Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 7ypb; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- transcription--DNA-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.48 Å)
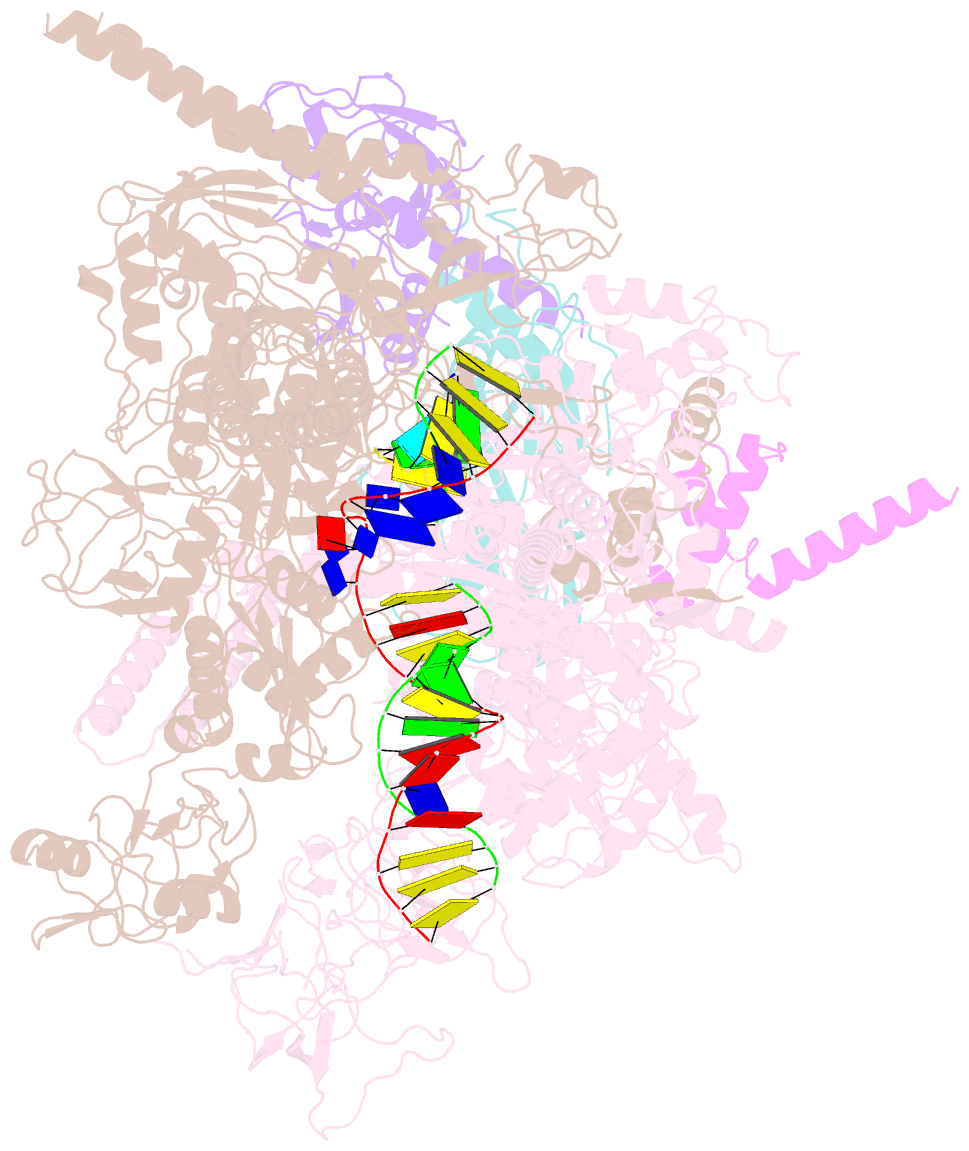
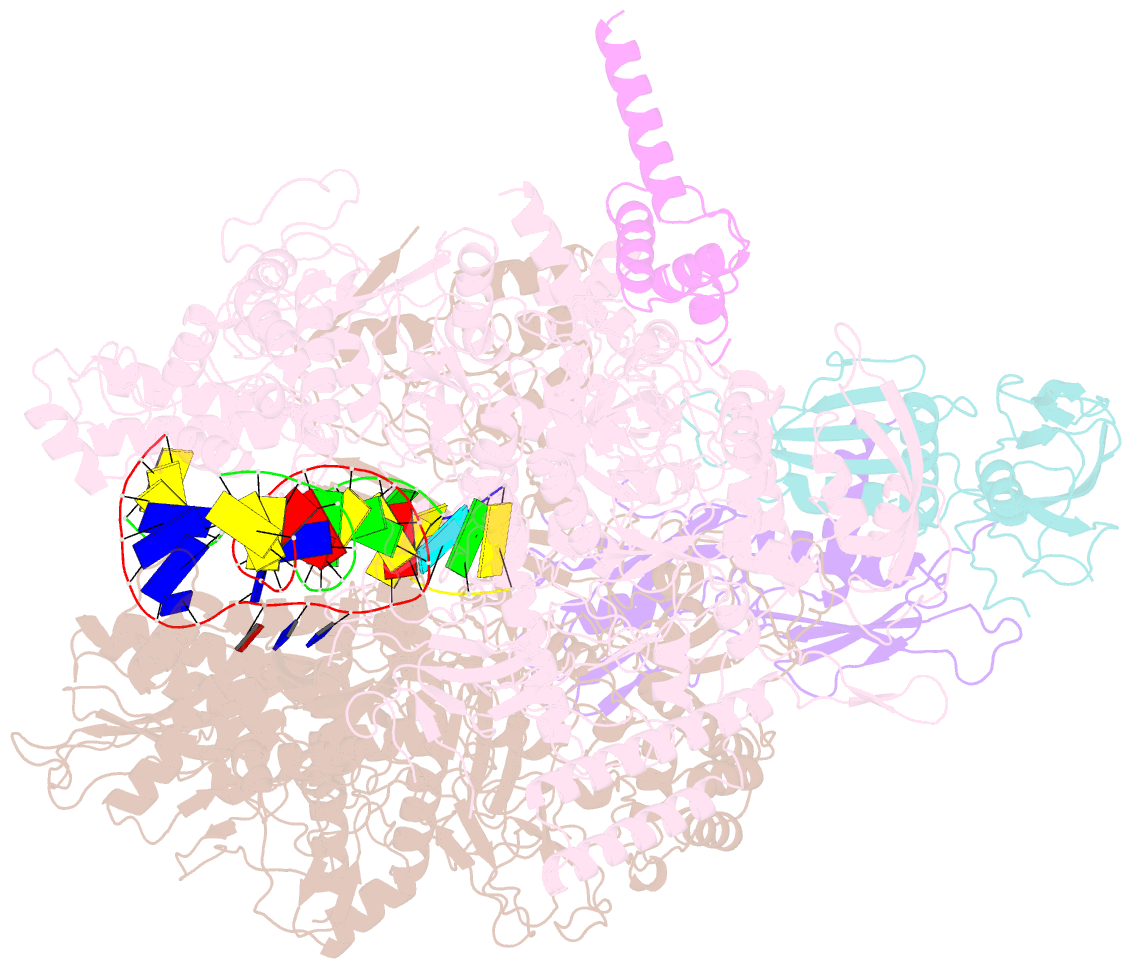
- Summary
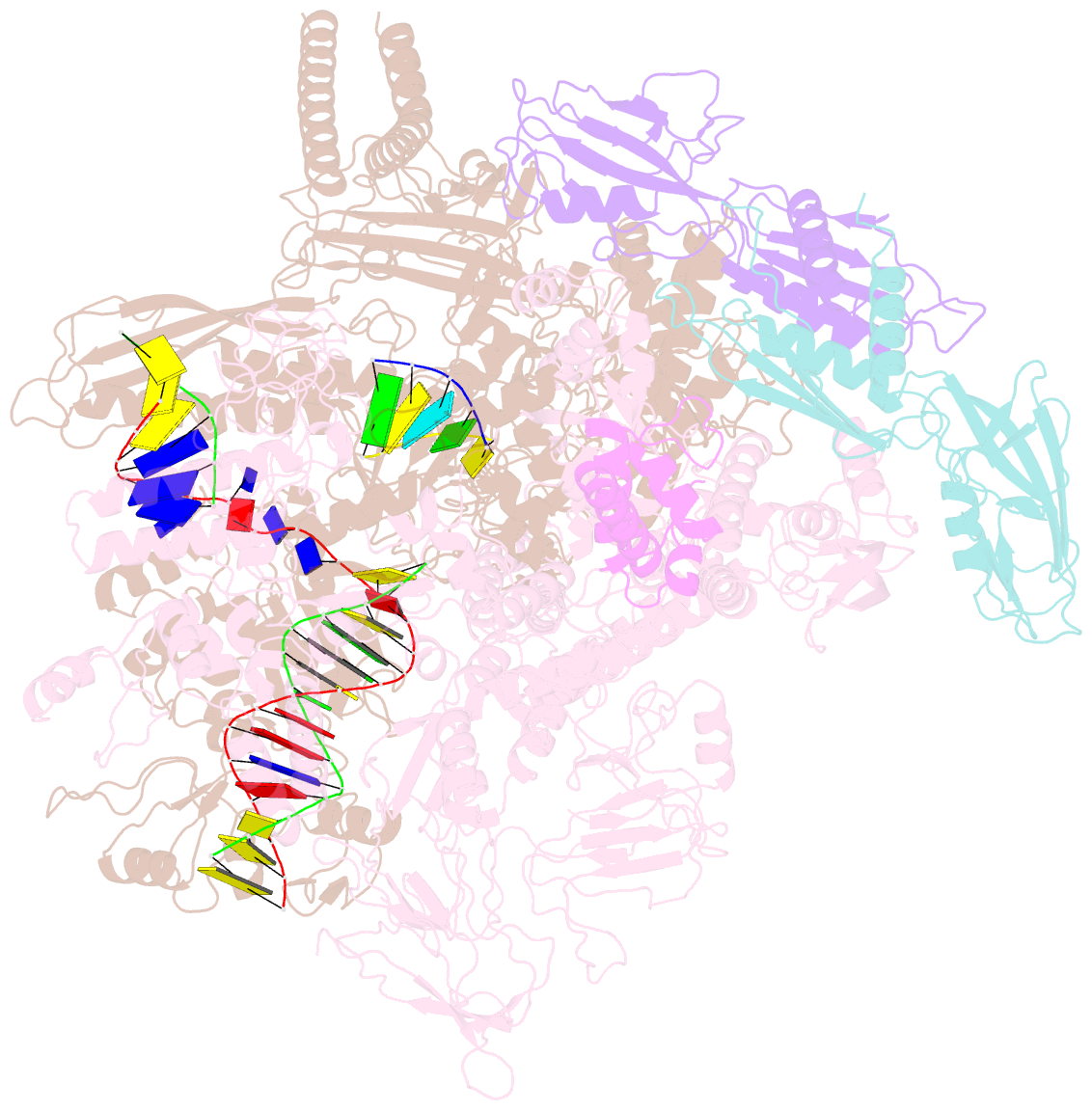
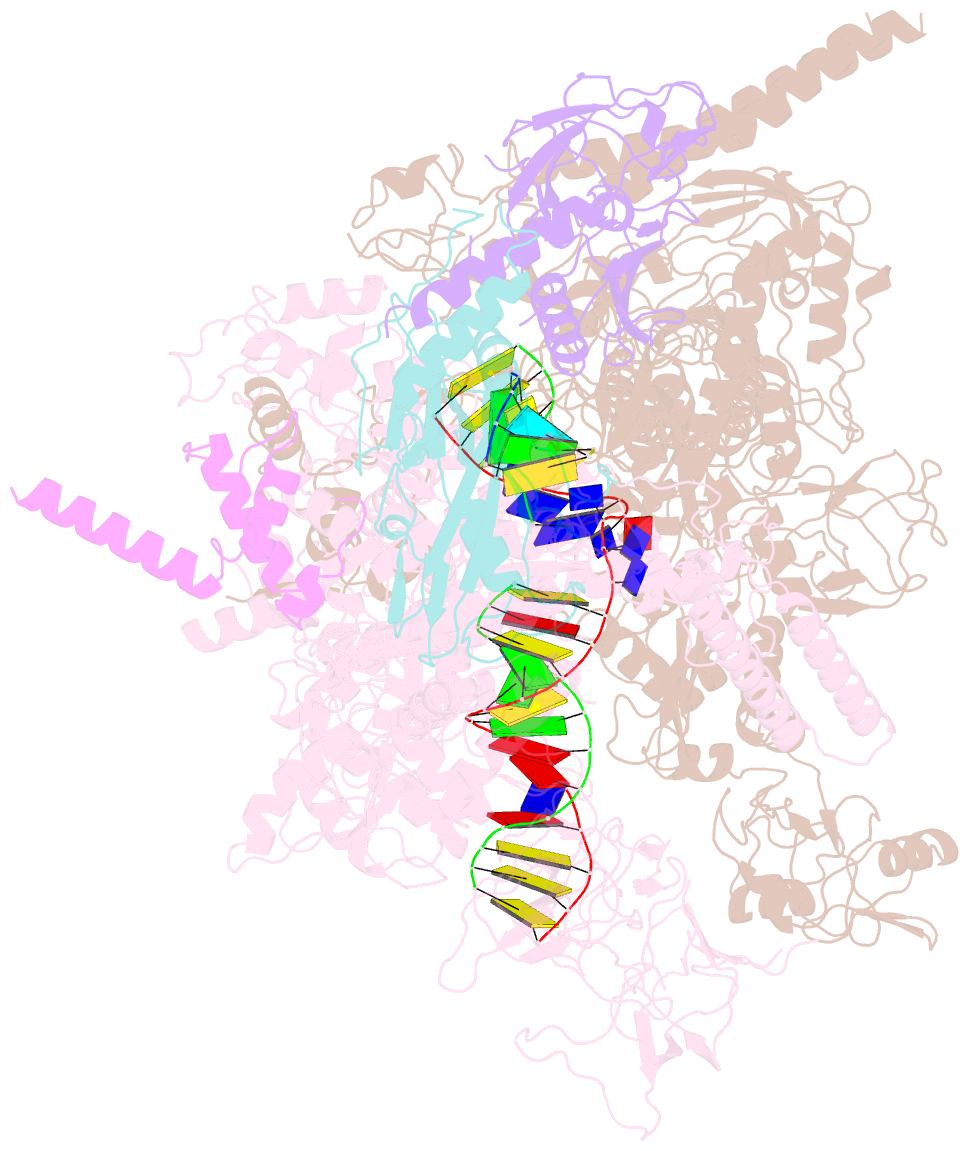
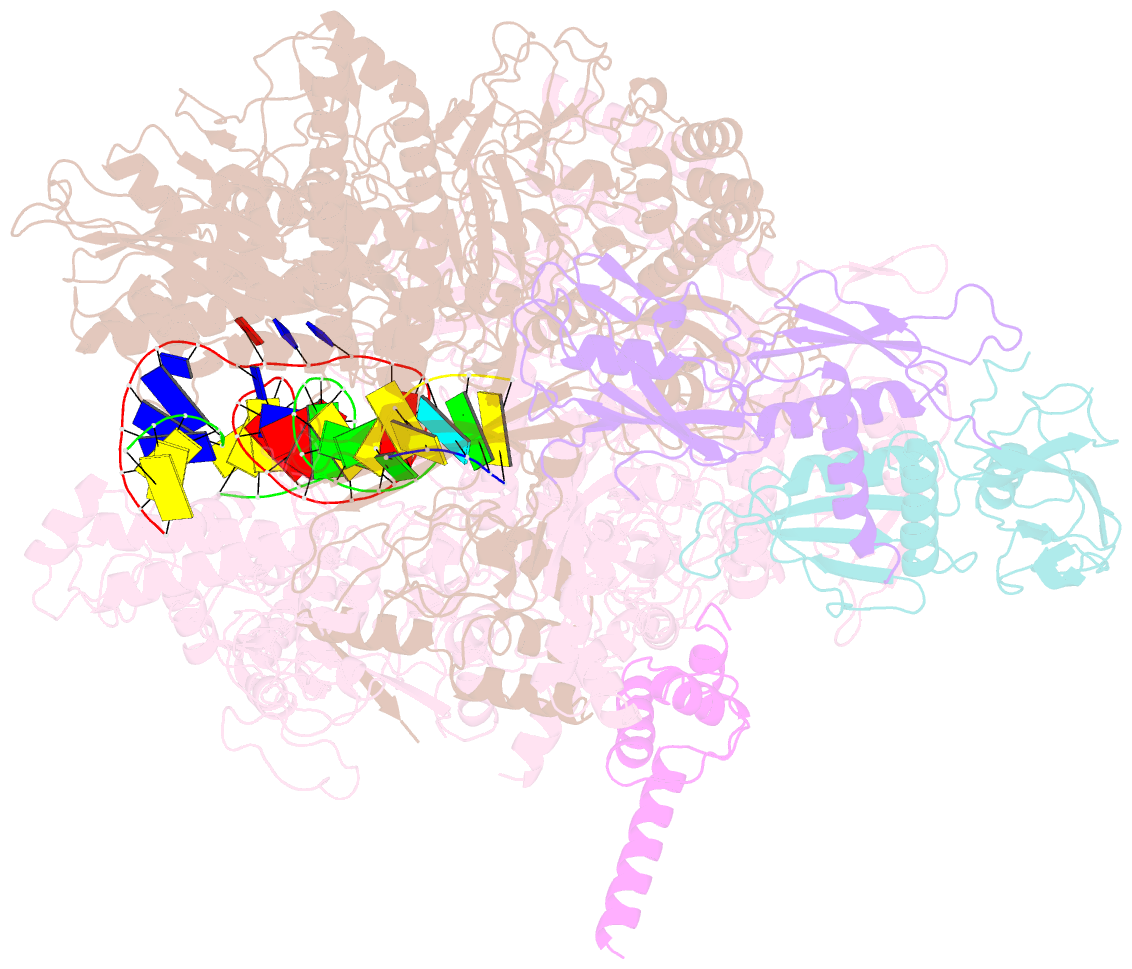
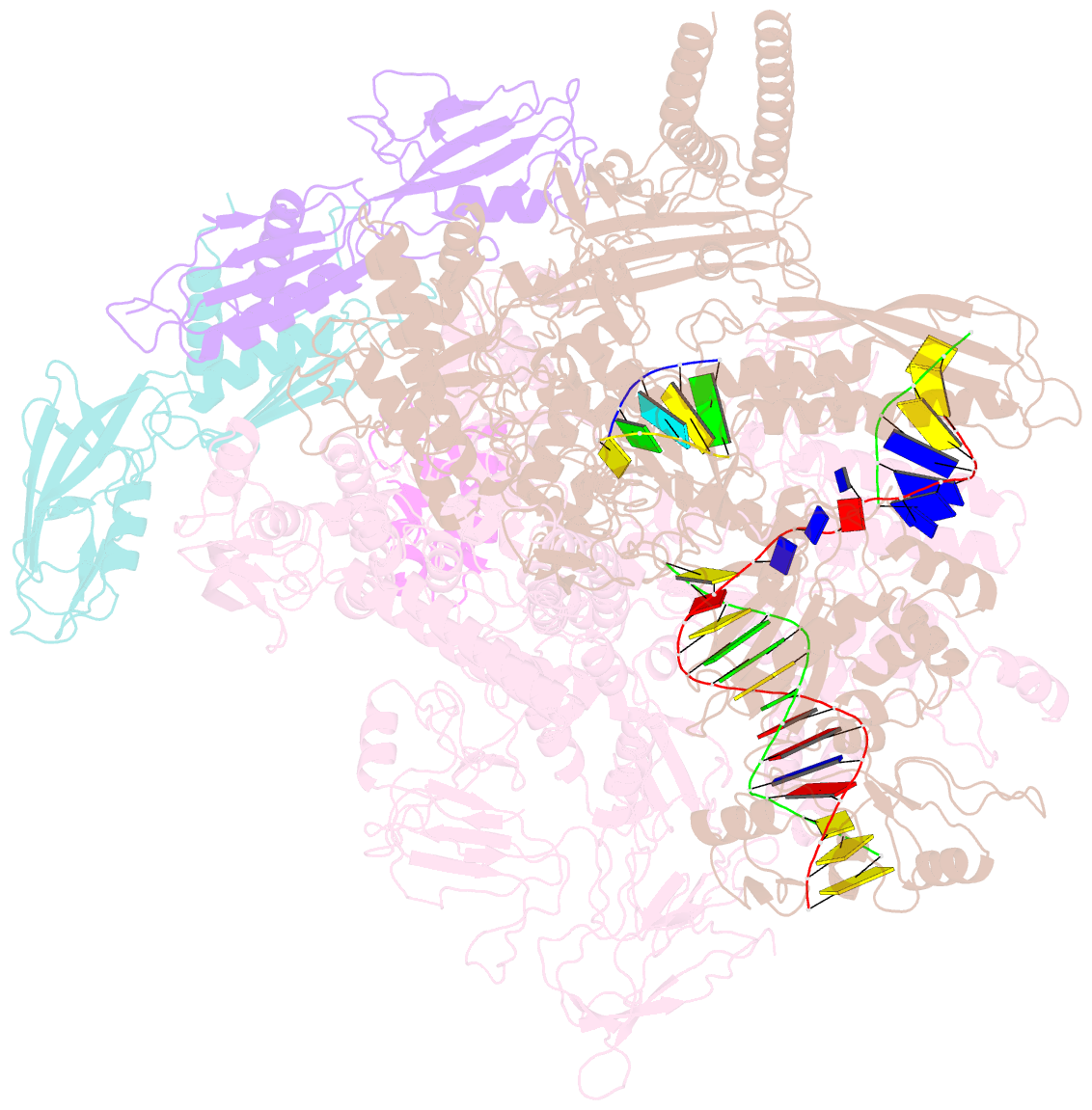
- cryo-EM structure of escherichia coli release complex of transcription termination (ttc-release)
- Reference
- You L, Omollo EO, Yu C, Mooney RA, Shi J, Shen L, Wu X, Wen A, He D, Zeng Y, Feng Y, Landick R, Zhang Y (2023): "Structural basis for intrinsic transcription termination." Nature, 613, 783-789. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05604-1.
- Abstract
- Efficient and accurate termination is required for gene transcription in all living organisms1,2. Cellular RNA polymerases in both bacteria and eukaryotes can terminate their transcription through a factor-independent termination pathway3,4-called intrinsic termination transcription in bacteria-in which RNA polymerase recognizes terminator sequences, stops nucleotide addition and releases nascent RNA spontaneously. Here we report a set of single-particle cryo-electron microscopy structures of Escherichia coli transcription intrinsic termination complexes representing key intermediate states of the event. The structures show how RNA polymerase pauses at terminator sequences, how the terminator RNA hairpin folds inside RNA polymerase, and how RNA polymerase rewinds the transcription bubble to release RNA and then DNA. These macromolecular snapshots define a structural mechanism for bacterial intrinsic termination and a pathway for RNA release and DNA collapse that is relevant for factor-independent termination by all RNA polymerases.