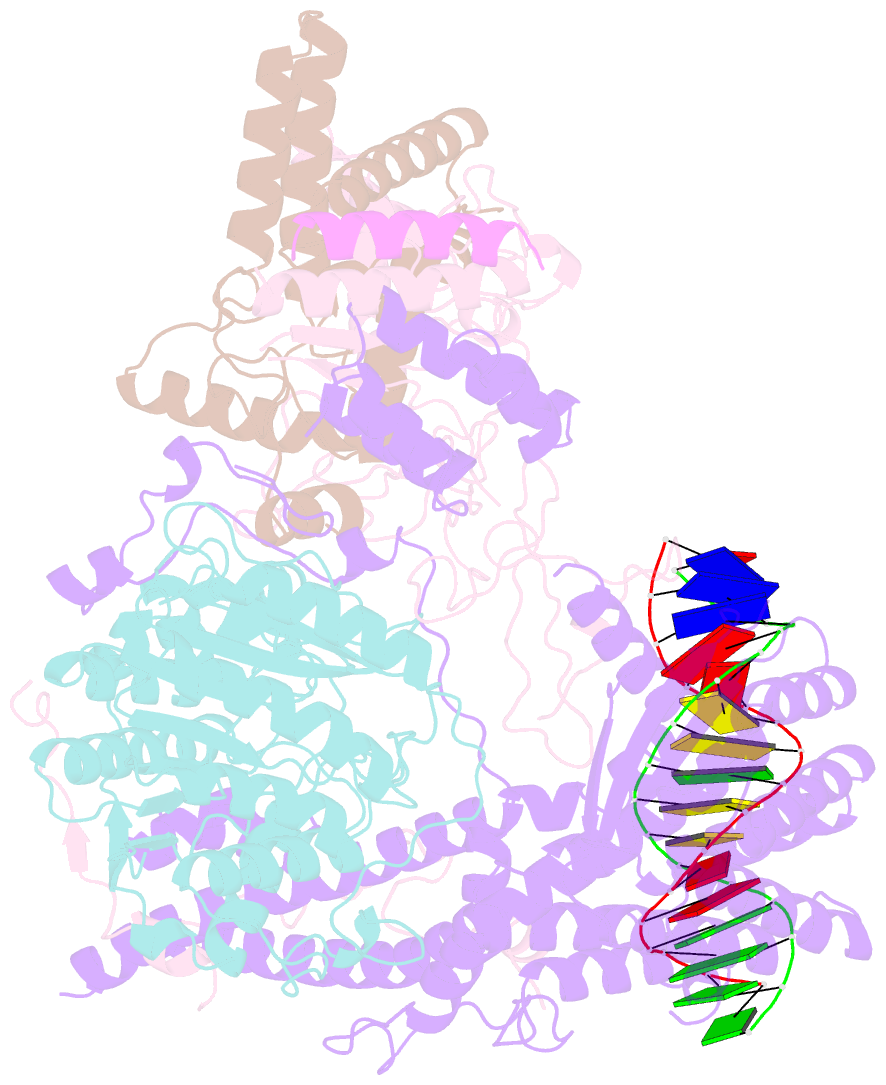
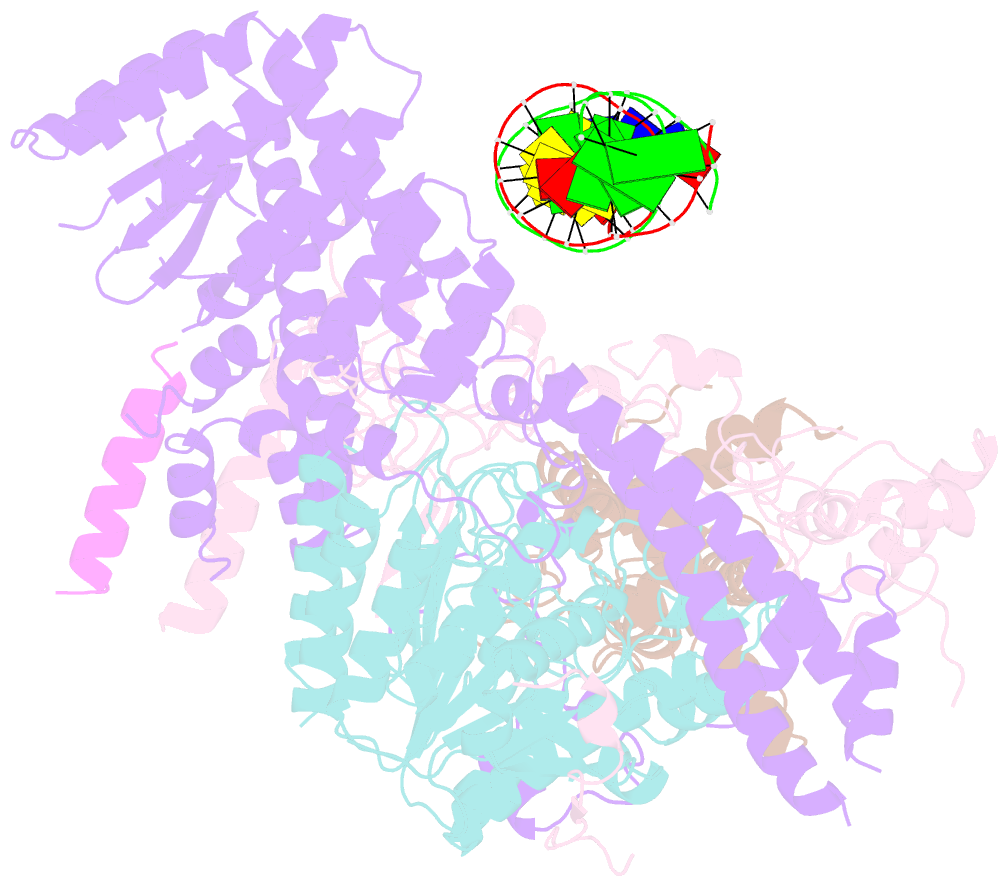
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7yi2; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- gene regulation
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.4 Å)
- Summary
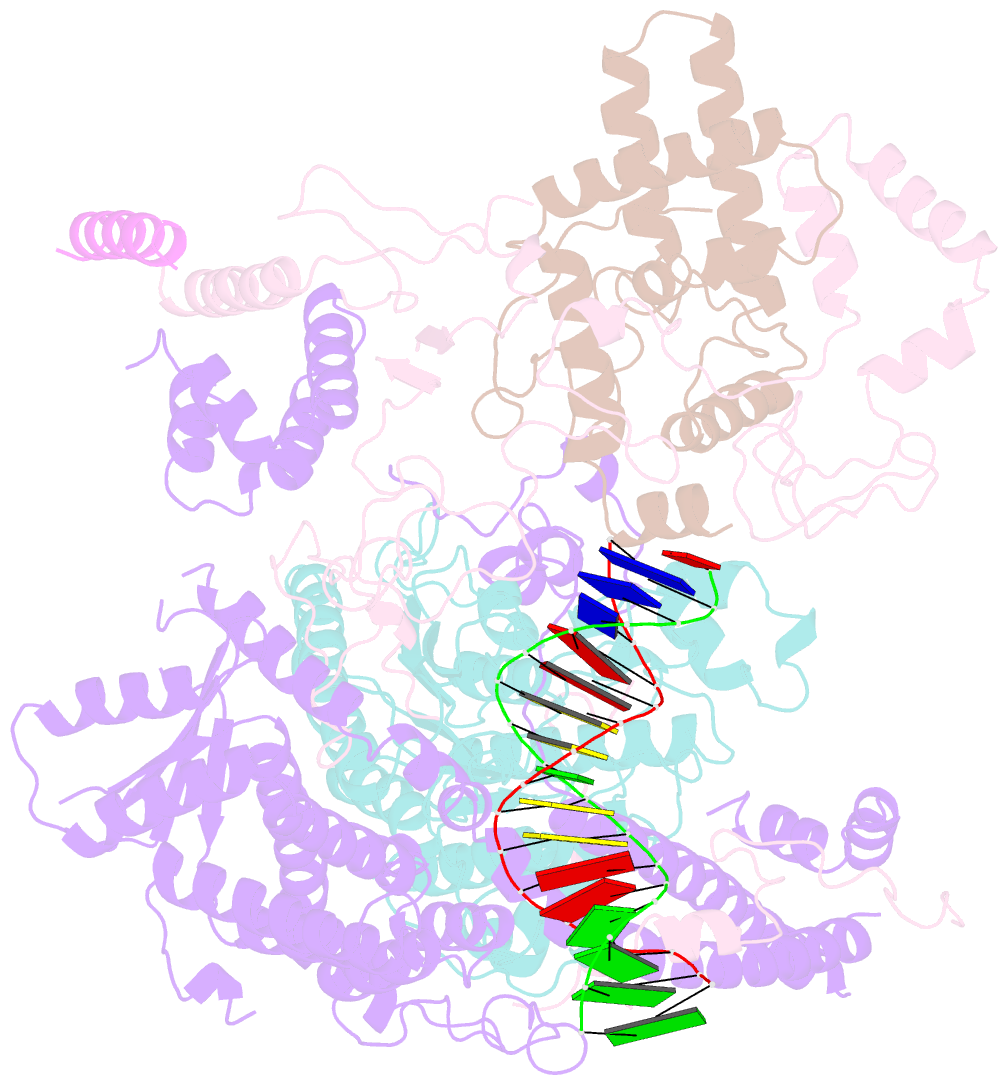
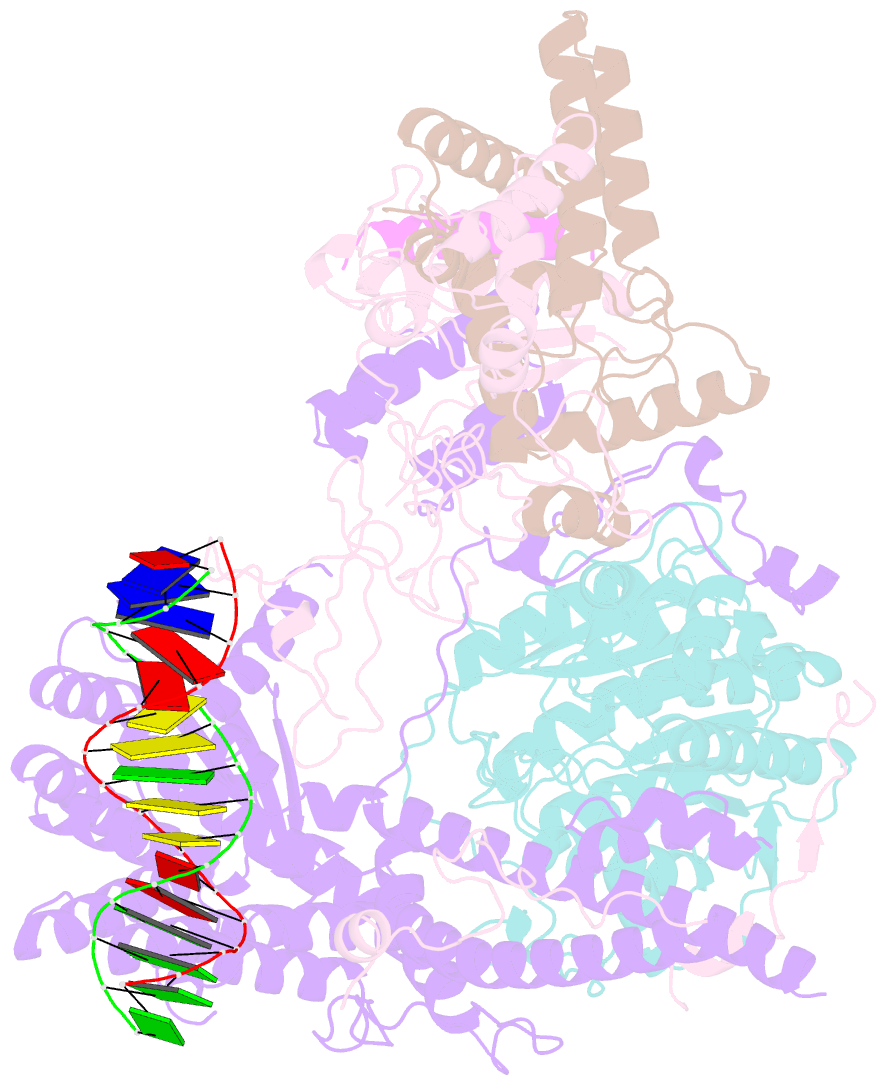
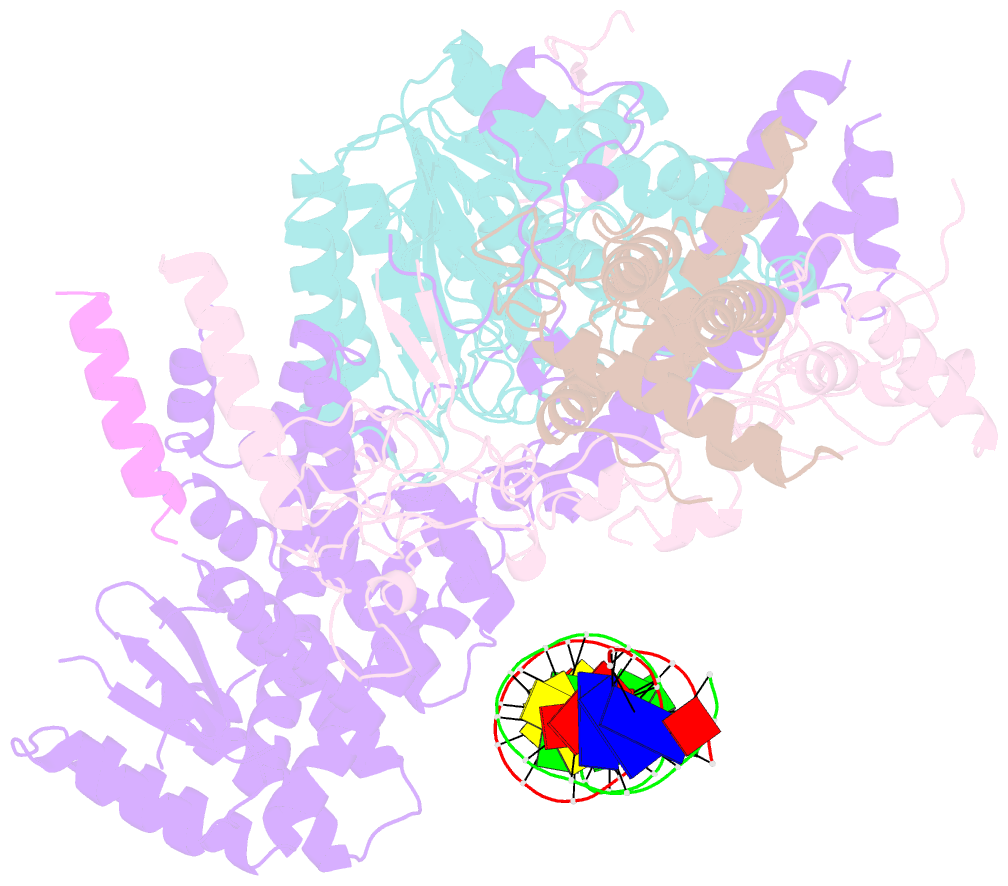
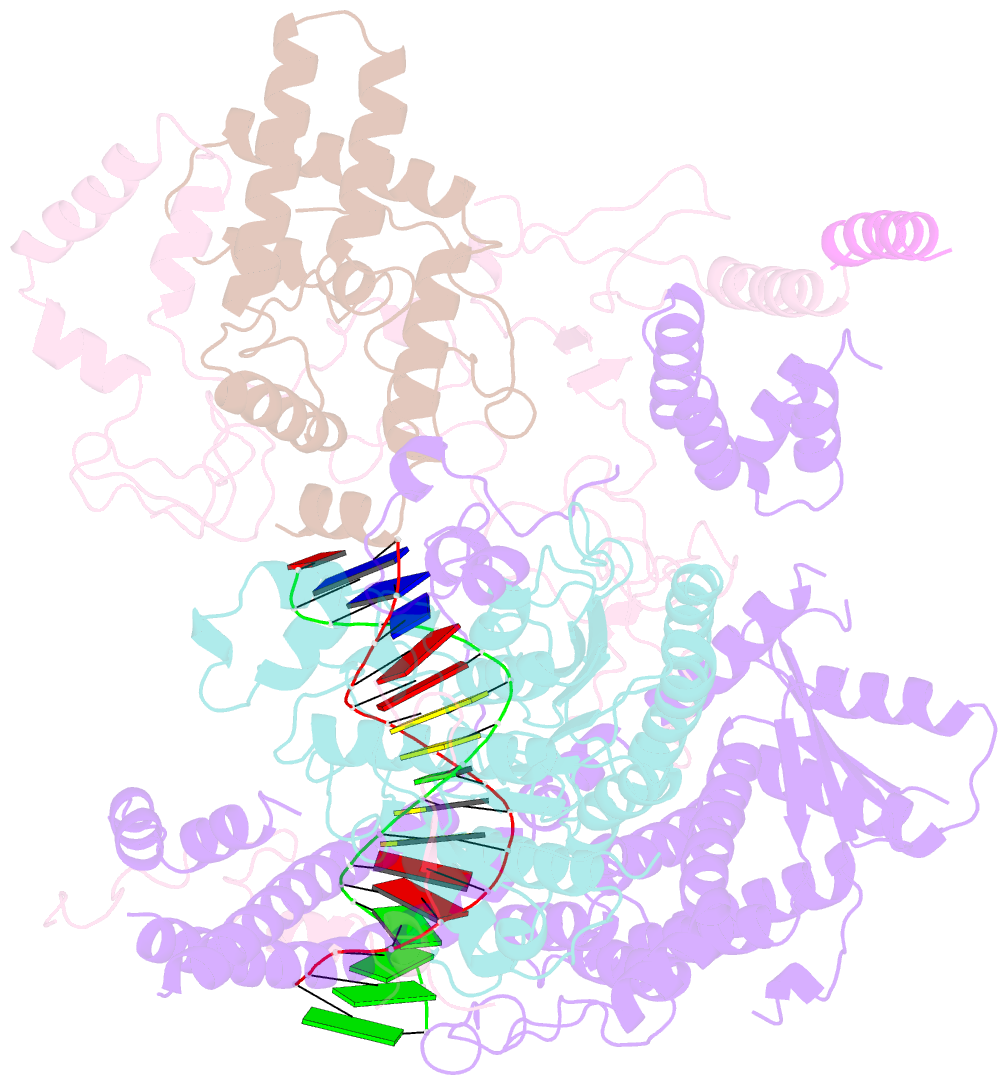
- cryo-EM structure of rpd3s in loose-state rpd3s-ncp complex
- Reference
- Guan H, Wang P, Zhang P, Ruan C, Ou Y, Peng B, Zheng X, Lei J, Li B, Yan C, Li H (2023): "Diverse modes of H3K36me3-guided nucleosomal deacetylation by Rpd3S." Nature, 620, 669-675. doi: 10.1038/s41586-023-06349-1.
- Abstract
- Context-dependent dynamic histone modifications constitute a key epigenetic mechanism in gene regulation1-4. The Rpd3 small (Rpd3S) complex recognizes histone H3 trimethylation on lysine 36 (H3K36me3) and deacetylates histones H3 and H4 at multiple sites across transcribed regions5-7. Here we solved the cryo-electron microscopy structures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Rpd3S in its free and H3K36me3 nucleosome-bound states. We demonstrated a unique architecture of Rpd3S, in which two copies of Eaf3-Rco1 heterodimers are asymmetrically assembled with Rpd3 and Sin3 to form a catalytic core complex. Multivalent recognition of two H3K36me3 marks, nucleosomal DNA and linker DNAs by Eaf3, Sin3 and Rco1 positions the catalytic centre of Rpd3 next to the histone H4 N-terminal tail for deacetylation. In an alternative catalytic mode, combinatorial readout of unmethylated histone H3 lysine 4 and H3K36me3 by Rco1 and Eaf3 directs histone H3-specific deacetylation except for the registered histone H3 acetylated lysine 9. Collectively, our work illustrates dynamic and diverse modes of multivalent nucleosomal engagement and methylation-guided deacetylation by Rpd3S, highlighting the exquisite complexity of epigenetic regulation with delicately designed multi-subunit enzymatic machineries in transcription and beyond.