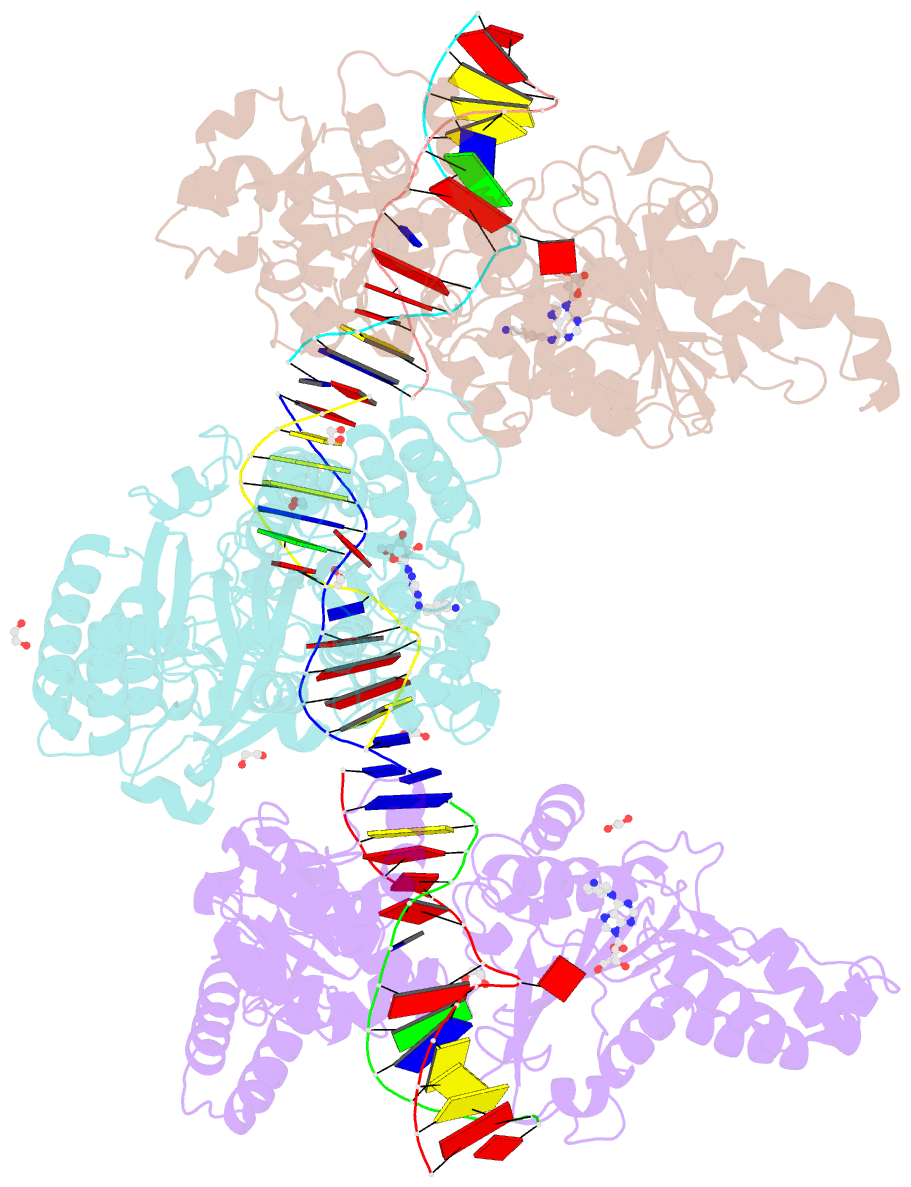
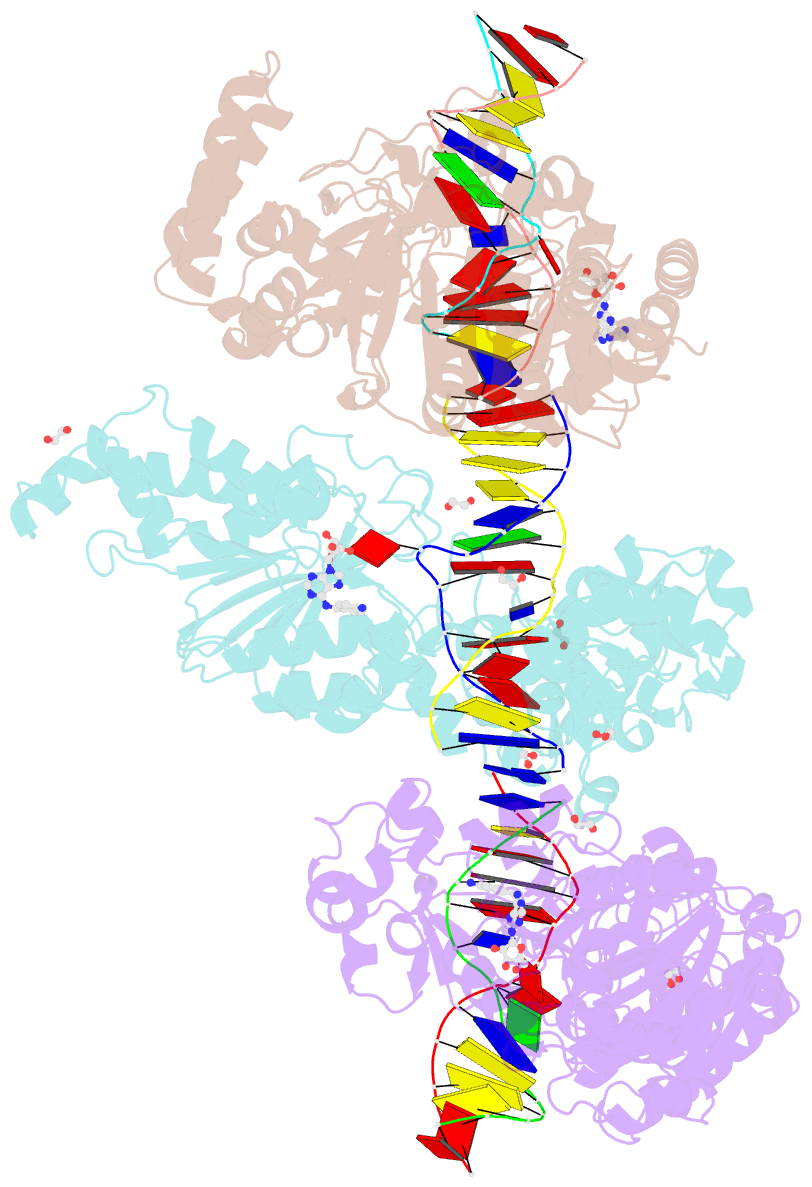
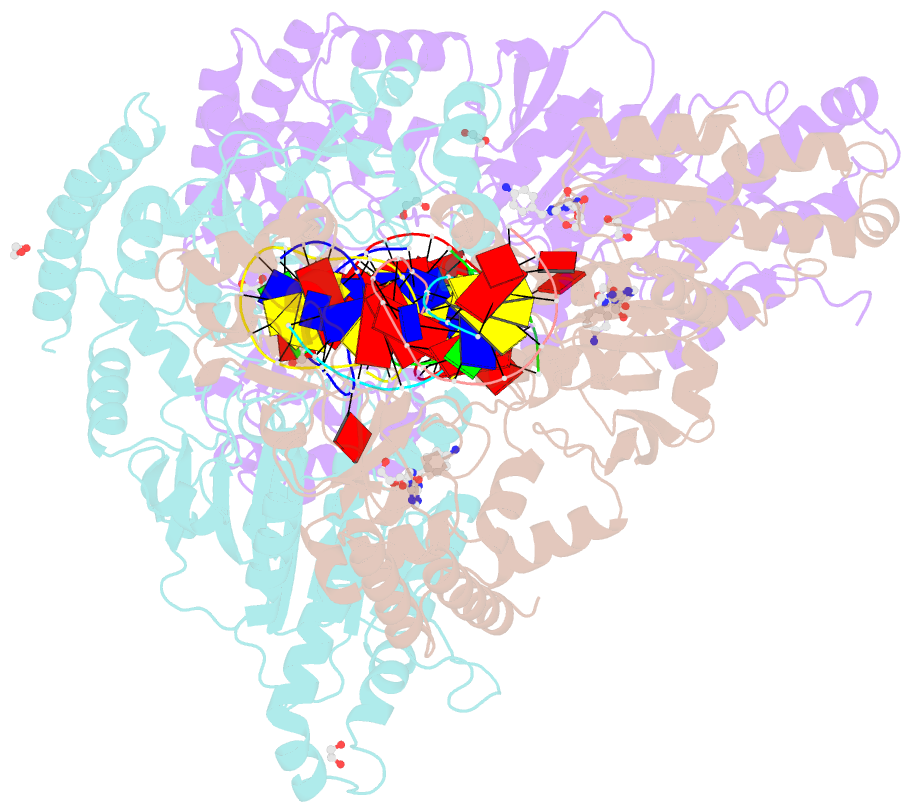
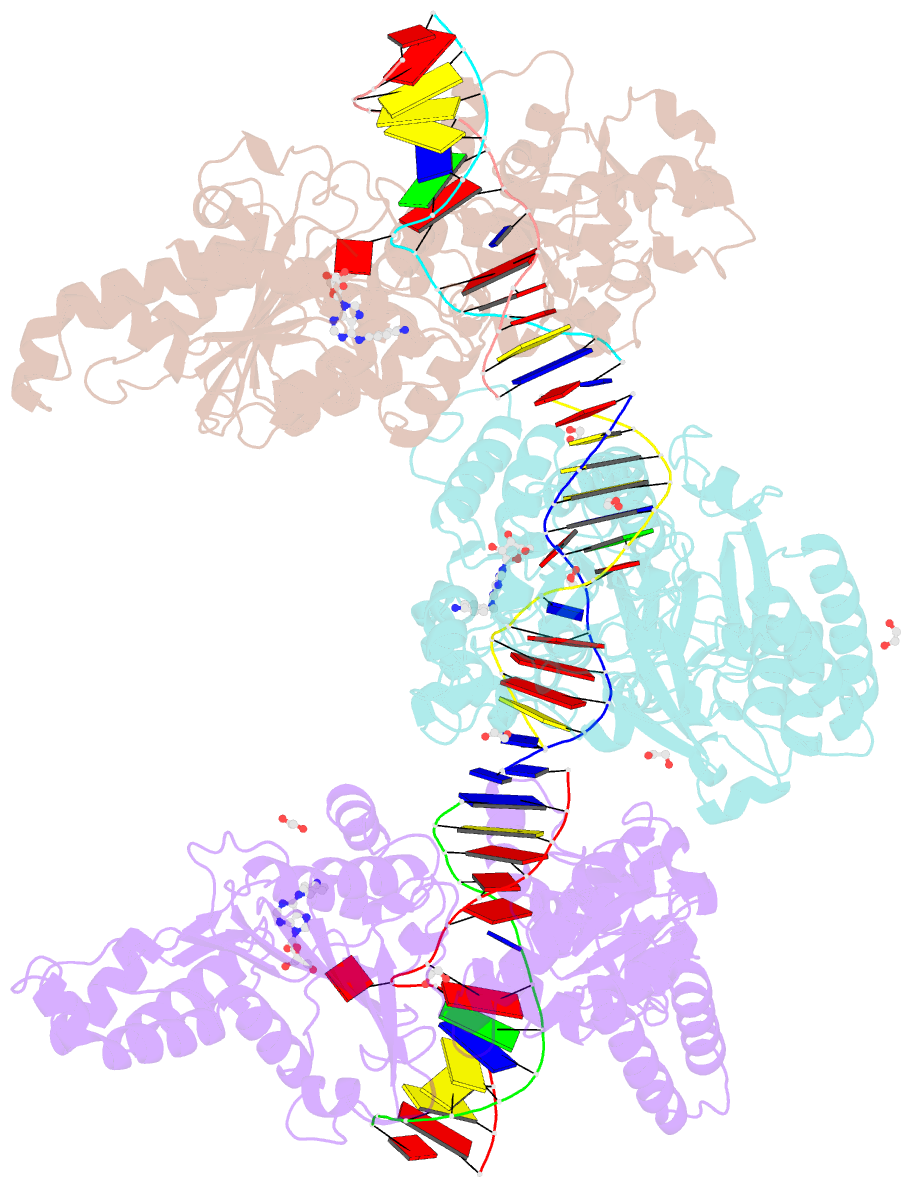
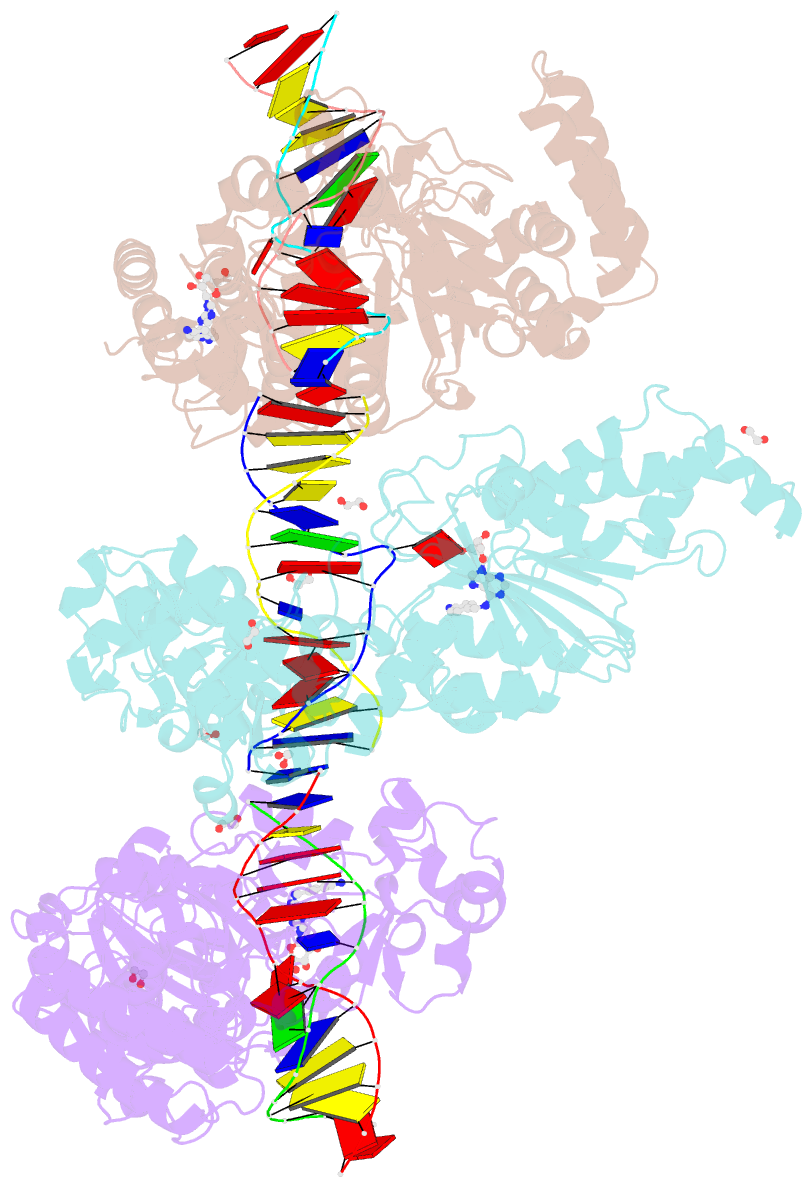
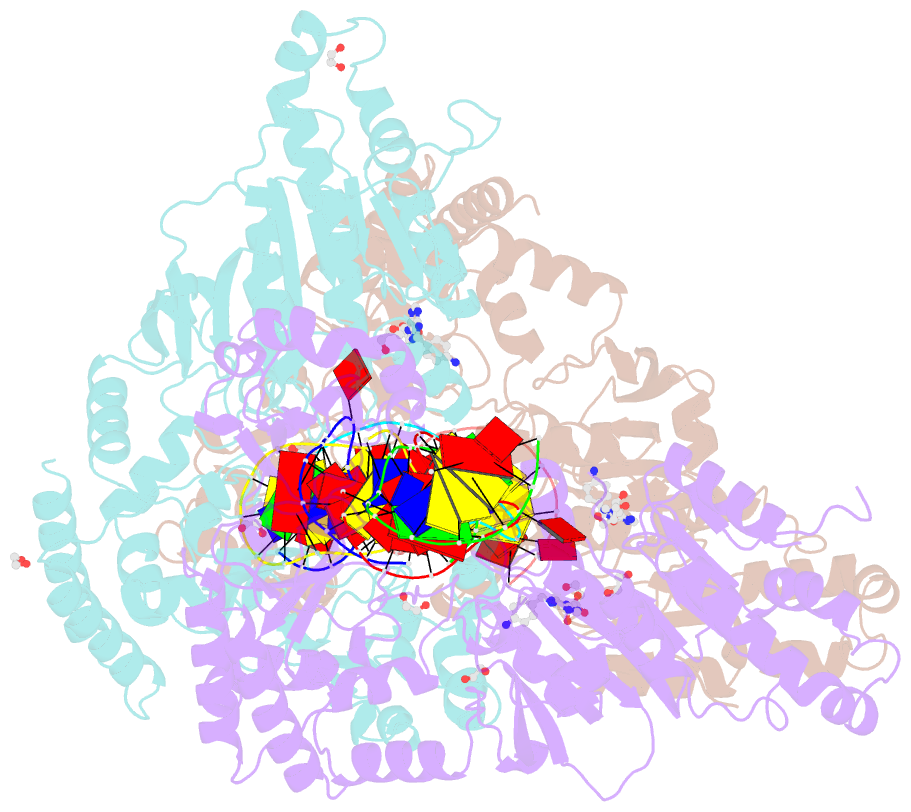
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8cxu; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.28 Å)
- Summary
- Cama adenine methyltransferase complexed to cognate substrate DNA and compound 2
- Reference
- Zhou J, Horton JR, Menna M, Fiorentino F, Ren R, Yu D, Hajian T, Vedadi M, Mazzoccanti G, Ciogli A, Weinhold E, Huben M, Blumenthal RM, Zhang X, Mai A, Rotili D, Cheng X (2023): "Systematic Design of Adenosine Analogs as Inhibitors of a Clostridioides difficile- Specific DNA Adenine Methyltransferase Required for Normal Sporulation and Persistence." J.Med.Chem., 66, 934-950. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c01789.
- Abstract
- Antivirulence agents targeting endospore-transmitted Clostridioides difficile infections are urgently needed. C. difficile-specific DNA adenine methyltransferase (CamA) is required for efficient sporulation and affects persistence in the colon. The active site of CamA is conserved and closely resembles those of hundreds of related S-adenosyl-l-methionine (SAM)-dependent methyltransferases, which makes the design of selective inhibitors more challenging. We explored the solvent-exposed edge of the SAM adenosine moiety and systematically designed 42 analogs of adenosine carrying substituents at the C6-amino group (N6) of adenosine. We compare the inhibitory properties and binding affinity of these diverse compounds and present the crystal structures of CamA in complex with 14 of them in the presence of substrate DNA. The most potent of these inhibitors, compound