Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7x58; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.93 Å)
- Summary
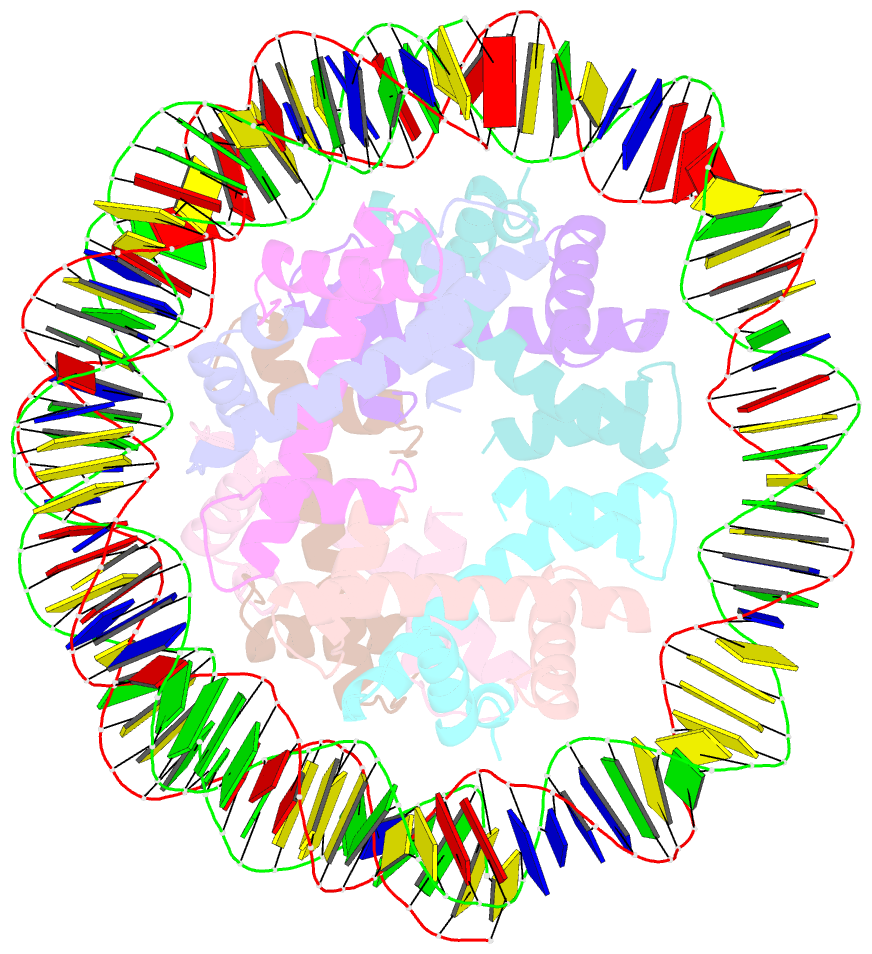
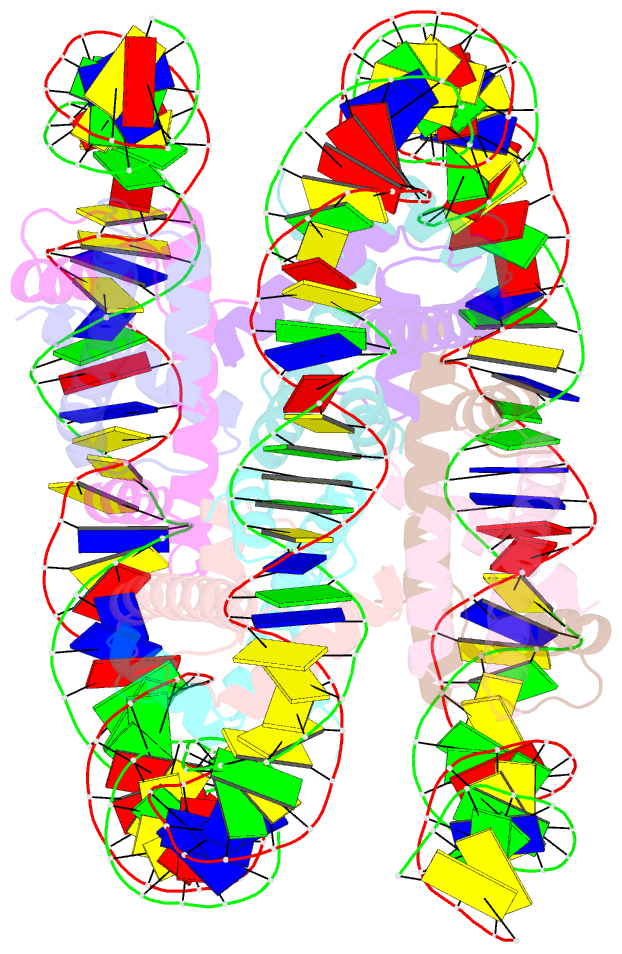
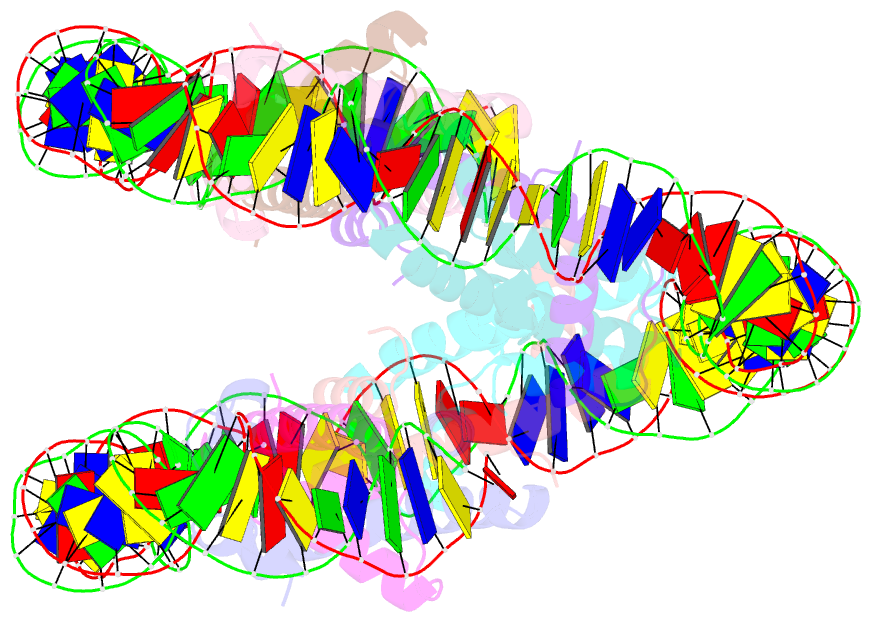
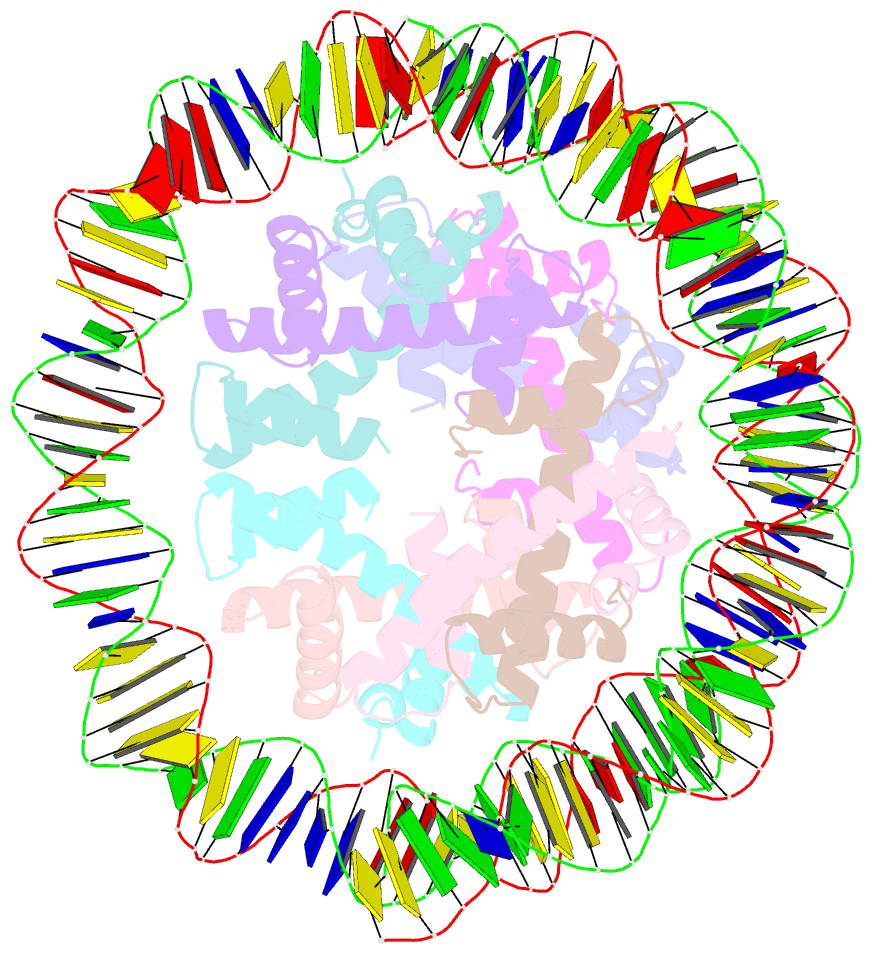
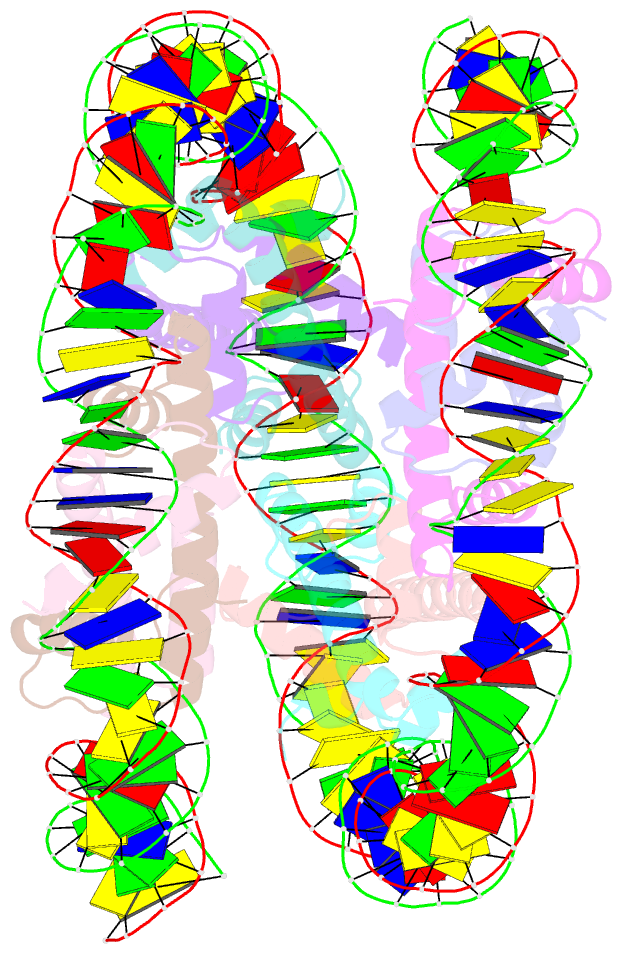
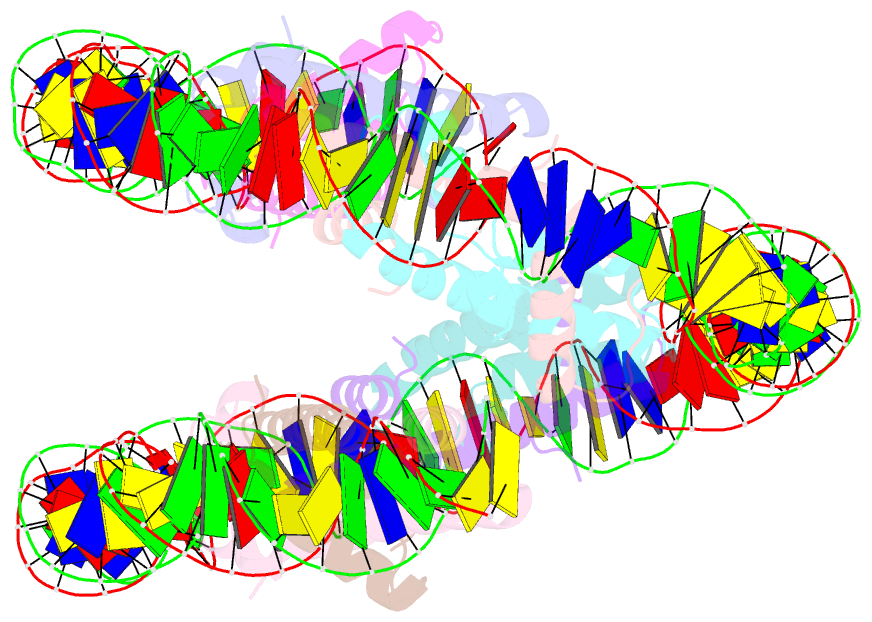
- cryo-EM structure of human subnucleosome (open form)
- Reference
- Nozawa K, Takizawa Y, Pierrakeas L, Sogawa-Fujiwara C, Saikusa K, Akashi S, Luk E, Kurumizaka H (2022): "Cryo-electron microscopy structure of the H3-H4 octasome: A nucleosome-like particle without histones H2A and H2B." Proc.Natl.Acad.Sci.USA, 119, e2206542119. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2206542119.
- Abstract
- The canonical nucleosome, which represents the major packaging unit of eukaryotic chromatin, has an octameric core composed of two histone H2A-H2B and H3-H4 dimers with ∼147 base pairs (bp) of DNA wrapped around it. Non-nucleosomal particles with alternative histone stoichiometries and DNA wrapping configurations have been found, and they could profoundly influence genome architecture and function. Using cryo-electron microscopy, we solved the structure of the H3-H4 octasome, a nucleosome-like particle with a di-tetrameric core consisting exclusively of the H3 and H4 histones. The core is wrapped by ∼120 bp of DNA in 1.5 negative superhelical turns, forming two stacked disks that are connected by a H4-H4' four-helix bundle. Three conformations corresponding to alternative interdisk angles were observed, indicating the flexibility of the H3-H4 octasome structure. In vivo crosslinking experiments detected histone-histone interactions consistent with the H3-H4 octasome model, suggesting that H3-H4 octasomes or related structural features exist in cells.