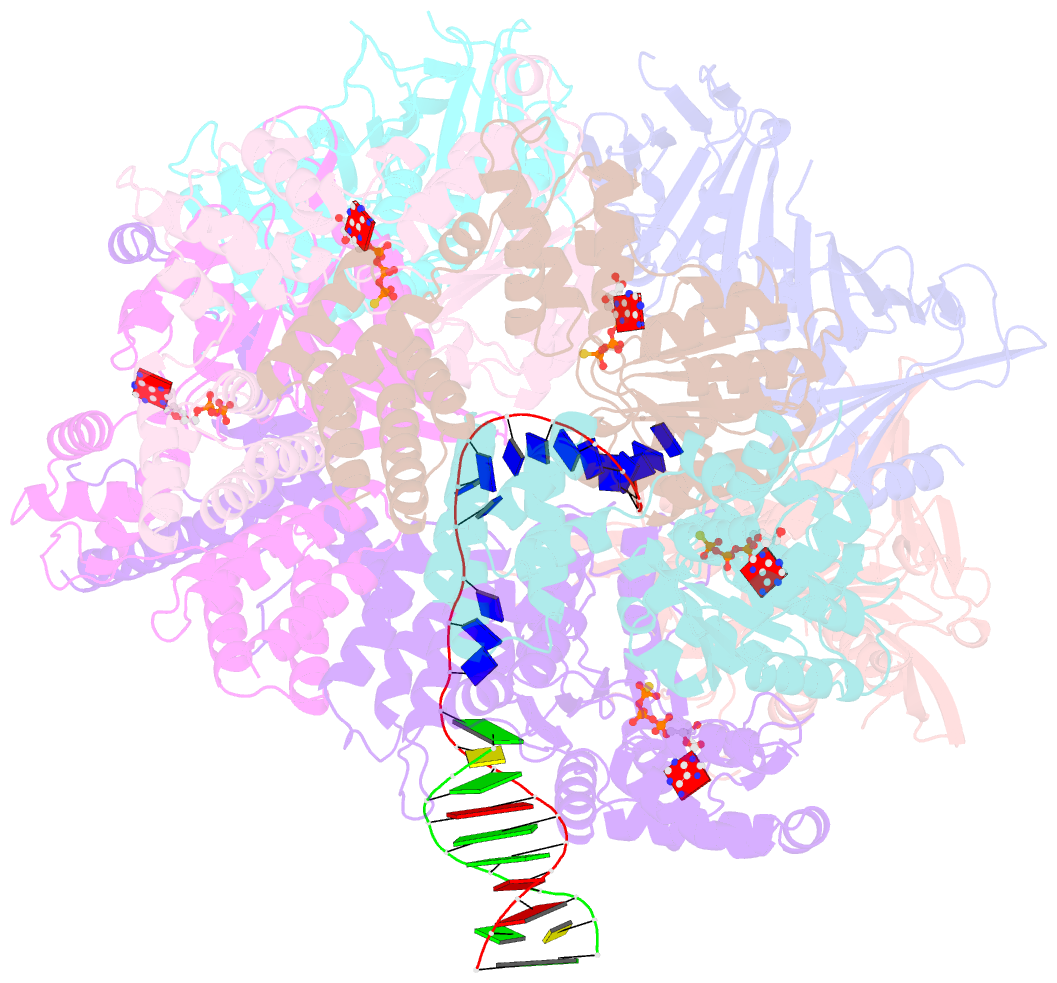
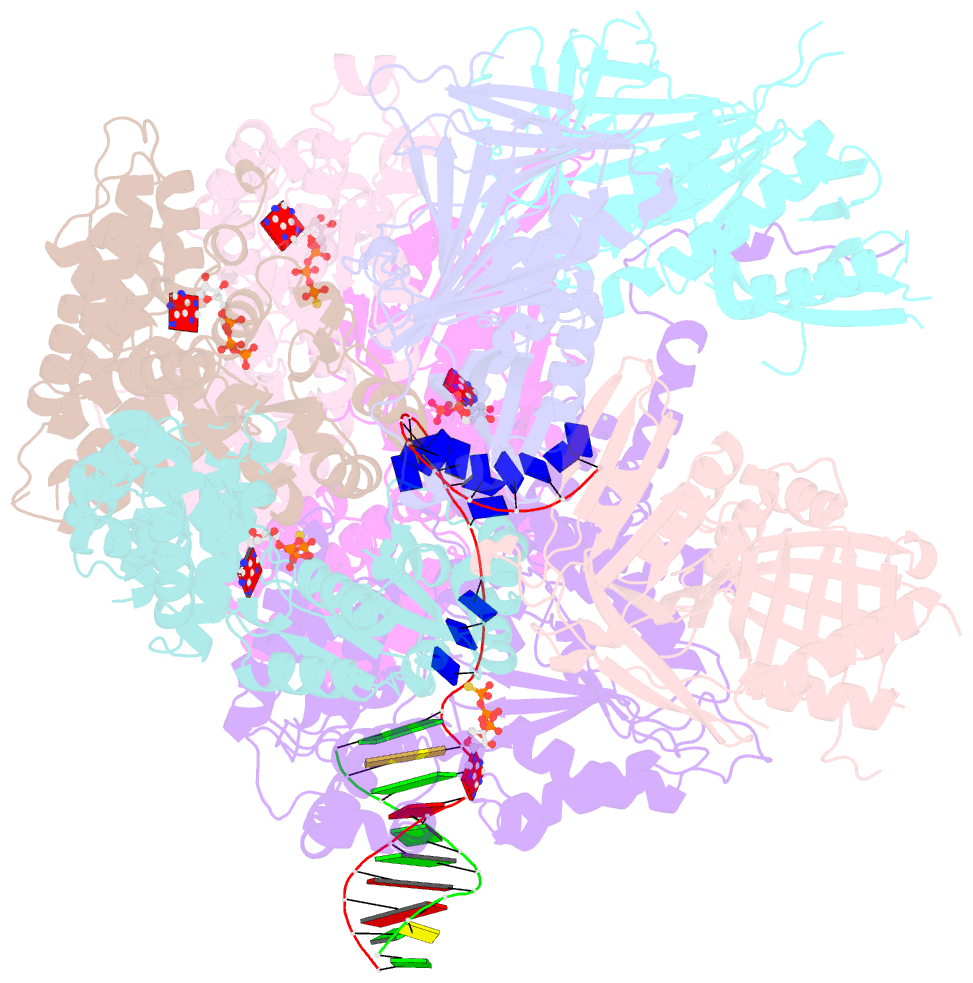
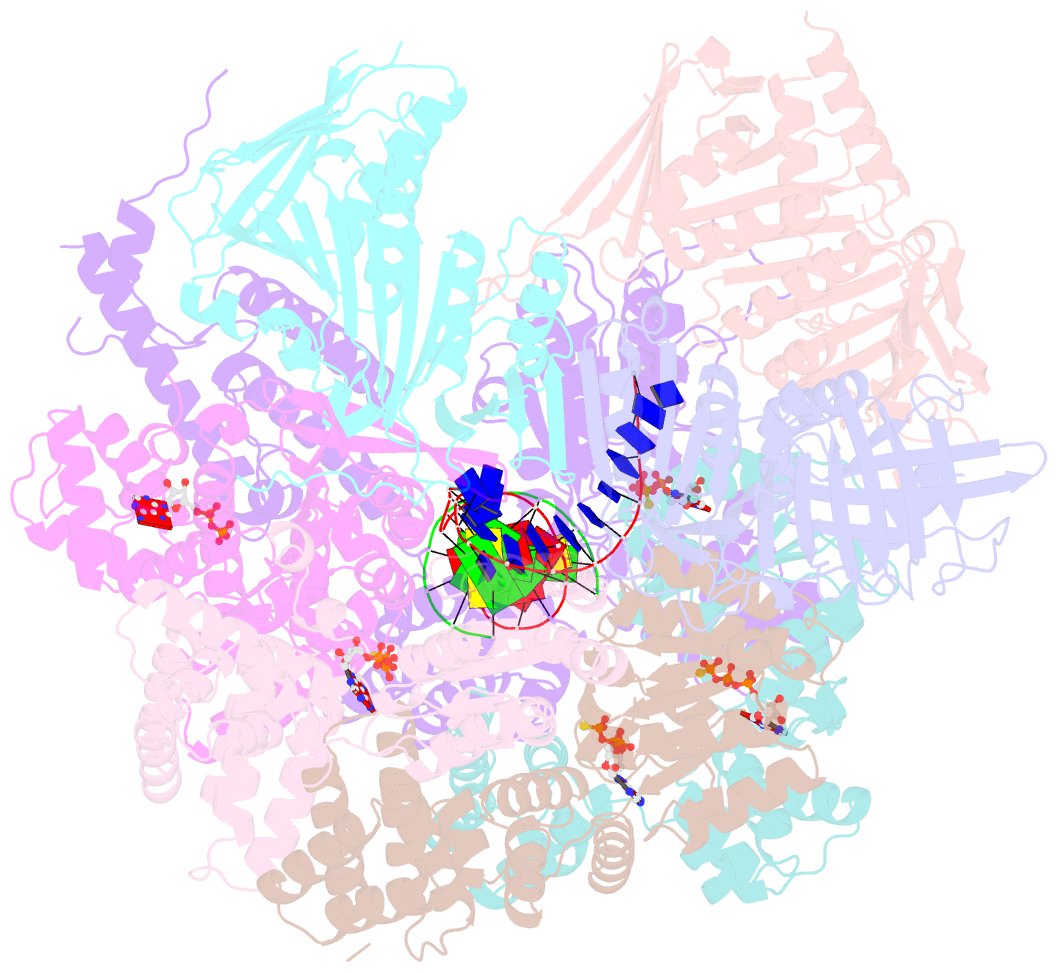
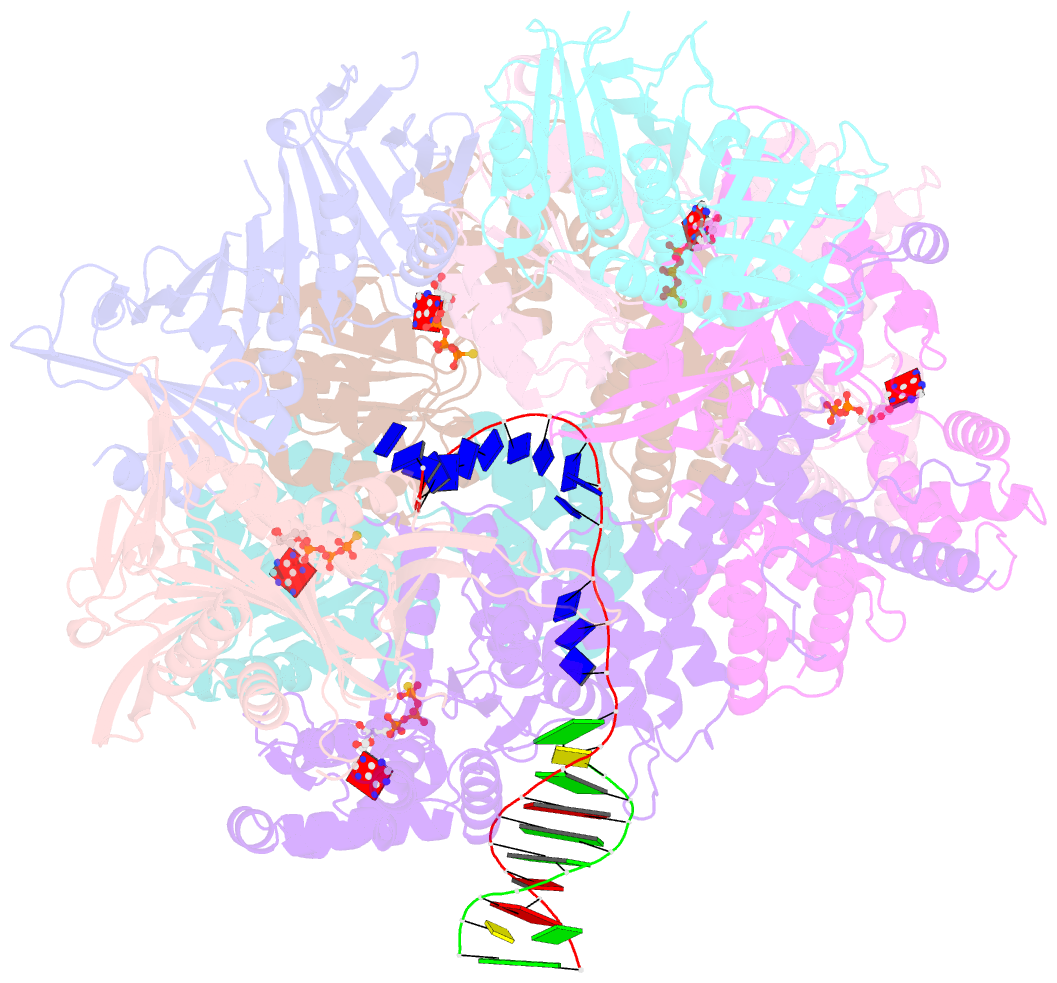
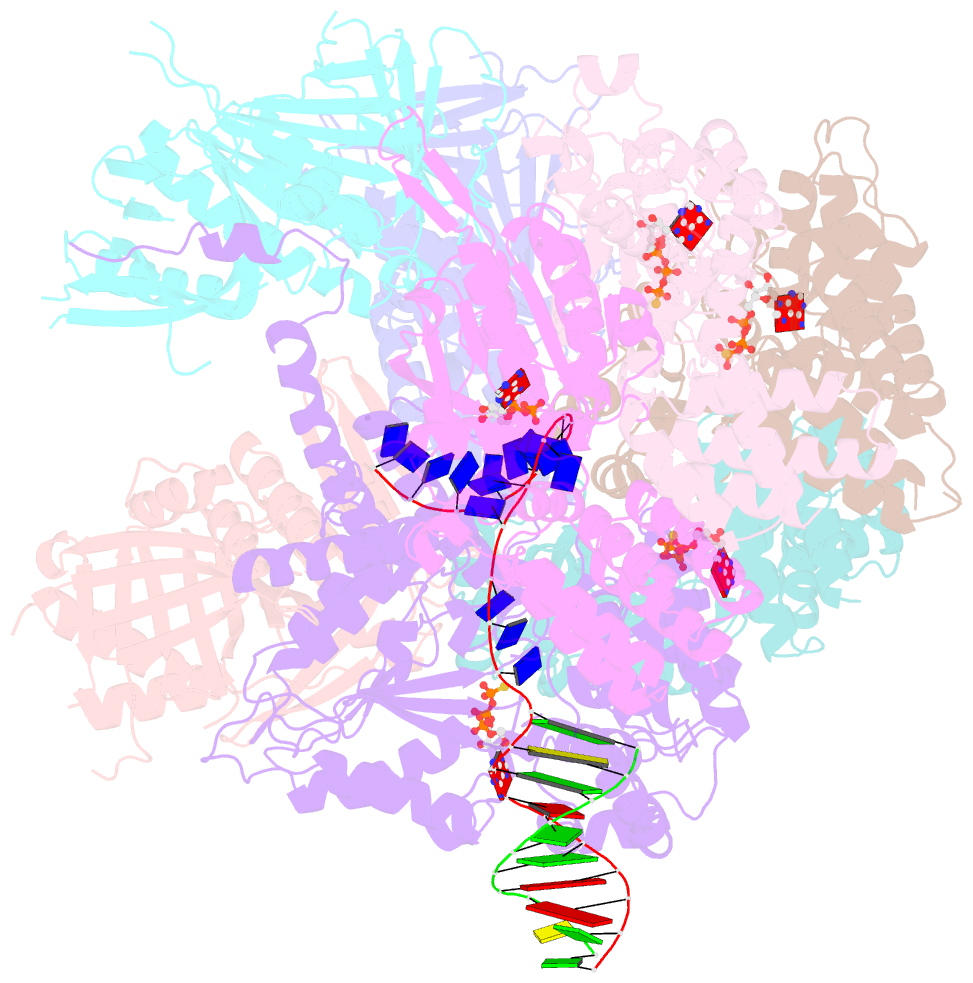
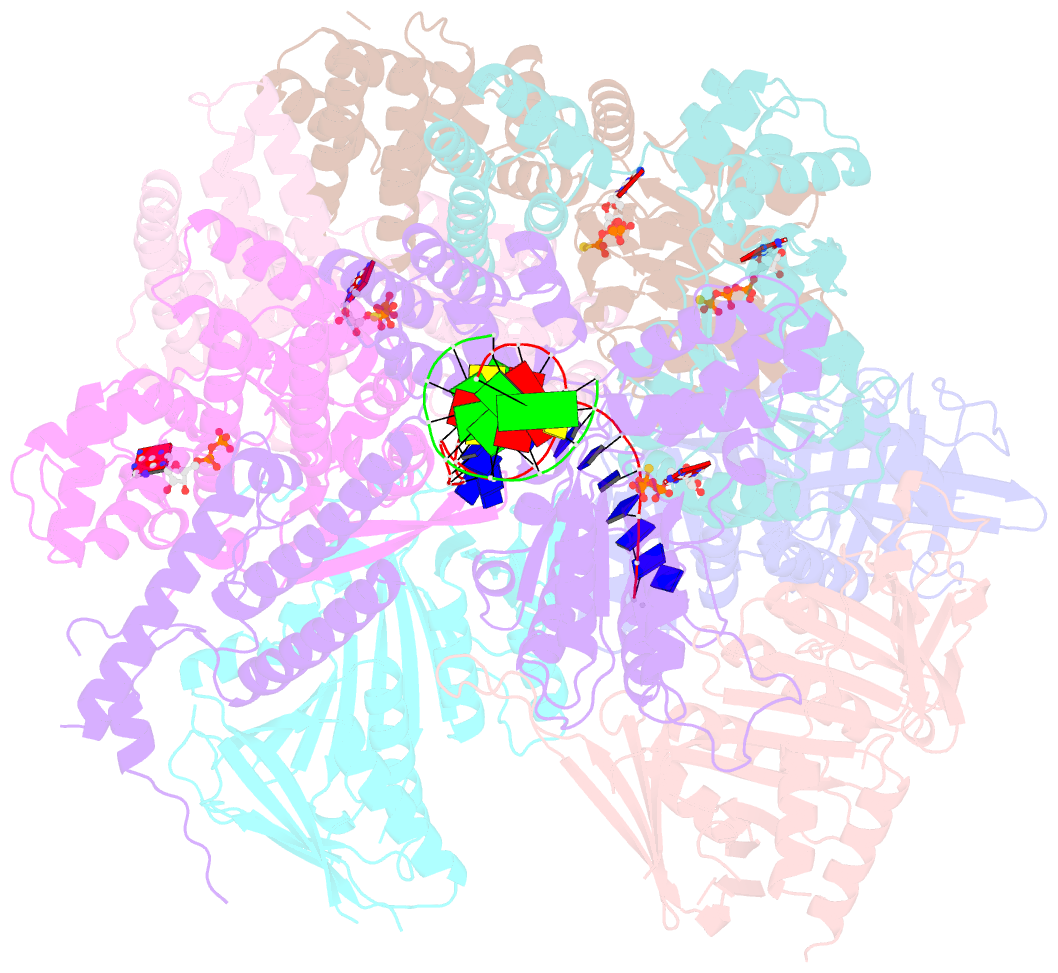
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7st9; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- replication-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.2 Å)
- Summary
- Open state of rad24-rfc:9-1-1 bound to a 5' ss-dsDNA junction
- Reference
- Castaneda JC, Schrecker M, Remus D, Hite RK (2022): "Mechanisms of loading and release of the 9-1-1 checkpoint clamp." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol., 29, 369-375. doi: 10.1038/s41594-022-00741-7.
- Abstract
- Single-stranded or double-stranded DNA junctions with recessed 5' ends serve as loading sites for the checkpoint clamp, 9-1-1, which mediates activation of the apical checkpoint kinase, ATRMec1. However, the basis for 9-1-1's recruitment to 5' junctions is unclear. Here, we present structures of the yeast checkpoint clamp loader, Rad24-replication factor C (RFC), in complex with 9-1-1 and a 5' junction and in a post-ATP-hydrolysis state. Unexpectedly, 9-1-1 adopts both closed and planar open states in the presence of Rad24-RFC and DNA. Moreover, Rad24-RFC associates with the DNA junction in the opposite orientation of processivity clamp loaders with Rad24 exclusively coordinating the double-stranded region. ATP hydrolysis stimulates conformational changes in Rad24-RFC, leading to disengagement of DNA-loaded 9-1-1. Together, these structures explain 9-1-1's recruitment to 5' junctions and reveal new principles of sliding clamp loading.