Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8d9j; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- hydrolase-DNA
- Method
- X-ray (2.82 Å)
- Summary
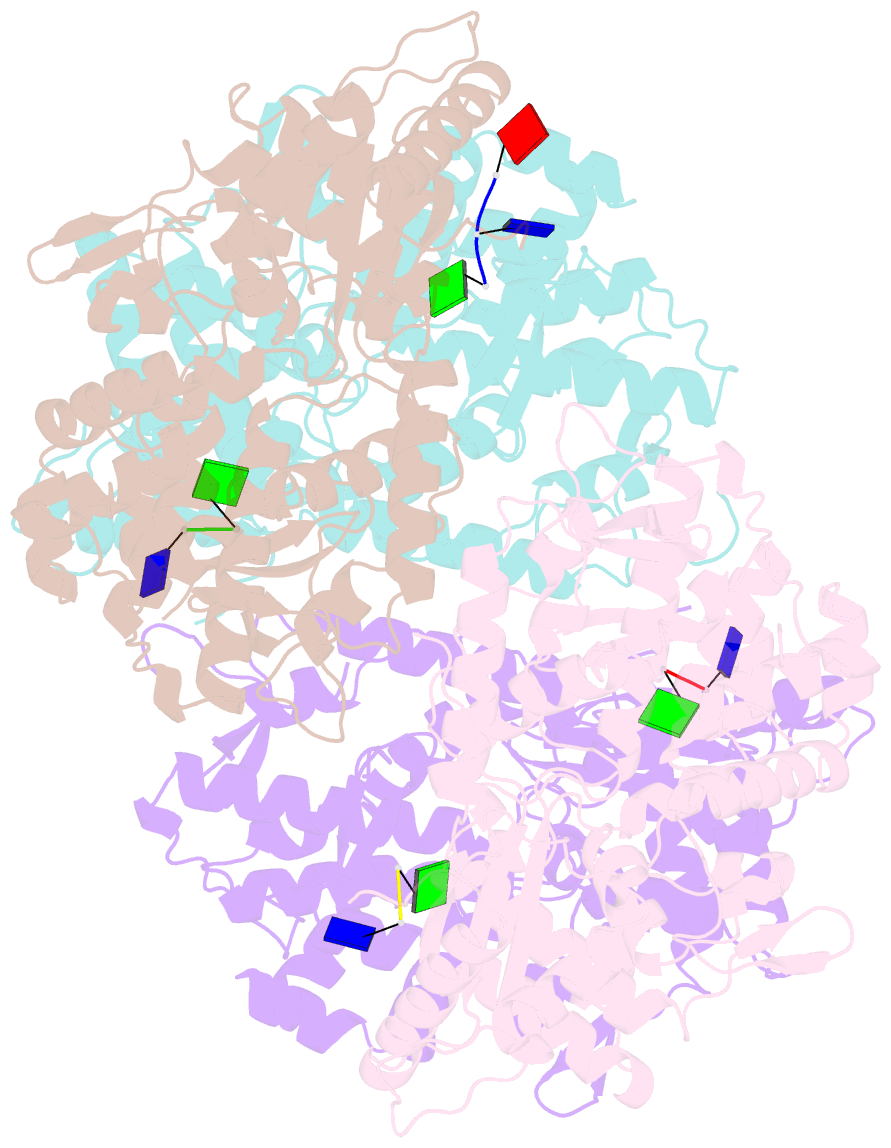
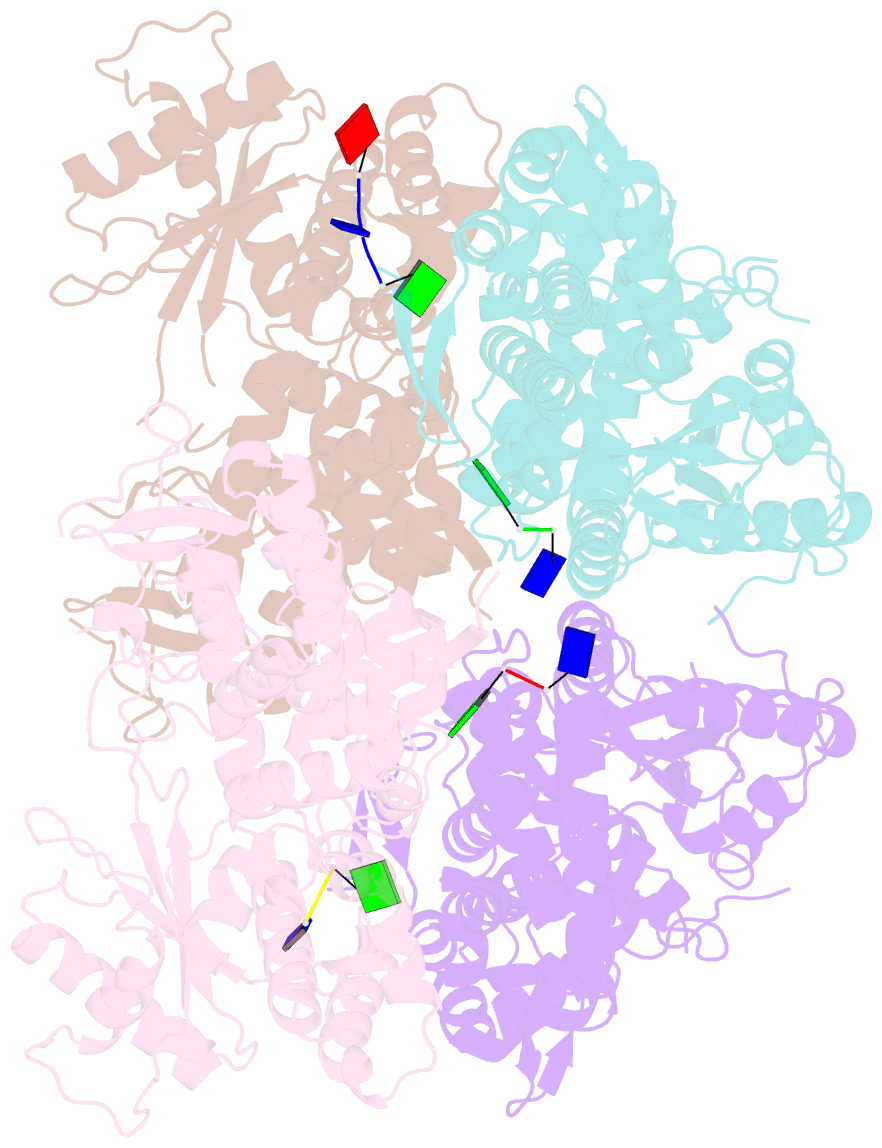
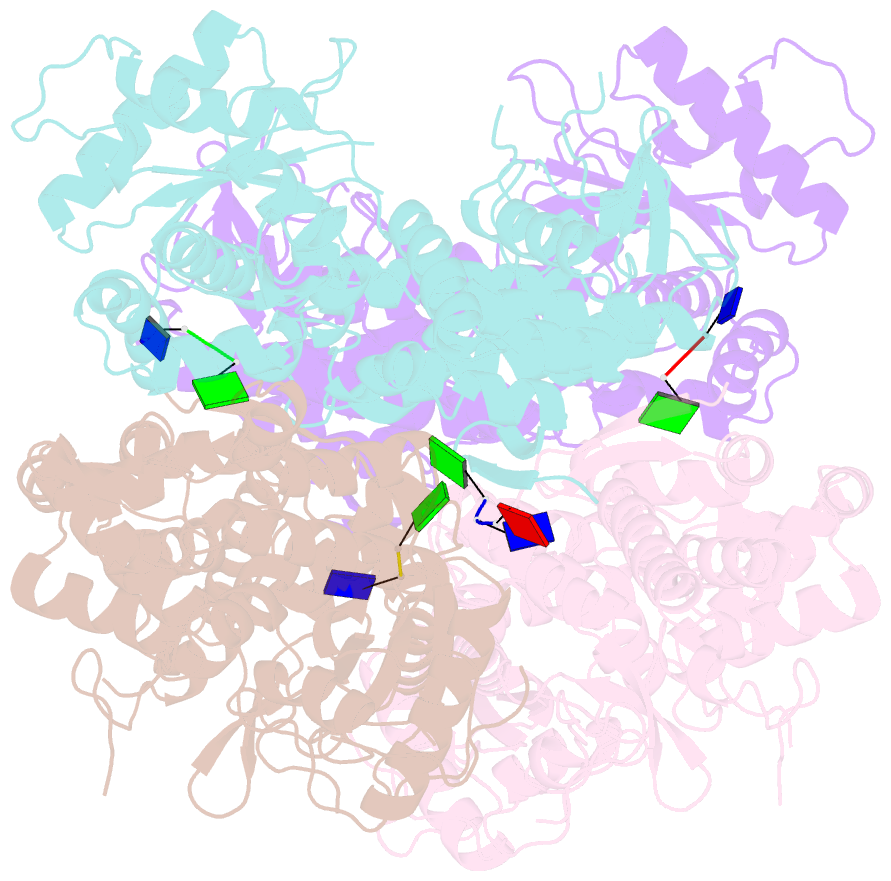
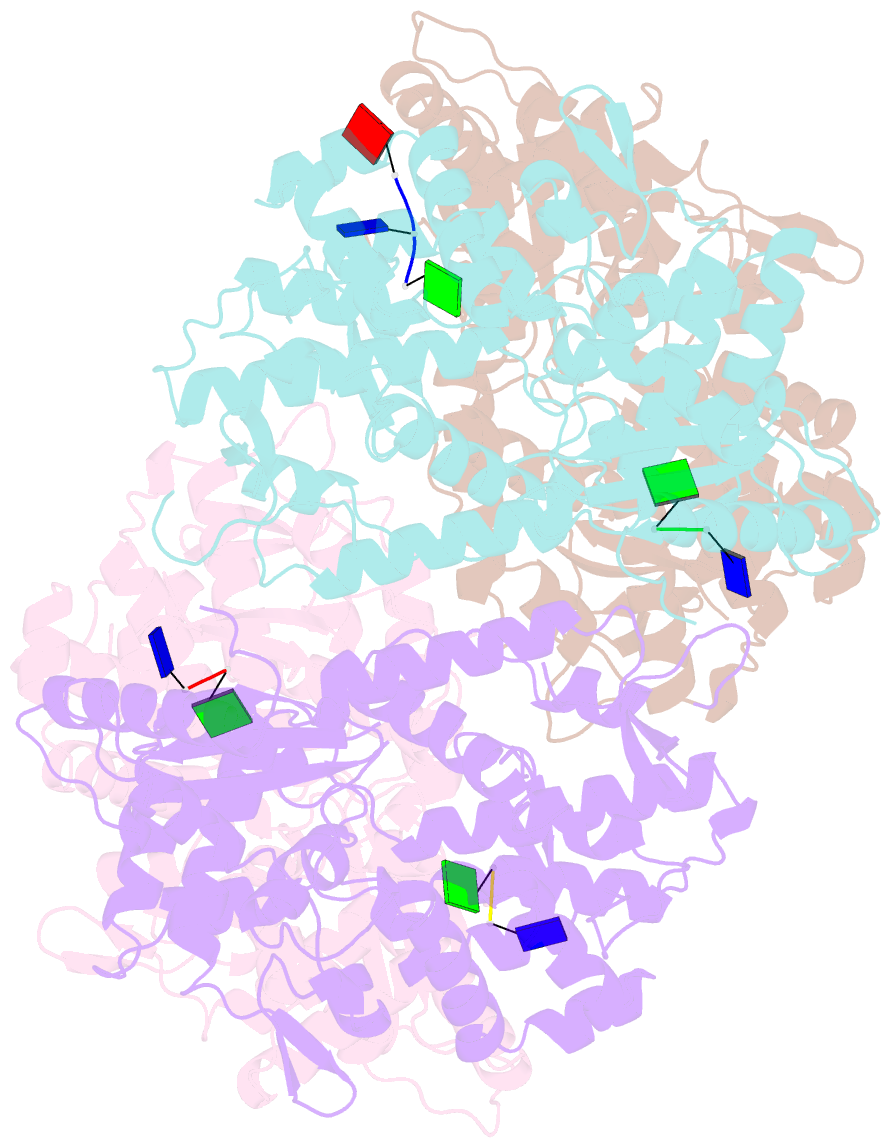
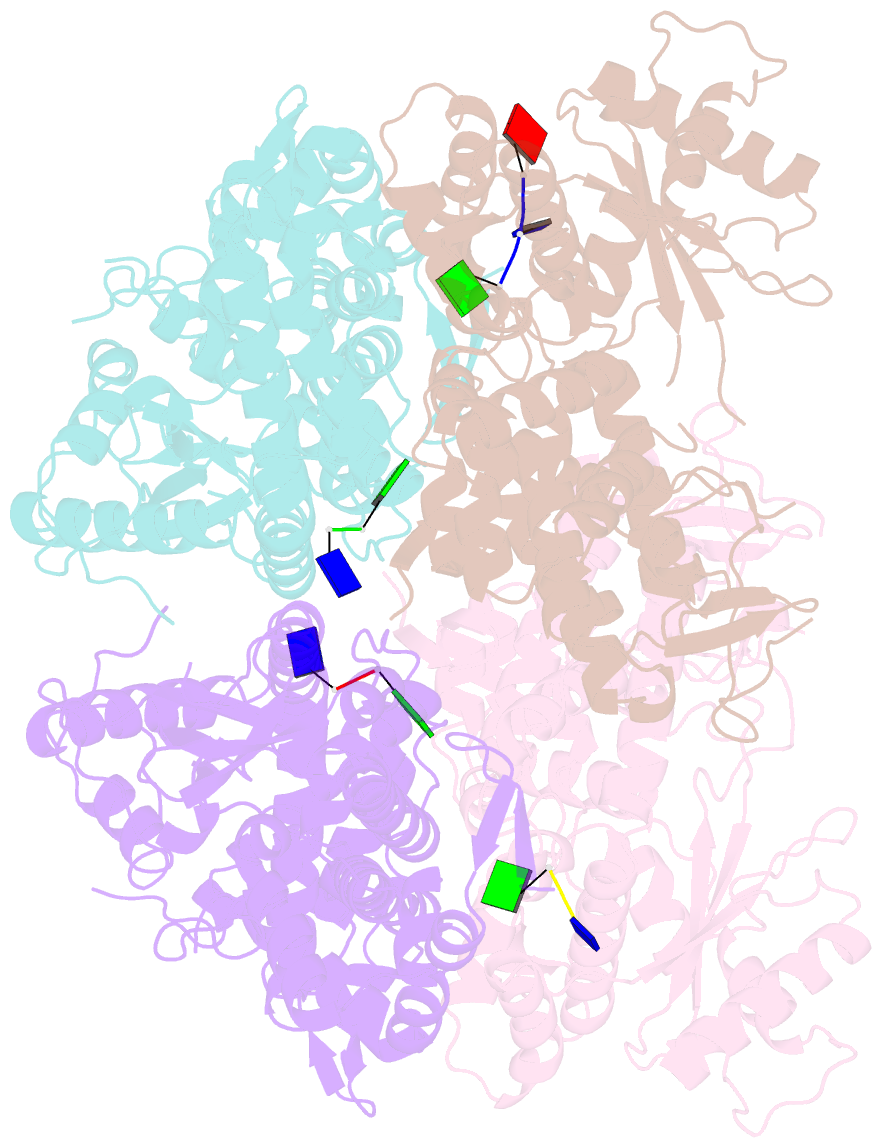
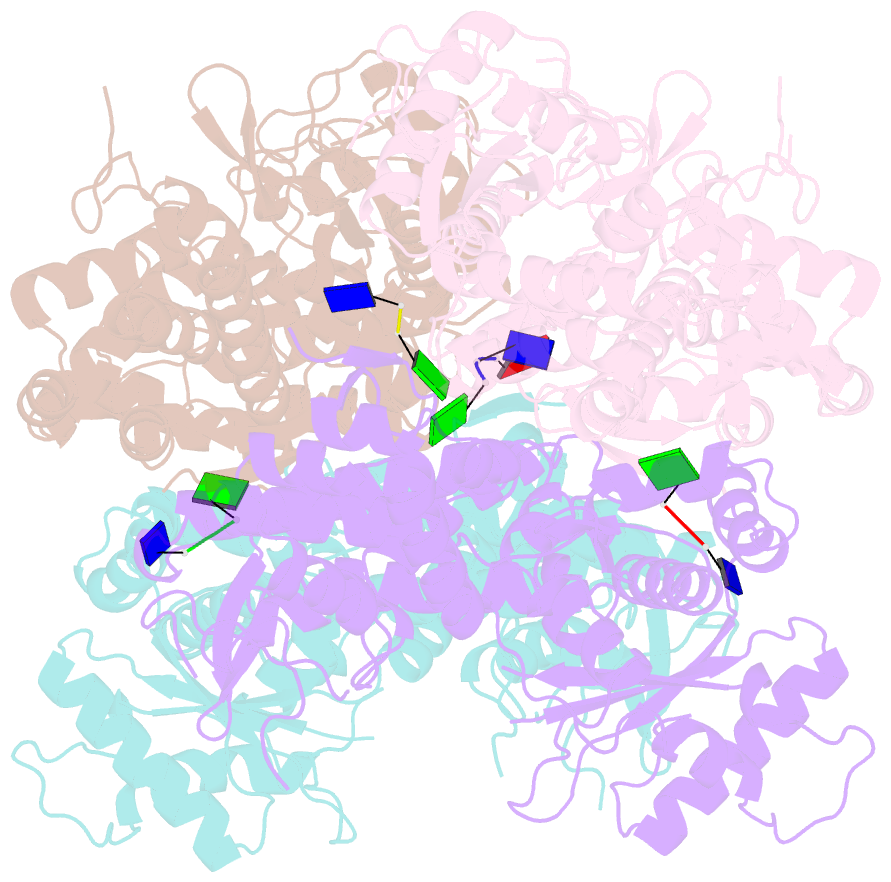
- Samhd1-DNA complex
- Reference
- Simermeyer TL, Batalis S, Rogers LC, Zalesak OJ, Hollis T (2023): "Protein oxidation increases SAMHD1 binding ssDNA via its regulatory site." Nucleic Acids Res., 51, 7014-7024. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad447.
- Abstract
- SAMHD1 dNTP hydrolase activity places it at the crossroad of several important biological pathways, such as viral restriction, cell cycle regulation, and innate immunity. Recently, a dNTPase independent function for SAMHD1 in homologous recombination (HR) of DNA double-strand breaks has been identified. SAMHD1 function and activity is regulated by several post-translational modifications, including protein oxidation. Here, we showed that oxidation of SAMHD1 increases ssDNA binding affinity and occurs in a cell cycle-dependent manner during S phase consistent with a role in HR. We determined the structure of oxidized SAMHD1 in complex with ssDNA. The enzyme binds ssDNA at the regulatory sites at the dimer interface. We propose a mechanism that oxidation of SAMHD1 acts as a functional switch to toggle between dNTPase activity and DNA binding.