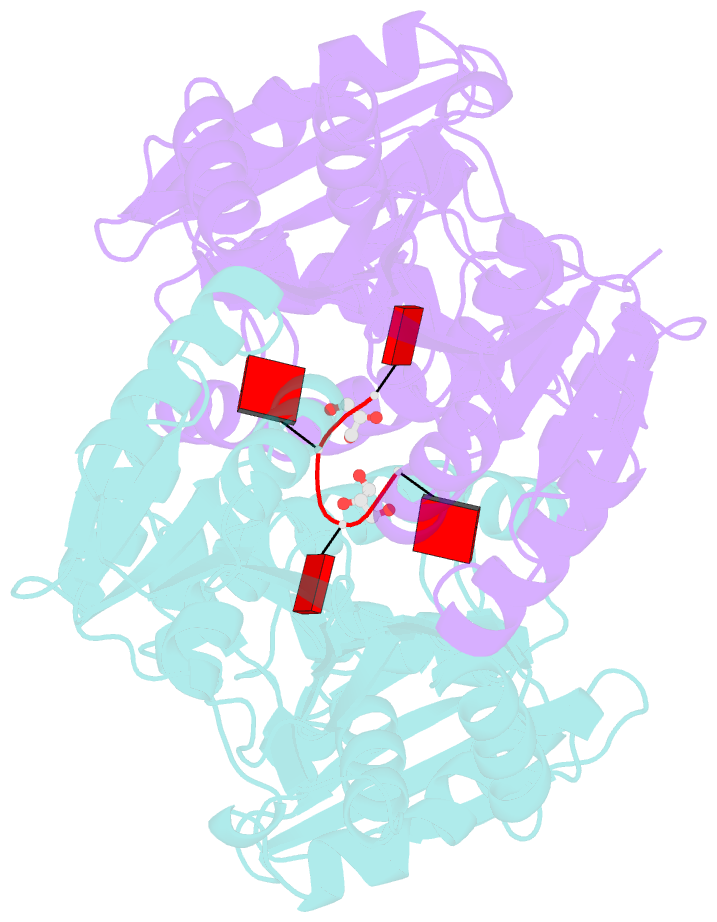
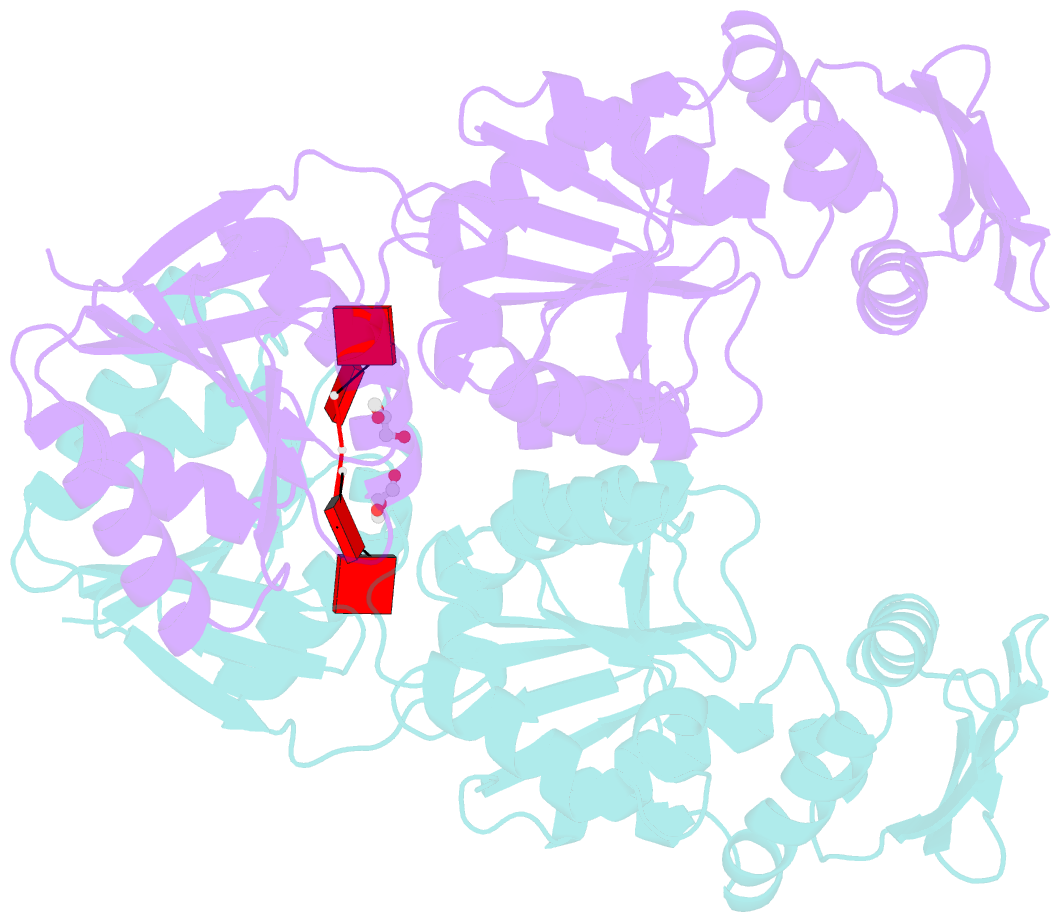
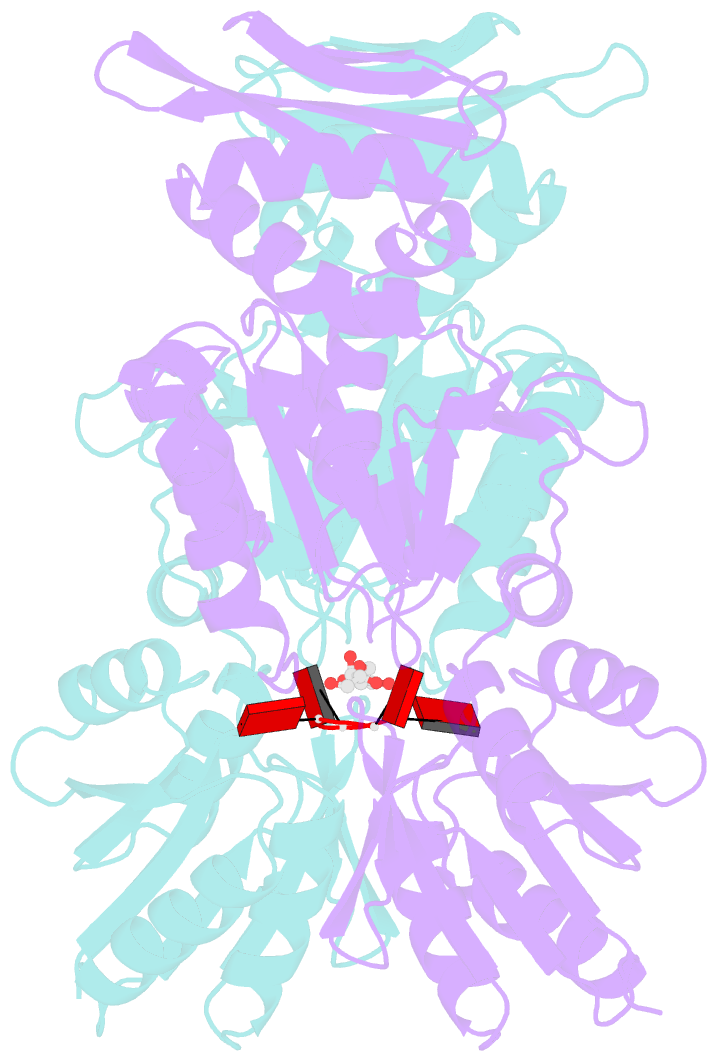
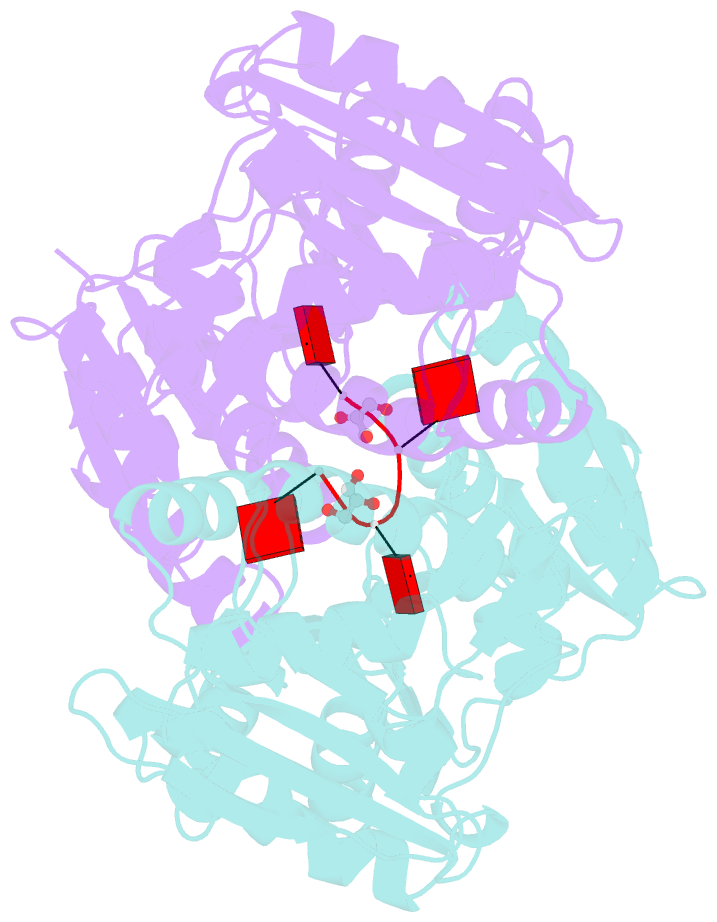
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8bao; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein
- Method
- X-ray (2.06 Å)
- Summary
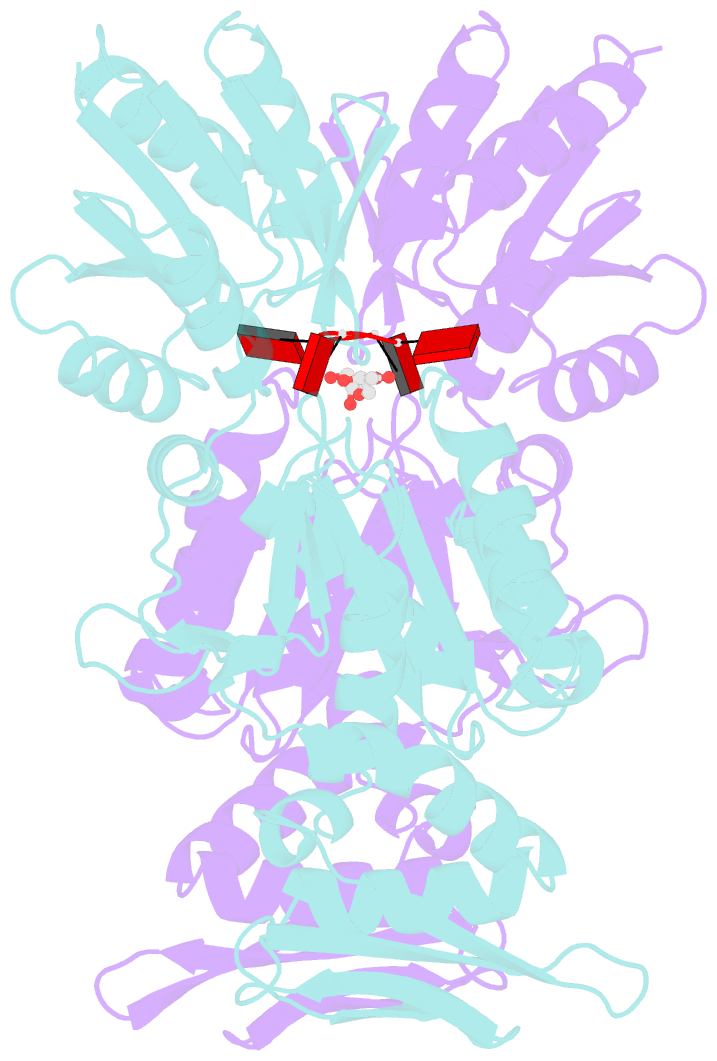
- Dysgonamonadaceae bacterium crispr ancillary nuclease 2
- Reference
- Zabrady M, Zabrady K, Li AWH, Doherty AJ (2023): "Reverse transcriptases prime DNA synthesis." Nucleic Acids Res., 51, 7125-7142. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad478.
- Abstract
- Reverse transcriptases (RTs) are replicative enzymes that copy RNA into DNA and undertake roles, including viral replication, retrotransposition and telomere maintenance. The initiation of RT synthesis activities is usually dependent on the presence of a primer. The current dogma proposes that a variety of indirect, RT-independent, priming mechanisms instigate synthesis. However, this study establishes that CRISPR-associated RTs (CARTs) are capable of priming DNA synthesis from scratch, which enables the capture of foreign genetic material for storage in CRISPR arrays. The authors also report that other notable RT family members, including retrotransposon RTs, telomerase and retroviral RT are, surprisingly, able to directly catalyze primer synthesis. These findings significantly alter our understanding of priming mechanisms utilised by RTs in various biological pathways.