Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8d0b; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- replication-DNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (3.43 Å)
- Summary
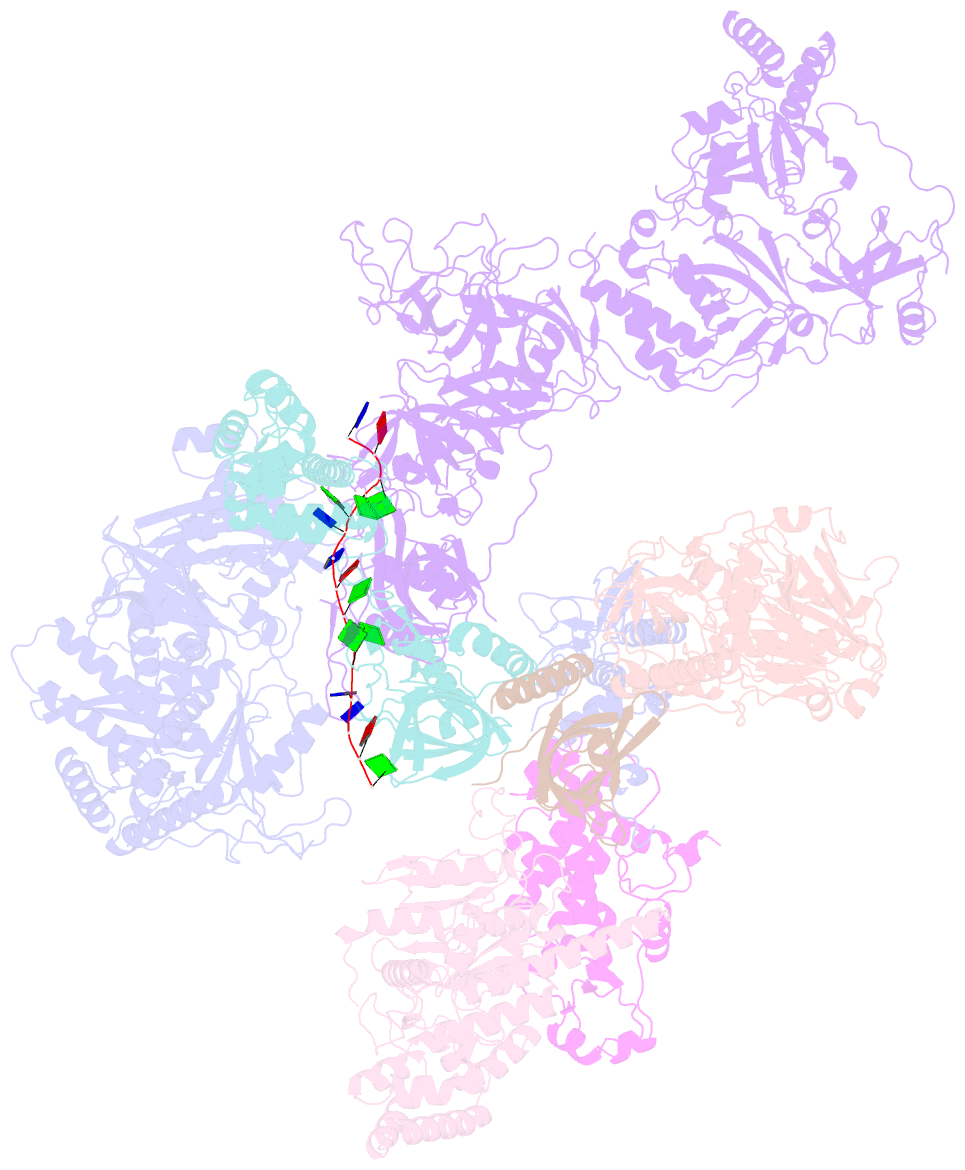
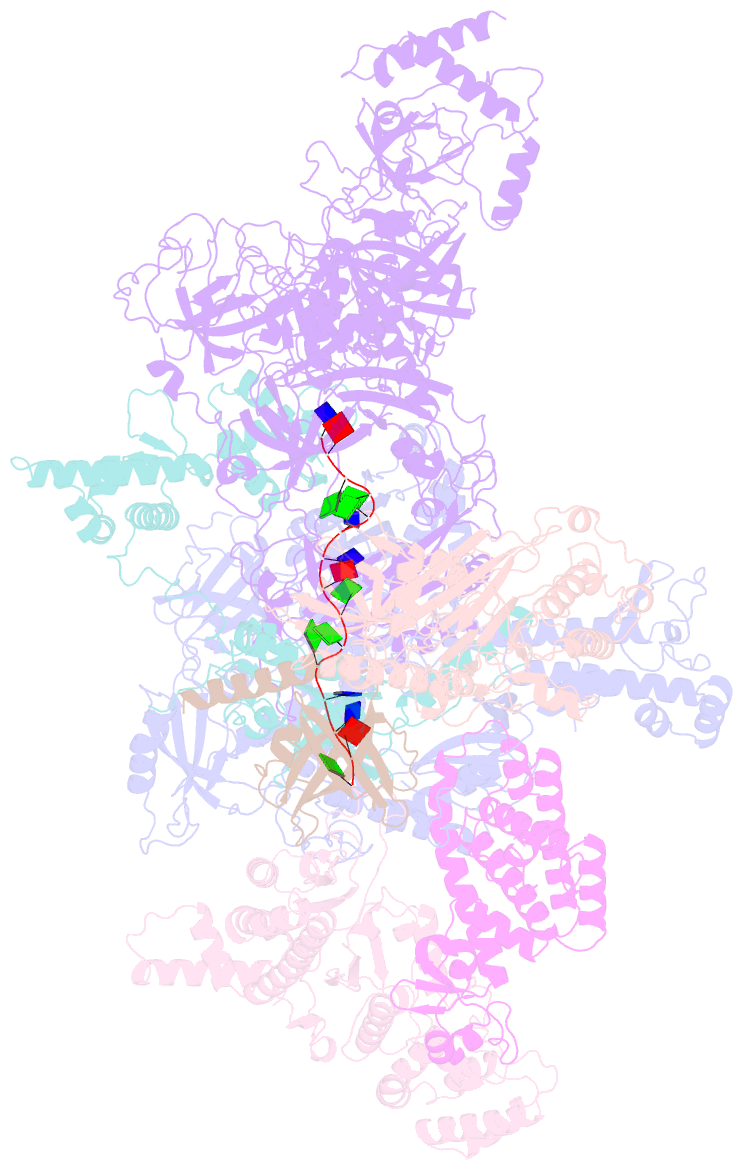
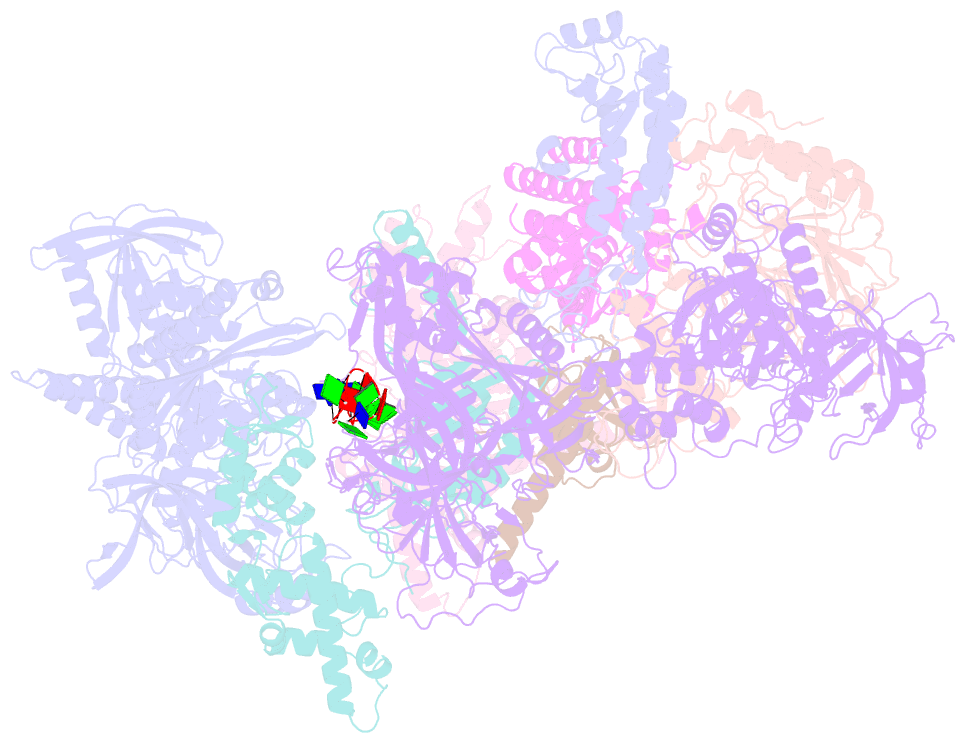
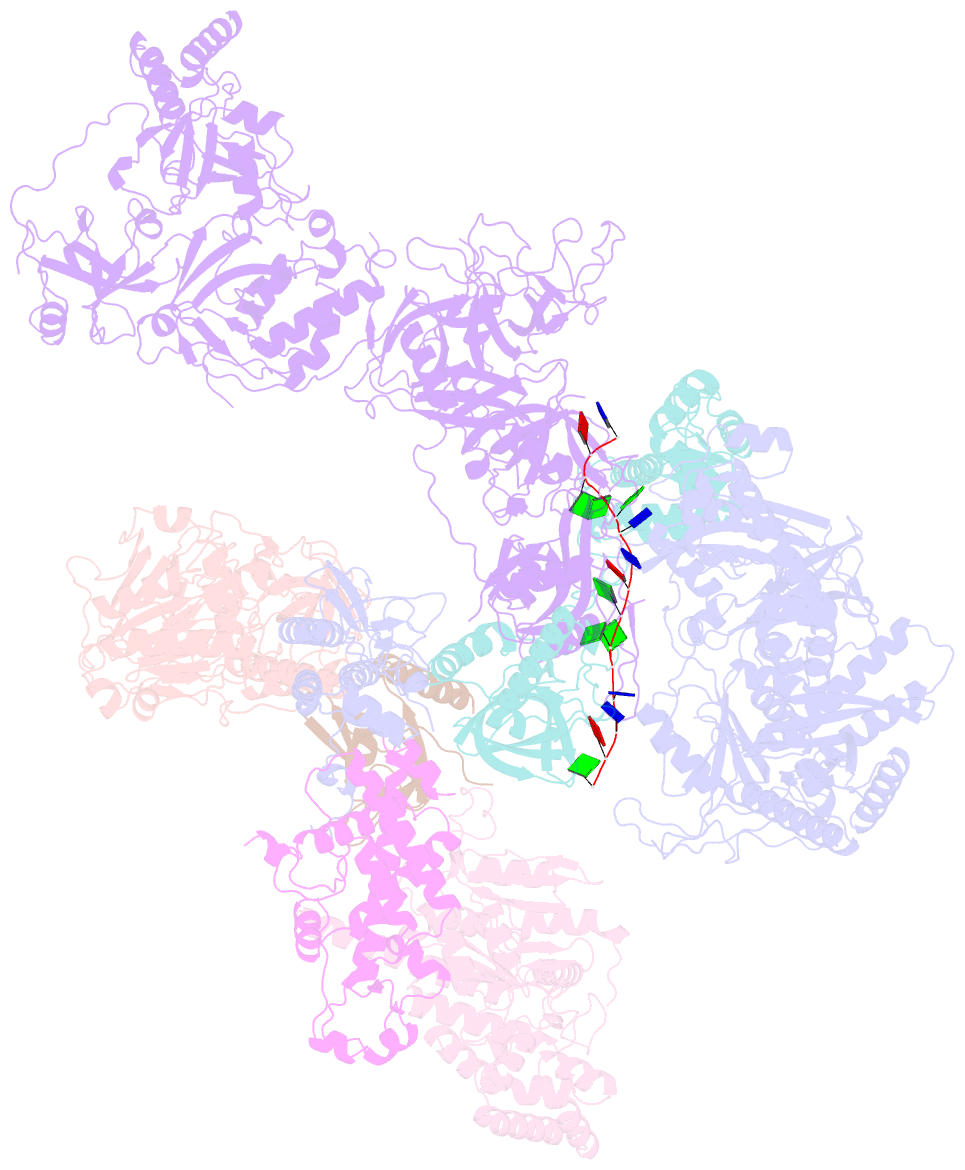
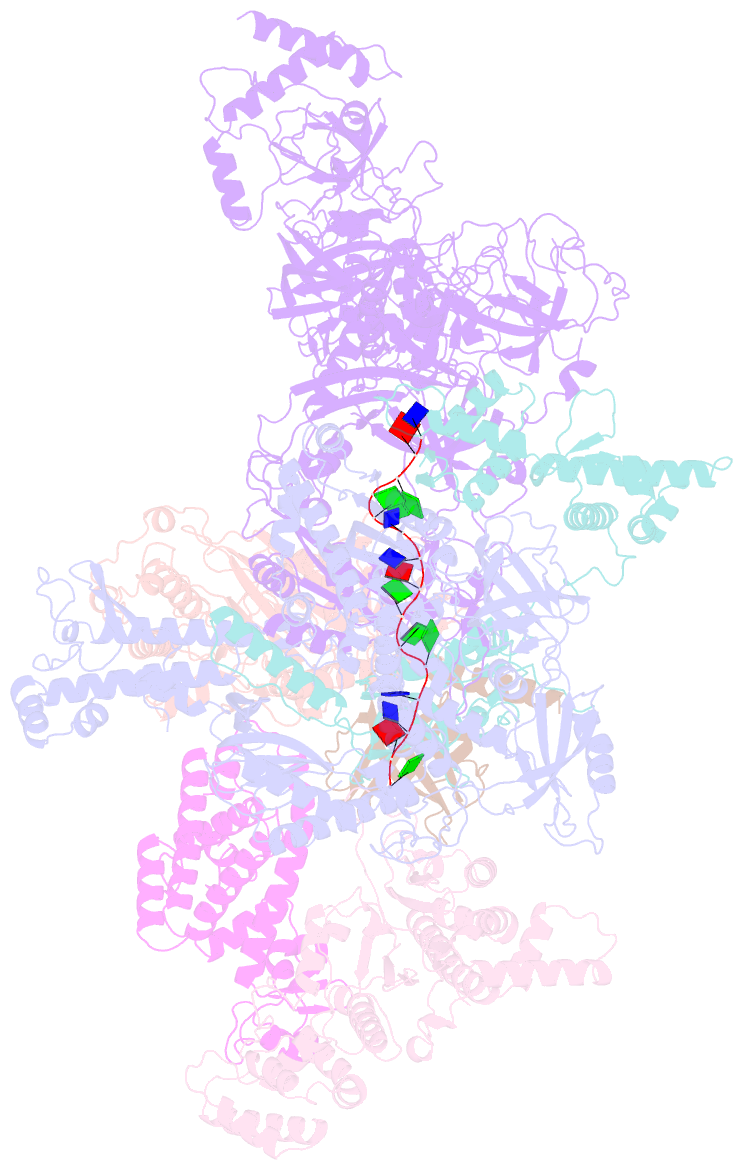
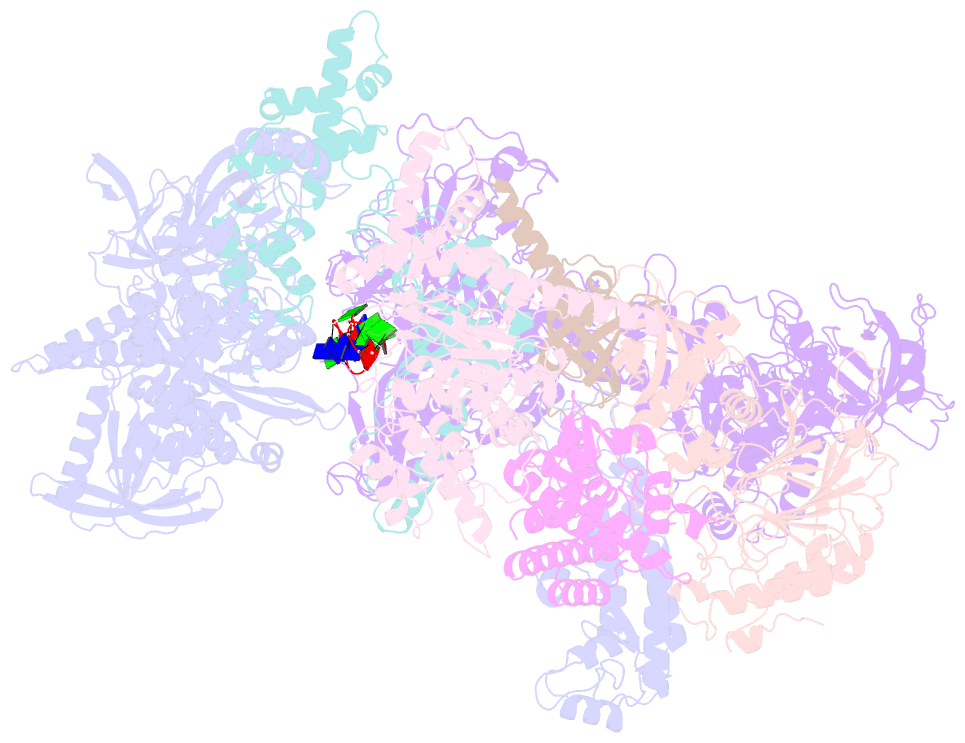
- Human cst-DNA polymerase alpha-primase preinitiation complex bound to 4xtel-foldback template
- Reference
- He Q, Lin X, Chavez BL, Agrawal S, Lusk BL, Lim CJ (2022): "Structures of the human CST-Pol alpha-primase complex bound to telomere templates." Nature, 608, 826-832. doi: 10.1038/s41586-022-05040-1.
- Abstract
- The mammalian DNA polymerase-alpha/primase (pol-α/primase) is essential for DNA metabolism, providing the de novo RNA-DNA primer for several DNA replication pathways1-4 such as lagging-strand synthesis and telomere C-strand fill-in. The underlying physical mechanism of how pol-α/primase, alone or in partnership with accessory proteins, performs its complicated multistep primer synthesis function is unknown. Here, we show that CST, a single-stranded DNA-binding accessory protein complex of pol-α/primase, physically sets up the enzyme for efficient primer synthesis. Cryo-electron microscopy structures of CST-pol-α/primase preinitiation complex (PIC) bound to various types of telomere overhang reveal template-bound CST partitions the DNA and RNA catalytic centers of pol-α/primase into two separate domains and effectively arrange them in RNA-DNA synthesis order. The PIC architecture provides a single solution for the multiple structural needs for pol-α/primase RNA-DNA primer synthesis. Multiple insights into CST template-binding specificity, template requirement for CST-pol-α/primase PIC assembly, and activation are also revealed in this study.