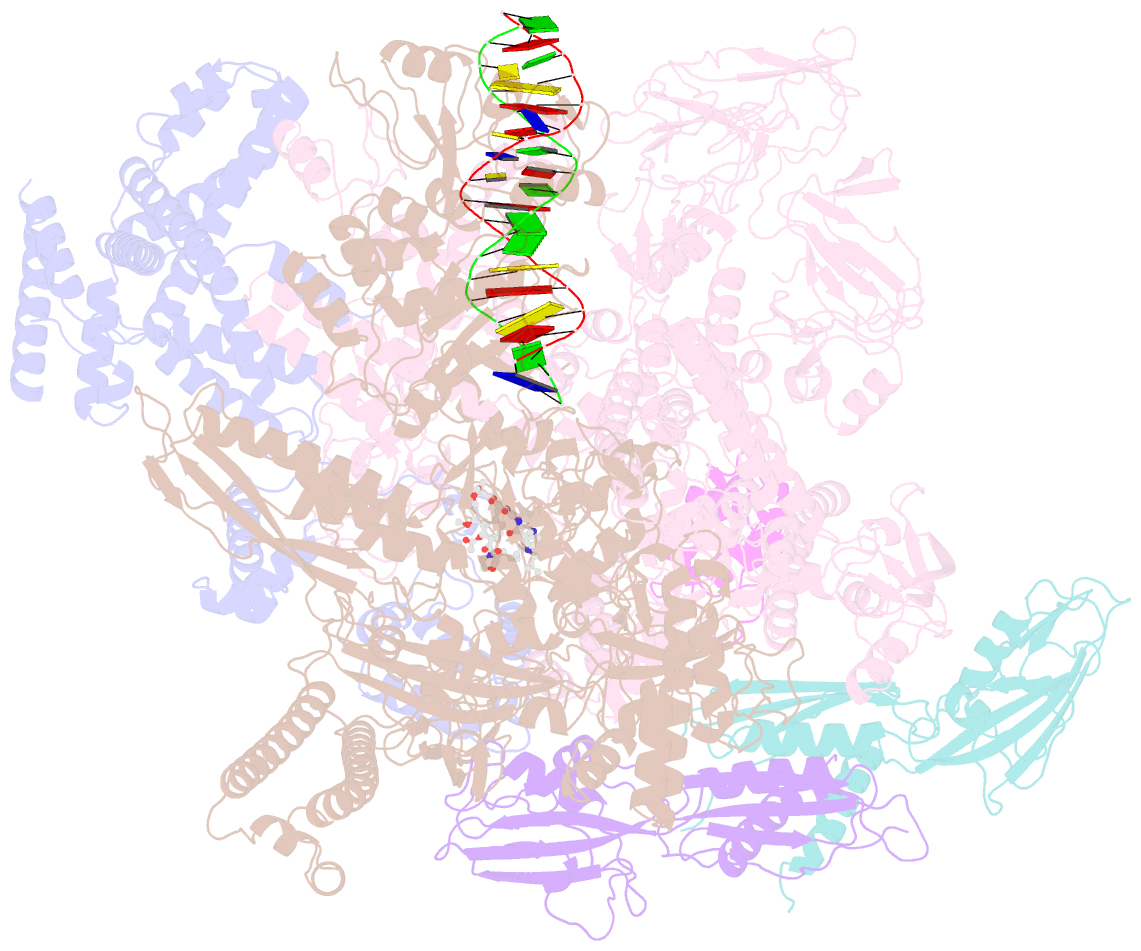
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7szk; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transferase-DNA-antibiotic
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.94 Å)
- Summary
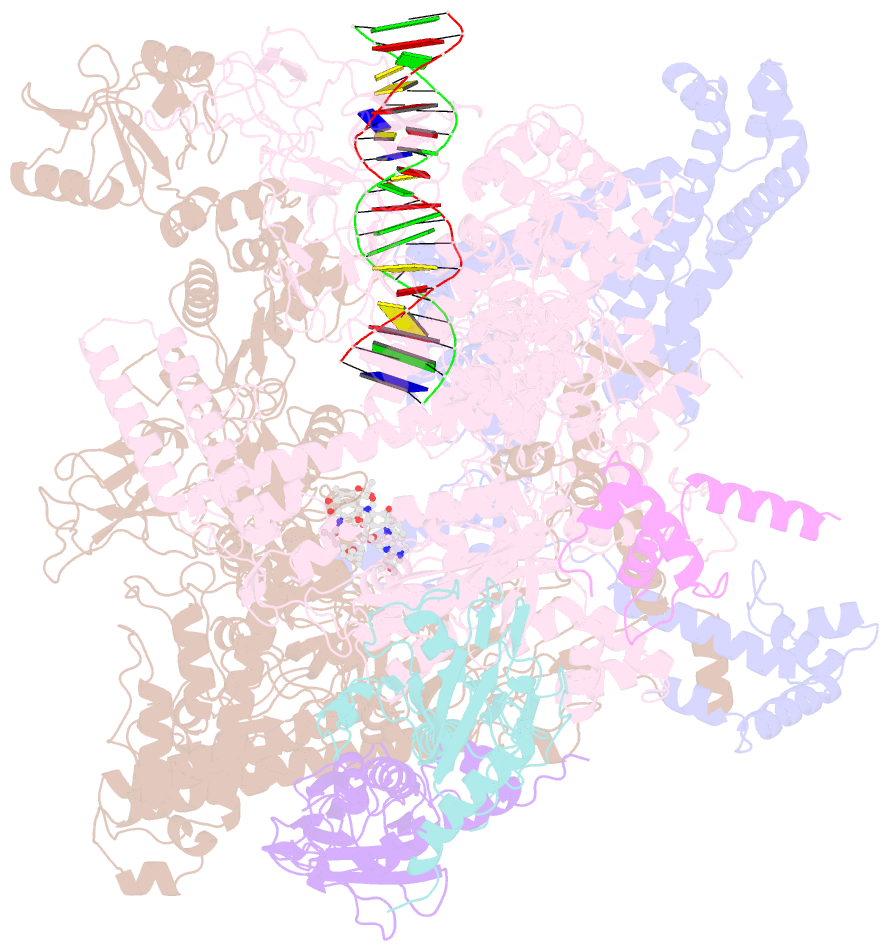
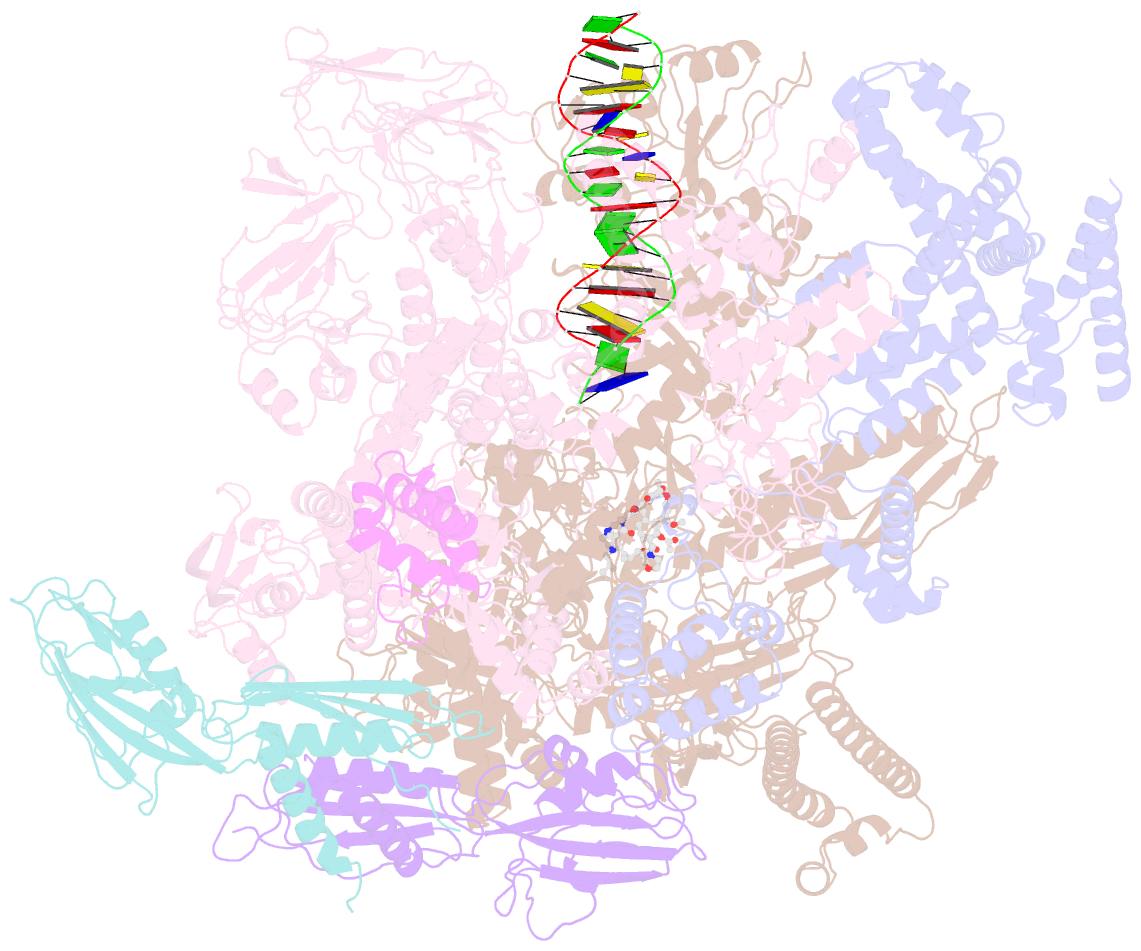
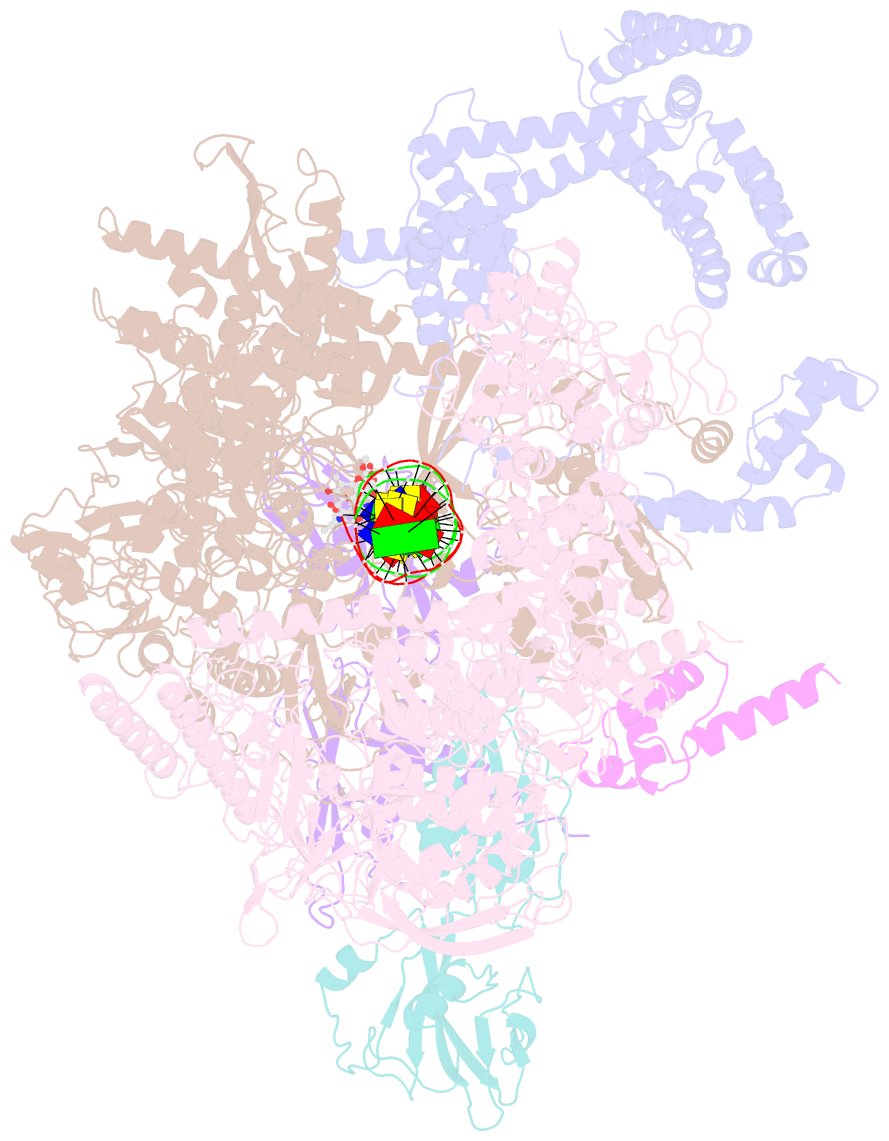
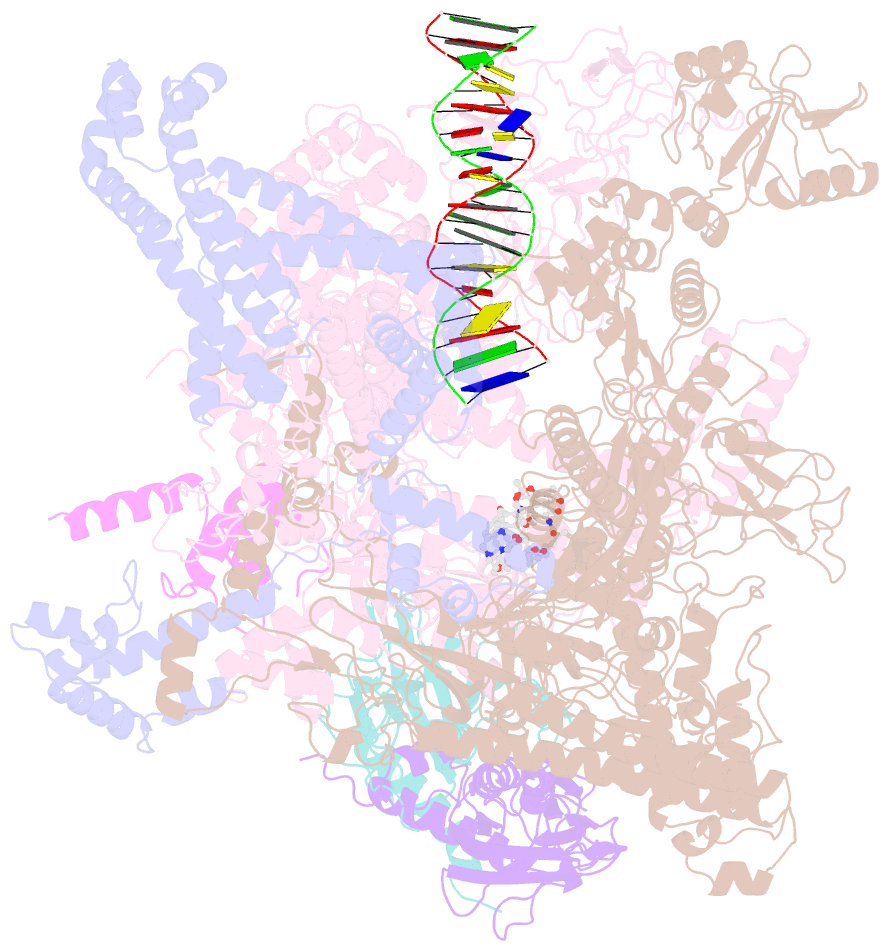
- cryo-EM structure of 27a bound to e. coli rnap and rrnbp1 promoter complex
- Reference
- Rajeswaran W, Ashkar SR, Lee PH, Yeomans L, Shin Y, Franzblau SG, Murakami KS, Showalter HD, Garcia GA (2022): "Optimization of Benzoxazinorifamycins to Improve Mycobacterium tuberculosis RNA Polymerase Inhibition and Treatment of Tuberculosis." Acs Infect Dis., 8, 1422-1438. doi: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00636.
- Abstract
- Rifampin (RMP), a very potent inhibitor of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis (MTB) RNA polymerase (RNAP), remains a keystone in the treatment of tuberculosis since its introduction in 1965. However, rifamycins suffer from serious drawbacks, including 3- to 9-month treatment times, Cyp450 induction (particularly problematic for HIV-MTB coinfection), and resistant mutations within RNAP that yield RIF-resistant (RIFR) MTB strains. There is a clear and pressing need for improved TB therapies. We have utilized a structure-based drug design approach to synthesize and test novel benzoxazinorifamycins (bxRIF), congeners of the clinical candidate rifalazil. Our goal is to gain binding interactions that will compensate for the loss of RIF-binding affinity to the (RIFR) MTB RNAP and couple those with substitutions that we have previously found that essentially eliminate Cyp450 induction. Herein, we report a systematic exploration of 42 substituted bxRIFs that have yielded an analogue (