Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7y3m; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA-DNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.723 Å)
- Summary
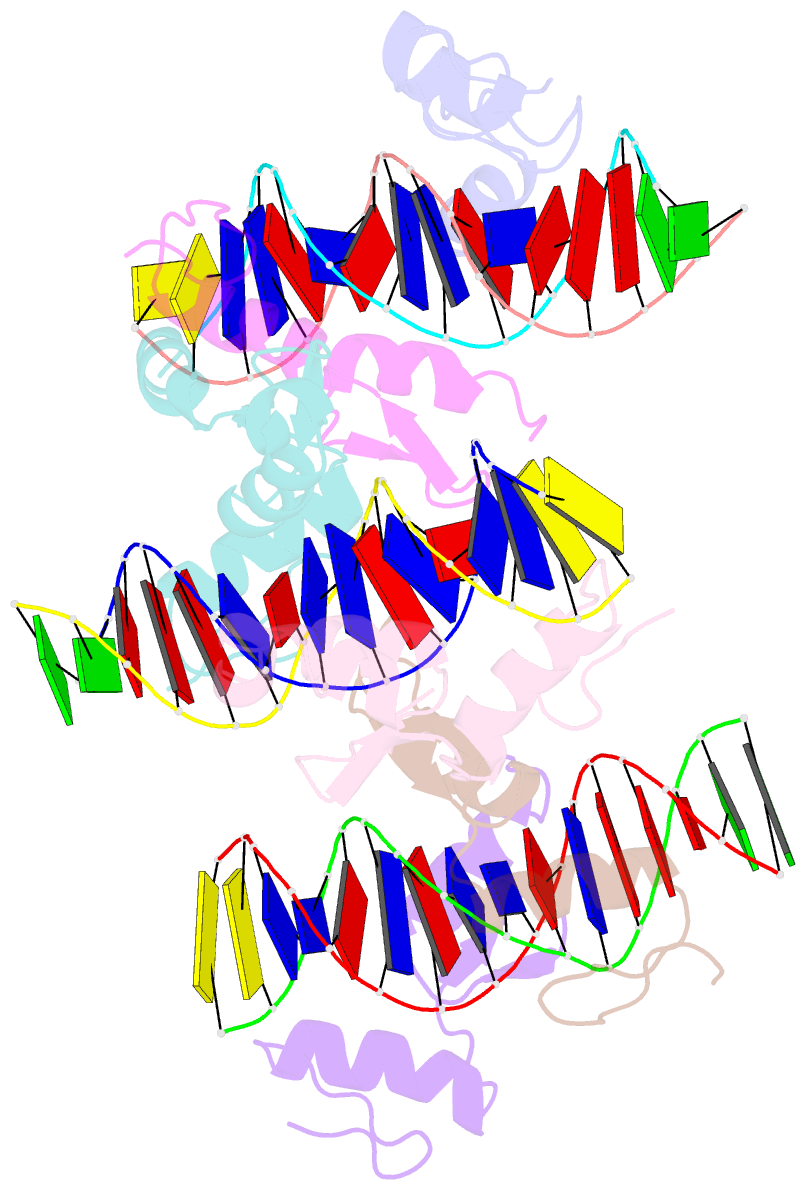
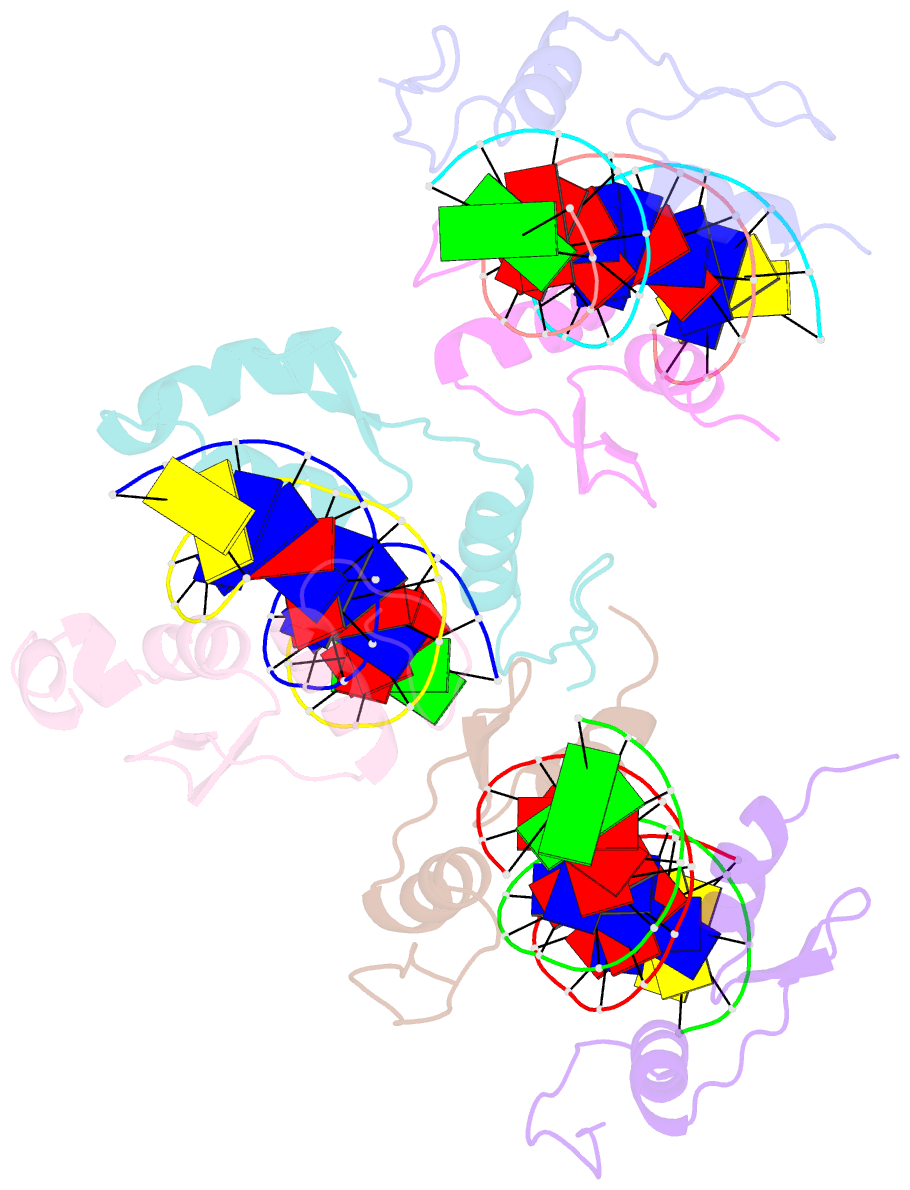
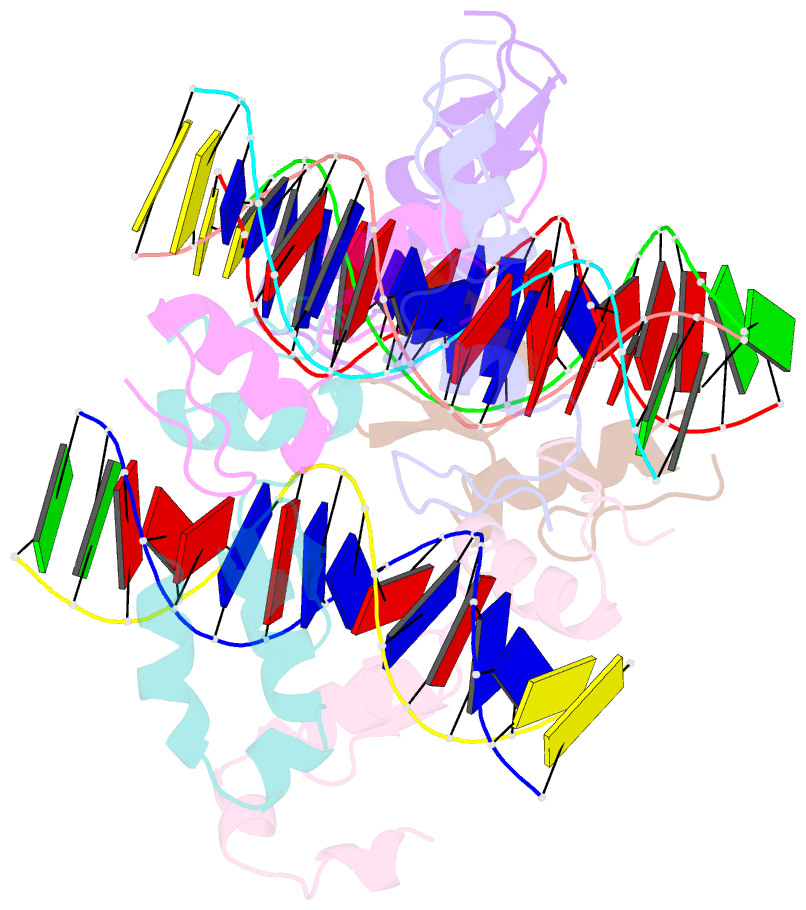
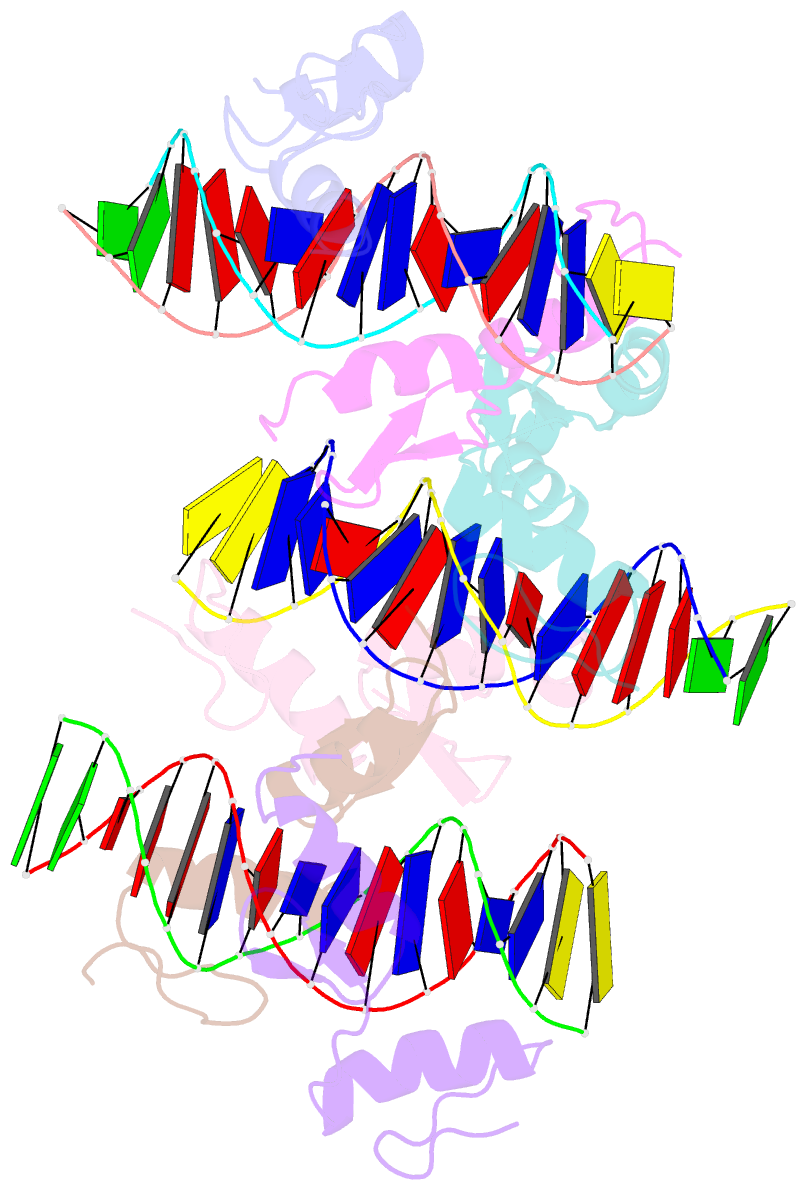
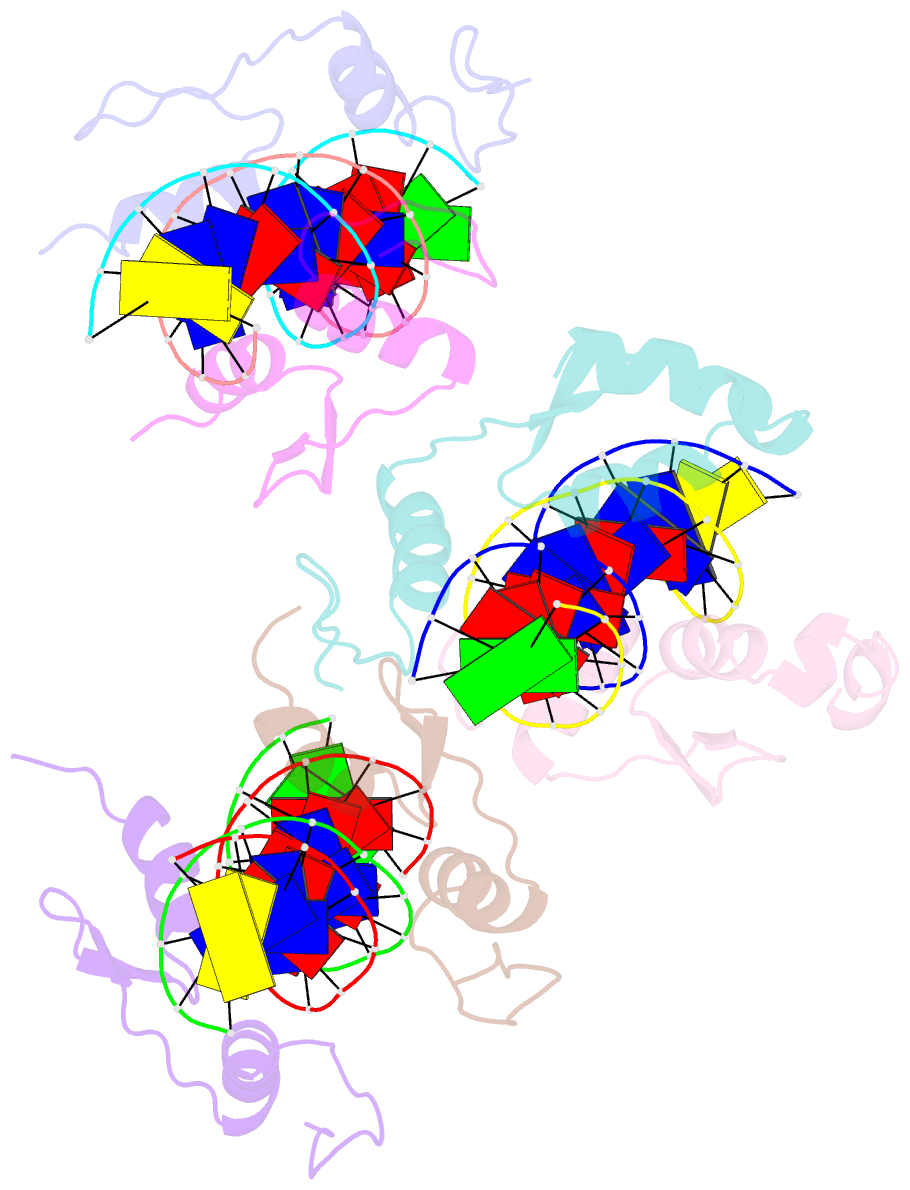
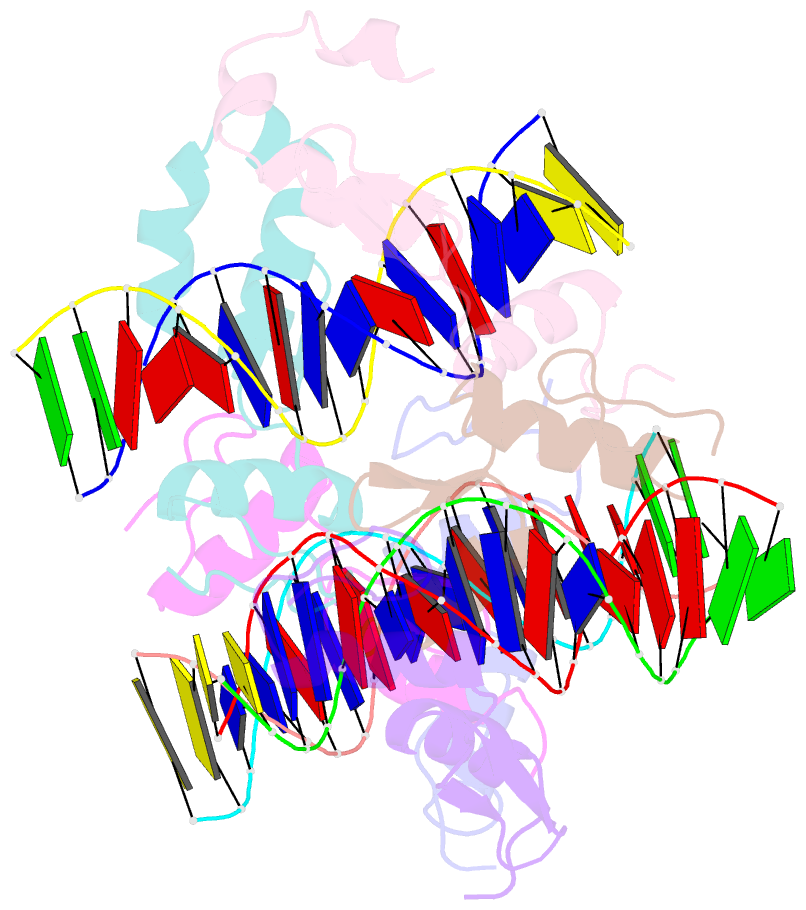
- Structure of sall4 zfc1 bound with 16 bp at-rich dsDNA
- Reference
- Ru W, Koga T, Wang X, Guo Q, Gearhart MD, Zhao S, Murphy M, Kawakami H, Corcoran D, Zhang J, Zhu Z, Yao X, Kawakami Y, Xu C (2022): "Structural studies of SALL family protein zinc finger cluster domains in complex with DNA reveal preferential binding to an AATA tetranucleotide motif." J.Biol.Chem., 298, 102607. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102607.
- Abstract
- The Spalt-like 4 transcription factor (SALL4) plays an essential role in controlling the pluripotent property of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) via binding to AT-rich regions of genomic DNA, but structural details on this binding interaction have not been fully characterized. Here we present crystal structures of the zinc finger cluster 4 (ZFC4) domain of SALL4 (SALL4ZFC4) bound with different double stranded DNAs containing a conserved AT-rich motif. In the structures, two zinc fingers of SALL4ZFC4 recognize an AATA tetranucleotide. We also solved the DNA-bound structures of SALL3ZFC4 and SALL4ZFC1. These structures illuminate a common preference for the AATA tetranucleotide shared by ZFC4 of SALL1, SALL3, and SALL4. Furthermore, our cell biology experiments demonstrate that the DNA-binding activity is essential for SALL4 function as DNA-binding defective mutants of mouse Sall4 failed to repress aberrant gene expression in Sall4-/- mESCs. Thus, these analyses provide new insights into the mechanisms of action underlying SALL family proteins in controlling cell fate via preferential targeting to AT-rich sites within genomic DNA during cell differentiation.