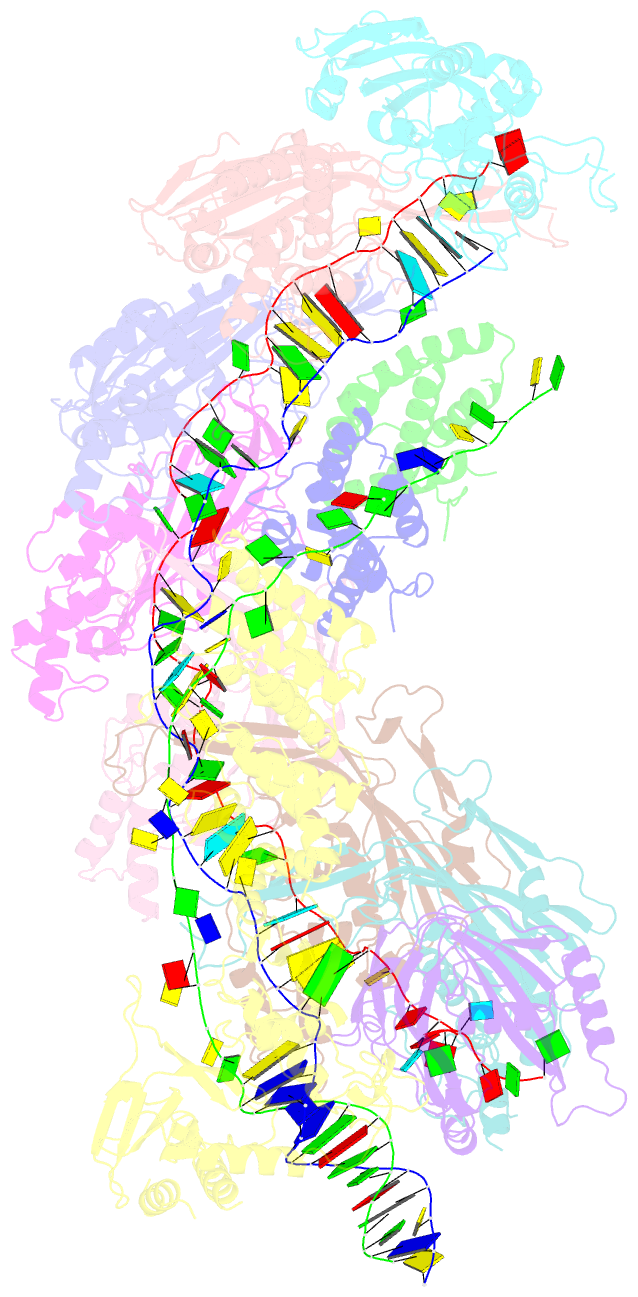
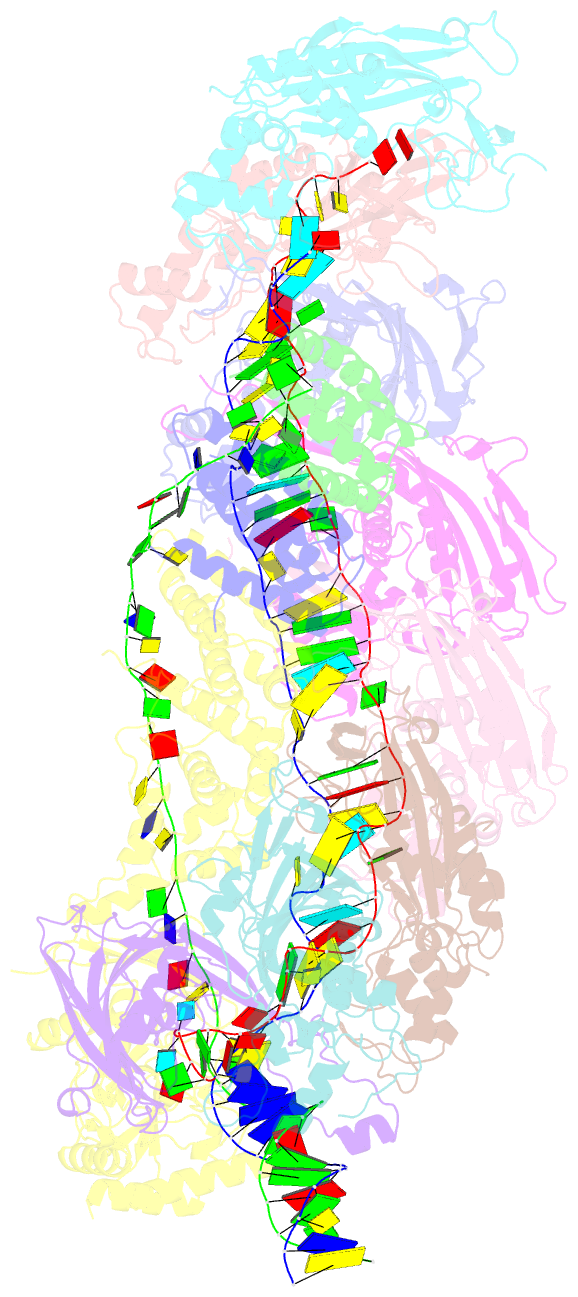
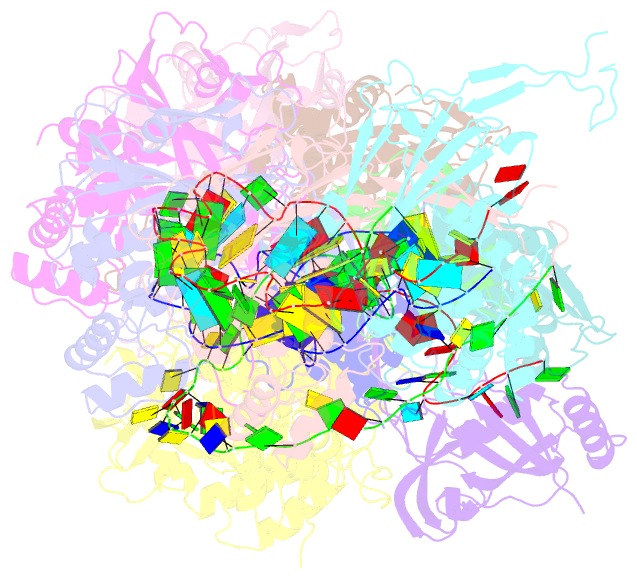
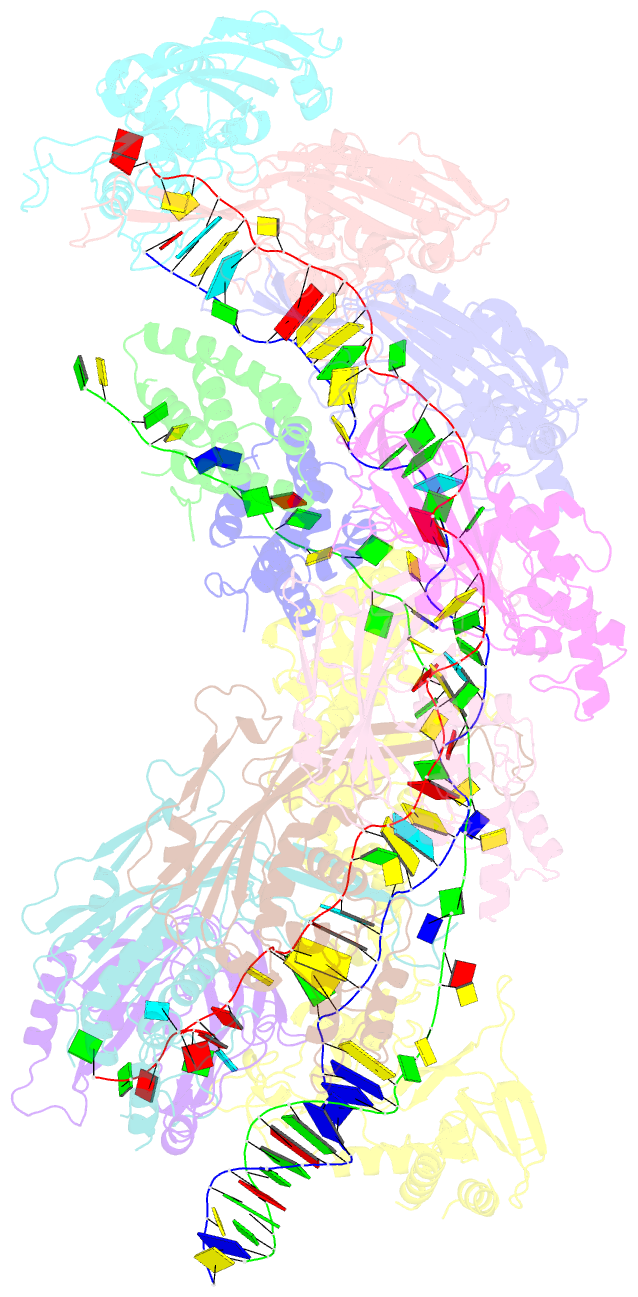
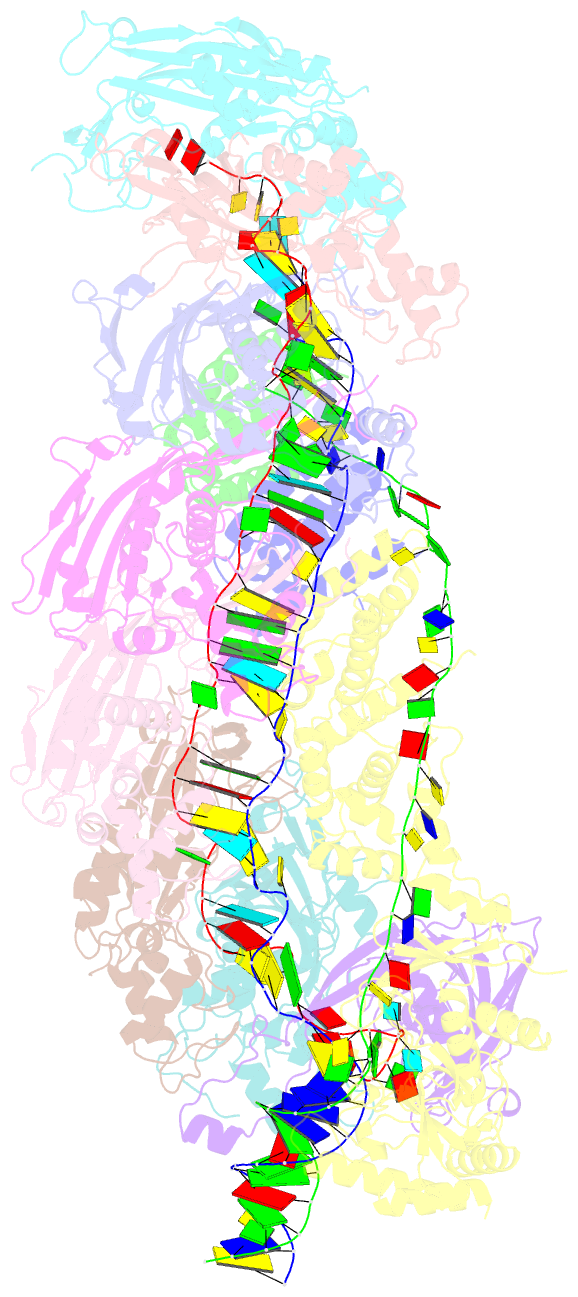
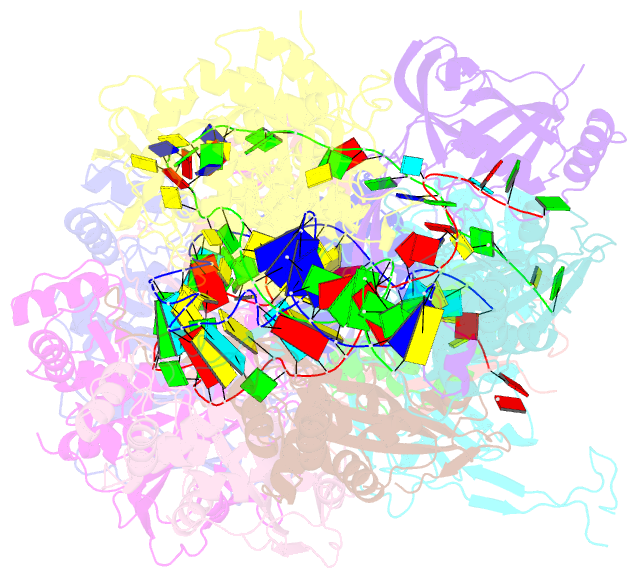
Summary information and primary citation
- PDB-id
- 8dej; SNAP-derived features in text and JSON formats;
DNAproDB
- Class
- DNA binding protein-DNA-RNA
- Method
- cryo-EM (2.86 Å)
- Summary
- D. vulgaris type i-c cascade bound to dsDNA target
- Reference
- O'Brien RE, Bravo JPK, Ramos D, Hibshman GN, Wright JT, Taylor DW (2023): "Structural snapshots of R-loop formation by a type I-C CRISPR Cascade." Mol.Cell, 83, 746. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.01.024.
- Abstract
- Type I CRISPR-Cas systems employ multi-subunit Cascade effector complexes to target foreign nucleic acids for destruction. Here, we present structures of D. vulgaris type I-C Cascade at various stages of double-stranded (ds)DNA target capture, revealing mechanisms that underpin PAM recognition and Cascade allosteric activation. We uncover an interesting mechanism of non-target strand (NTS) DNA stabilization via stacking interactions with the "belly" subunits, securing the NTS in place. This "molecular seatbelt" mechanism facilitates efficient R-loop formation and prevents dsDNA reannealing. Additionally, we provide structural insights into how two anti-CRISPR (Acr) proteins utilize distinct strategies to achieve a shared mechanism of type I-C Cascade inhibition by blocking PAM scanning. These observations form a structural basis for directional R-loop formation and reveal how different Acr proteins have converged upon common molecular mechanisms to efficiently shut down CRISPR immunity.