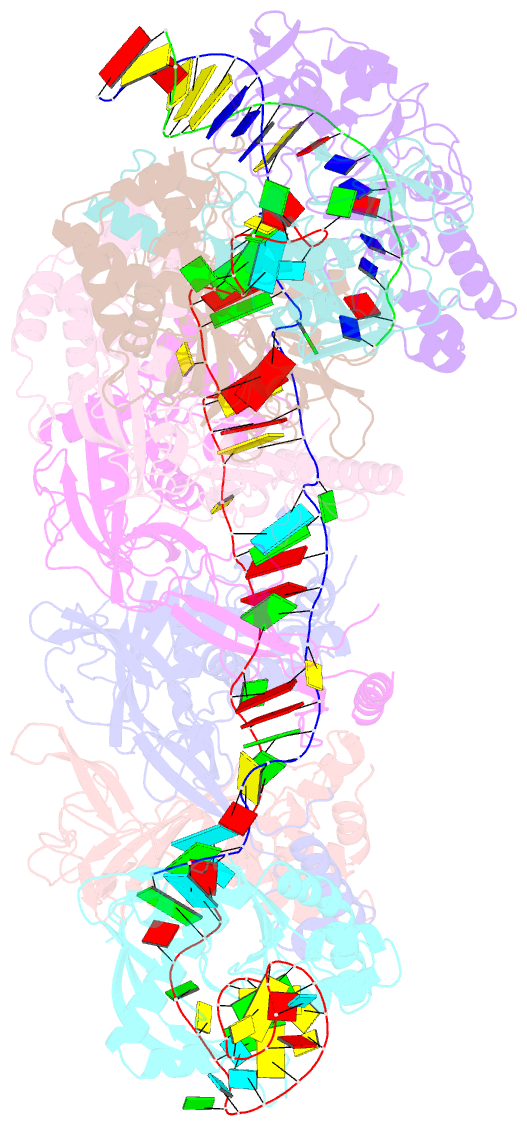
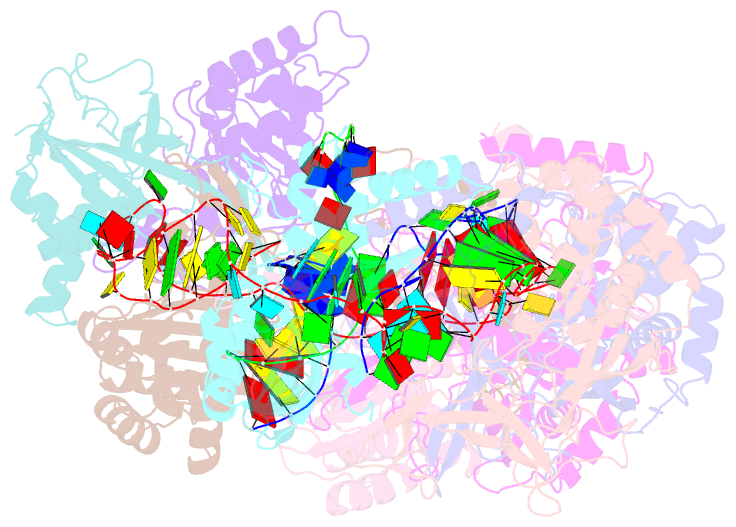
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7xg2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-RNA-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.8 Å)
- Summary
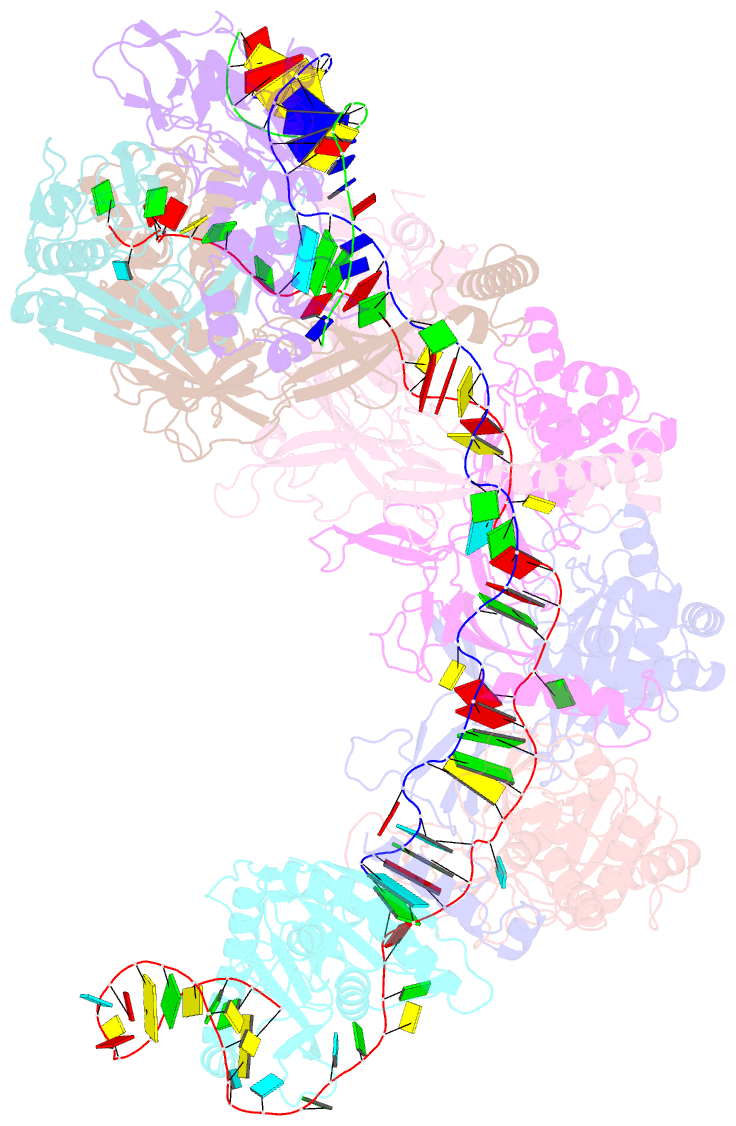
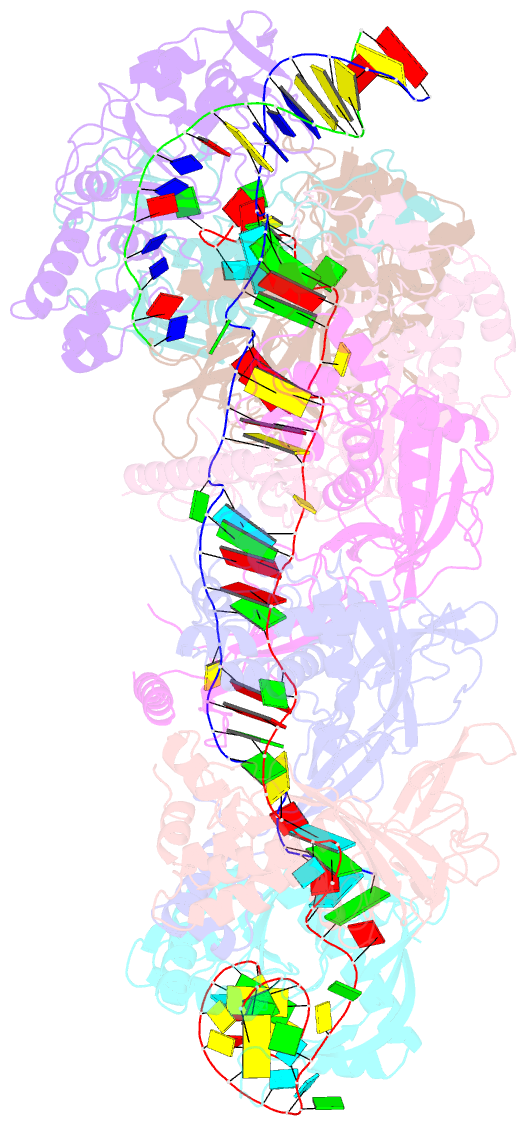
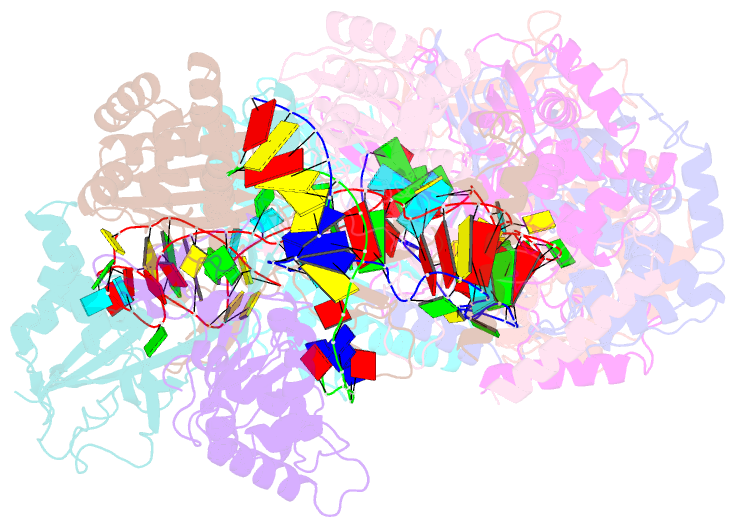
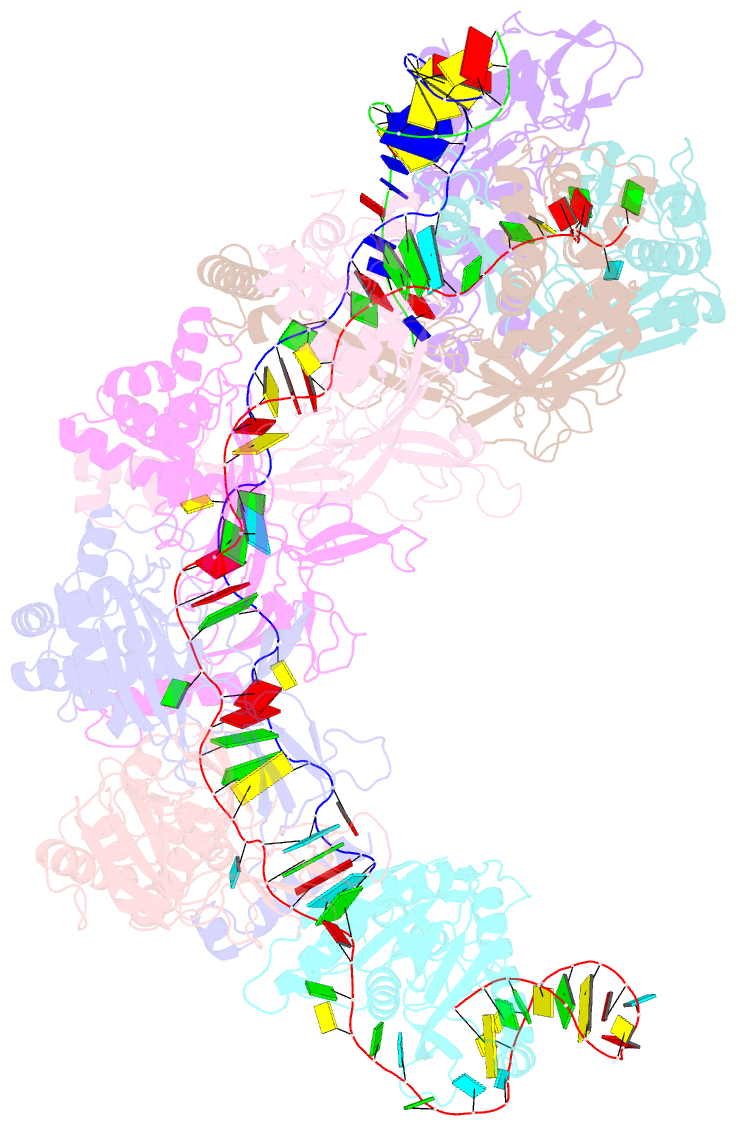
- Cryoem structure of type iv-a nts-nicked dsDNA bound csf-crrna ternary complex
- Reference
- Cui N, Zhang JT, Liu Y, Liu Y, Liu XY, Wang C, Huang H, Jia N (2023): "Type IV-A CRISPR-Csf complex: Assembly, dsDNA targeting, and CasDinG recruitment." Mol.Cell, 83, 2493-2508.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.05.036.
- Abstract
- Type IV CRISPR-Cas systems, which are primarily found on plasmids and exhibit a strong plasmid-targeting preference, are the only one of the six known CRISPR-Cas types for which the mechanistic details of their function remain unknown. Here, we provide high-resolution functional snapshots of type IV-A Csf complexes before and after target dsDNA binding, either in the absence or presence of CasDinG, revealing the mechanisms underlying CsfcrRNA complex assembly, "DWN" PAM-dependent dsDNA targeting, R-loop formation, and CasDinG recruitment. Furthermore, we establish that CasDinG, a signature DinG family helicase, harbors ssDNA-stimulated ATPase activity and ATP-dependent 5'-3' DNA helicase activity. In addition, we show that CasDinG unwinds the non-target strand (NTS) and target strand (TS) of target dsDNA from the CsfcrRNA complex. These molecular details advance our mechanistic understanding of type IV-A CRISPR-Csf function and should enable Csf complexes to be harnessed as genome-engineering tools for biotechnological applications.