Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7wkv; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- oxidoreductase-RNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.1 Å)
- Summary
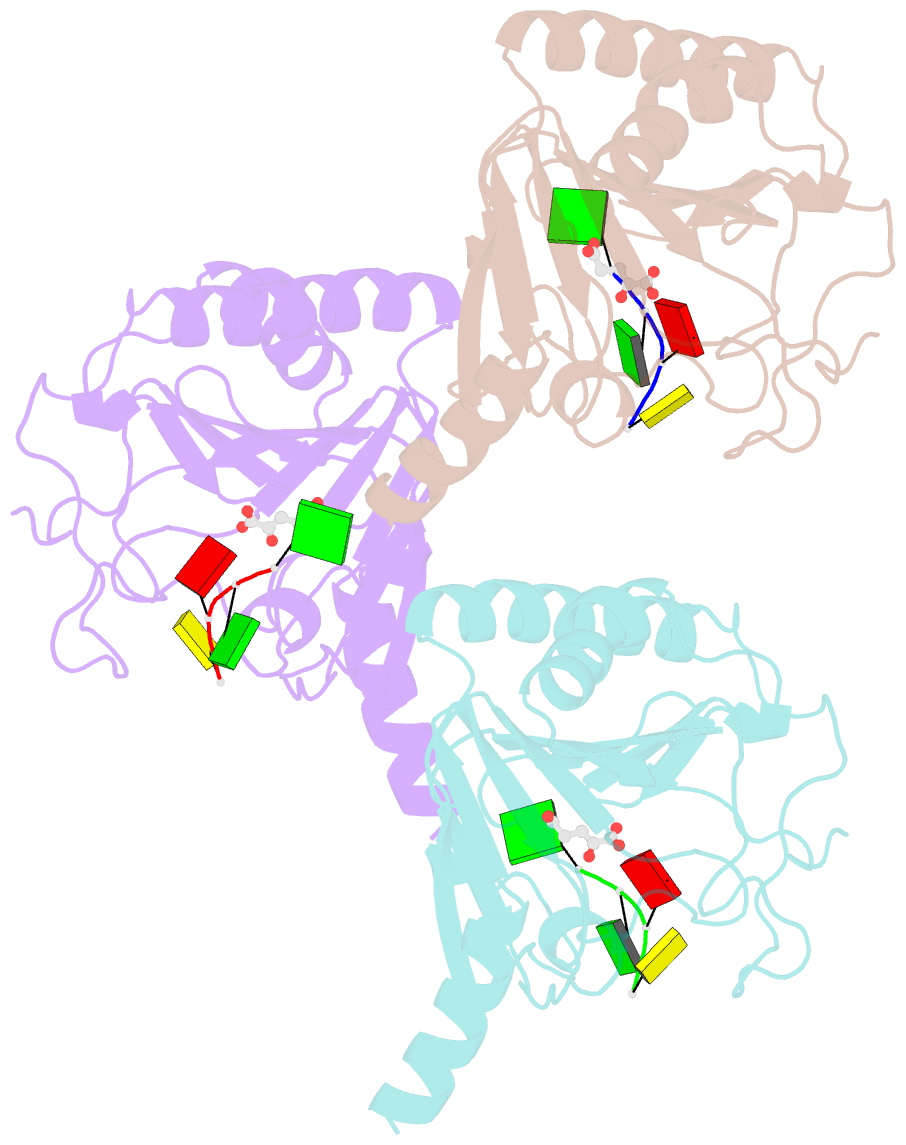
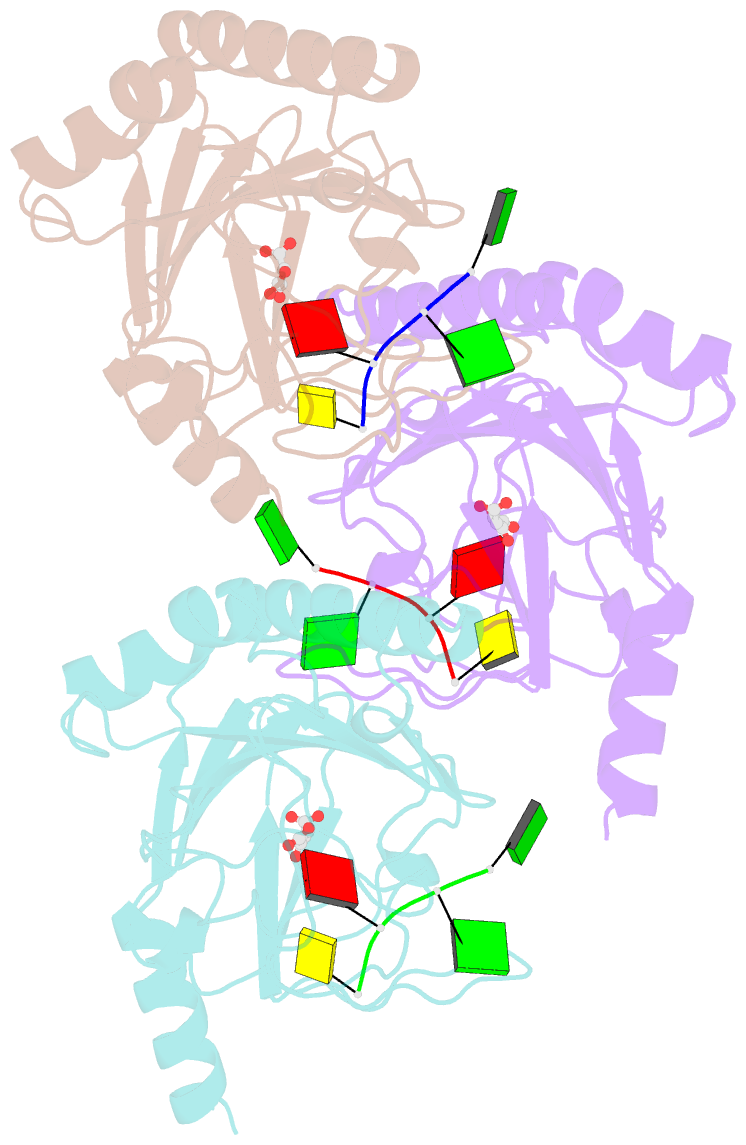
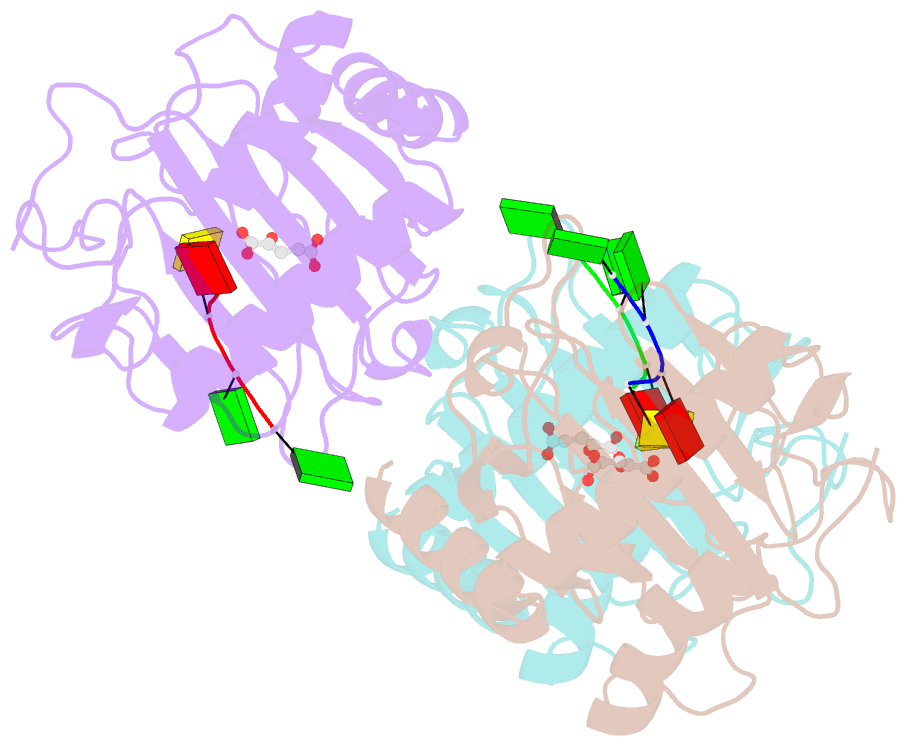
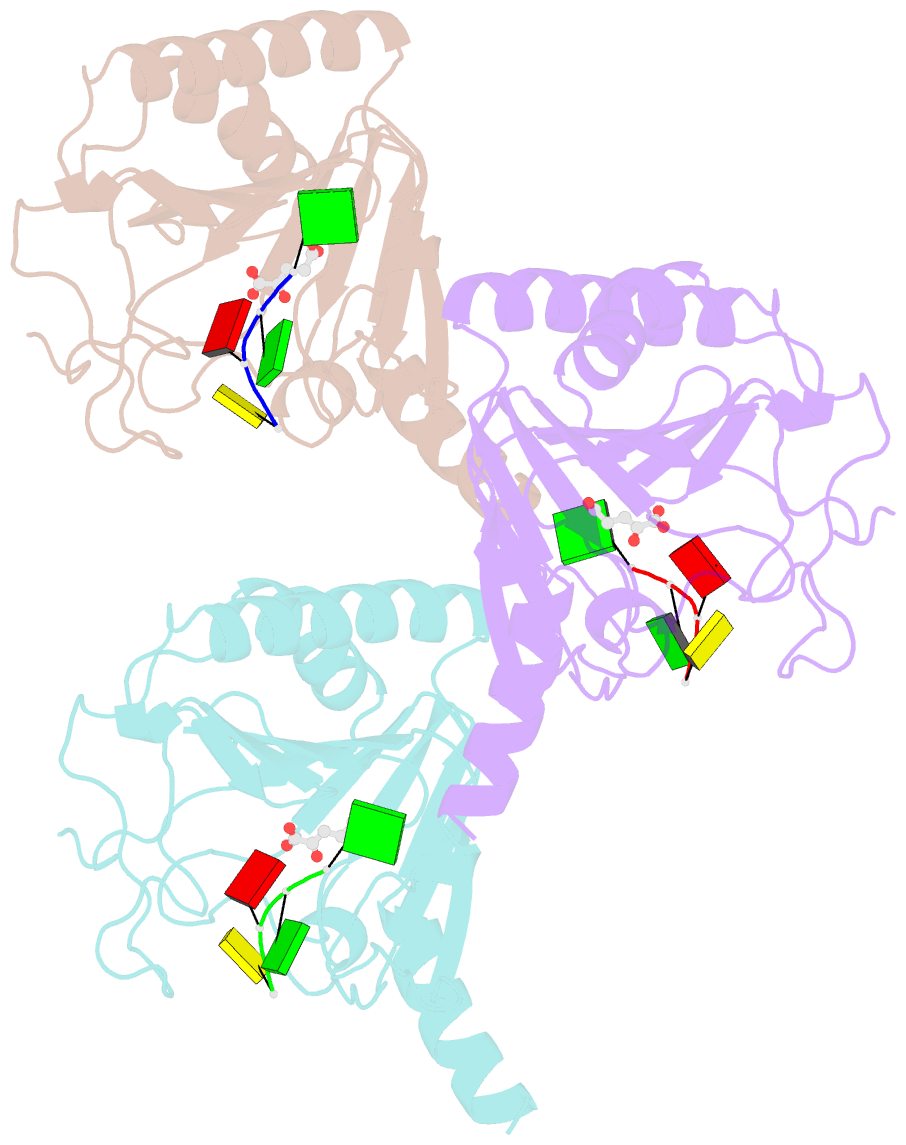
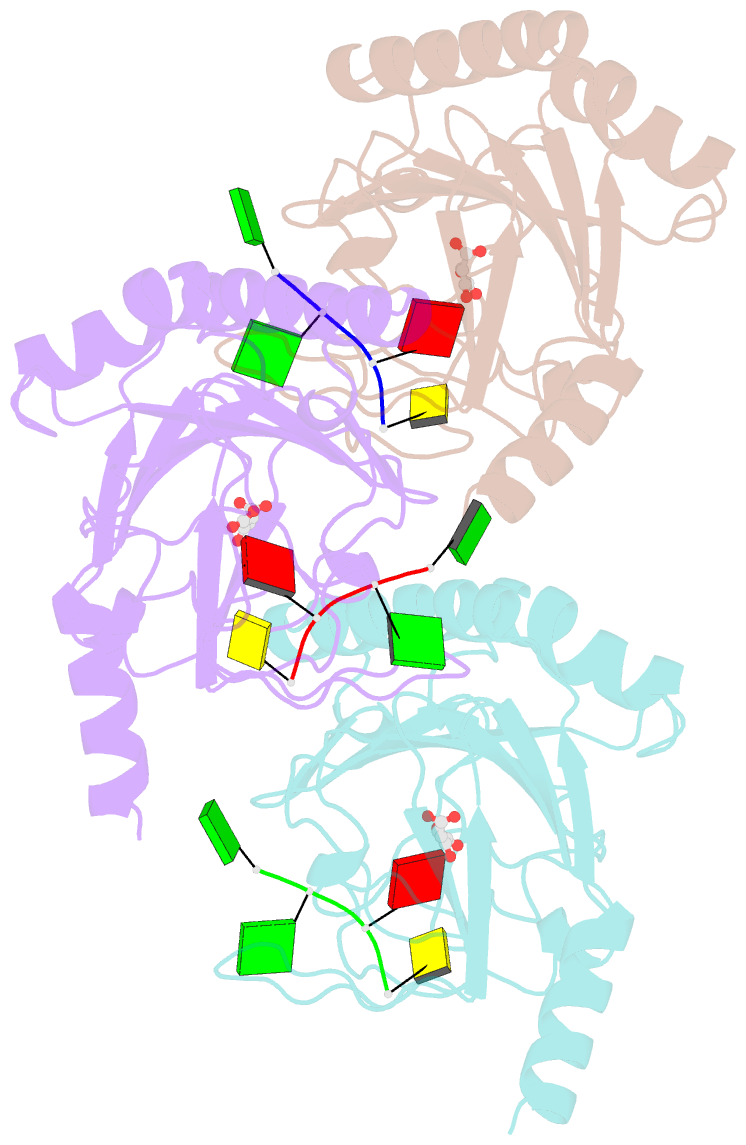
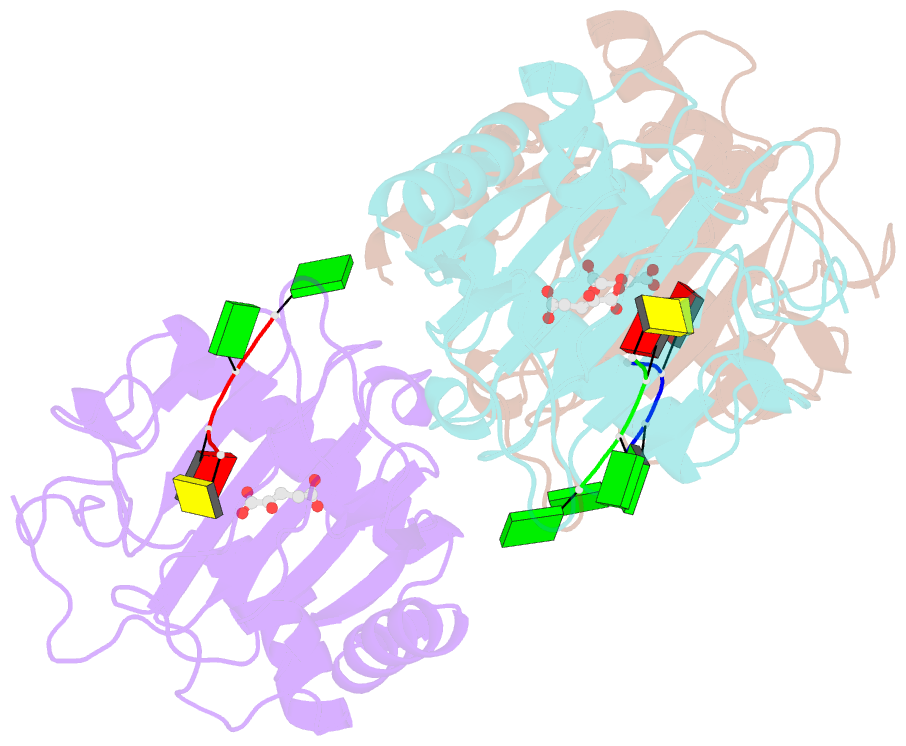
- Crystal structure of human alkbh5 in complex with 2-oxoglutarate (2og) and m6a-containing ssrna
- Reference
- Kaur S, Tam NY, McDonough MA, Schofield CJ, Aik WS (2022): "Mechanisms of substrate recognition and N6-methyladenosine demethylation revealed by crystal structures of ALKBH5-RNA complexes." Nucleic Acids Res., 50, 4148-4160. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac195.
- Abstract
- AlkB homologue 5 (ALKBH5) is a ferrous iron and 2-oxoglutarate dependent oxygenase that demethylates RNA N6-methyladenosine (m6A), a post-transcriptional RNA modification with an emerging set of regulatory roles. Along with the fat mass and obesity-associated protein (FTO), ALKBH5 is one of only two identified human m6A RNA oxidizing enzymes and is a potential target for cancer treatment. Unlike FTO, ALKBH5 efficiently catalyzes fragmentation of its proposed nascent hemiaminal intermediate to give formaldehyde and a demethylated nucleoside. A detailed analysis of the molecular mechanisms used by ALKBH5 for substrate recognition and m6A demethylation is lacking. We report three crystal structures of ALKBH5 in complex with an m6A-ssRNA 8-mer substrate and supporting biochemical analyses. Strikingly, the single-stranded RNA substrate binds to the active site of ALKBH5 in a 5'-3' orientation that is opposite to single-stranded or double-stranded DNA substrates observed for other AlkB subfamily members, including single-stranded DNA bound to FTO. The combined structural and biochemical results provide insight into the preference of ALKBH5 for substrates containing a (A/G)m6AC consensus sequence motif. The results support a mechanism involving formation of an m6A hemiaminal intermediate, followed by efficient ALKBH5 catalyzed demethylation, enabled by a proton shuttle network involving Lys132 and Tyr139.