Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7x7p; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- motor protein-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (7.02 Å)
- Summary
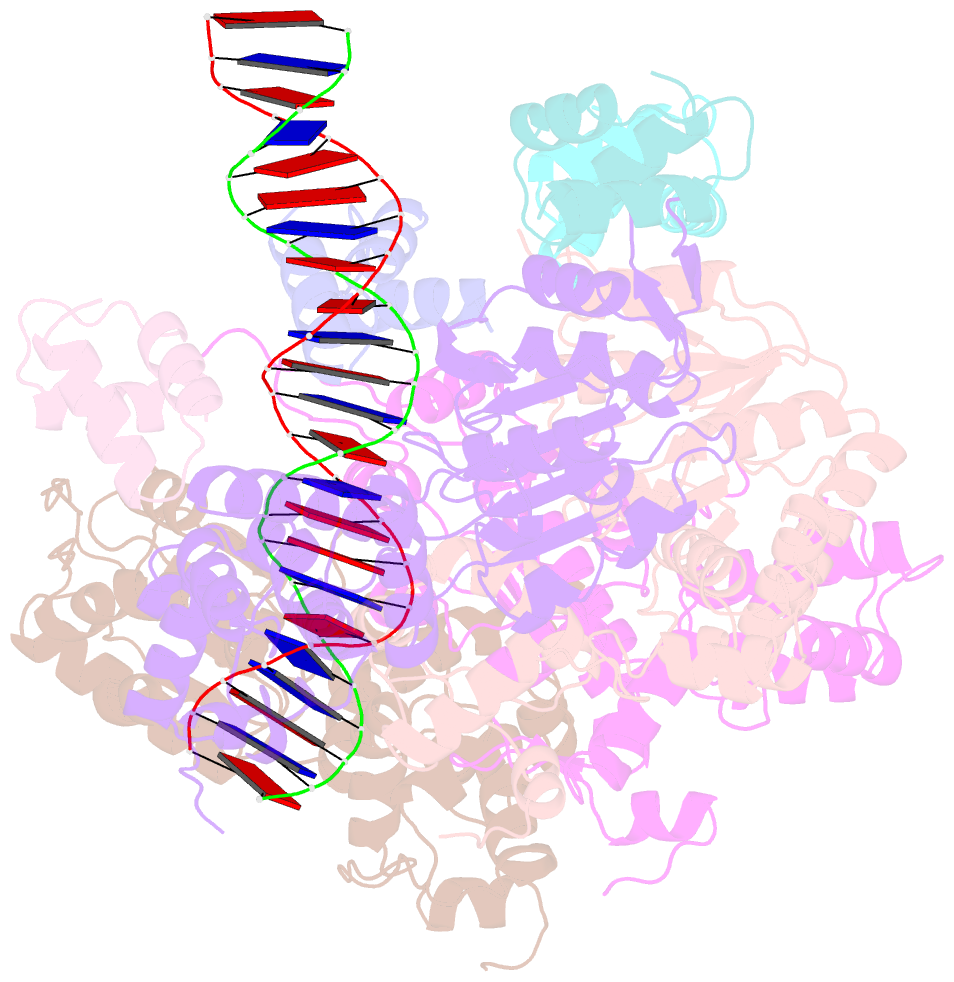
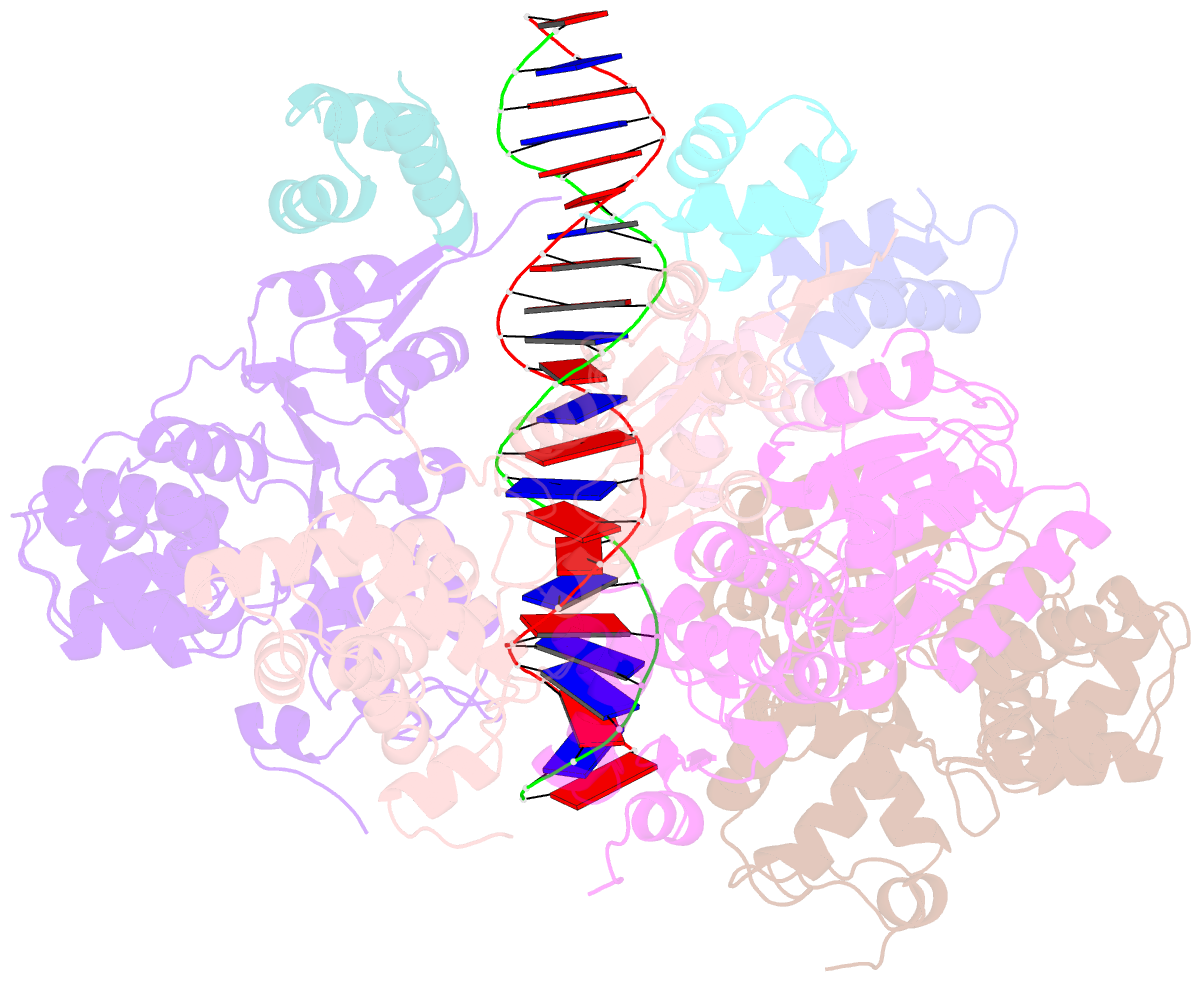
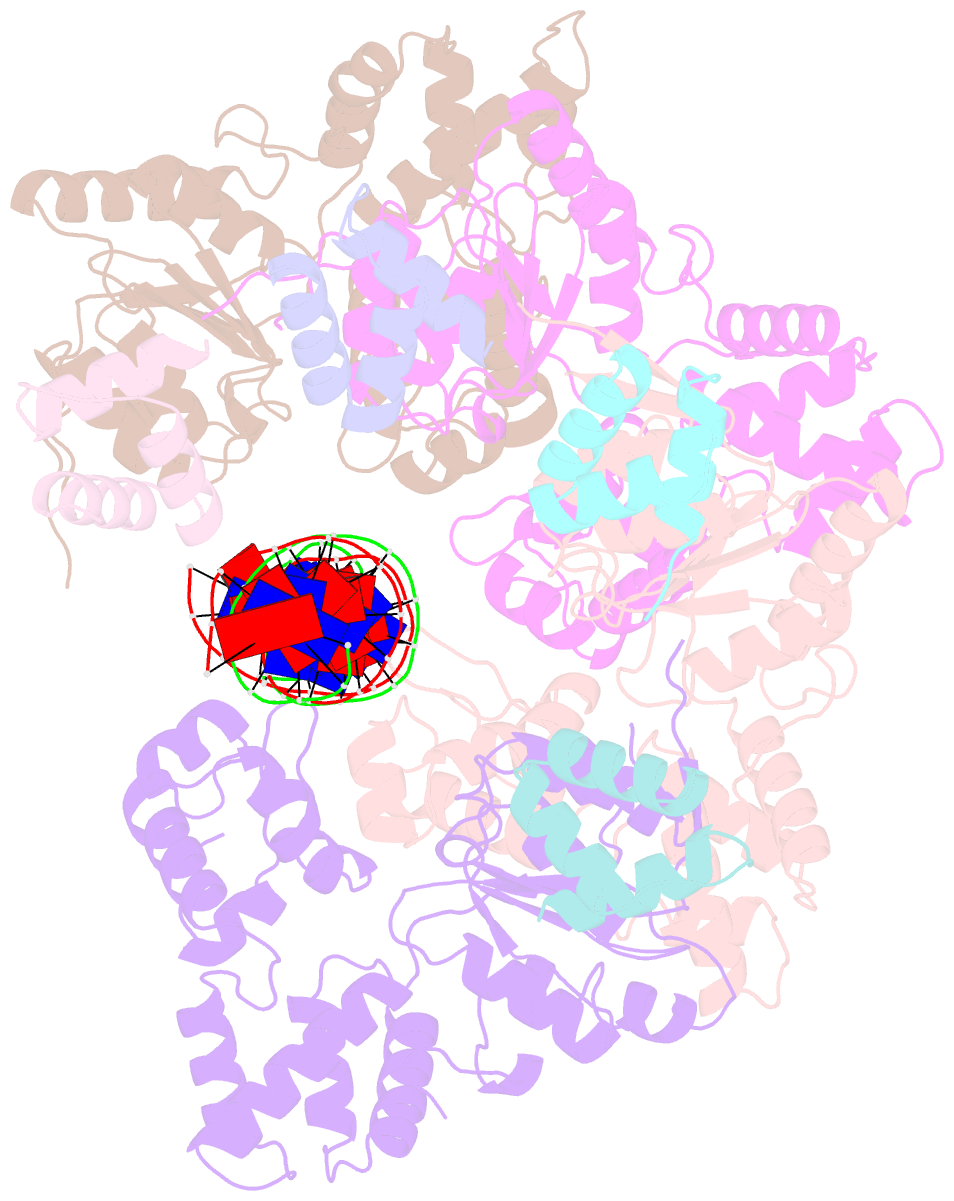
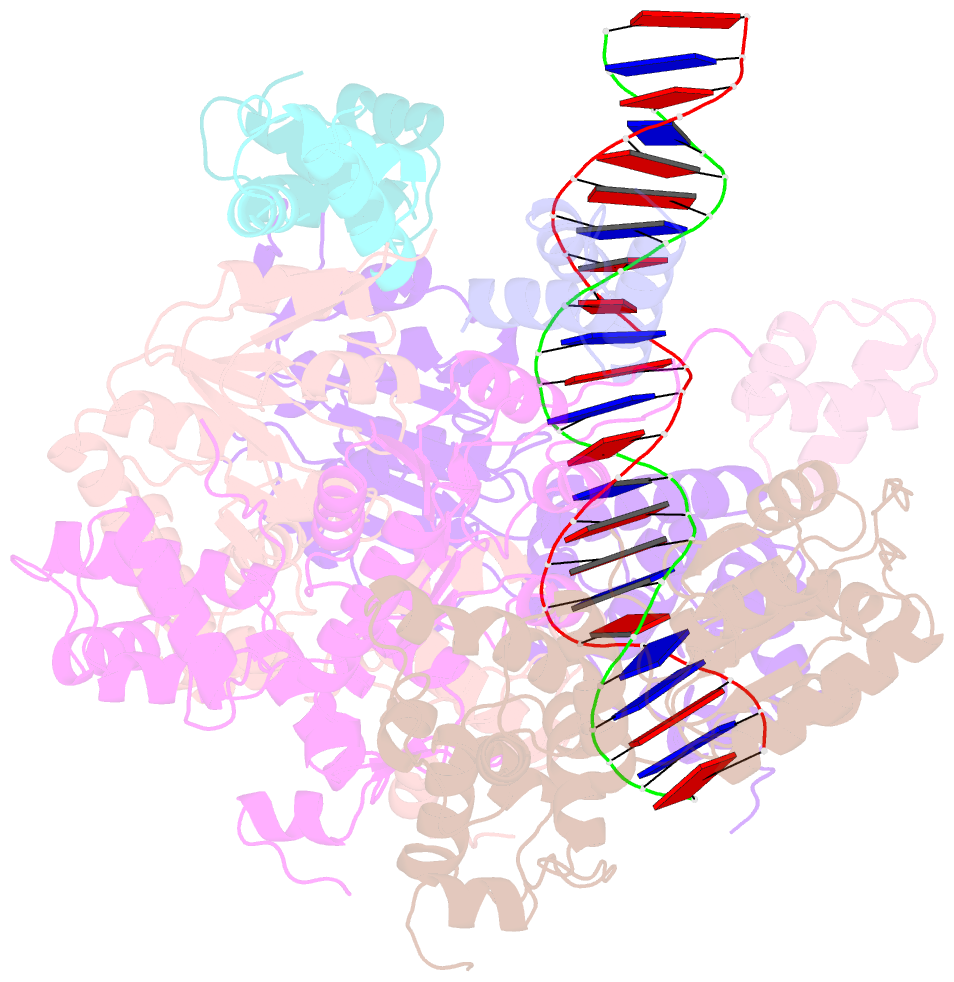
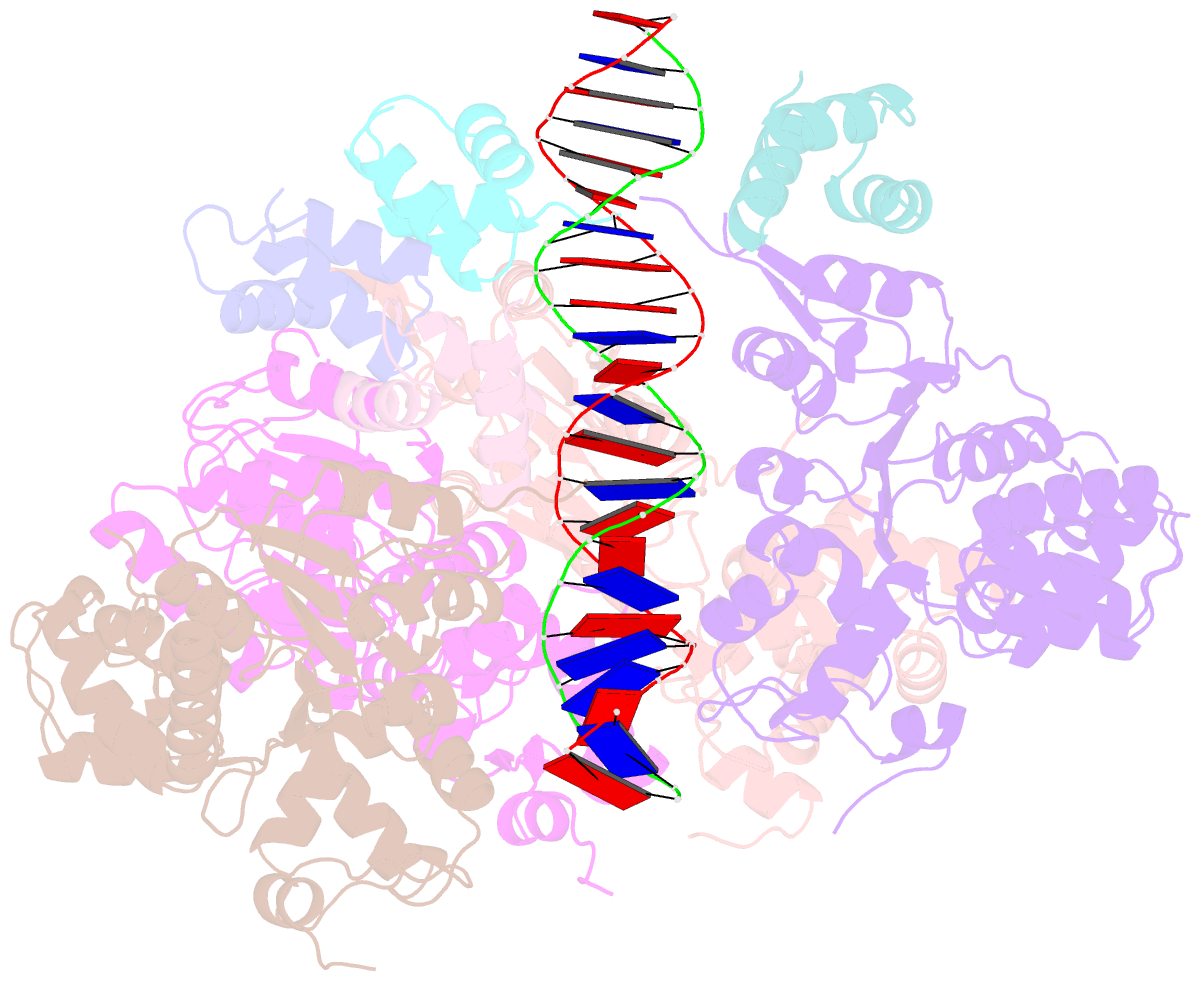
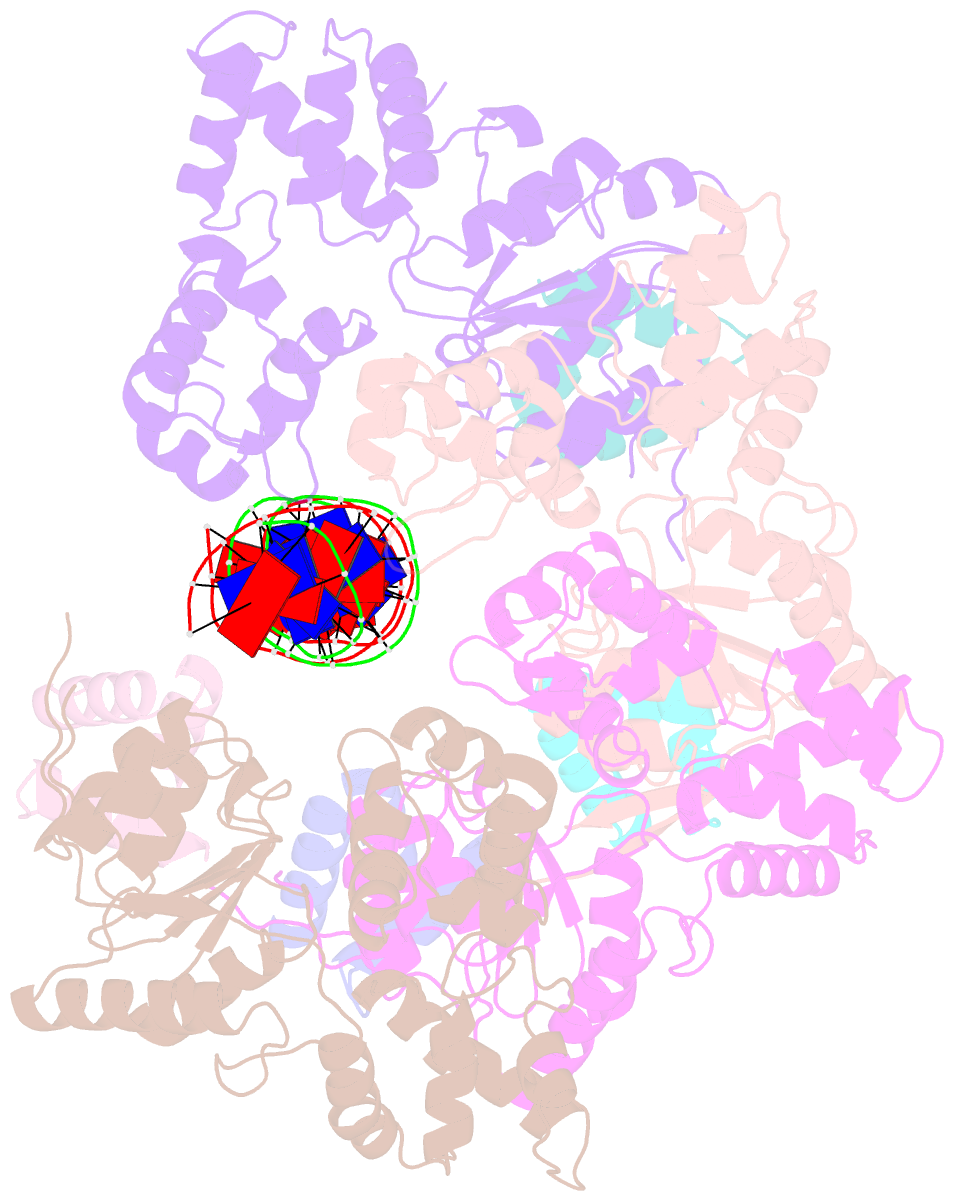
- Cryoem structure of dsDNA-ruvb-ruva domain3 complex
- Reference
- Zhang X, Zhou Z, Dai L, Chao Y, Liu Z, Huang M, Qu Q, Lin Z (2023): "Cryo-EM structure of the RuvAB-Holliday junction intermediate complex from Pseudomonas aeruginosa." Front Plant Sci, 14, 1139106. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1139106.
- Abstract
- Holliday junction (HJ) is a four-way structured DNA intermediate in homologous recombination. In bacteria, the HJ-specific binding protein RuvA and the motor protein RuvB together form the RuvAB complex to catalyze HJ branch migration. Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa, Pa) is a ubiquitous opportunistic bacterial pathogen that can cause serious infection in a variety of host species, including vertebrate animals, insects and plants. Here, we describe the cryo-Electron Microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the RuvAB-HJ intermediate complex from P. aeruginosa. The structure shows that two RuvA tetramers sandwich HJ at the junction center and disrupt base pairs at the branch points of RuvB-free HJ arms. Eight RuvB subunits are recruited by the RuvA octameric core and form two open-rings to encircle two opposite HJ arms. Each RuvB subunit individually binds a RuvA domain III. The four RuvB subunits within the ring display distinct subdomain conformations, and two of them engage the central DNA duplex at both strands with their C-terminal β-hairpins. Together with the biochemical analyses, our structure implicates a potential mechanism of RuvB motor assembly onto HJ DNA.