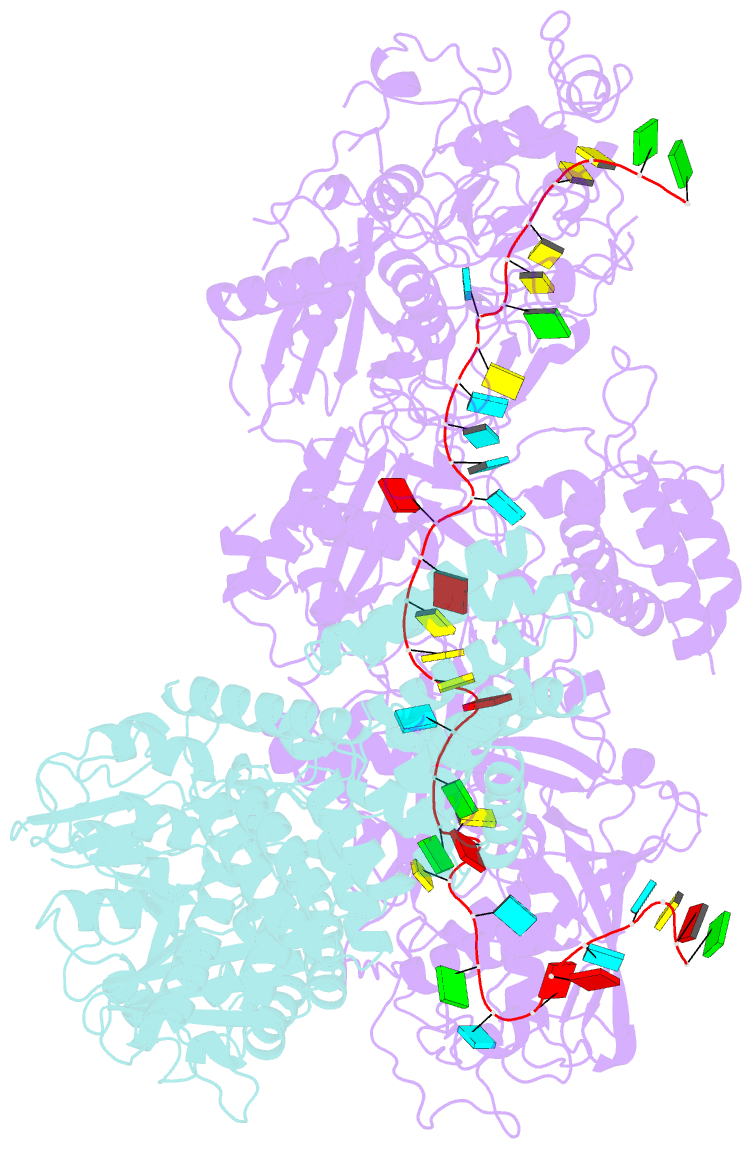
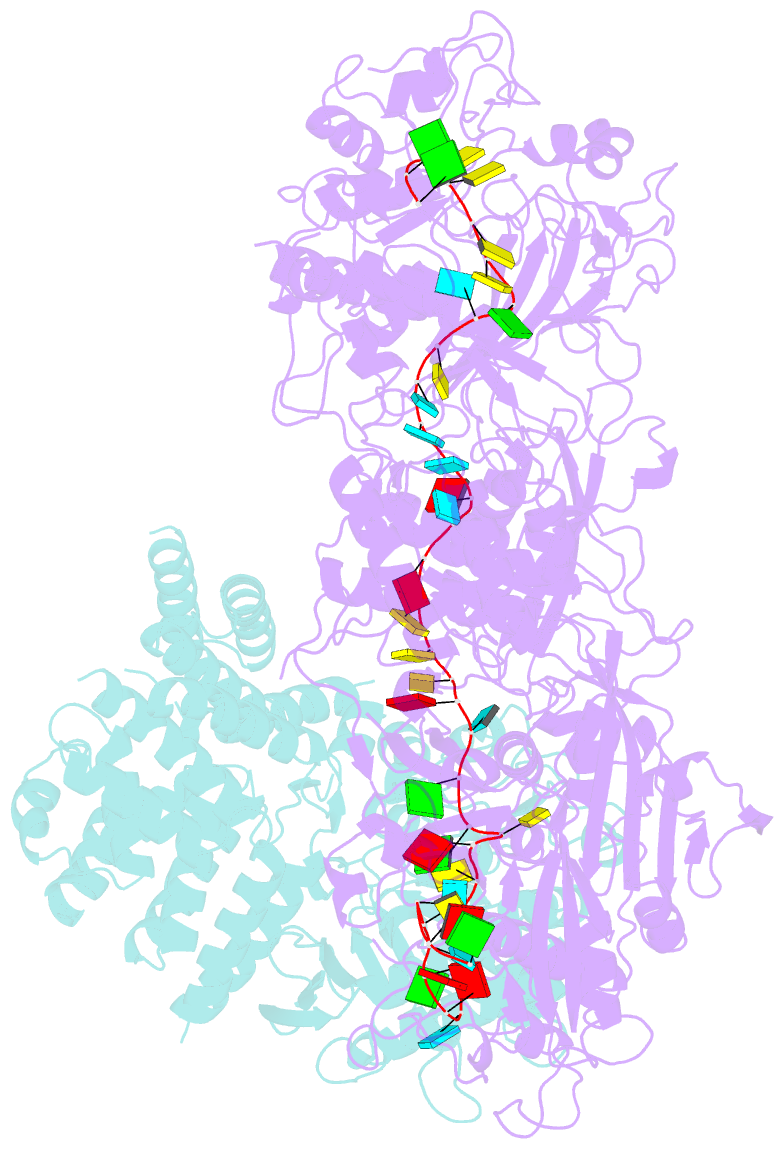
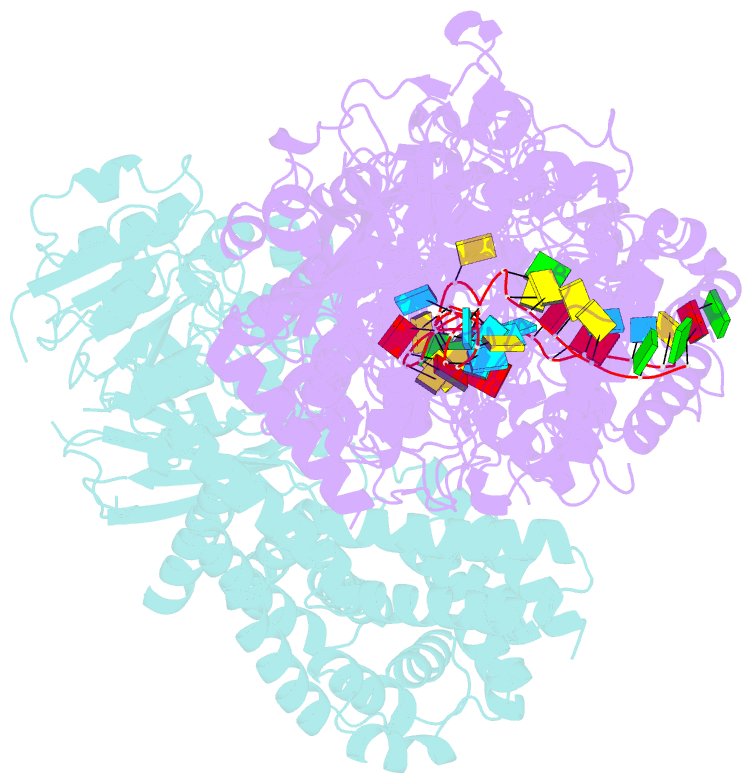
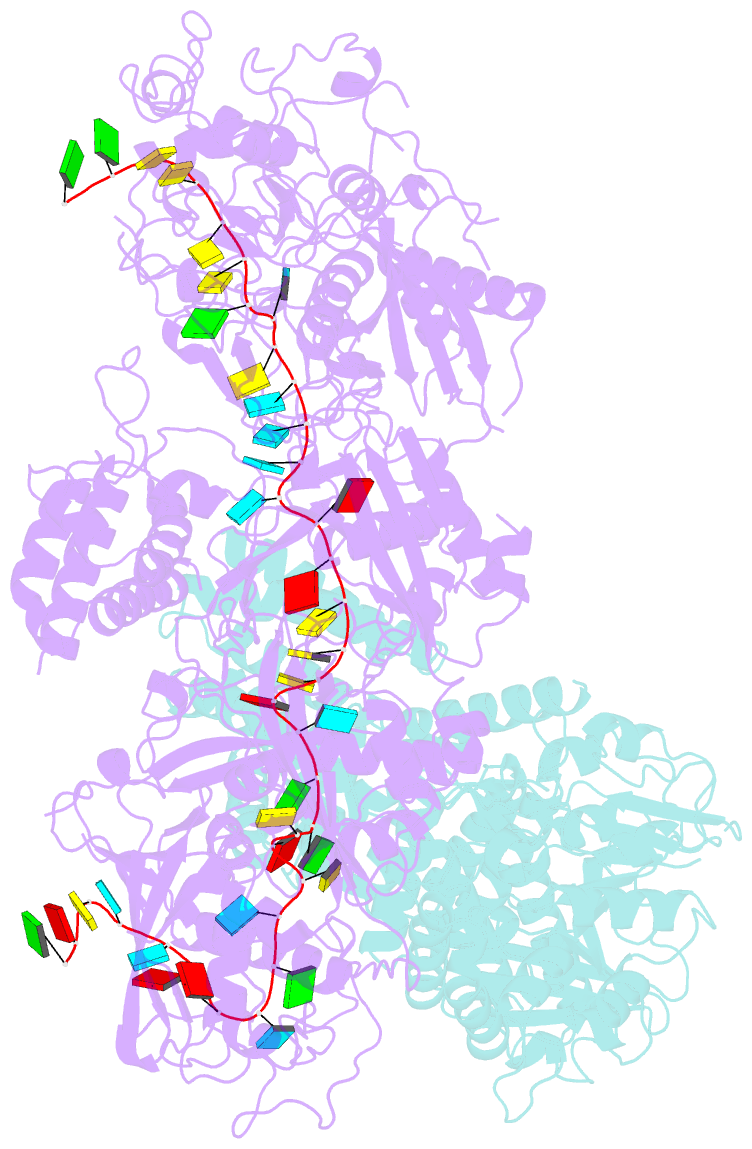
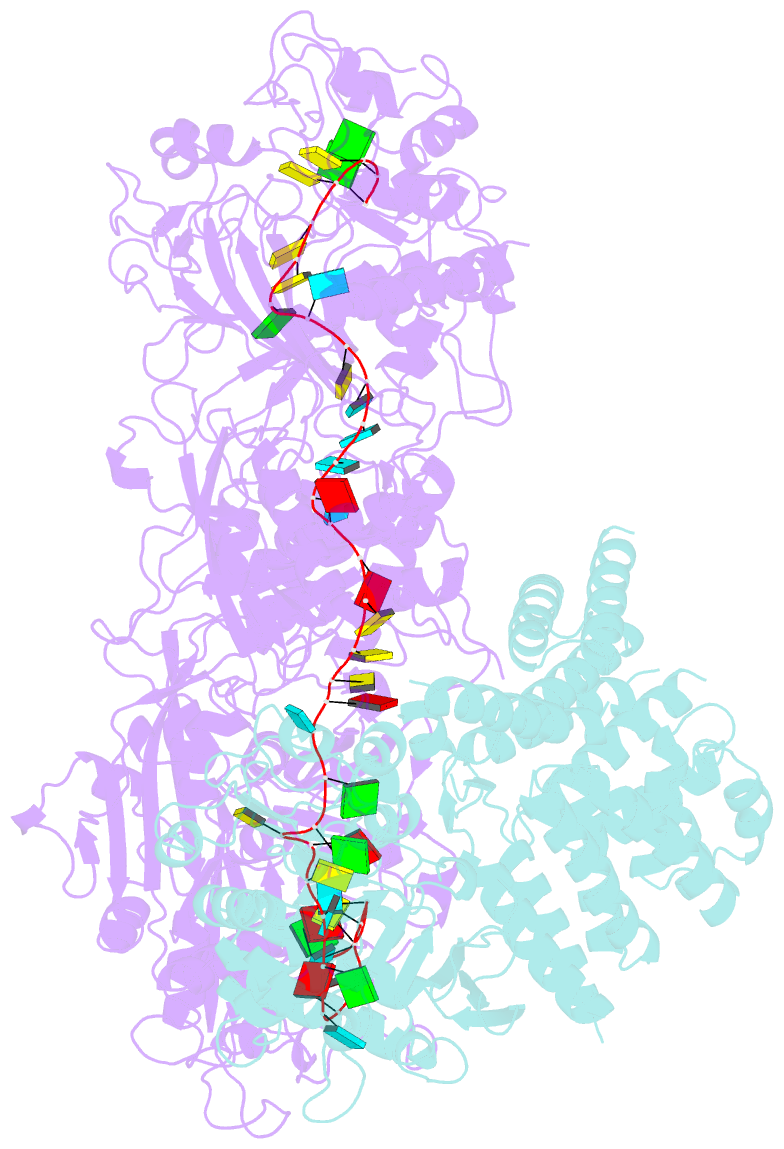
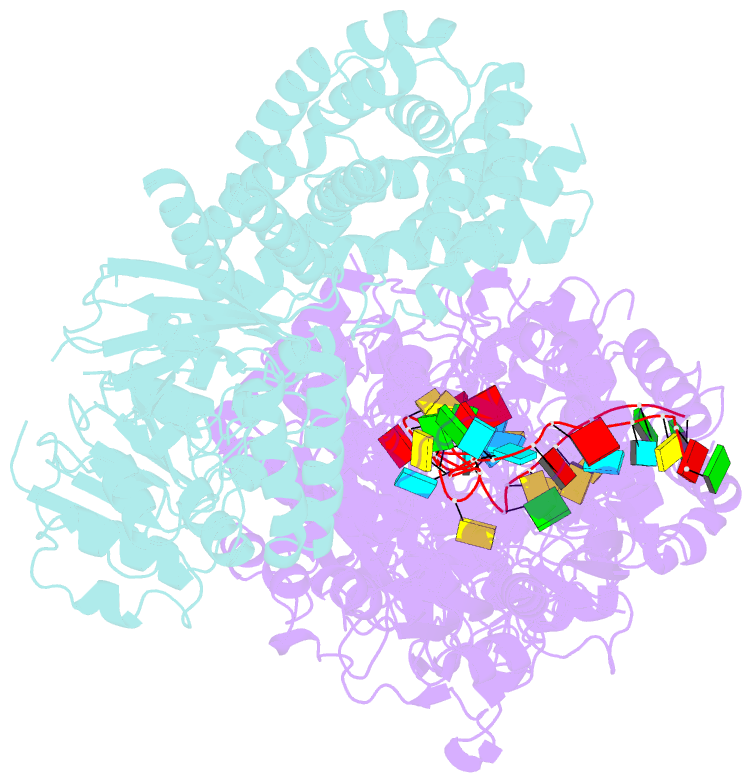
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7y84; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- structural protein-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.61 Å)
- Summary
- Cryoem structure of type iii-e crispr craspase gramp-crrna in complex with tpr-chat protease
- Reference
- Cui N, Zhang JT, Li Z, Liu XY, Wang C, Huang H, Jia N (2022): "Structural basis for the non-self RNA-activated protease activity of the type III-E CRISPR nuclease-protease Craspase." Nat Commun, 13, 7549. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-35275-5.
- Abstract
- The RNA-targeting type III-E CRISPR-gRAMP effector interacts with a caspase-like protease TPR-CHAT to form the CRISPR-guided caspase complex (Craspase), but their functional mechanism is unknown. Here, we report cryo-EM structures of the type III-E gRAMPcrRNA and gRAMPcrRNA-TPR-CHAT complexes, before and after either self or non-self RNA target binding, and elucidate the mechanisms underlying RNA-targeting and non-self RNA-induced protease activation. The associated TPR-CHAT adopted a distinct conformation upon self versus non-self RNA target binding, with nucleotides at positions -1 and -2 of the CRISPR-derived RNA (crRNA) serving as a sensor. Only binding of the non-self RNA target activated the TPR-CHAT protease, leading to cleavage of Csx30 protein. Furthermore, TPR-CHAT structurally resembled eukaryotic separase, but with a distinct mechanism for protease regulation. Our findings should facilitate the development of gRAMP-based RNA manipulation tools, and advance our understanding of the virus-host discrimination process governed by a nuclease-protease Craspase during type III-E CRISPR-Cas immunity.