Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7uws; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.47 Å)
- Summary
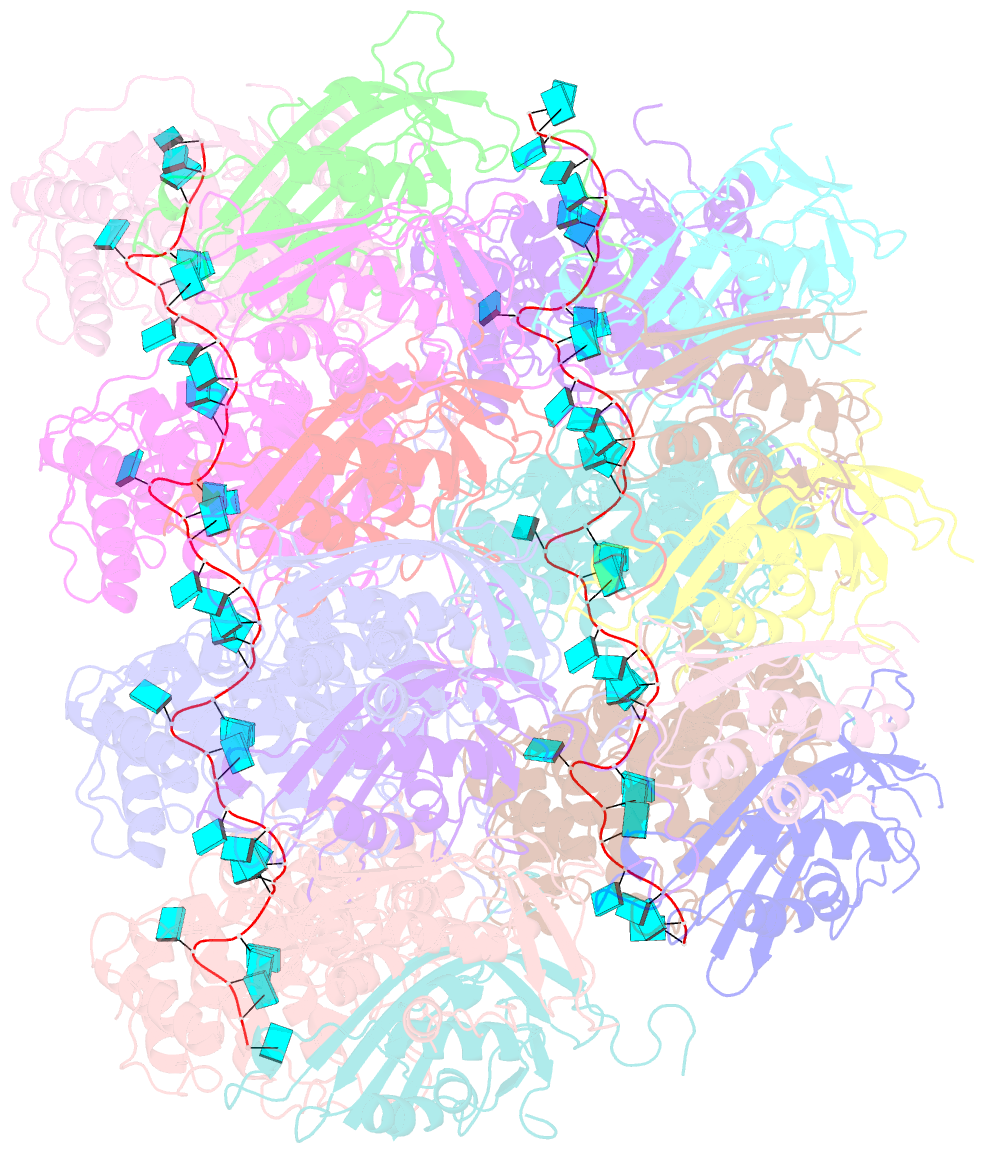
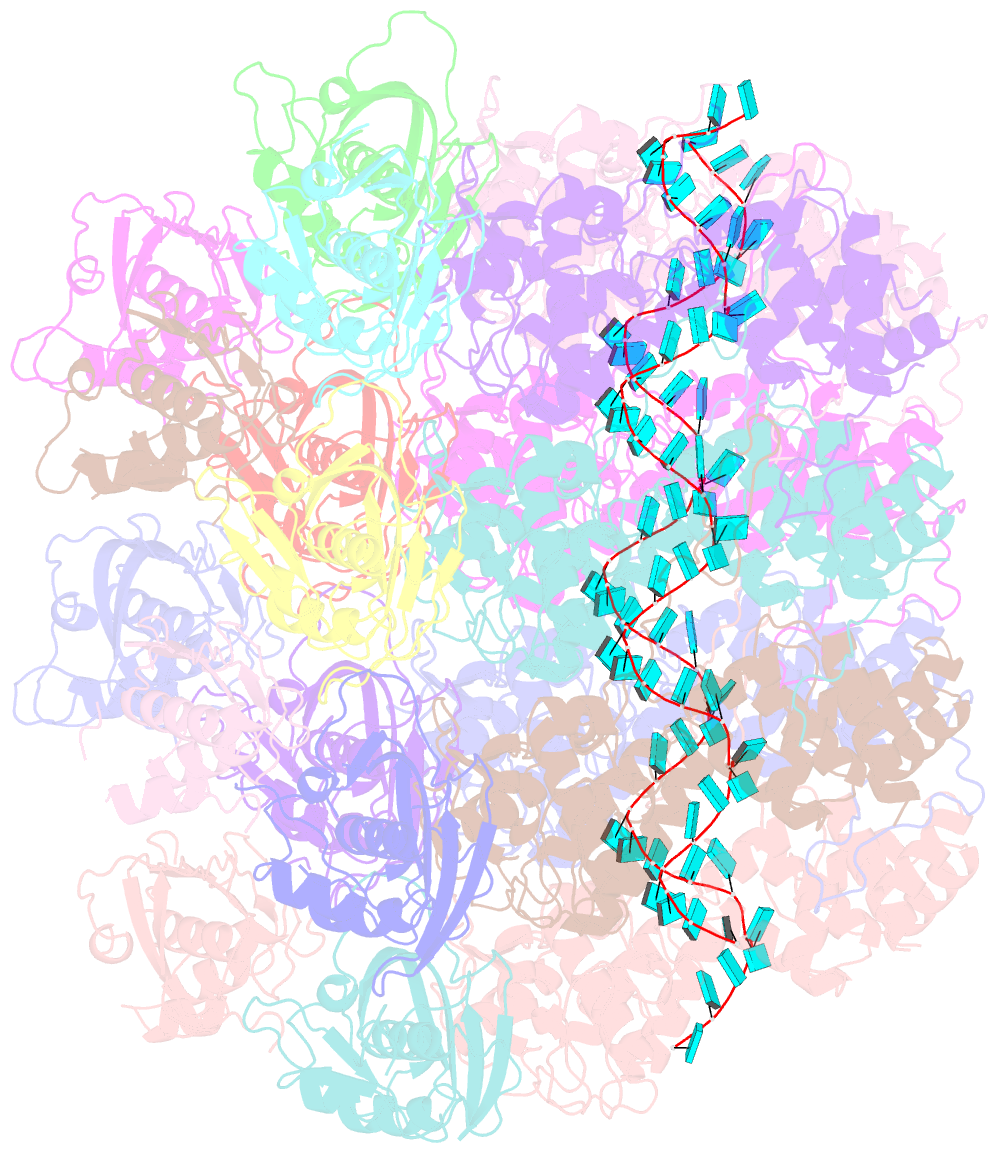
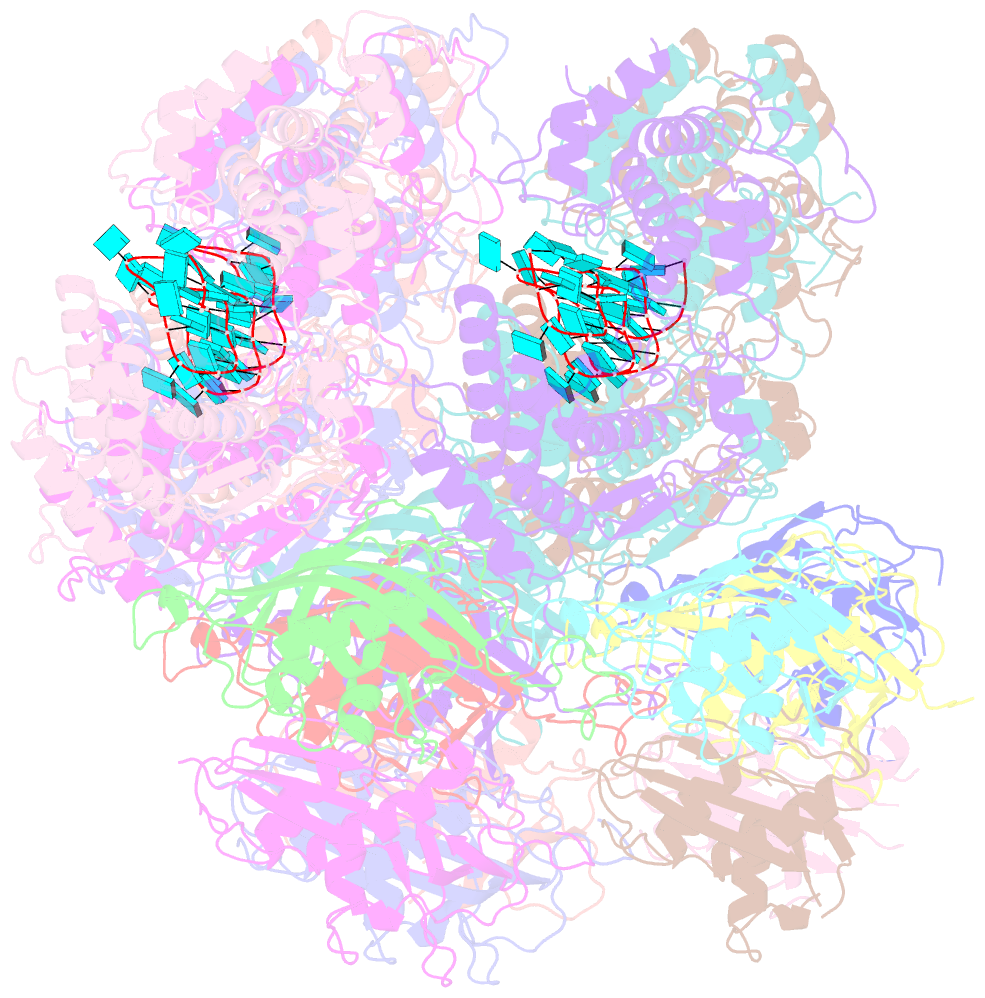
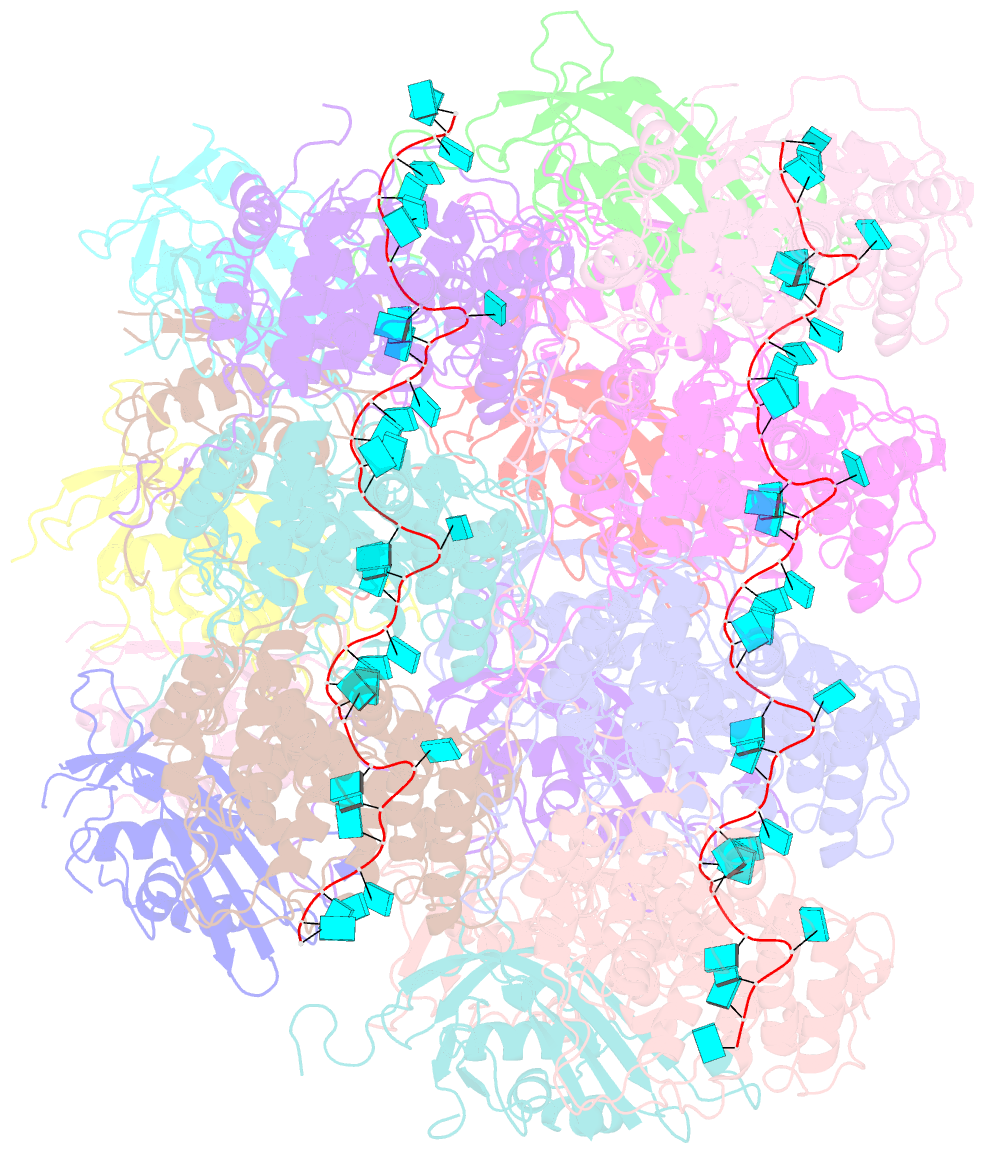
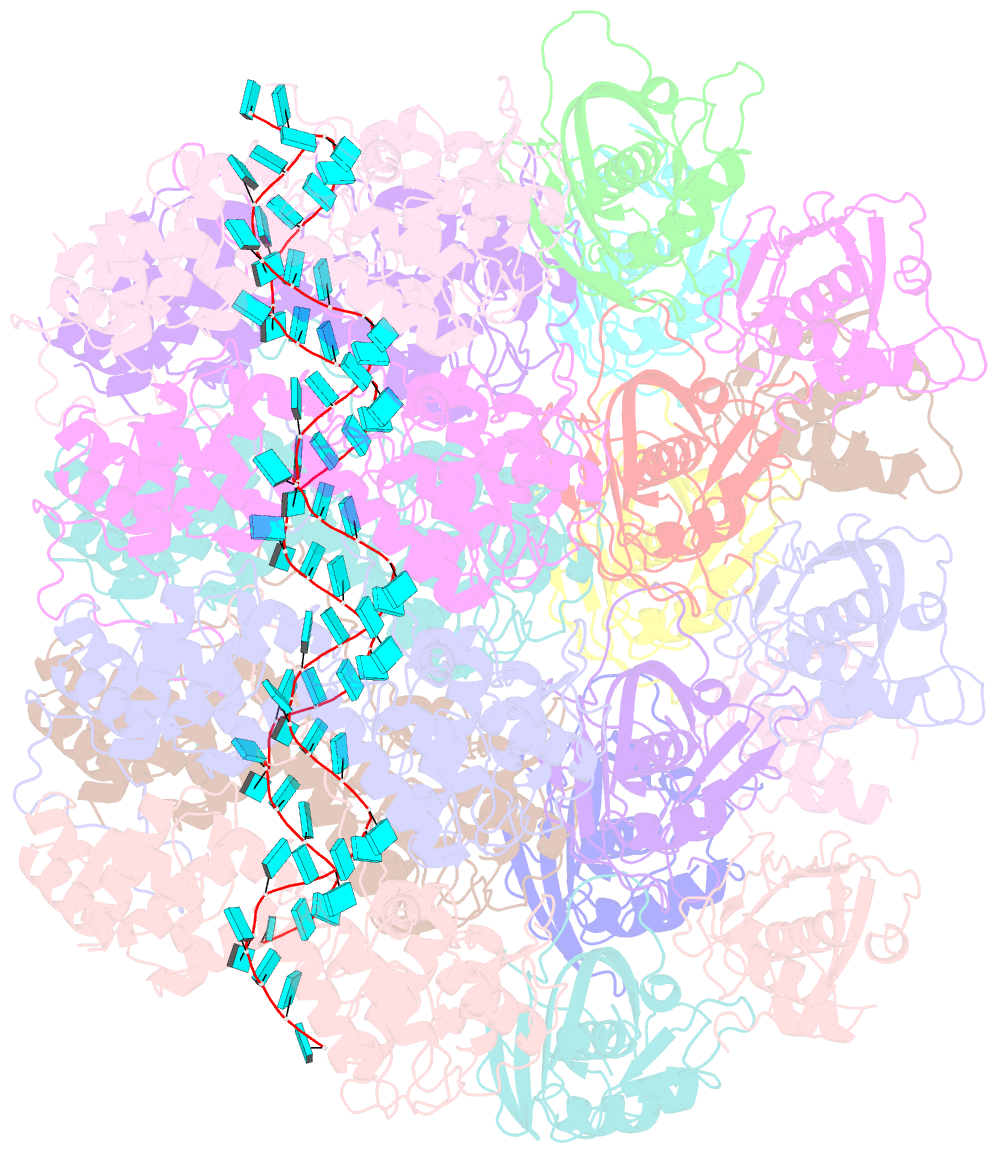
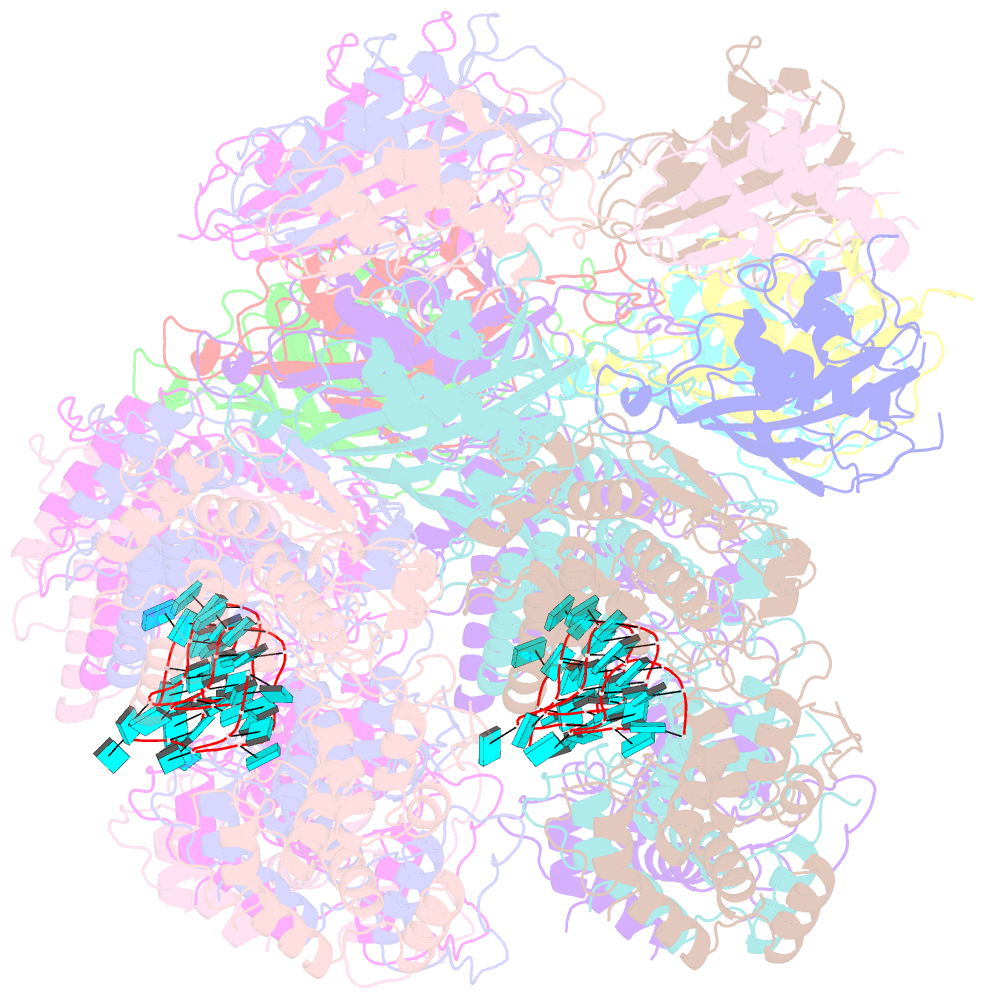
- Atomic model of the partial vsv nucleocapsid
- Reference
- Zhou K, Si Z, Ge P, Tsao J, Luo M, Zhou ZH (2022): "Atomic model of vesicular stomatitis virus and mechanism of assembly." Nat Commun, 13, 5980. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33664-4.
- Abstract
- Like other negative-strand RNA viruses (NSVs) such as influenza and rabies, vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) has a three-layered organization: a layer of matrix protein (M) resides between the glycoprotein (G)-studded membrane envelope and the nucleocapsid, which is composed of the nucleocapsid protein (N) and the encapsidated genomic RNA. Lack of in situ atomic structures of these viral components has limited mechanistic understanding of assembling the bullet-shaped virion. Here, by cryoEM and sub-particle reconstruction, we have determined the in situ structures of M and N inside VSV at 3.47 Å resolution. In the virion, N and M sites have a stoichiometry of 1:2. The in situ structures of both N and M differ from their crystal structures in their N-terminal segments and oligomerization loops. N-RNA, N-N, and N-M-M interactions govern the formation of the capsid. A double layer of M contributes to packaging of the helical nucleocapsid: the inner M (IM) joins neighboring turns of the N helix, while the outer M (OM) contacts G and the membrane envelope. The pseudo-crystalline organization of G is further mapped by cryoET. The mechanism of VSV assembly is delineated by the network interactions of these viral components.