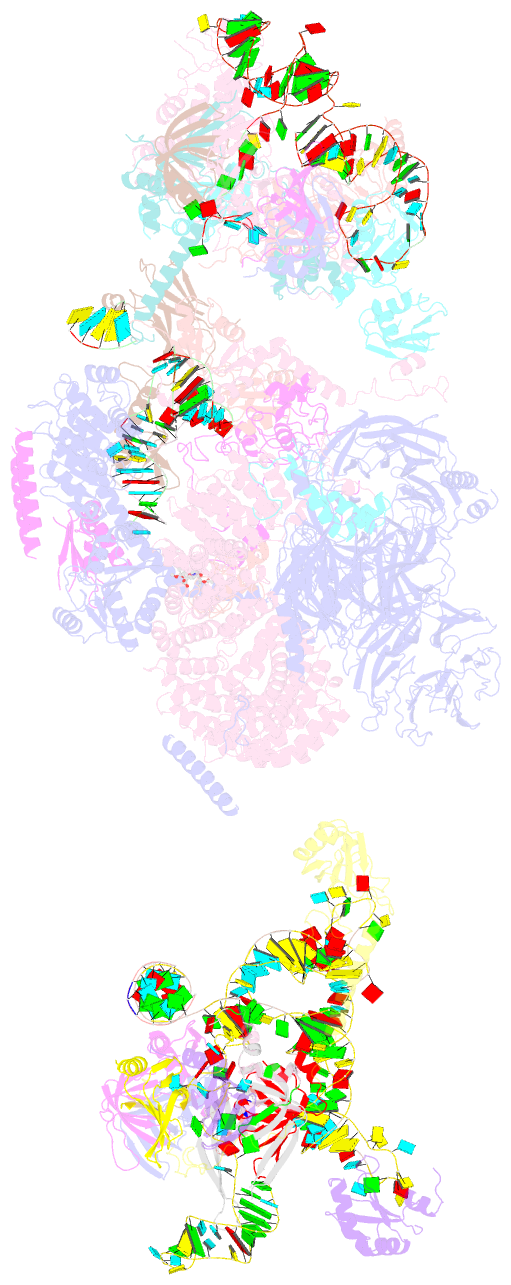
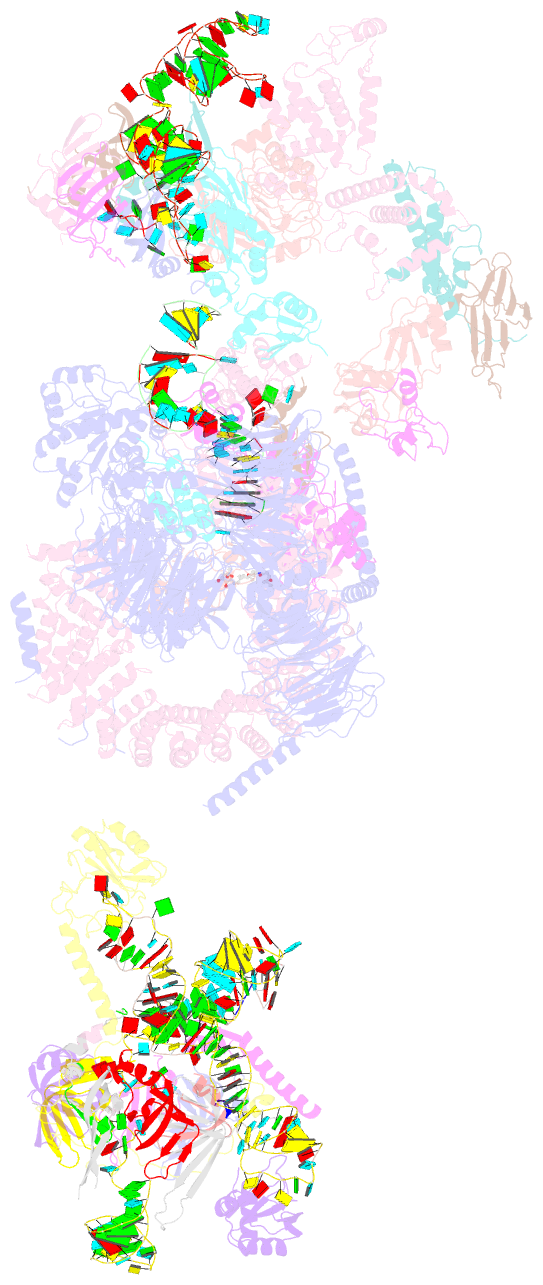
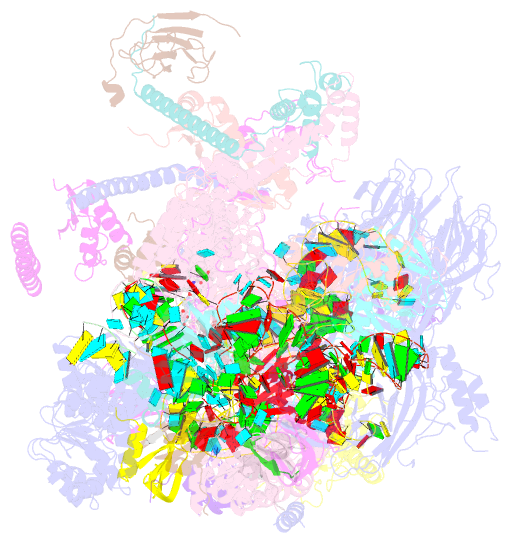
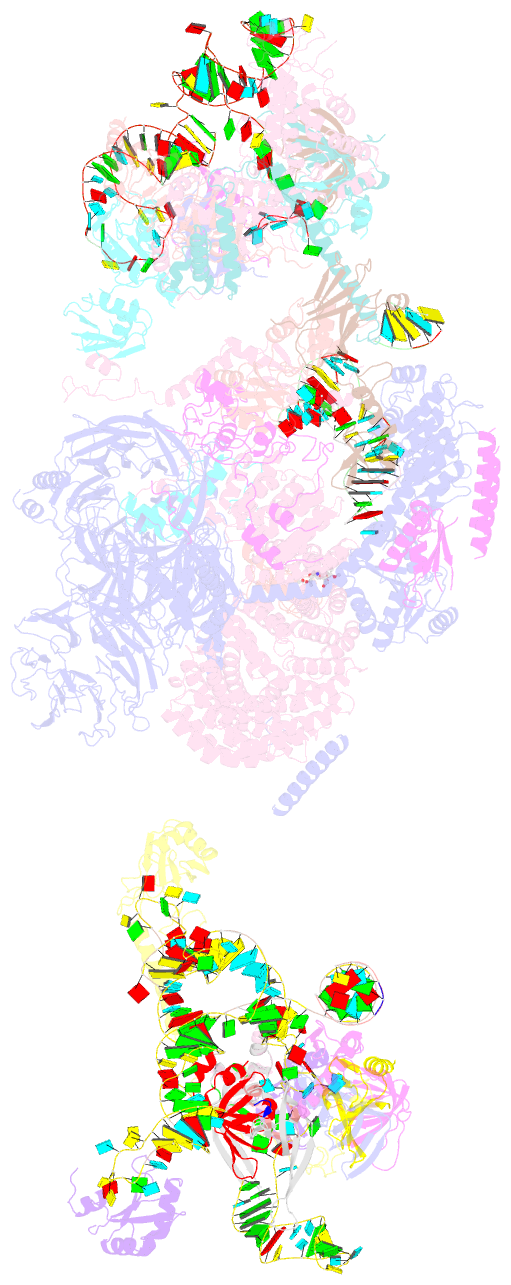
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7vpx; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- splicing
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.0 Å)
- Summary
- The cryo-EM structure of the human pre-a complex
- Reference
- Zhang X, Zhan X, Bian T, Yang F, Li P, Lu Y, Xing Z, Fan R, Zhang QC, Shi Y (2024): "Structural insights into branch site proofreading by human spliceosome." Nat.Struct.Mol.Biol. doi: 10.1038/s41594-023-01188-0.
- Abstract
- Selection of the pre-mRNA branch site (BS) by the U2 small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) is crucial to prespliceosome (A complex) assembly. The RNA helicase PRP5 proofreads BS selection but the underlying mechanism remains unclear. Here we report the atomic structures of two sequential complexes leading to prespliceosome assembly: human 17S U2 snRNP and a cross-exon pre-A complex. PRP5 is anchored on 17S U2 snRNP mainly through occupation of the RNA path of SF3B1 by an acidic loop of PRP5; the helicase domain of PRP5 associates with U2 snRNA; the BS-interacting stem-loop (BSL) of U2 snRNA is shielded by TAT-SF1, unable to engage the BS. In the pre-A complex, an initial U2-BS duplex is formed; the translocated helicase domain of PRP5 stays with U2 snRNA and the acidic loop still occupies the RNA path. The pre-A conformation is specifically stabilized by the splicing factors SF1, DNAJC8 and SF3A2. Cancer-derived mutations in SF3B1 damage its association with PRP5, compromising BS proofreading. Together, these findings reveal key insights into prespliceosome assembly and BS selection or proofreading by PRP5.