Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7w1m; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (6.5 Å)
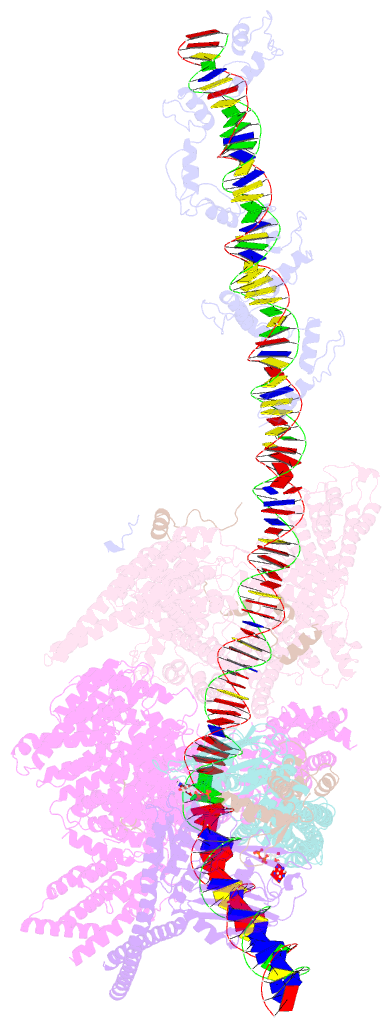
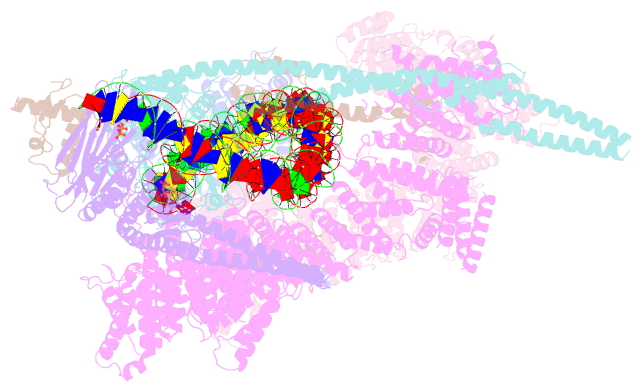
- Summary
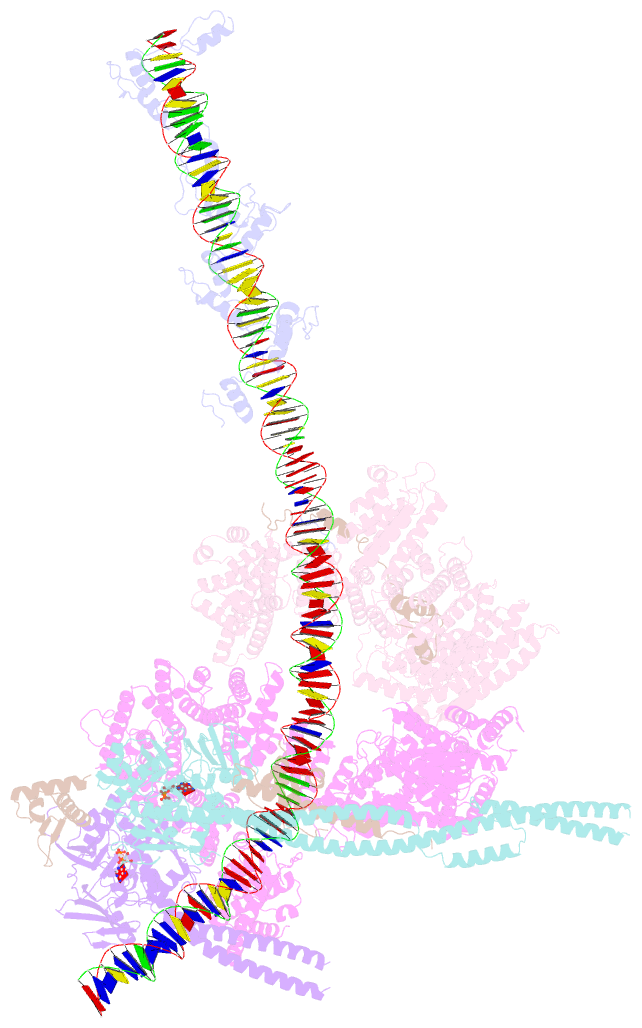
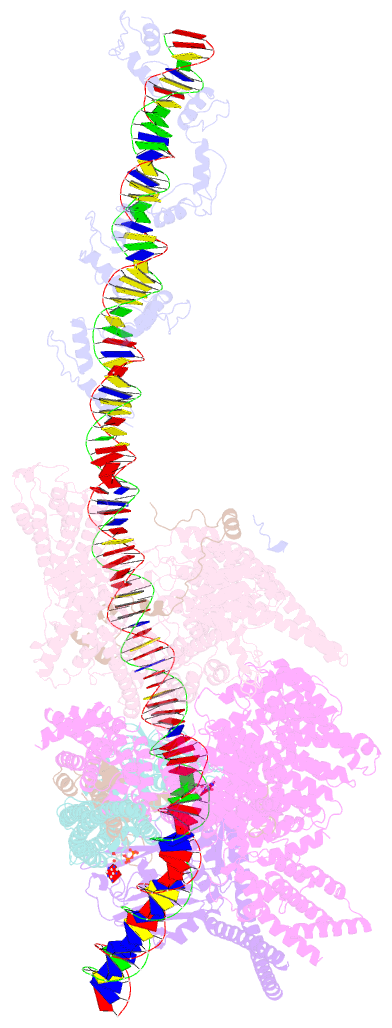
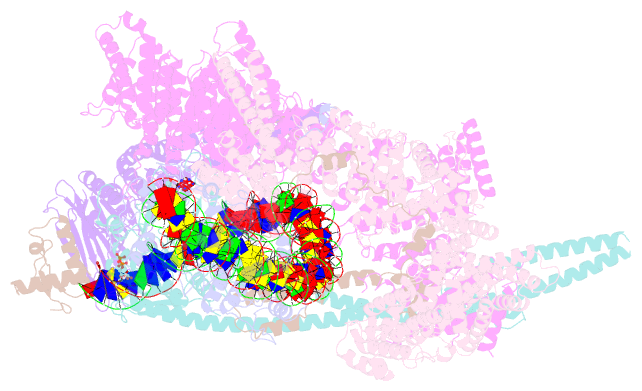
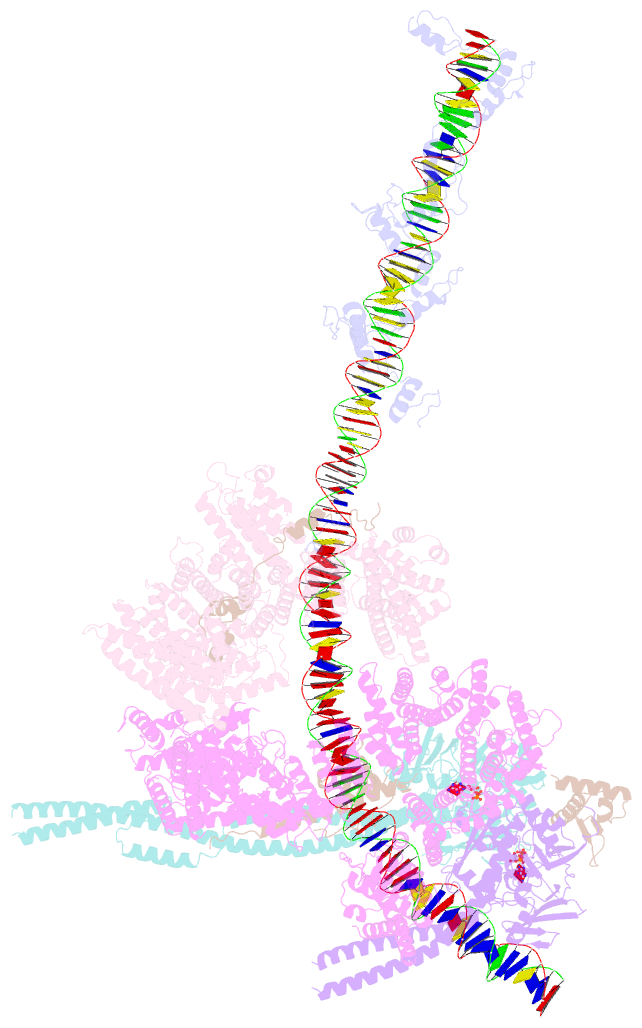
- cryo-EM structure of human cohesin-ctcf-DNA complex
- Reference
- Zhang H, Shi Z, Banigan EJ, Kim Y, Yu H, Bai XC, Finkelstein IJ (2023): "CTCF and R-loops are boundaries of cohesin-mediated DNA looping." Mol.Cell, 83, 2856-2871.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.07.006.
- Abstract
- Cohesin and CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) are key regulatory proteins of three-dimensional (3D) genome organization. Cohesin extrudes DNA loops that are anchored by CTCF in a polar orientation. Here, we present direct evidence that CTCF binding polarity controls cohesin-mediated DNA looping. Using single-molecule imaging, we demonstrate that a critical N-terminal motif of CTCF blocks cohesin translocation and DNA looping. The cryo-EM structure of the cohesin-CTCF complex reveals that this CTCF motif ahead of zinc fingers can only reach its binding site on the STAG1 cohesin subunit when the N terminus of CTCF faces cohesin. Remarkably, a C-terminally oriented CTCF accelerates DNA compaction by cohesin. DNA-bound Cas9 and Cas12a ribonucleoproteins are also polar cohesin barriers, indicating that stalling may be intrinsic to cohesin itself. Finally, we show that RNA-DNA hybrids (R-loops) block cohesin-mediated DNA compaction in vitro and are enriched with cohesin subunits in vivo, likely forming TAD boundaries.