Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8asb; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- viral protein
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.6 Å)
- Summary
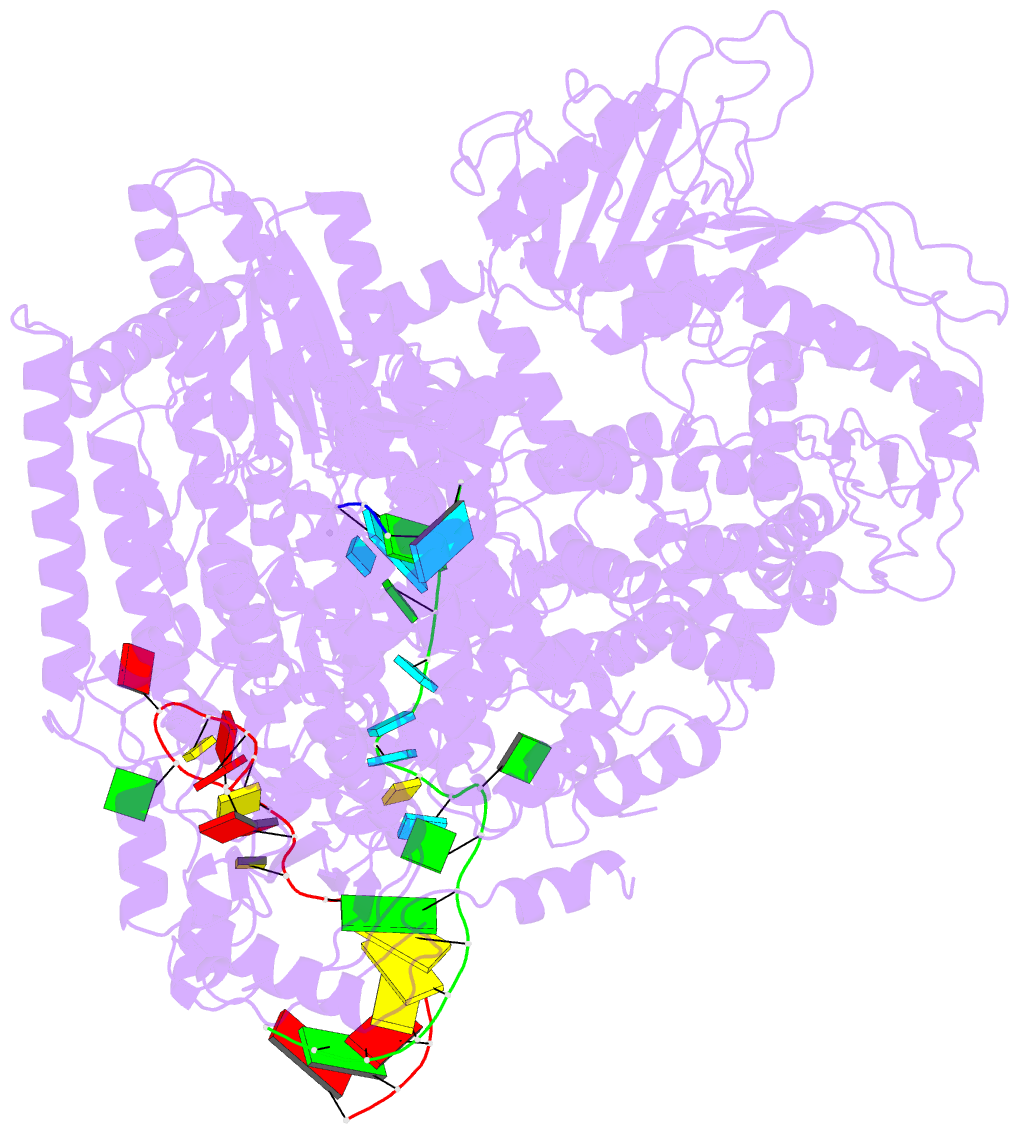
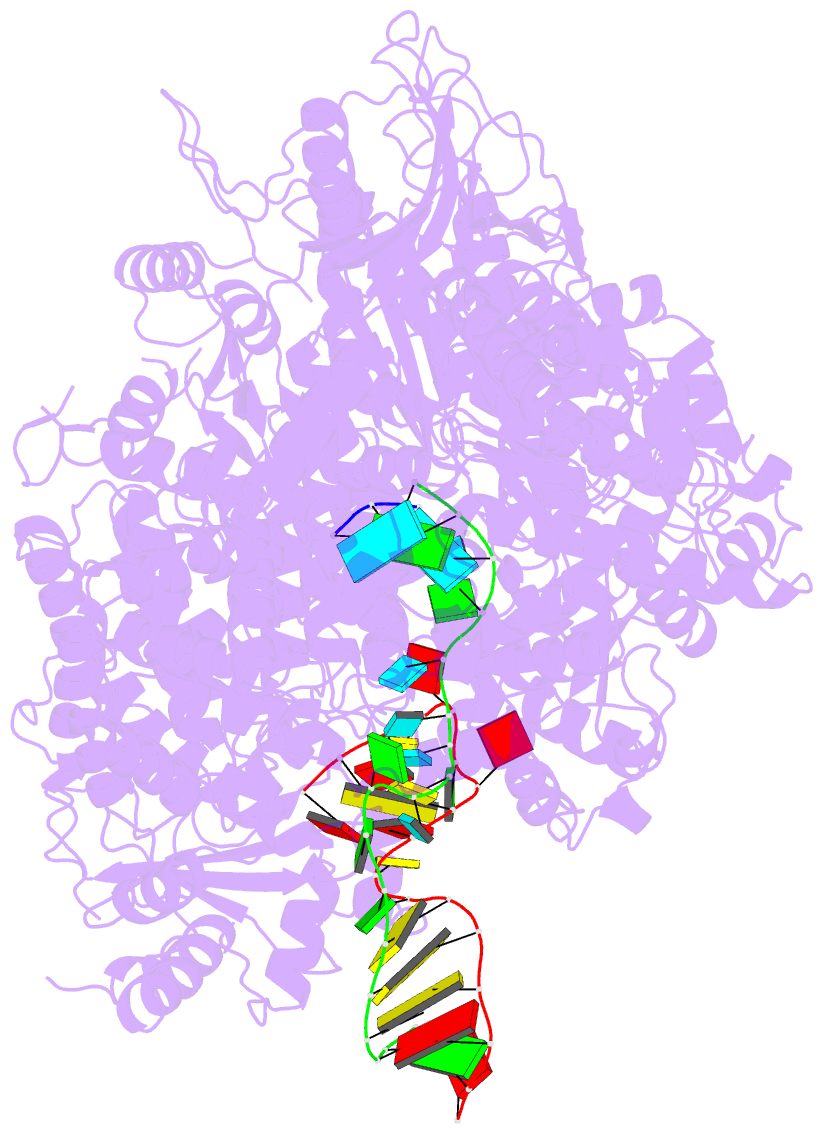
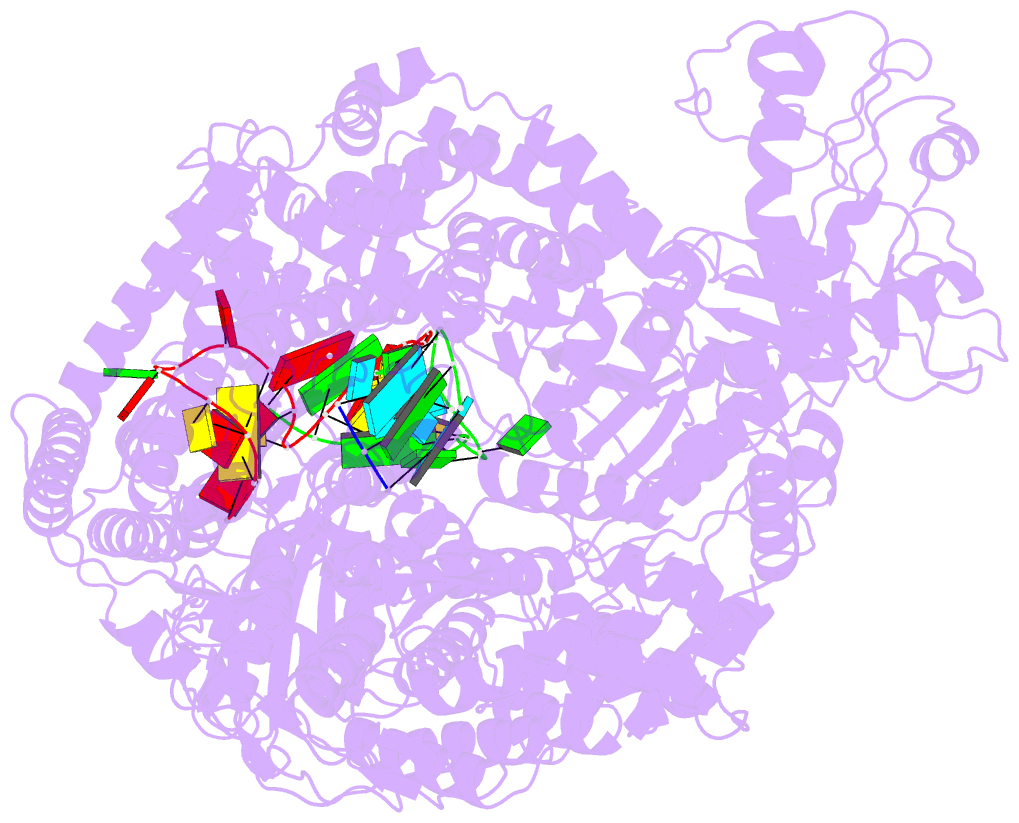
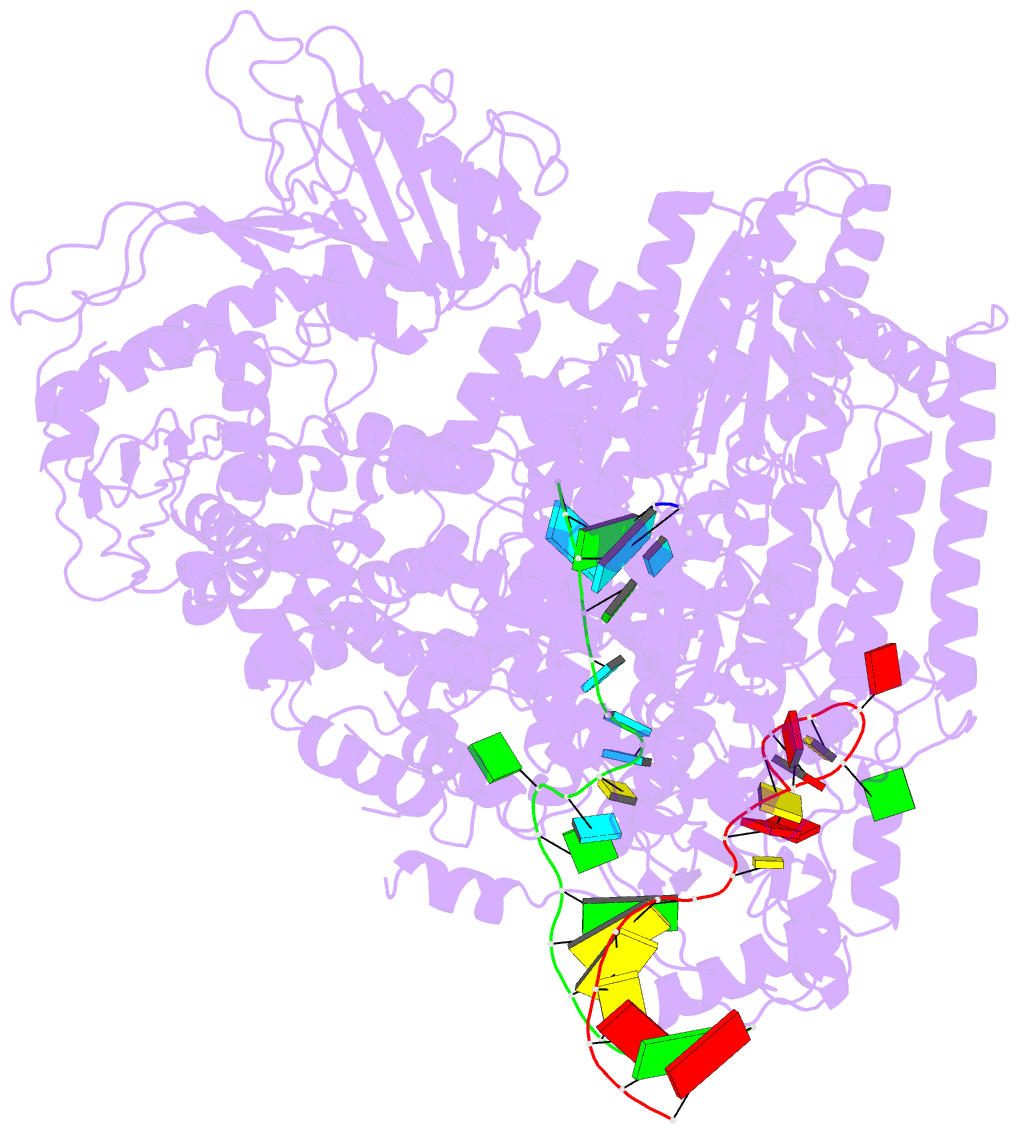
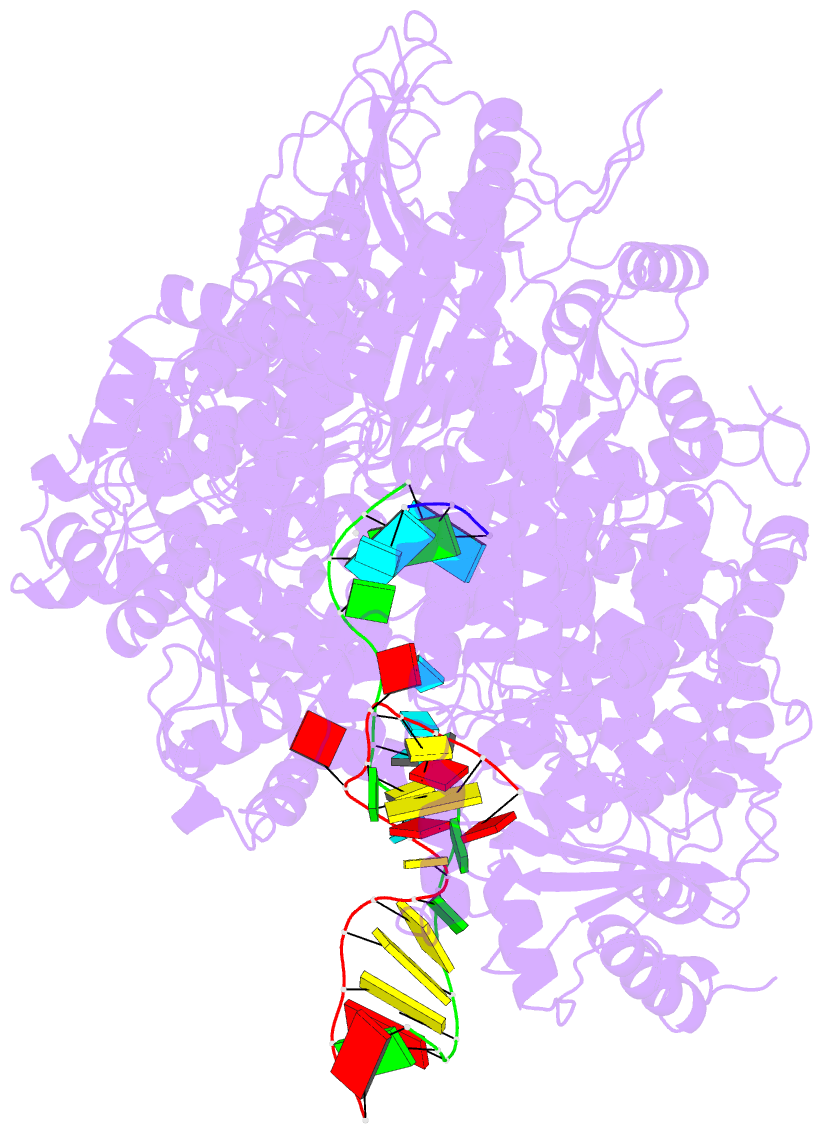
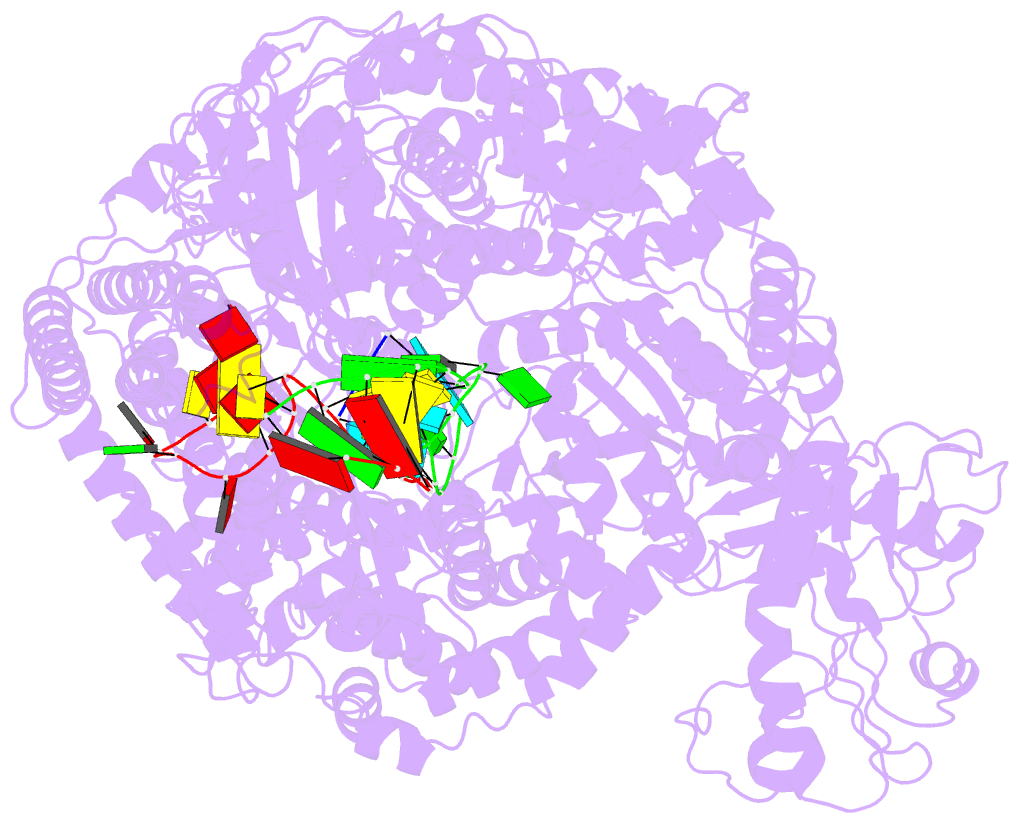
- Structure of the sftsv l protein stalled at early elongation with the endonuclease domain in a raised conformation [early-elongation-endo]
- Reference
- Williams HM, Thorkelsson SR, Vogel D, Milewski M, Busch C, Cusack S, Grunewald K, Quemin ERJ, Rosenthal M (2023): "Structural insights into viral genome replication by the severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus L protein." Nucleic Acids Res., 51, 1424-1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkac1249.
- Abstract
- Severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome virus (SFTSV) is a phenuivirus that has rapidly become endemic in several East Asian countries. The large (L) protein of SFTSV, which includes the RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), is responsible for catalysing viral genome replication and transcription. Here, we present 5 cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of the L protein in several states of the genome replication process, from pre-initiation to late-stage elongation, at a resolution of up to 2.6 Å. We identify how the L protein binds the 5' viral RNA in a hook-like conformation and show how the distal 5' and 3' RNA ends form a duplex positioning the 3' RNA terminus in the RdRp active site ready for initiation. We also observe the L protein stalled in the early and late stages of elongation with the RdRp core accommodating a 10-bp product-template duplex. This duplex ultimately splits with the template binding to a designated 3' secondary binding site. The structural data and observations are complemented by in vitro biochemical and cell-based mini-replicon assays. Altogether, our data provide novel key insights into the mechanism of viral genome replication by the SFTSV L protein and will aid drug development against segmented negative-strand RNA viruses.