Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8a5q; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.3 Å)
- Summary
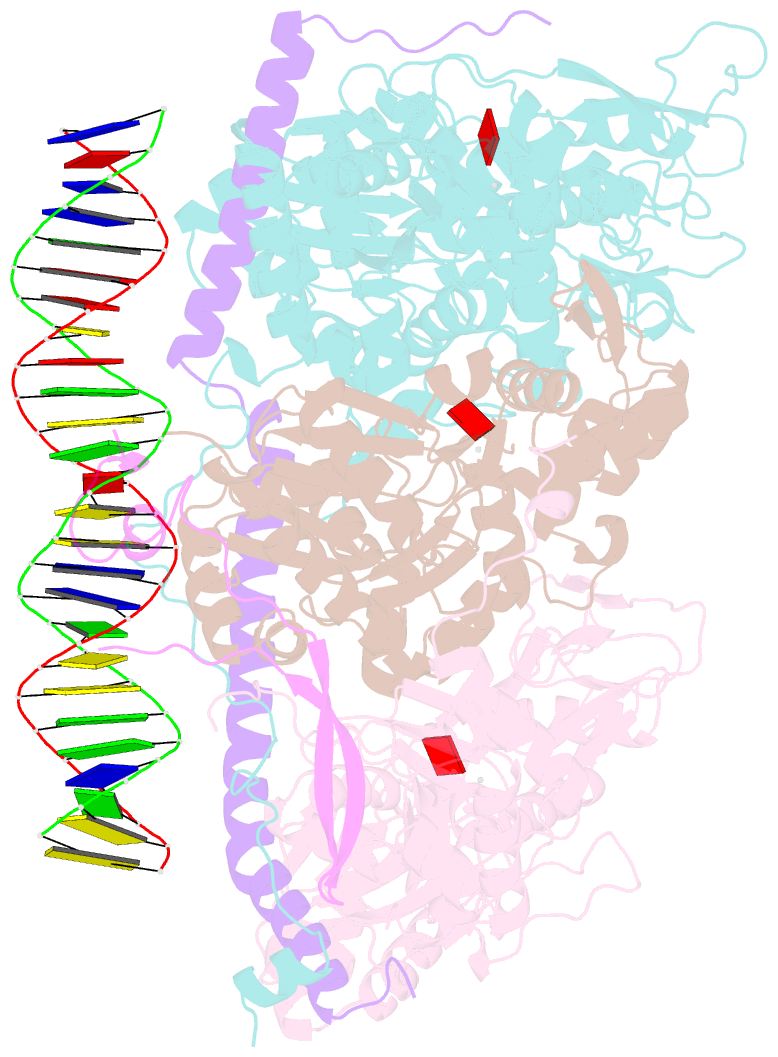
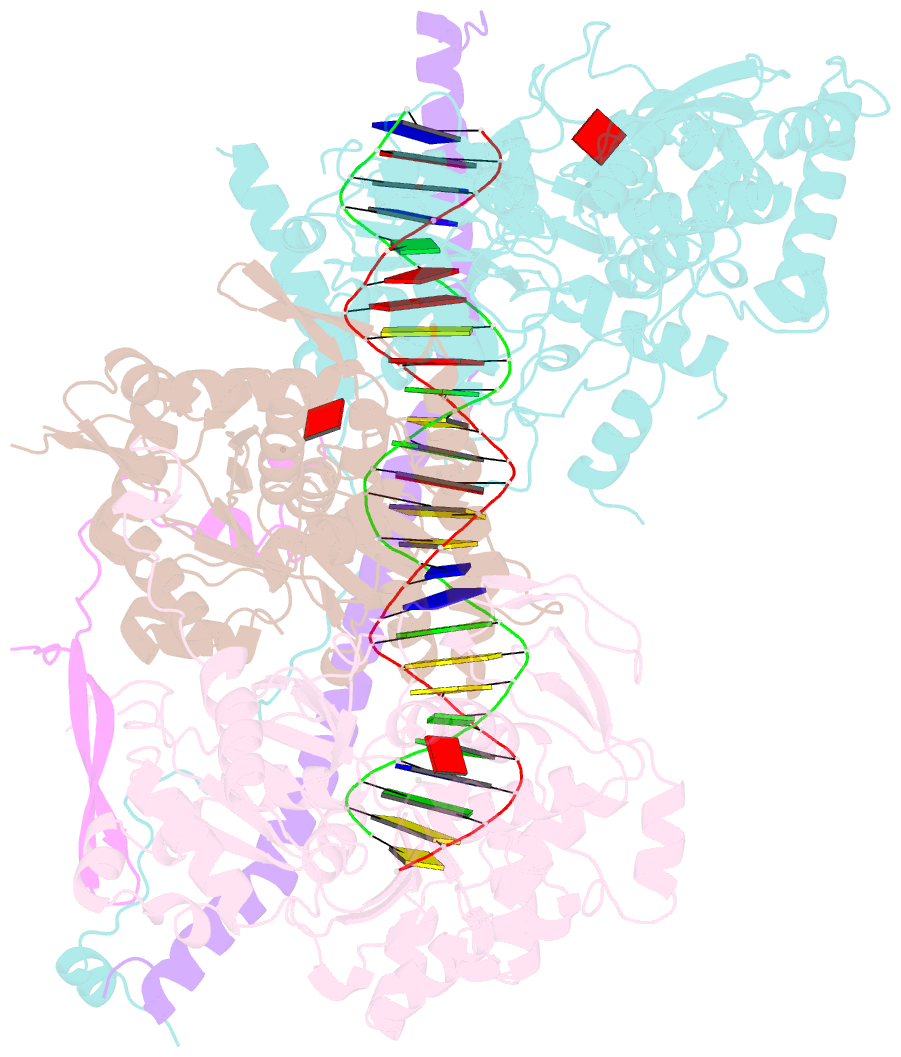
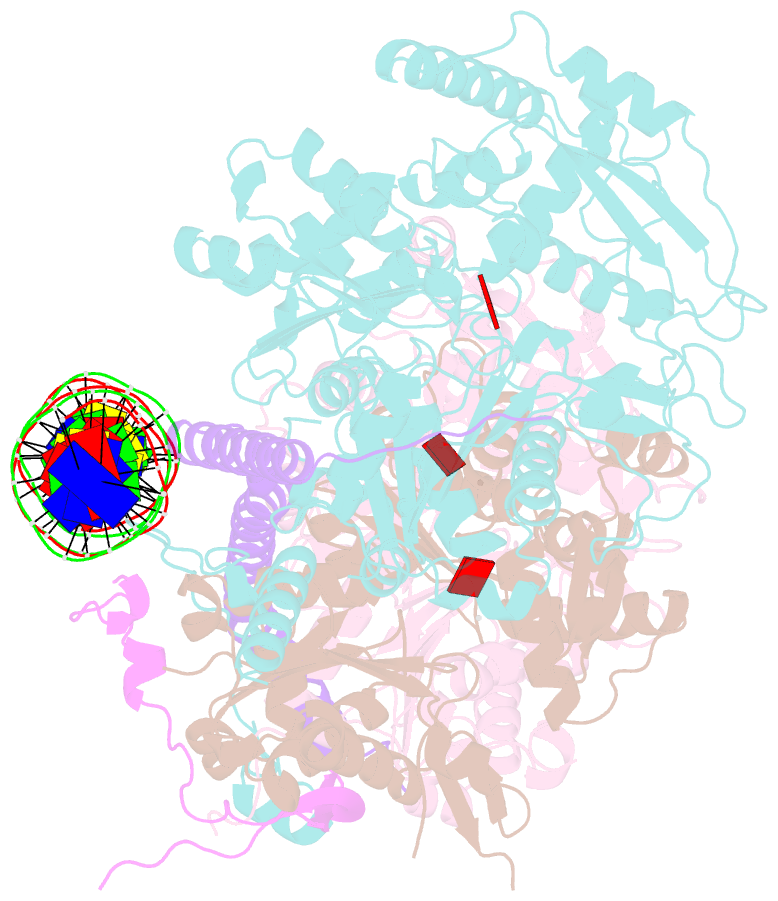
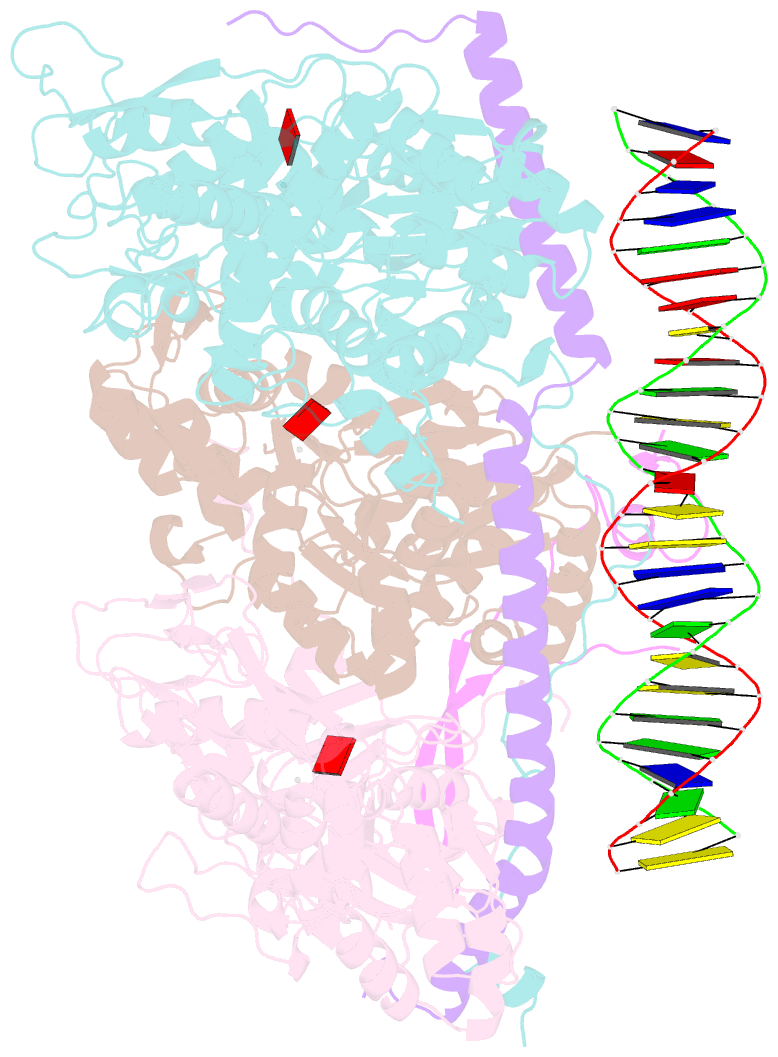
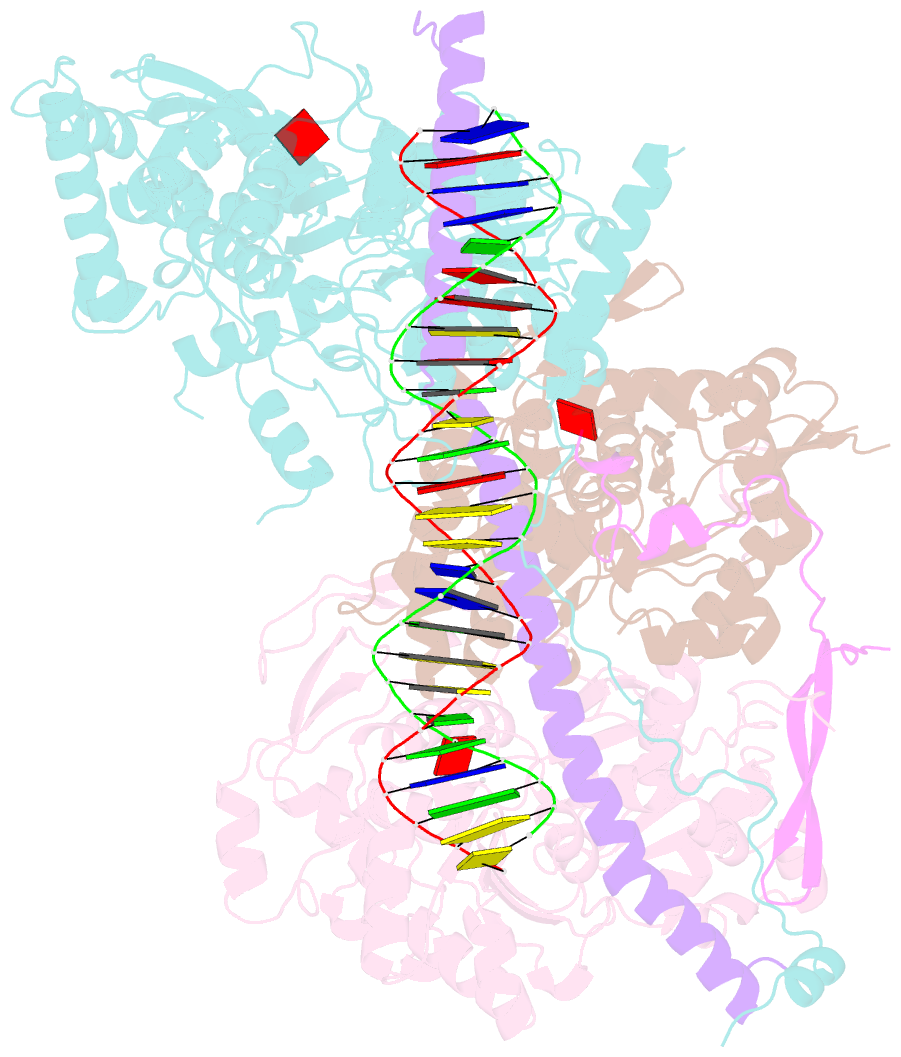
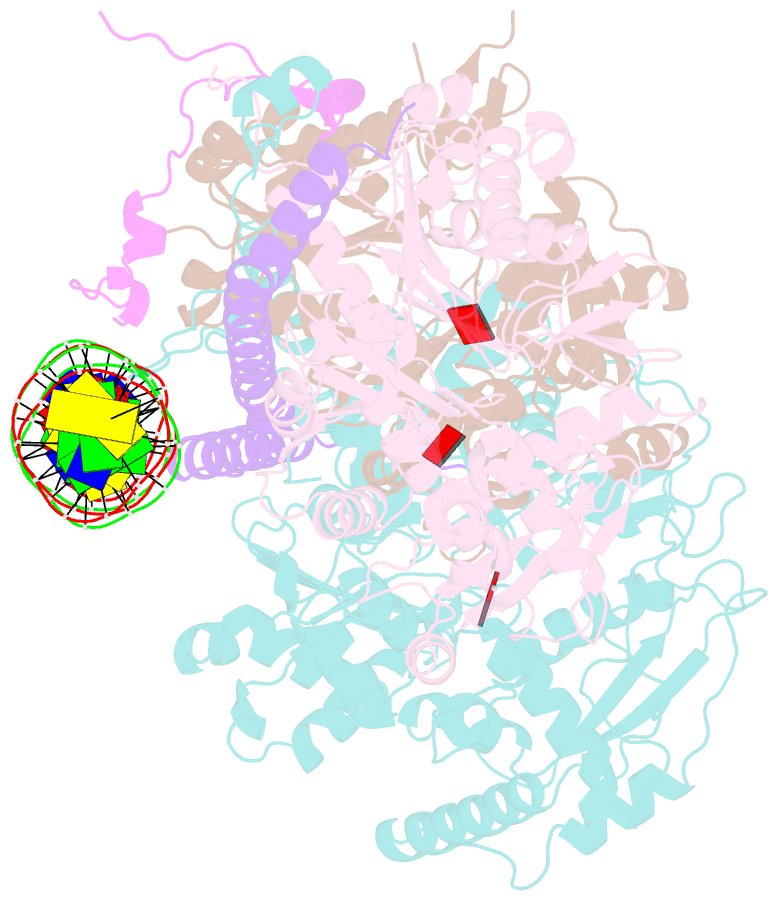
- Structure of arp4-ies4-n-actin-arp8-ino80hsa subcomplex (a-module) of chaetomium thermophilum ino80 on straight DNA
- Reference
- Kunert F, Metzner FJ, Jung J, Hopfler M, Woike S, Schall K, Kostrewa D, Moldt M, Chen JX, Bantele S, Pfander B, Eustermann S, Hopfner KP (2022): "Structural mechanism of extranucleosomal DNA readout by the INO80 complex." Sci Adv, 8, eadd3189. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.add3189.
- Abstract
- The nucleosomal landscape of chromatin depends on the concerted action of chromatin remodelers. The INO80 remodeler specifically places nucleosomes at the boundary of gene regulatory elements, which is proposed to be the result of an ATP-dependent nucleosome sliding activity that is regulated by extranucleosomal DNA features. Here, we use cryo-electron microscopy and functional assays to reveal how INO80 binds and is regulated by extranucleosomal DNA. Structures of the regulatory A-module bound to DNA clarify the mechanism of linker DNA binding. The A-module is connected to the motor unit via an HSA/post-HSA lever element to chemomechanically couple the motor and linker DNA sensing. Two notable sites of curved DNA recognition by coordinated action of the four actin/actin-related proteins and the motor suggest how sliding by INO80 can be regulated by extranucleosomal DNA features. Last, the structures clarify the recruitment of YY1/Ies4 subunits and reveal deep architectural similarities between the regulatory modules of INO80 and SWI/SNF complexes.